Biomes
HOME SWEET BIOME
What is the biosphere?
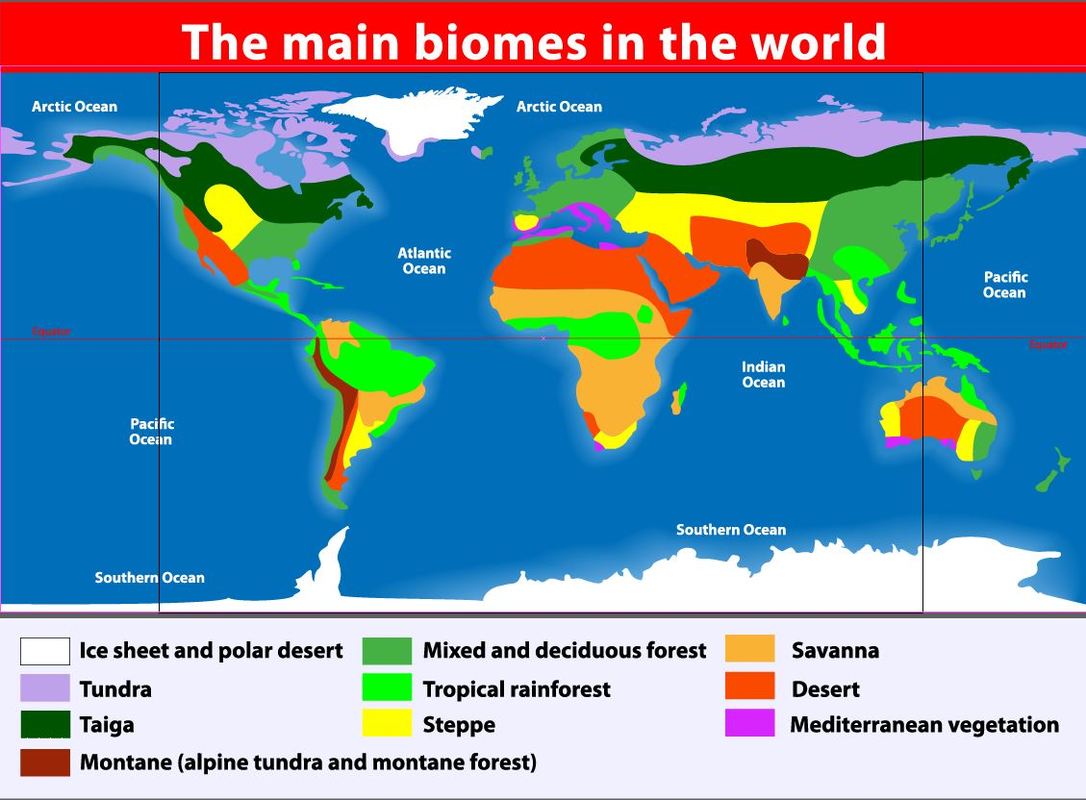
The biosphere includes all of the living organisms that call planet Earth their home. The biosphere includes life on land and in the oceans. The biosphere contains many large regions known as biomes.
The biosphere includes all of the living organisms that call planet Earth their home. The biosphere includes life on land and in the oceans. The biosphere contains many large regions known as biomes.

A biome is defined as a major regional ecological community of plants and animals. These biomes are characterized according to the plant and animal species they support. There are many biomes on Earth. They are made up of different types of organisms and climates. Temperature, soil, light, access to water and rainfall are all major factors in defining a biome.
A biome consists of a larger area that an ecosystem and usually consists of many ecosystems. An ecosystem is more narrowly defined and is the interaction of living and nonliving things in a given environment. Biomes are not fixed in space. As the climate changes, so the biomes.
