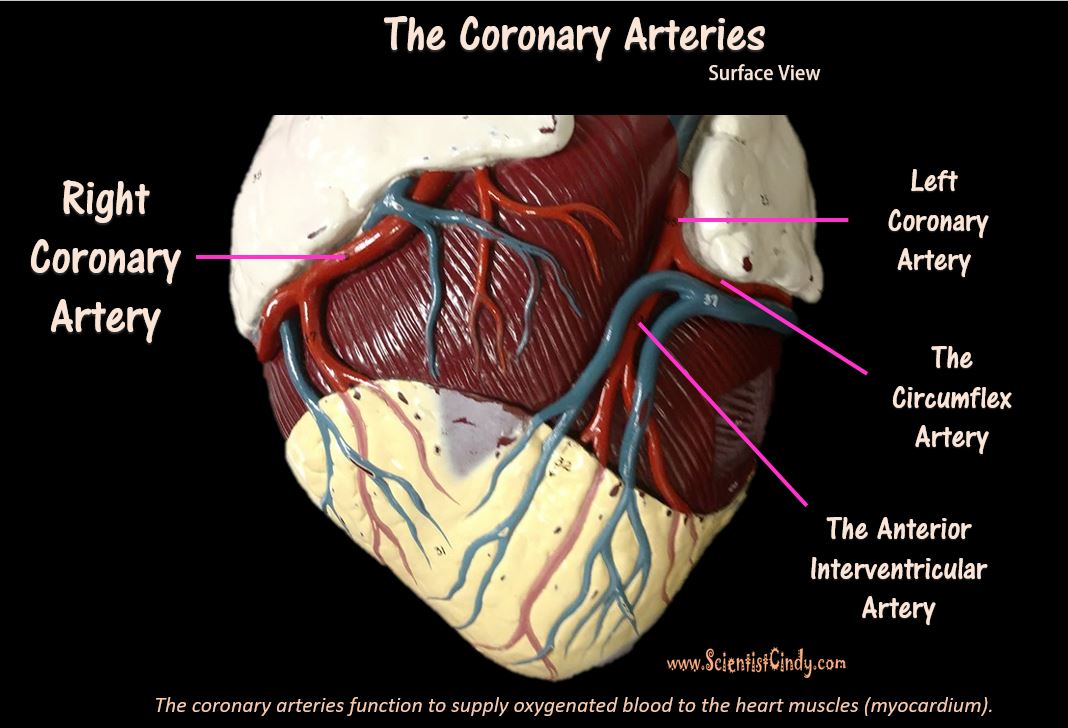
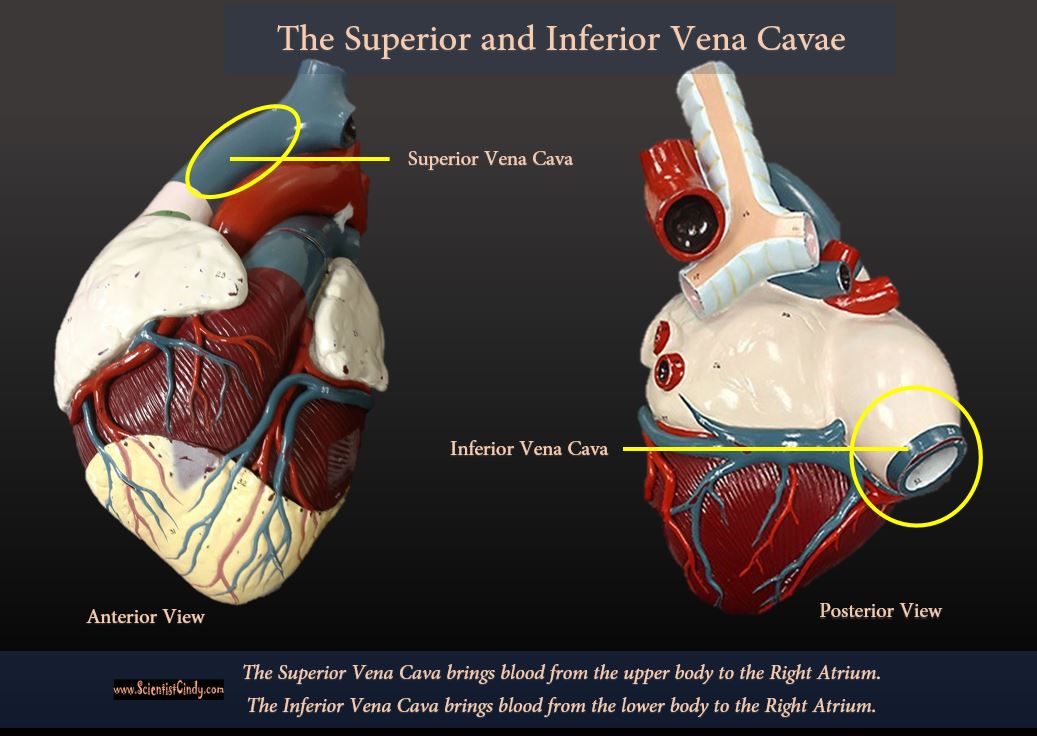
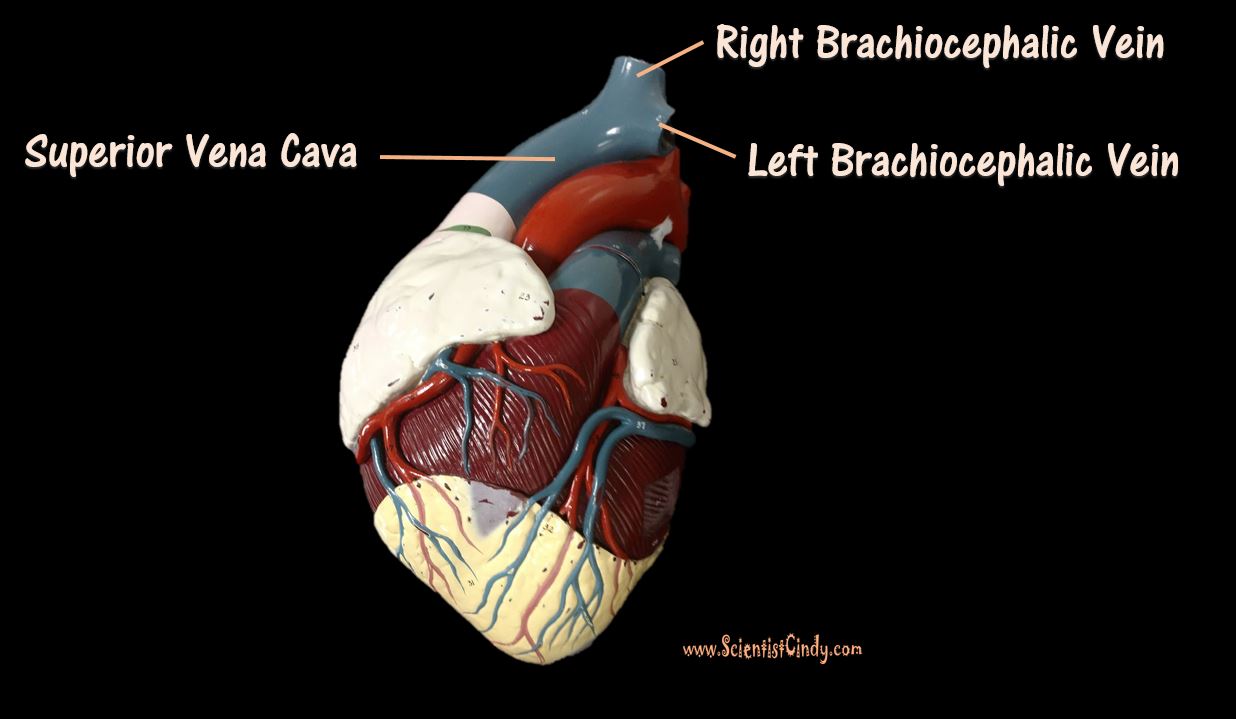
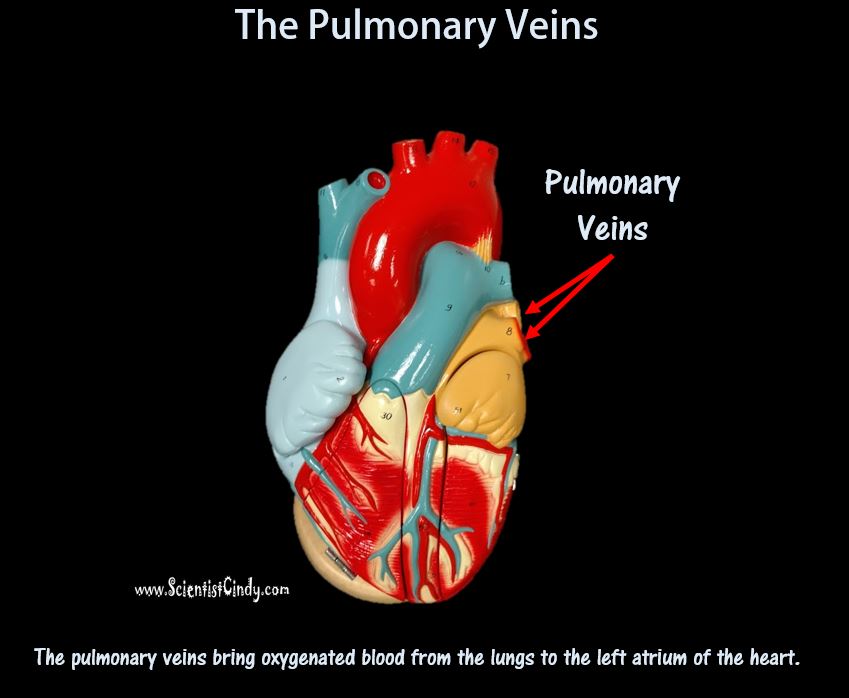
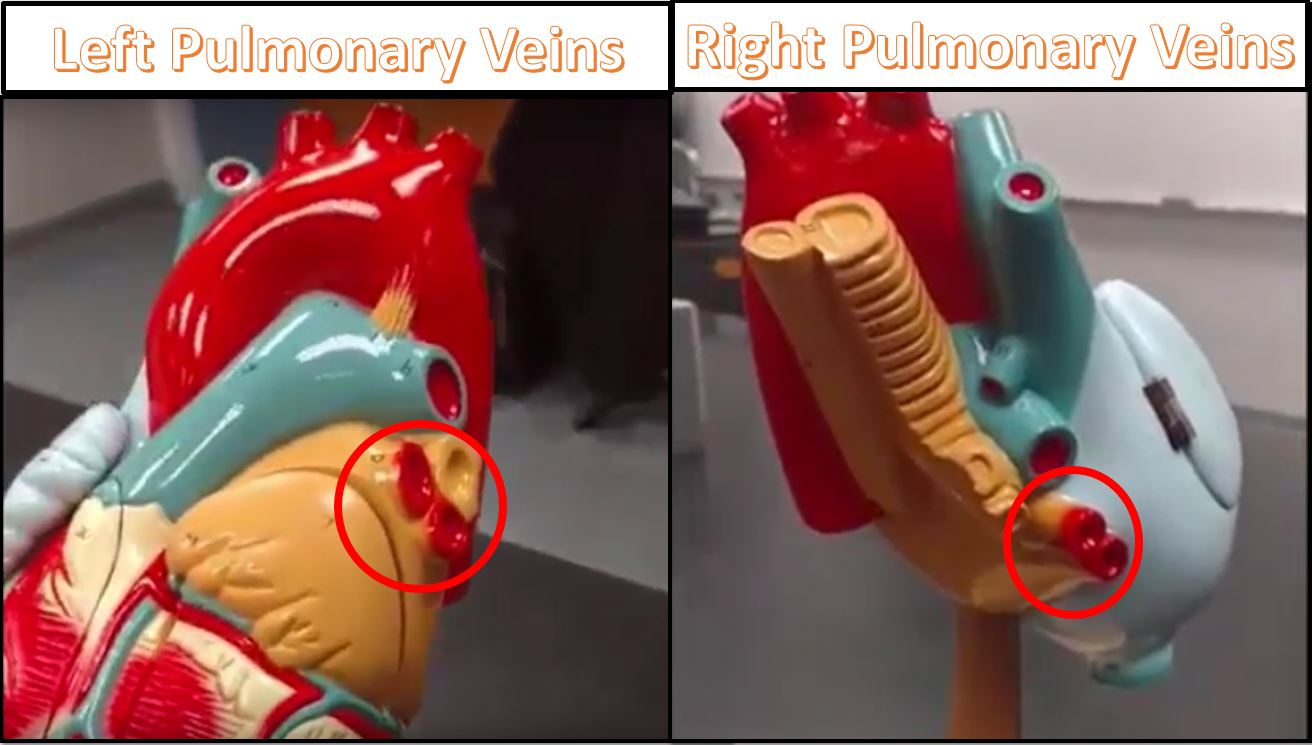
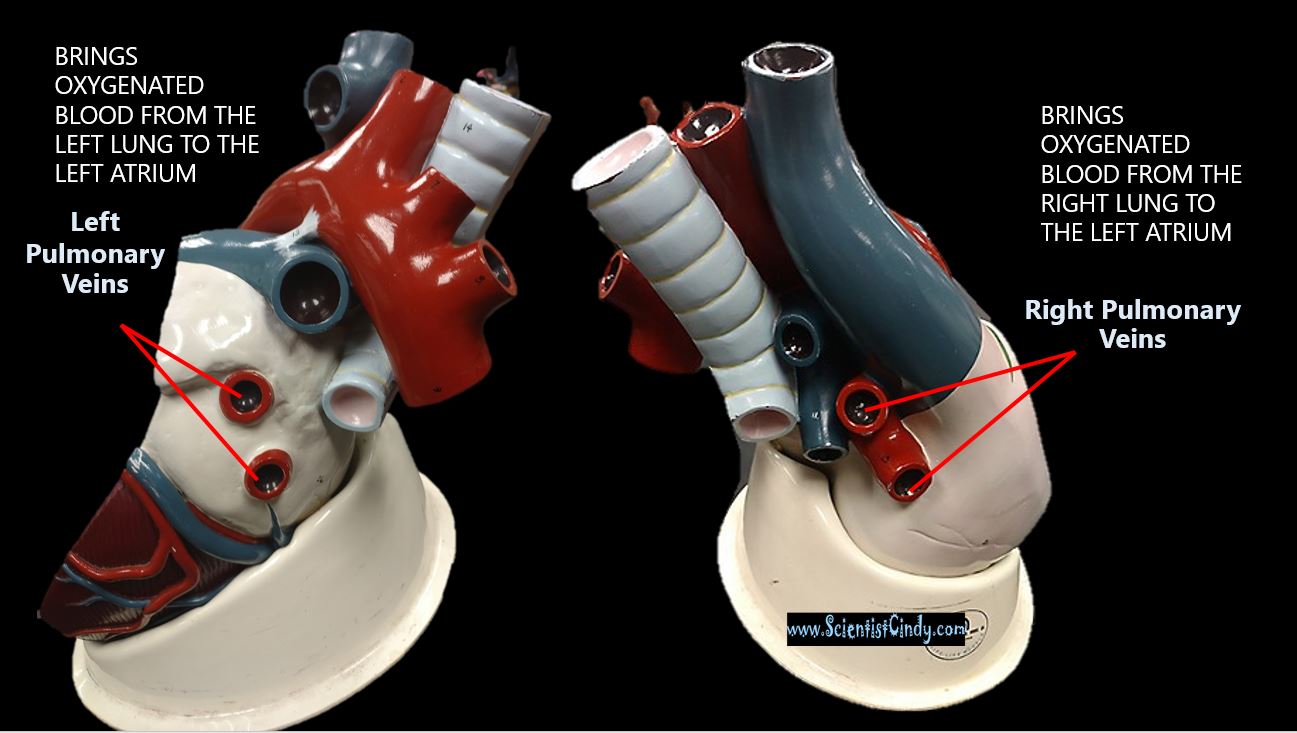
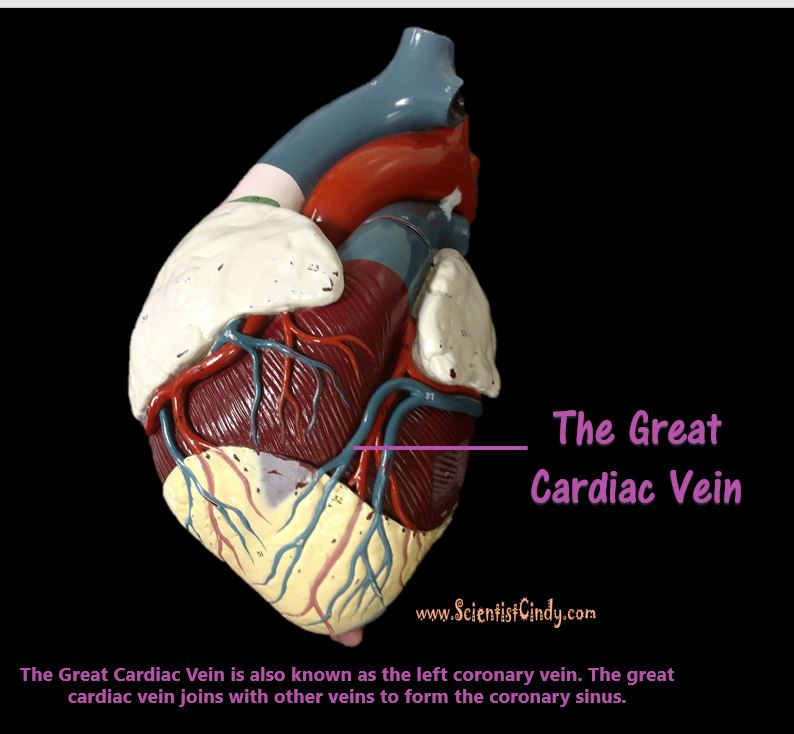
