BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES
Cartilage of the Skeleton
Cartilage of our skeleton can be categorized either by their histological features, or by their location in the body.
Cartilage is a connective tissue that is separated into 3 main types;
The human body has 3 categories of cartilage based on their location.
Cartilage is a connective tissue that is separated into 3 main types;
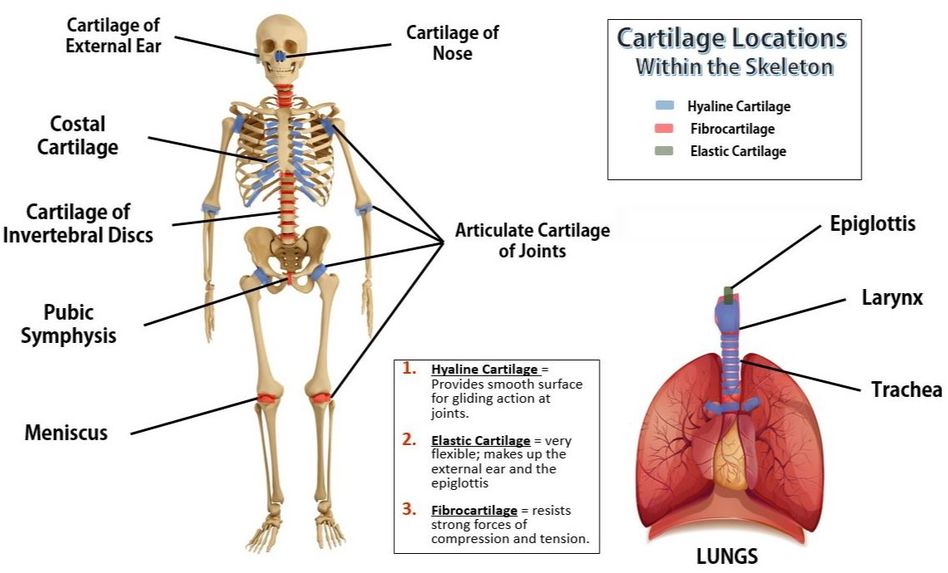
- Hyaline Cartilage, - The majority of our cartilage is hyaline cartilage. It provides a smooth surface within our joints for movement.
- Elastic Cartilage - The rarest type of cartilage is elasic cartilage. It forms the external portions of our ears and our epiglottis, which acts to keep food out of your trachea.
- Fibrocartilage. - The strongest cartilage in our bodies is fibrocartilage. This cartilage is found in areas of our body that undergo a lot of mechanical stress due to compression and tension forces, like our knee joints and invertebral discs.
The human body has 3 categories of cartilage based on their location.
- Articular Cartilage – covers the ends of most bones
- Costal Cartilage – connects the ribs to the sternum
- Respiratory Cartilage – makes up the larynx and epiglottis and reinforces air passages
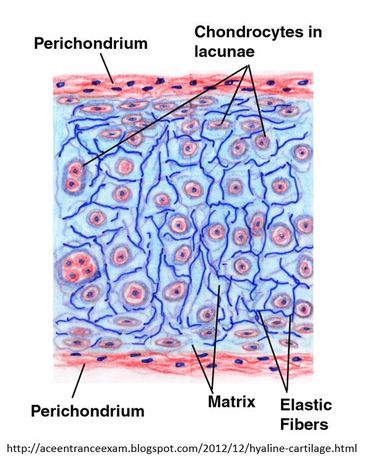
Cartilage is a connective tissue consisting chondrocytes and a dense matrix of collagen fibres and elastic fibers and a calcified ground substance. The matrix is produced by chondroblasts (immature chondrocytes).
The surfaces of most of the cartilage in your body is surrounded by a membrane of dense irregular connective tissue called perichondium. Chondrocytes that are outside of the perichondrium are surrounded by a space called a lacuna (lacunae for plural). Chondroblasts that exist in the perichondrium don't have lacunae.
Cartilage does not contain blood vessels or nerves except for the area of he perichondrium.
Cartilage Comes Before Bone
All of your bone started out as cartilage before you were born. A lot of this cartilage is converted into spongy bone and then much of the spongy bone gets replaced by compact bone. As an adult, only 20% or so of your bone remains as spongy bone. The spongy bone of an adult can be found in the center of the long bones in the arms and legs, as well as the pelvic bones, ribs, skull, and the vertebrae in the spinal column.
BONE TISSUE
The Two Types of Bone Tissues; Spongy and Compact
Bones consist of two types of osseous tissue; spongy bone and compact bone. These two bone tissue types work together in each bone and provide complementary functions. Compact bone is the hard outer portion of the bone, and spongy bone is the spongy, honeycomb-like bone tissue that is found at the ends of long bones and in the middle of your vertebrae. |
e.