A biome consists of a larger area that an ecosystem and usually consists of many ecosystems. An ecosystem is more narrowly defined and is the interaction of living and nonliving things in a given environment. Biomes are not fixed in space. As the climate changes, so the biomes.
|
There are 8 basic terrestrial biomes on our planet.
|
Some Definitions:
|
Robert H. Whittaker (1920—1980)
|
When ecologist, Robert Whittaker, first analyzed the locations of these different biomes in terms of annual rainfall and mean temperature, a climate pattern emerged. Whittaker discovered that the amount of yearly rainfall is highest around the equator. The yearly precipitation gradually decreases as you get further from the equator. Similarly, the mean annual temperatures are the warmest at the equator and begin to cool as the distance from the equator increases. Also, there are more seasonal variations (hours of sunlight in a given day) as you move further from the equator.
|

Portrait and autograph of professor Robert Harding Whittaker courtesy of National Academy of Sciences: Robert H. Whittaker (1920—1980)
- A Biographical Memoir by Walter E. Westman, Robrt K. Peet and Gene E. Likens. READ MORE AT: http://books.nap.edu/html/biomems/rwhittaker.pdf |
Elevation also affects the climate. As you increase in elevation, the temperature decreases about 10 degrees Celsius for every 1,000 meters gained in elevation. Cool air holds less water than warm air, so these areas of high elevation are commonly dry.
Plant Life
For example, grasses do not require as much carbon to grow and thrive as more complex woody trees and shrubs. For this reason, we can say that grasses maintain a higher proportion of there biomass in structures needed for photosynthesis. The biomass refers to the amount of matter that makes up an organism.
|
Drought tolerant trees include the evergreens. The evergreens are a phylum of trees that retain their leaves throughout the year. The leaves of evergreens are thick and often waxy which assists them in retaining water. Some evergreens have needle-like leaves, such as pine trees. Others may have broad leaves like the rhododendron and This makes them think all trees with needles are evergreens ( not so: the larch is a tree with needles, but loses them every year), or that all evergreens have needles; also not true, there are many broadleaf evergreens. Some examples of evergreens with needles: pines, spruce, cedars.
|
Ecosystems that are warm with plenty of rainfall and no real seasonal changes will have evergreen trees with broad leaves. These are the tropical and subtropical forests. In dryer, cooler, temperate climates with moderate rainfall, the plant life switches to drought-deciduous trees that loose their leaves in times of scarce rainfall. These are the seasonal tropical forests. Areas with even less rainfall and cooler temperatures will have woodland shrubs that are short and sparsely scattered through the area among many species of grasses. This would be characterized as a savanna or woodland biome. In areas of very low yearly precipitation, trees do not grow. Instead, in these arid regions, sparse populations of cactus, wildflowers and desert plants may be found. These areas would be representative of a desert biome.
Tropical forests are located near the Earth's equator, where the weather is warm, the hours of daylight are consistent and the rainfall is plenty. The largest rain forest in the world in the Amazon Rain Forest in South America. Southeast Asia and West Africa contain the second and third largest rain forests, respectively.

70% of the our planet’s surface is covered in water. It has been argued that we know more about our solar system than we do about our deep ocean. The Earth was once completely covered with water. Life evolved to live in water billions of years before the first land-dwelling organisms appeared. The ocean is home to the largest mammal on Earth, the blue whale, which can be up to 110 feet in length!
Life in the ocean takes on many forms, with new species being discovered all of the time. Some species spend their entire lives at the ocean floor, while others may migrate thousands of miles to mate and reproduce. Some creatures even burrow beneath the ocean floor to make their home, while others stay in shallow waters or spend most of their time near the ocean's surface. The ocean contains photosynthetic organisms like algae and phytoplankton which make their own food using the light's energy. These organisms are the primary producers in most marine food chains.
Similar to the terrestrial biomes, the temperature of the ocean biome decreases as you move away from the Earth's equator. Water near the North and South poles are the coldest regions of ocean water. Also, as you get deeper in the ocean, the temperature decreases as well. Some marine lifeforms are able to live in a variety of marine habitats where others may require very specific temperatures and nutrients, etc.
Life in the ocean takes on many forms, with new species being discovered all of the time. Some species spend their entire lives at the ocean floor, while others may migrate thousands of miles to mate and reproduce. Some creatures even burrow beneath the ocean floor to make their home, while others stay in shallow waters or spend most of their time near the ocean's surface. The ocean contains photosynthetic organisms like algae and phytoplankton which make their own food using the light's energy. These organisms are the primary producers in most marine food chains.