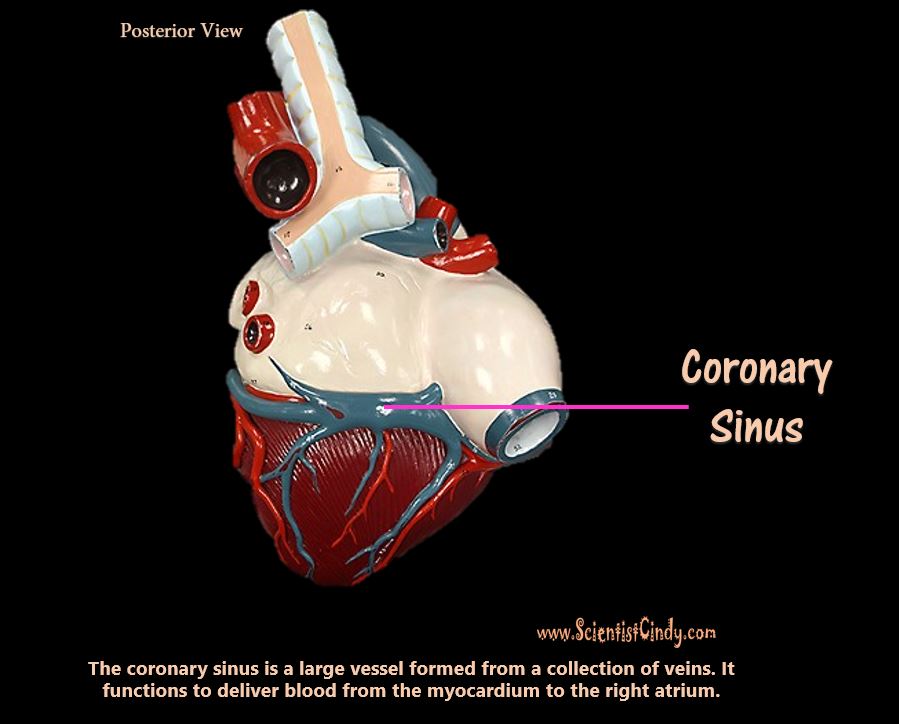
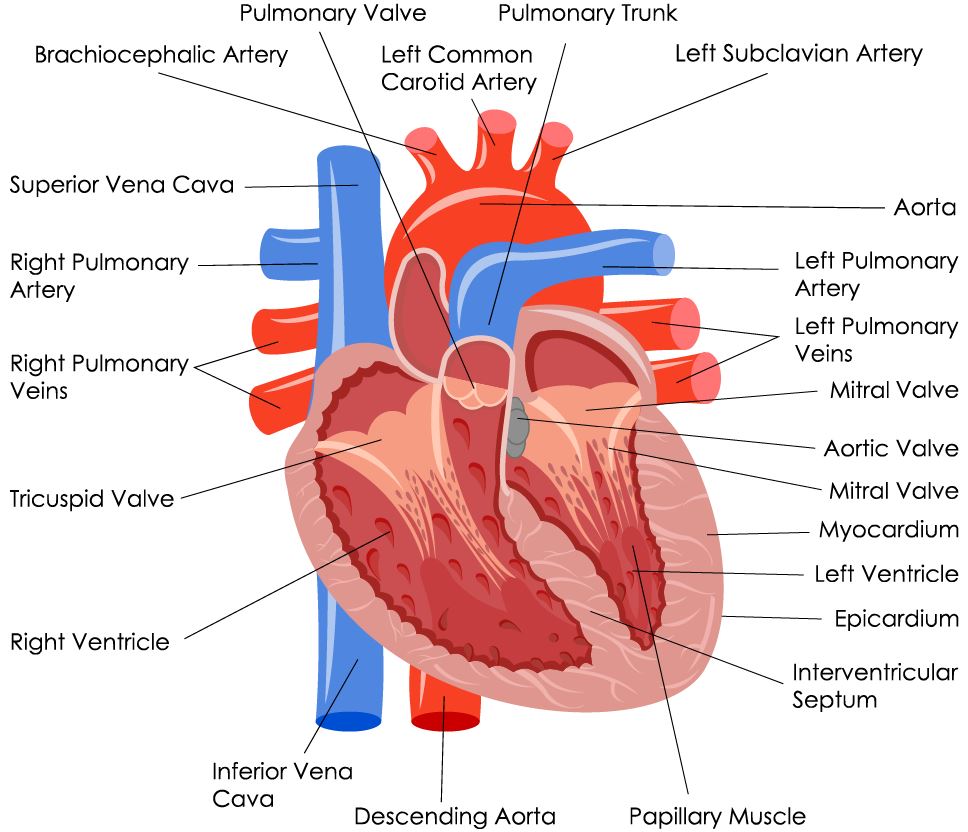
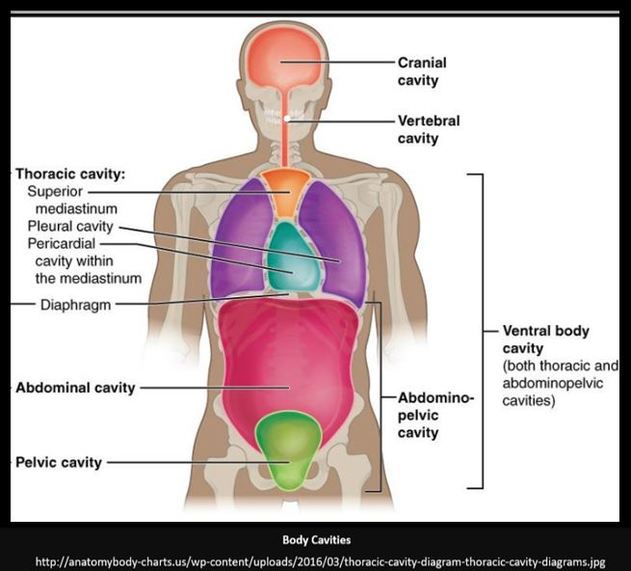
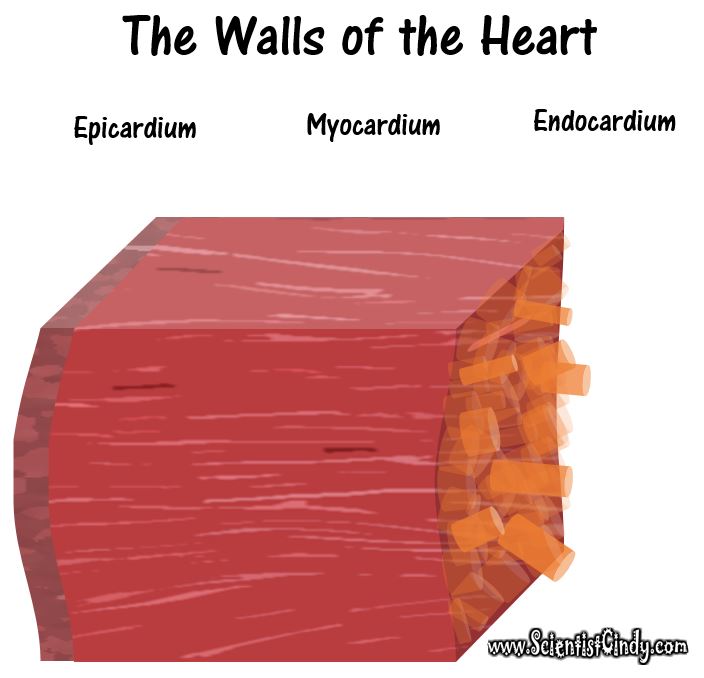
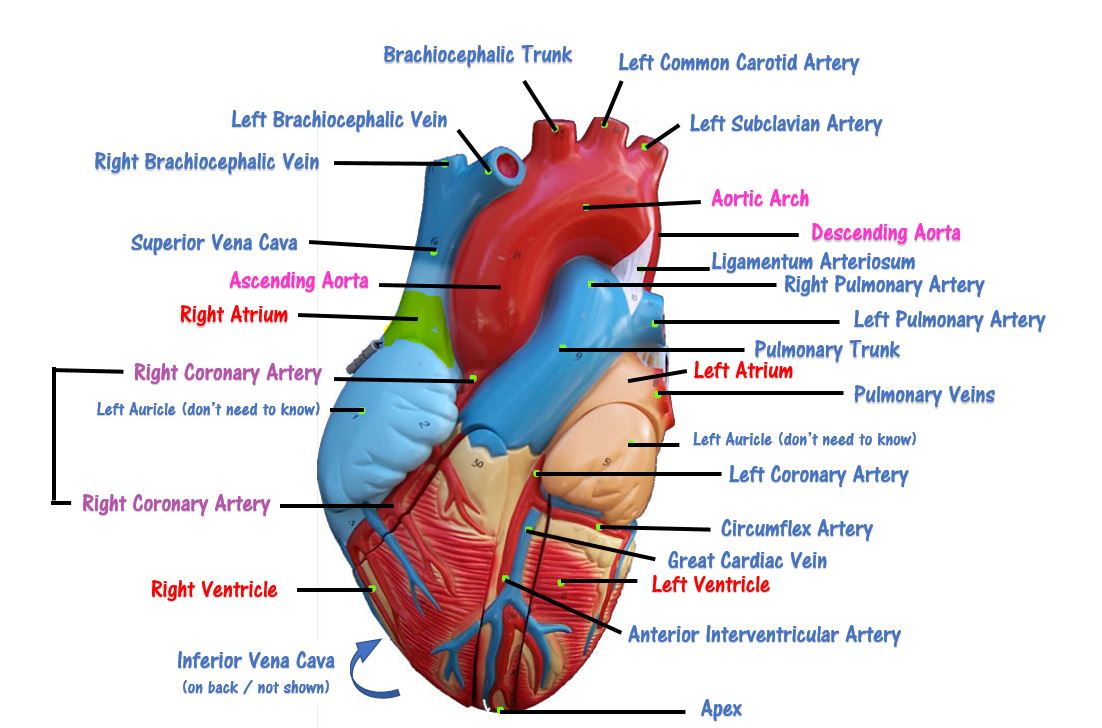
THE HEART
|
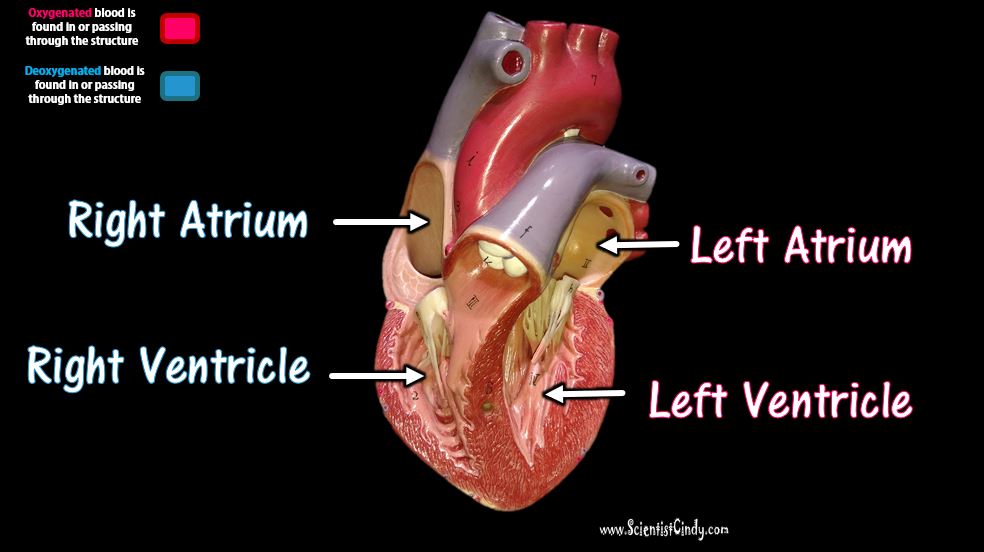
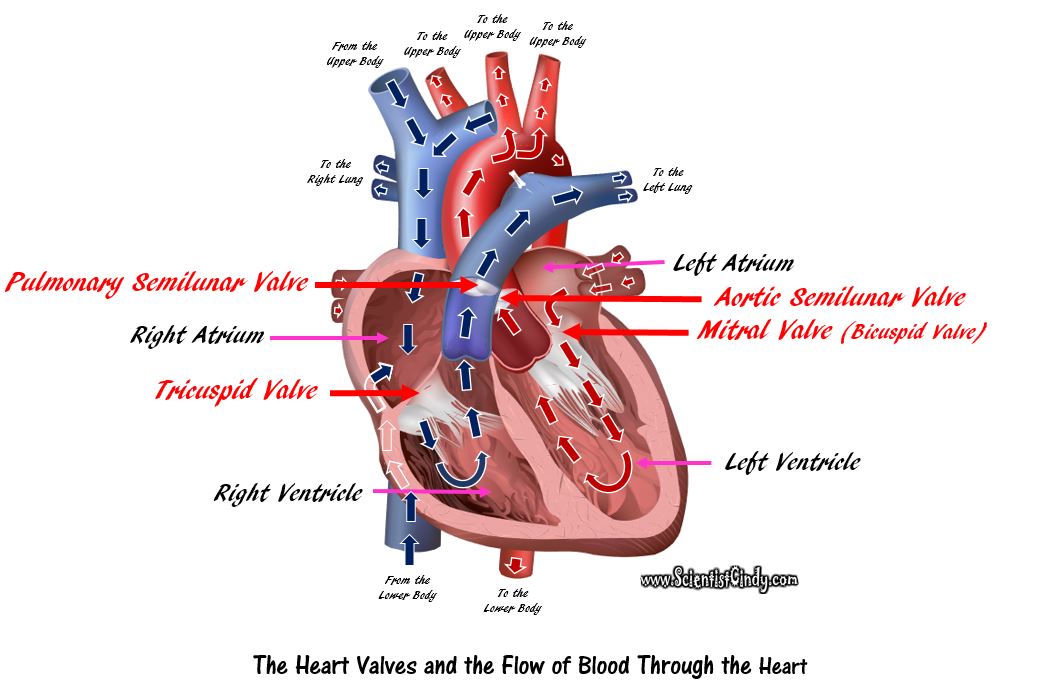