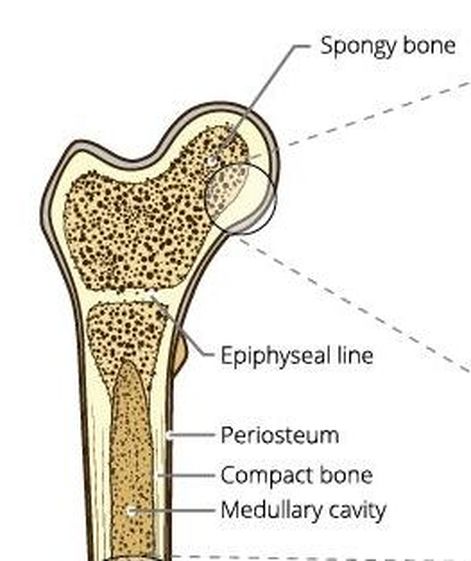
Spongy (Cancellous) Bone
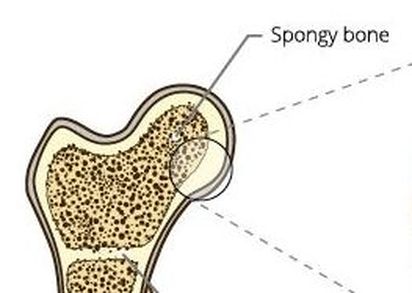
The internal portions of your bones contain spongy bone, also called trabecular bone or cancellous bone. Spongy bone is easily recognized by its honeycomb, spongy structure of small pointy or flat pieces called trabeculae. The open spaces between the trabeculae are filled with red or yellow bone marrow.
Spongy bone lives up to its name in its appearance. It looks 'spongy'. Some people describe the appearance of spongy bone to be similar to a honeycomb. Spongy bone is made up of trabeculae, which has many open spaces connected by flat planes.
Spongy bone lives up to its name in its appearance. It looks 'spongy'. Some people describe the appearance of spongy bone to be similar to a honeycomb. Spongy bone is made up of trabeculae, which has many open spaces connected by flat planes.
Spongy bone is made up of trabeculae. At the ends of long bones like the femur, the bone is actually not solid but is full of holes that are connected to each other by thin rods and plates of bone tissue known as trabeculae.
Slide of Spongy Bone
Animation of Spongy Bone Trabeculae
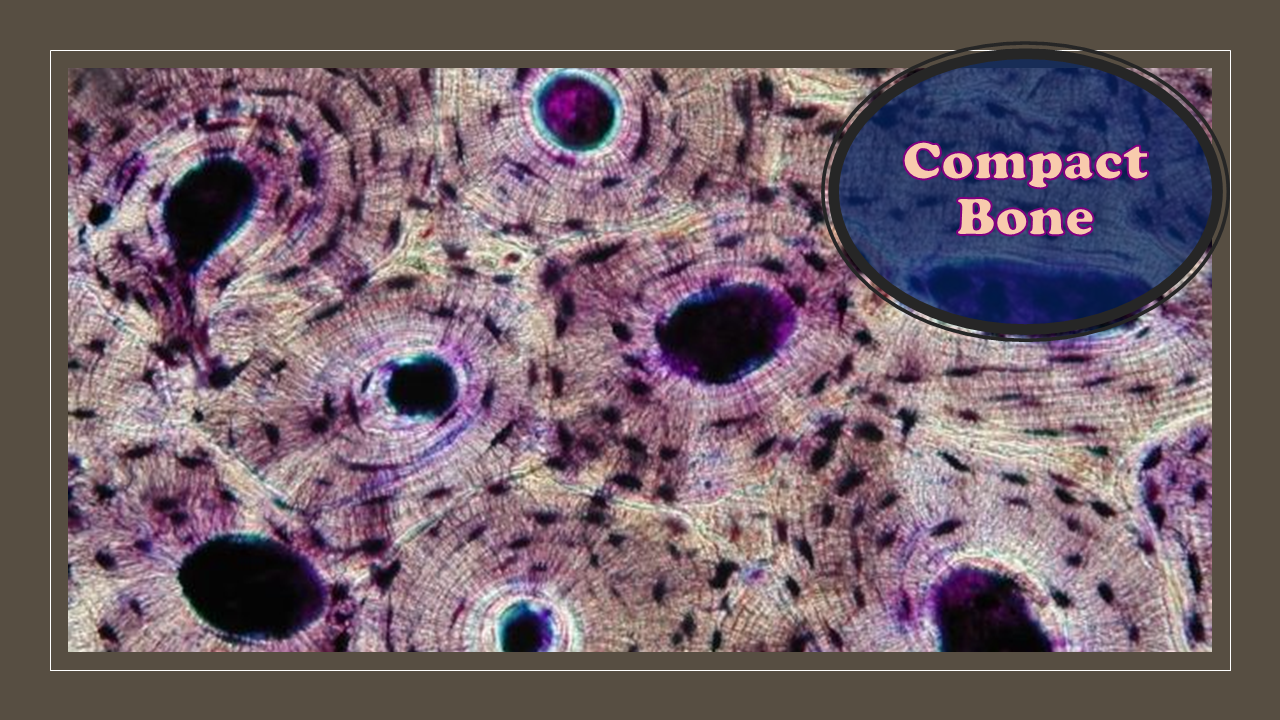
Compact (Cortical) Bone
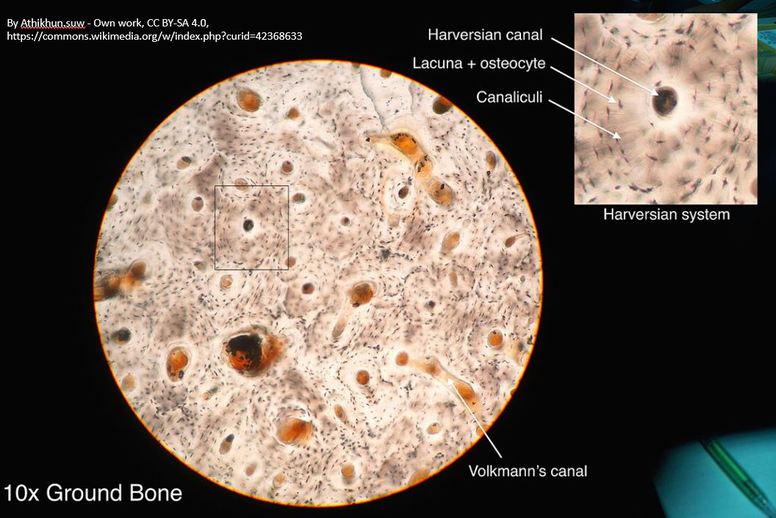