Similar to the terrestrial biomes, the temperature of the ocean biome decreases as you move away from the Earth's equator. Water near the North and South poles are the coldest regions of ocean water. Also, as you get deeper in the ocean, the temperature decreases as well. Some marine lifeforms are able to live in a variety of marine habitats where others may require very specific temperatures and nutrients, etc.
The Atmosphere |
|
The Earth would not be our home without the atmosphere. The atmosphere keeps the Earth's temperatures within the range needed for liquid water and for life to develop. Experts estimate that without the atmosphere, the Earth temperatures would swing wildly from more than 200 degrees Celsius below zero to 200 degrees Celsius above zero. The atmosphere is needed for the water cycle and to protect yourself from the sun's radiation.
These atmospheric gases are critical to life on our planet. Carbon, Oxygen, Hydrogen, and Nitrogen are needed to build biologically relevant molecules such as amino acids, proteins, and nucleotides needed for RNA and, DNA.
Nitrogen
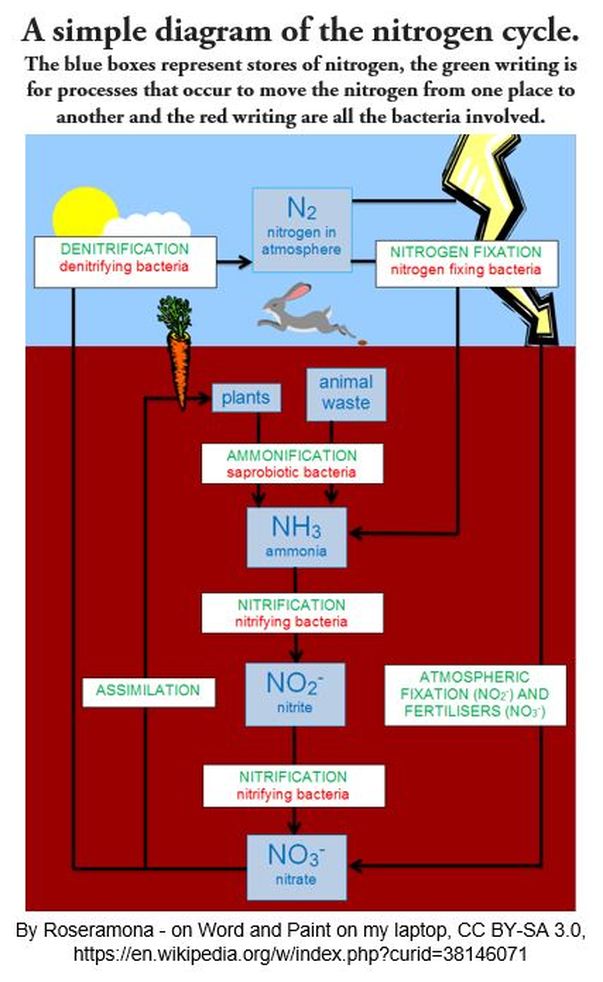
Nitrogen gas in the atmosphere is not readily available for organisms to use. Specialized bacteria function in the ecosystem to break down nitrogen (N2) from the atmosphere. Some bacteria are able to perform a vital function called notrogen fixation. Nitrogen fixation converts nitrogen (N2) into ammonia (NH3) which can be used by other organisms to form biologically relevant biomolecules.
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria include cyanobacteria which are among the oldest life-forms to develop on Earth. Fossils of cyanobacteria that have been dated to be more than 3.8 billion years old! Bacteria are a fundamental part of Earth's ecosystems. Different kinds of bacteria live closely together and work together in a mutually-beneficial way.
Plants are the foundation of the food chain and these plants demand a lot of nitrogen for synthesizing the molecules they need to grow and thrive. Plants depend on the nitrogenous compounds they obtain from the soil. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria replenish the usable nitrogen content in the soil.