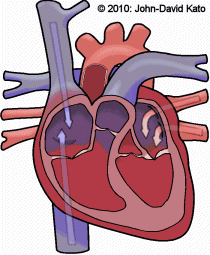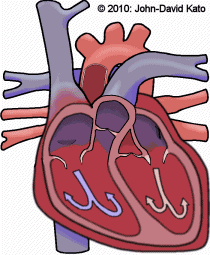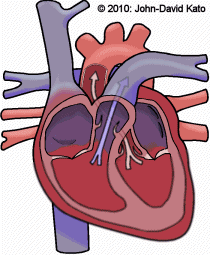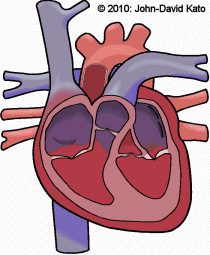
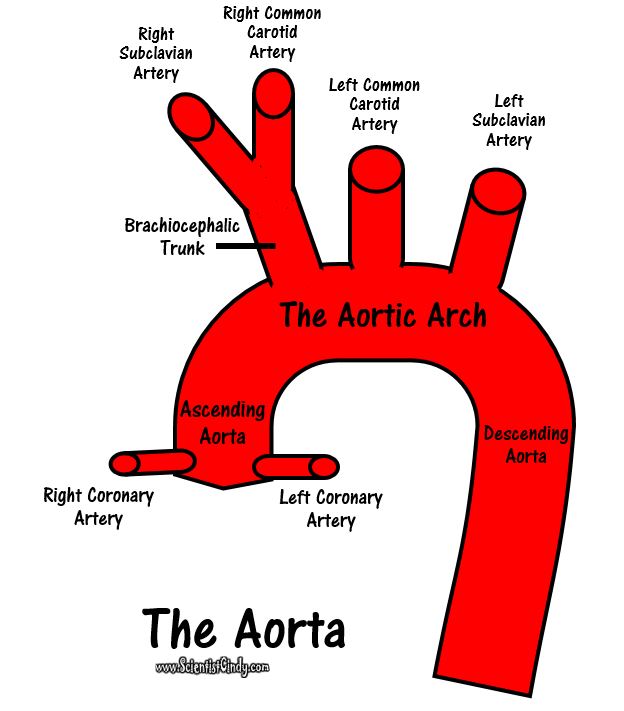
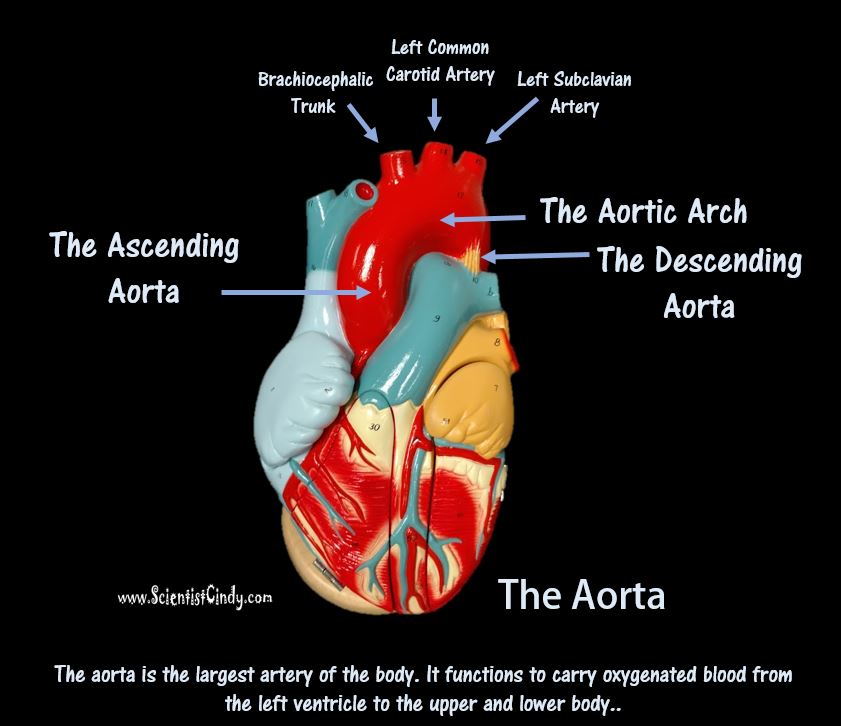
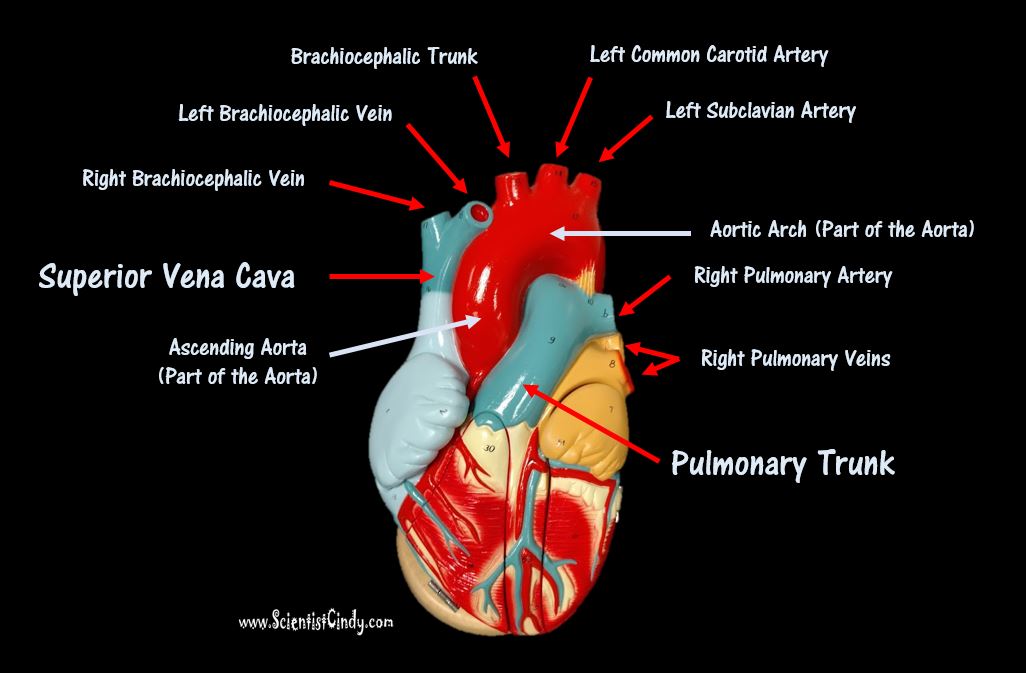
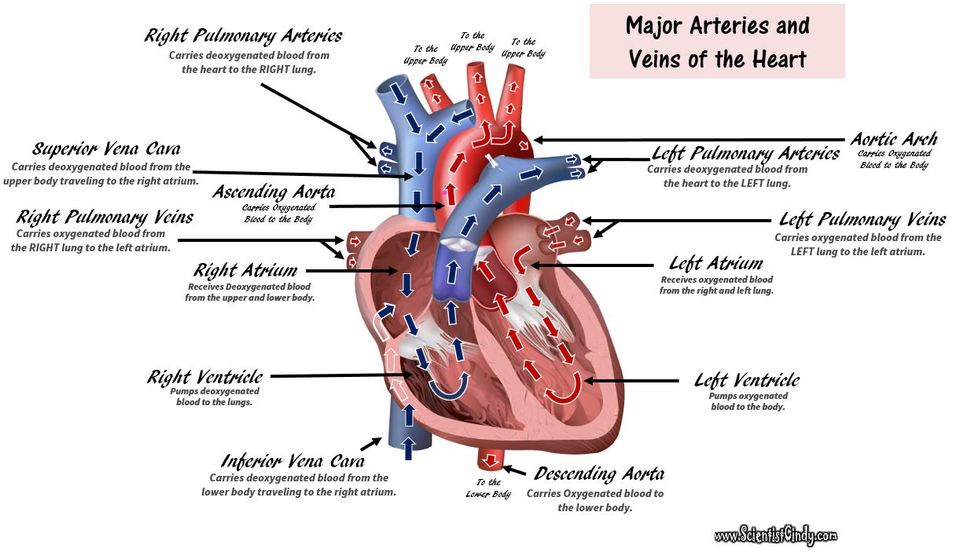
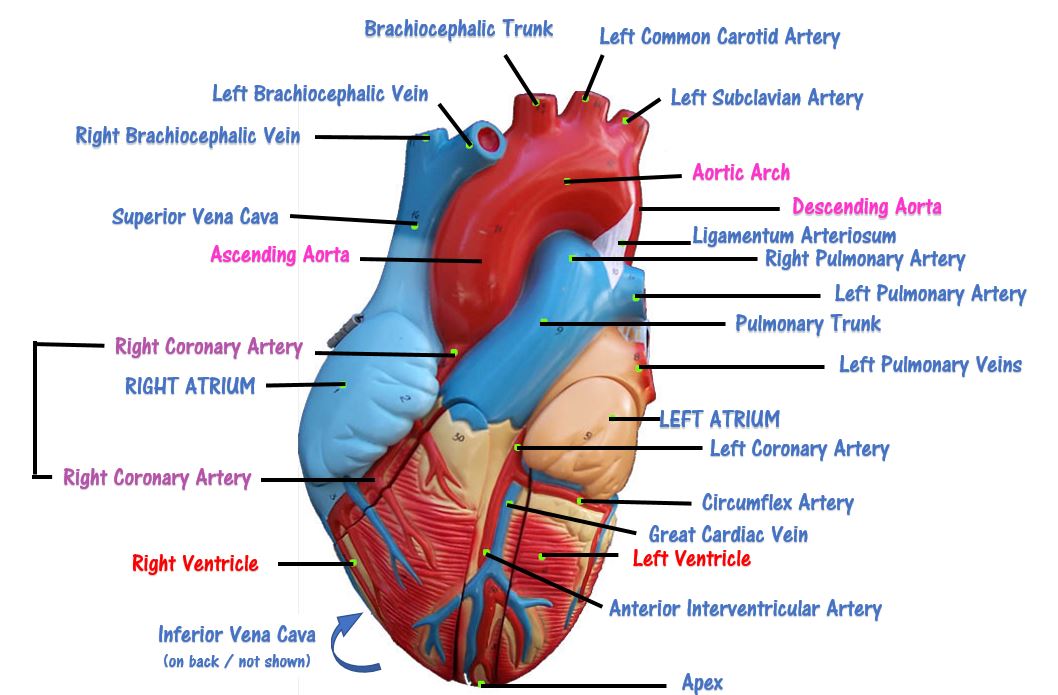
Detailed Demonstration of the Anatomy, Blood Flow and Relevant Functions of the Structures of the Large Heart Model
|
A Walk Through the Anatomy of the Small Heart Model
|
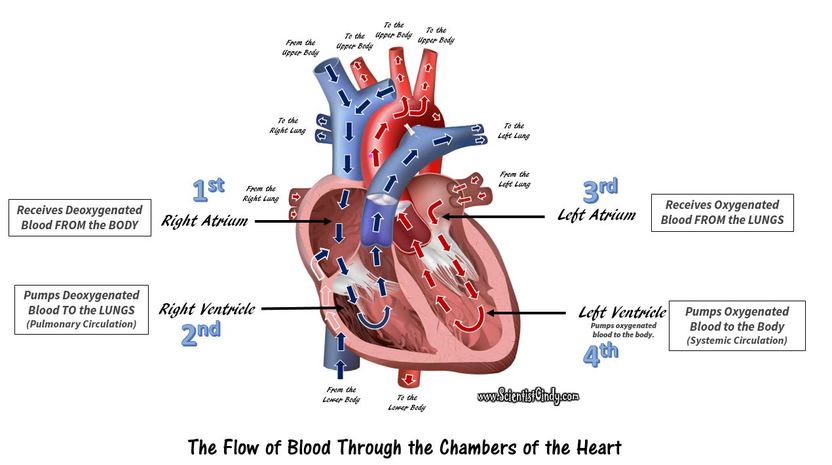
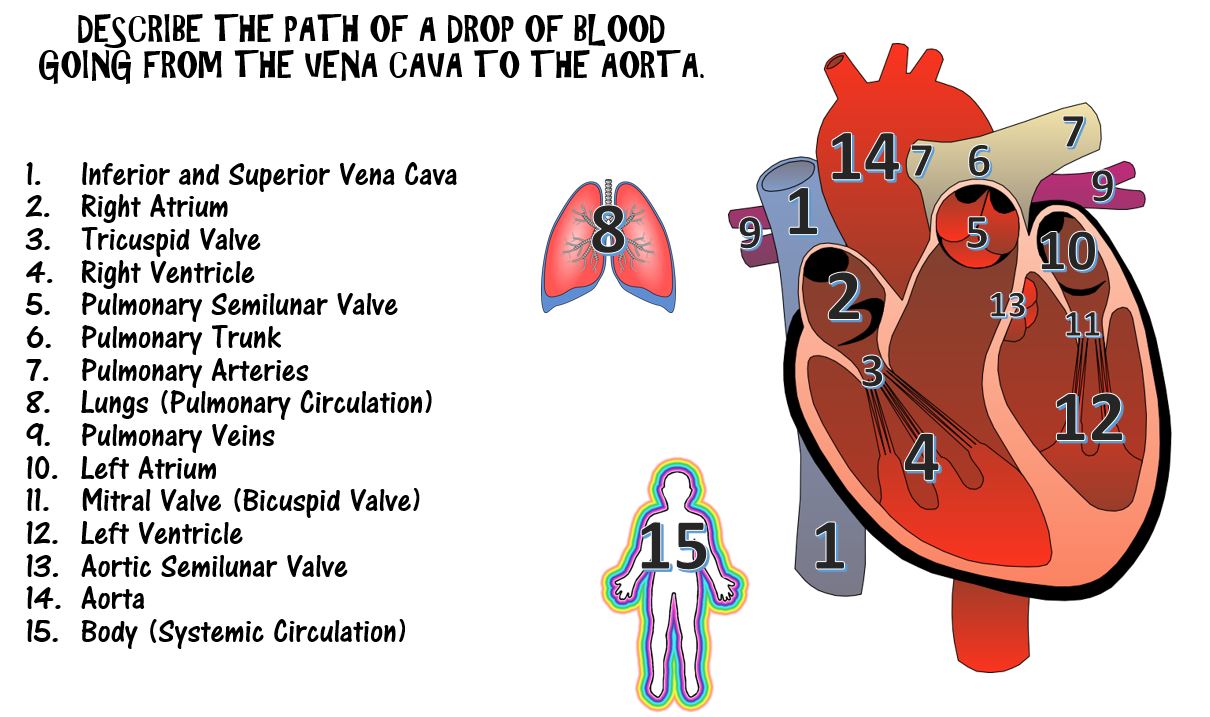