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria include cyanobacteria which are among the oldest life-forms to develop on Earth. Fossils of cyanobacteria that have been dated to be more than 3.8 billion years old! Bacteria are a fundamental part of Earth's ecosystems. Different kinds of bacteria live closely together and work together in a mutually-beneficial way.
Plants are the foundation of the food chain and these plants demand a lot of nitrogen for synthesizing the molecules they need to grow and thrive. Plants depend on the nitrogenous compounds they obtain from the soil. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria replenish the usable nitrogen content in the soil.
Oxygen |
|
Atoms of oxygen are incorporated into many biomolecules.
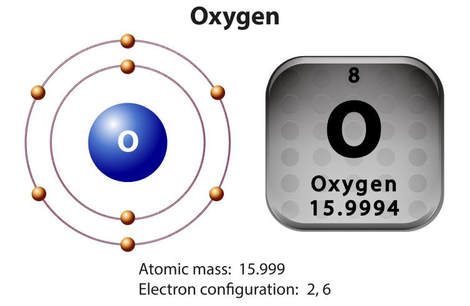
Vertebrate animals depend upon red blood cells to deliver oxygen to the individual cells of the body. The oxygen is needed for the cellular processes that make energy for the cell.
The formation of the protective ozone layer in the atmosphere was a direct consequence of the added oxygen content from early photosynthesizers. The ozone layer shields life-forms from harmful UV radiation from the sun.
The formation of the protective ozone layer in the atmosphere was a direct consequence of the added oxygen content from early photosynthesizers. The ozone layer shields life-forms from harmful UV radiation from the sun.
Carbon Dioxide
|
When bacteria first evolved on Earth, more than 3.5 billion years ago, the atmosphere contained very little oxygen. Instead, carbon dioxide was plentiful in the atmosphere. The earliest life-forms were able to obtain energy and nutrition from the sun and/or other inorganic molecules that were available at that time. The process of photosynthesis gives off oxygen as a waste product. These early photosynthetic organisms changed the early atmosphere by using up carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen into the atmosphere. Today, the atmosphere is about 20% oxygen.
|
The carbon on our atmosphere is in the form of carbon dioxide. The carbon in the atmosphere is the primary source of carbon for life on Earth. Organisms depend on carbon as the major building block for the biomolecules needed for energy and growth. |
|
Carbon
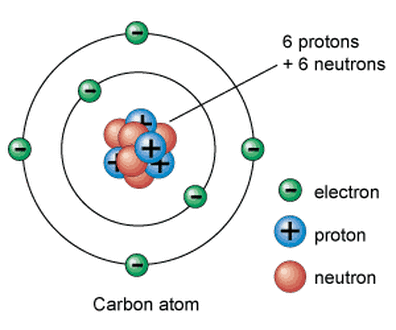
Have you ever heard that all life on Earth are "carbon-based lifeforms"? Carbon has unique properties that no other element has. A carbon atom has 4 electrons in its valence shell that holds 8. Carbon is able to completes its outer shell by sharing electrons with other atoms in four covalent bonds.What this means, is that carbon is the most versatile element, since it is able to form 4 strong bonds. This allows for a vast array of carbon-based molecules (called organic molecules) to form. Carbon is able to form large complex molecules. Organic molecules tend to carry a number of hydrogen atoms as well.
Weather
 A Dandelion
A Dandelion
The atmosphere provides weather. Wind is created due to pressure differences between different nearby areas of the atmosphere. Molecules that make up the atmosphere will always diffuse , traveling from areas of high concentration to areas of lower concentration.
Many plant species use the wind for reproduction. The wind carries light-weight seeds and pollen to other areas. This dispersion creates variability in the population which is important for the long-term survival of the plant species. Pine trees, fir trees, grasses, flowers and oak trees are just a few of the plants that use wind as part of their reproductive strategy.