An Animation of the Flow of Blood Through the Chambers of the Heart and the Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits of the Circulatory System.
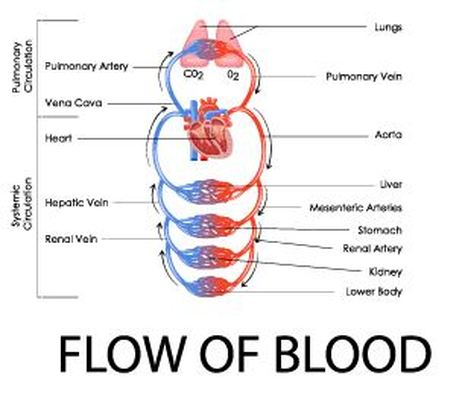
Overview of the Circulatory System
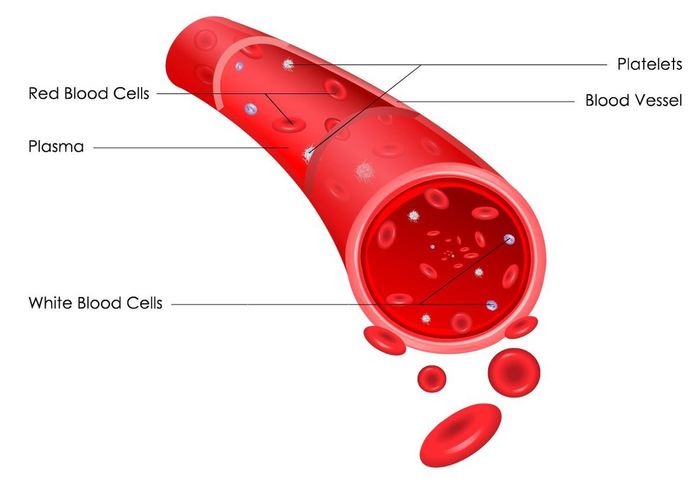
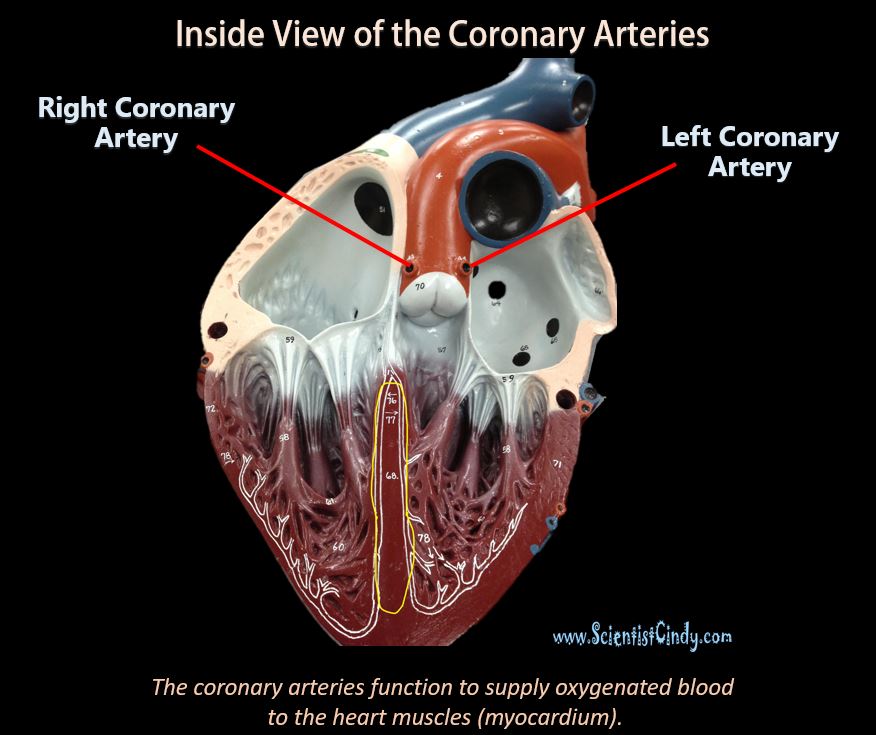
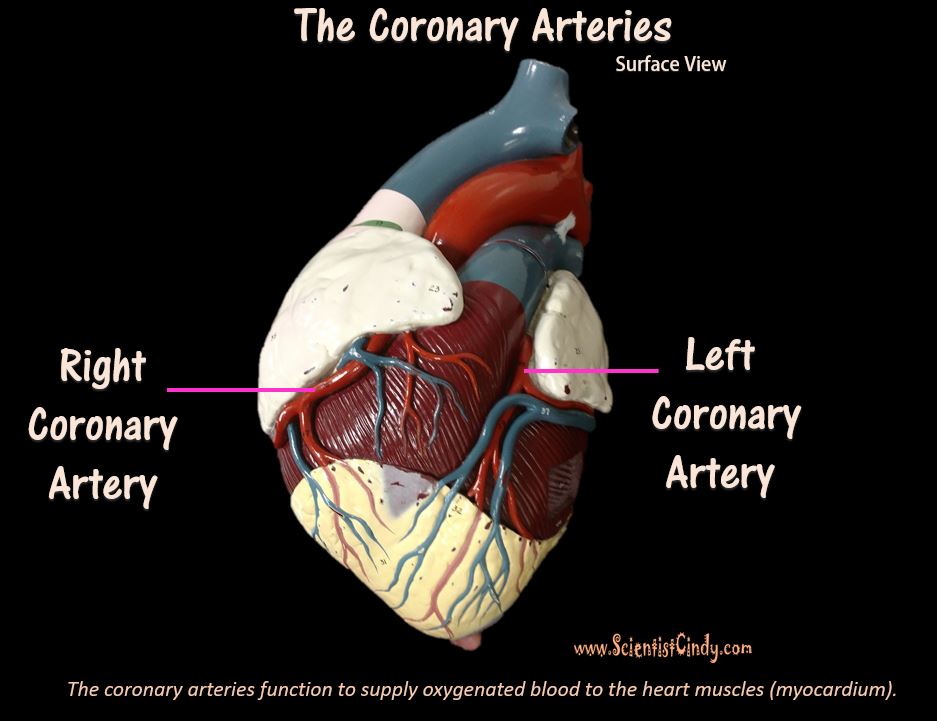
The circulatory system functions to circulate blood through the body. The blood carries vital nutrients, oxygen and hormones to the cells, and also picks up unwanted toxins, waste and carbon dioxide from the cells.