Many plant species use the wind for reproduction. The wind carries light-weight seeds and pollen to other areas. This dispersion creates variability in the population which is important for the long-term survival of the plant species. Pine trees, fir trees, grasses, flowers and oak trees are just a few of the plants that use wind as part of their reproductive strategy.
|
The wind carries pheromones, which are signaling molecules plants and animals use to influence other organisms. For example, locusts emit pheromones that assists the developmental process of juvenile locusts, called nymphs. Bees release pheromones under stress that trigger an aggressive response from the colony. Plants release pheromones as a defense mechanism.
Winds also allow animals to find food, prey, mates and avoid predators. Many animals have a very heightened sense of smell which allows them to sense their surroundings to a much greater extent than what they can sense visually. |
Patterns of wind influence the distribution of moisture in the air, which influences the amount of rainfall. The amount of rainfall, elevation, soil, and temperature will dictate what plant species can survive in a given area. In turn, the types of plants in the area will influence what animal species will inhabit the area.
DESERT
|
4 major types of desert
COLD DESERT - Cold deserts have cold winters, with snowfall and short occasional rain. They have a short, moist and moderately warm summers. AREAS: Antarctic, Greenland and highlands of North America
HOT AND DRY DESERT - Warm throughout the year, very hot summers with small amounts of winter rain. AREAS: North American deserts like the Mojave. SEMIARID - Long. dry summers that are not too hot, with low winter rainfall. AREAS: Deserts of Utah and Montana. COASTAL DESERT - Long, pleasantly warm summers with cool winters. AREAS: Deserts of Chile. |
|
|
Tundra
Climate: Freezing Cold and limited sunlight Temperature: Average temperature is below freezing. Soil: Ground covered with little snow. Below the surface soil is permanently frozen (permafrost). Decomposition is very slow because of the extreme cold. Tundra Abiotic Factors
Tundra Biotic Factors
Animal Adaptations
Types of Tundra:
The Arctic Tundra The arctic alpine tundra biomes are the coldest locations on Earth. The arctic tundra is found located between the North Pole and Coniferous Forest or Taiga regions. Temperatures are freezing and land is frozen year-round into what is called "permafrost". Short growing season of only 50-60 days. Locations: Northern Alaska, Canada, Greenland, Scandinavia and Siberia |
|
|
|

Alpine Tundra
The alpine tundra biomes are located on mountainous regions with altitudes too high for growth of trees. As your increase in elevation, the temperatures get colder, the air gets dryer and the atmosphere gets thinner. For the plants that do grow here, the growing season is approximately 180 days. These biomes and windy and snow-covered most of the year.
Locations:
North America- Alaska, Canada, U.S.A. and Mexico
Northern Europe- Finland, Norway, Russia, and Sweden
Asia- Southern Asia( Mt. Himalayan ) and Japan (Mt. Fuji)
Africa- Mt. Kilimanjava
South America- Andes Mountains
The alpine tundra biomes are located on mountainous regions with altitudes too high for growth of trees. As your increase in elevation, the temperatures get colder, the air gets dryer and the atmosphere gets thinner. For the plants that do grow here, the growing season is approximately 180 days. These biomes and windy and snow-covered most of the year.
Locations:
North America- Alaska, Canada, U.S.A. and Mexico
Northern Europe- Finland, Norway, Russia, and Sweden
Asia- Southern Asia( Mt. Himalayan ) and Japan (Mt. Fuji)
Africa- Mt. Kilimanjava
South America- Andes Mountains
|
Taiga (Coniferous Forest)
The word "coniferous" means “coming from the cones”. This is due to the numerous pine trees with needle-like leaves and pine cones that dominate these regions. Climate: Long, cold snowy winters lasting 6 months. Cold summers 60 cm of avg snowfall. lasting to about half a year; precipitation is in the form of snow about 60 cm. Temperature: Below -20 0C in winter and about 15 0C in summer. Soil: Not fertile. It takes very long for needle-like leaves to decompose due to the cold temperatures. Ground is often covered in snow. Abiotic factors
Plant Life: Coniferous (needle-bearing) trees have adapted to this harsh environment.
|
Rainforest Biome

Tropical Rainforest
Climate:
The seasons do not change and it has been hot and wet for millions of years. The average temperature ranges from 70-85 degrees. It rains about 100-400 inches per year.