|
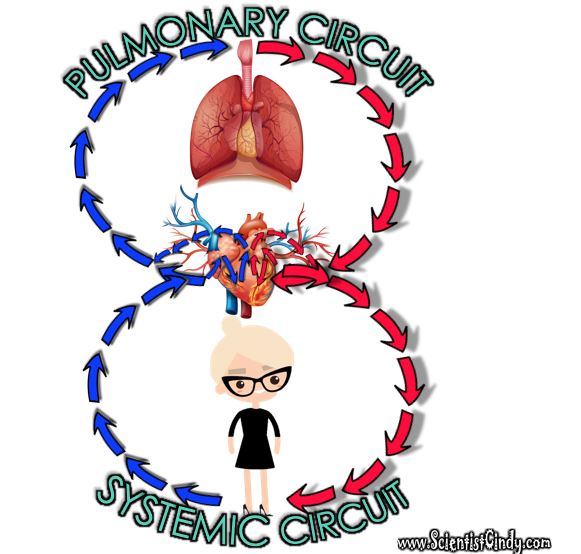
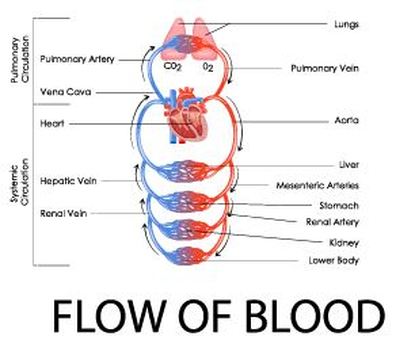
The circulatory system circulates blood around two loops.
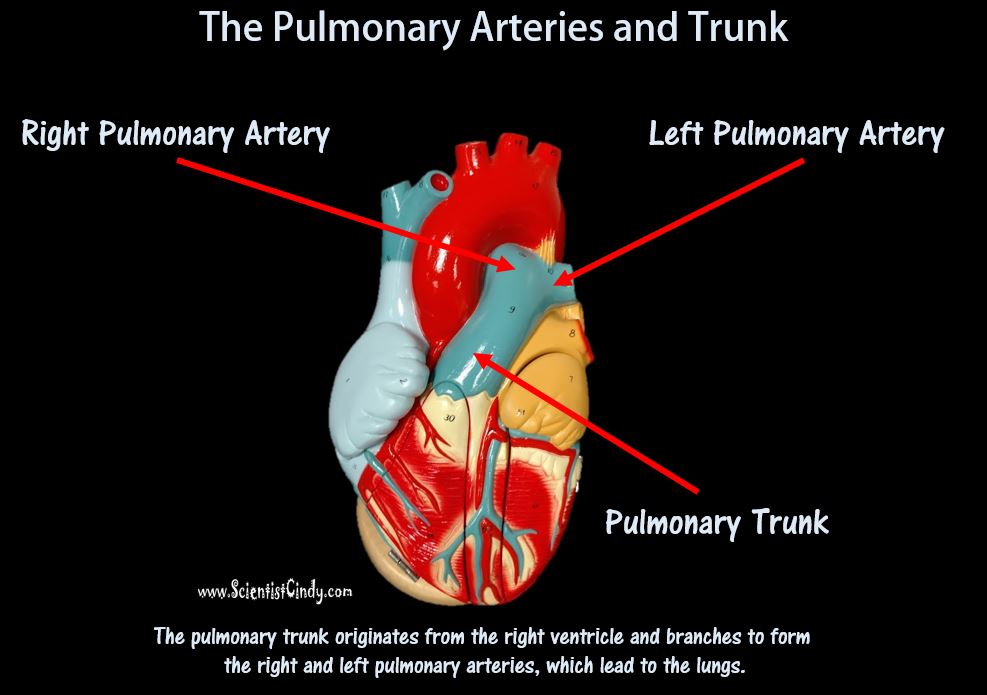
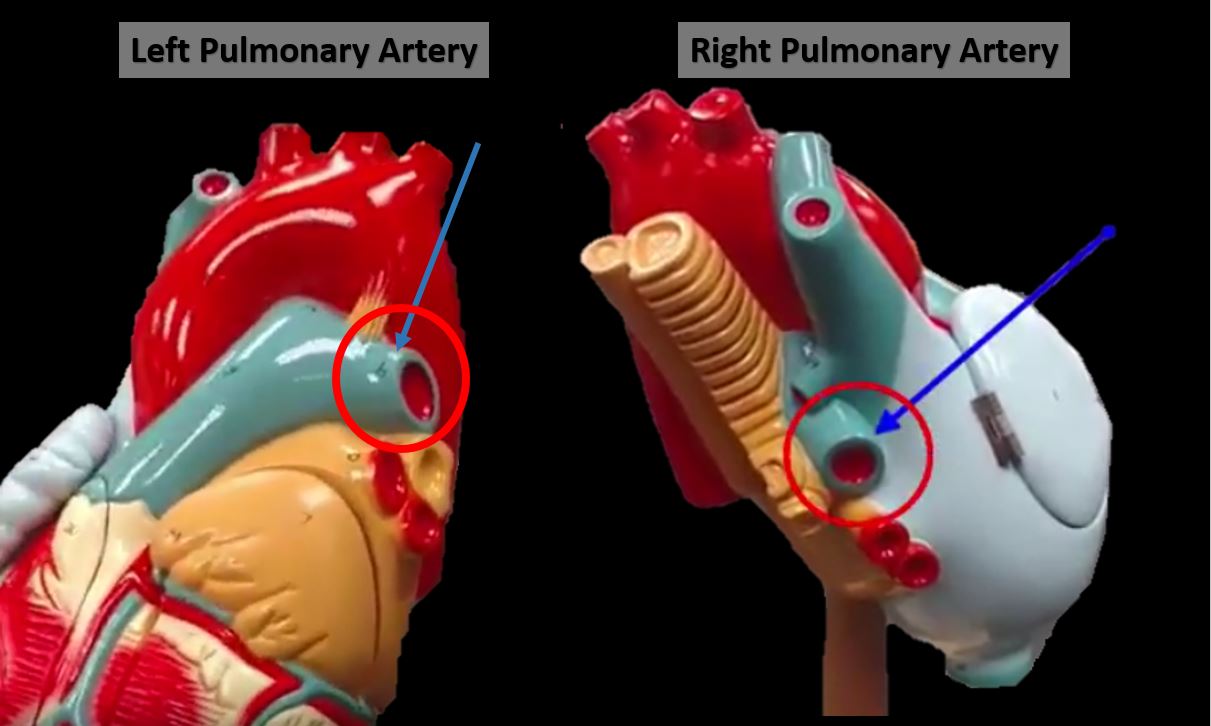
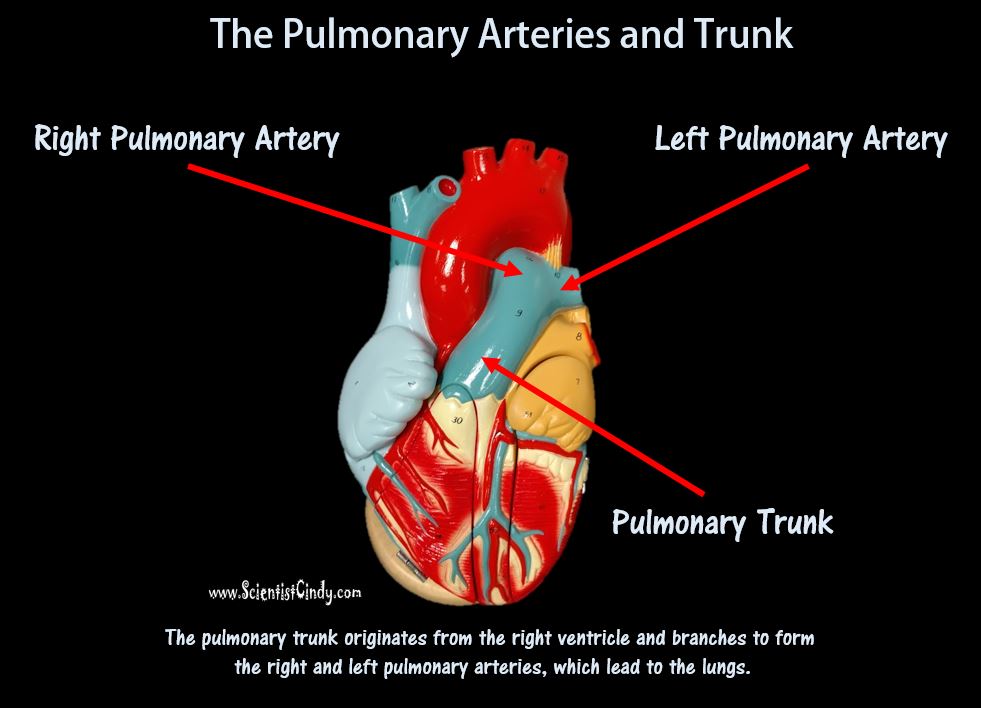
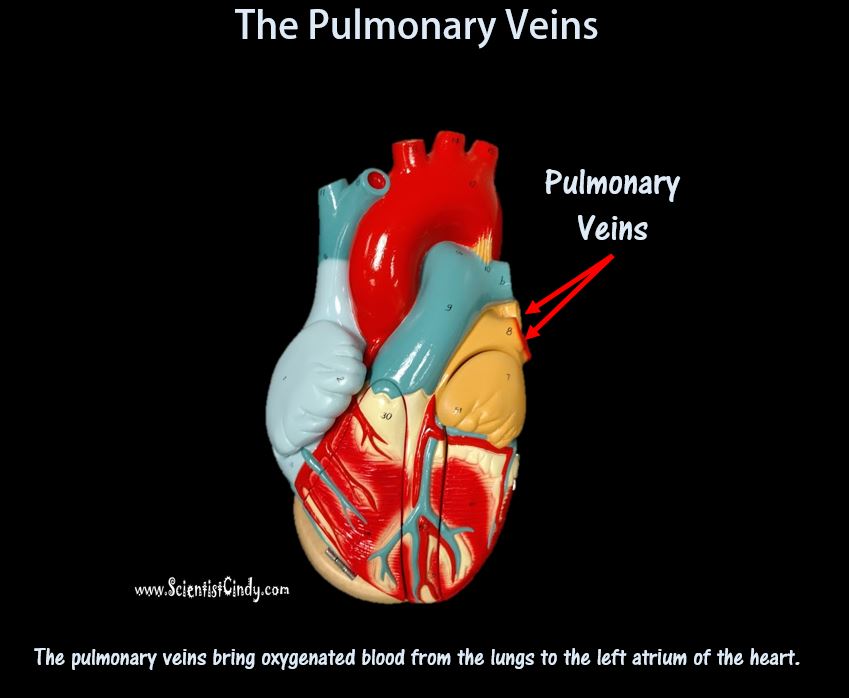
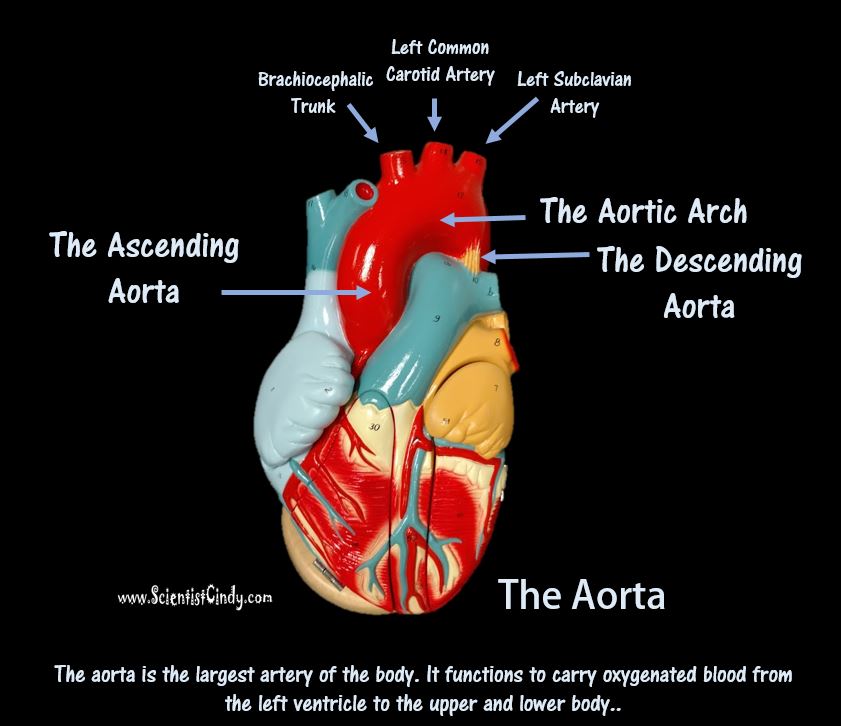
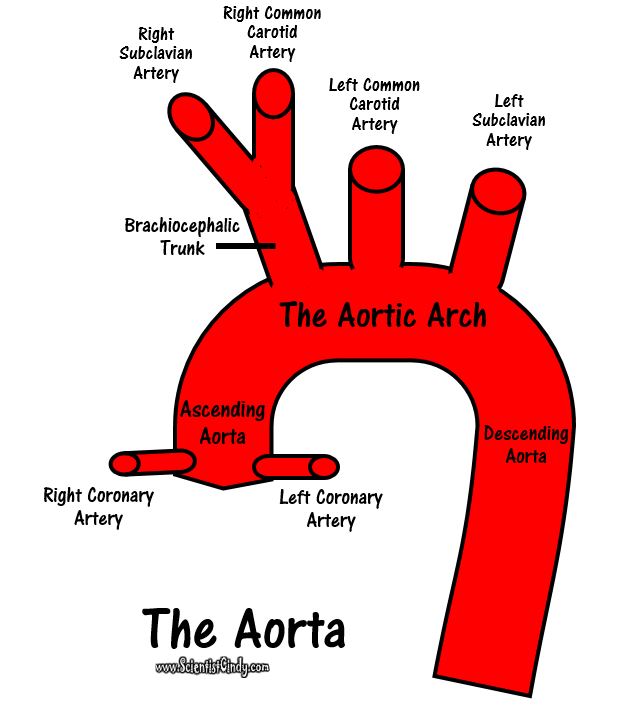
1) THE PULMONARY CIRCUIT - Functions to bring blood from the heart to the lungs and back to the heart 2) THE SYSTEMIC CIRCUIT - Functions to bring blood from the heart to all the parts of the body (except the lungs) and then back to the heart. |