Abiotic factors
High biodiversity and biomass both hot and moist; ideal for bacteria and other microorganisms; they quickly decompose matter on the forest floor allowing nutrients to be recycled.
Soil:Lacks minerals and contains little remains of dead plants and animals.
Decomposition is rapid on warm wet soil.
<1 cm of topsoil; not very fertile
Sunlight is a major limiting factor
Shallow, wide roots since soil is so thin and poor in nutrients
Little sun reaches the floor
Tropical rainforest is the richest source of plants life on earth. Plants grow in layers (canopy receives most light). It is the perfect place for growing plants.
Climate:
The seasons do not change and it has been hot and wet for millions of years. The average temperature ranges from 70-85 degrees. It rains about 100-400 inches per year.
Abiotic factors
High biodiversity and biomass both hot and moist; ideal for bacteria and other microorganisms; they quickly decompose matter on the forest floor allowing nutrients to be recycled.
Soil:Lacks minerals and contains little remains of dead plants and animals.
Decomposition is rapid on warm wet soil.
<1 cm of topsoil; not very fertile
Sunlight is a major limiting factor
Shallow, wide roots since soil is so thin and poor in nutrients
Little sun reaches the floor
Tropical rainforest is the richest source of plants life on earth. Plants grow in layers (canopy receives most light). It is the perfect place for growing plants.
Temperate Rainforest
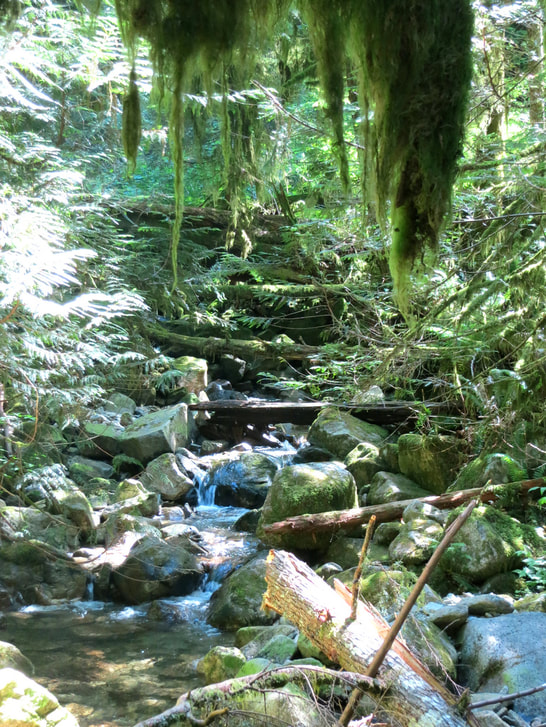

Climate:
Also wet, but not as rainy as tropical rainforest.
Rains about 100 inches per year.
It is cooler than tropical rainforests but the temperature is still mild.
has 2 distinct seasons: one long wet winter and a short drier summer.
Temperate Rainforest
Soil:
Typically much thicker than the tropical rainforest.
It is structurally more complex, comprising several layers.
Generally much deeper and more fertile than those of tropical rainforests.
Temperate Rainforest
Plants:
There are about 10-20 species of trees on temperate rainforests that are mostly coniferous. Trees in the temperate forest can live for 500-1000 years.
Also wet, but not as rainy as tropical rainforest.
Rains about 100 inches per year.
It is cooler than tropical rainforests but the temperature is still mild.
has 2 distinct seasons: one long wet winter and a short drier summer.
Temperate Rainforest
Soil:
Typically much thicker than the tropical rainforest.
It is structurally more complex, comprising several layers.
Generally much deeper and more fertile than those of tropical rainforests.
Temperate Rainforest
Plants:
There are about 10-20 species of trees on temperate rainforests that are mostly coniferous. Trees in the temperate forest can live for 500-1000 years.
Grasslands
|
Savannas (Tropical Grasslands)
Tropical Savanna
Temperate grassland Climate:
|