Compact (cortical) bone more dense and strong. It's primary purpose is to provide structural support for the body. Compact bone is made up of osteons which can be visualized on the slide below. This slide shows a cross-section of the femur (bone of upper leg), which is the longest bone in the human body. The circular pattern seen on a slide of bone tissue are osteons.
Each osteon consists of ringed layers, or lamellae, of compact bone tissue that surround a central canal (Haversian canal). The Haversian canal contains the bone's nerve and blood supplies.
Osteons are units of collagen tubes within other collagen tubes. Osteons allow bones to resist twisting stress.
Click on the short video below, to learn more about the structure of osteons.
Each osteon consists of ringed layers, or lamellae, of compact bone tissue that surround a central canal (Haversian canal). The Haversian canal contains the bone's nerve and blood supplies.
Osteons are units of collagen tubes within other collagen tubes. Osteons allow bones to resist twisting stress.
Click on the short video below, to learn more about the structure of osteons.
Video of Osteon Model
courtesy of https://youtu.be/As8oqkMDoT4
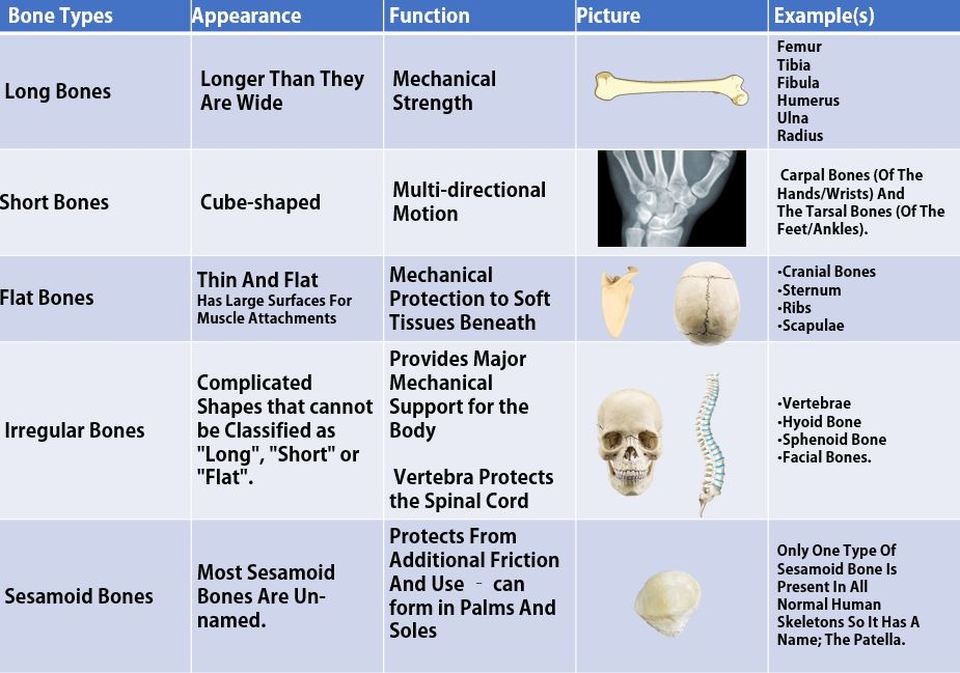
- Bone Classifications -
Classifications of Bones by Location
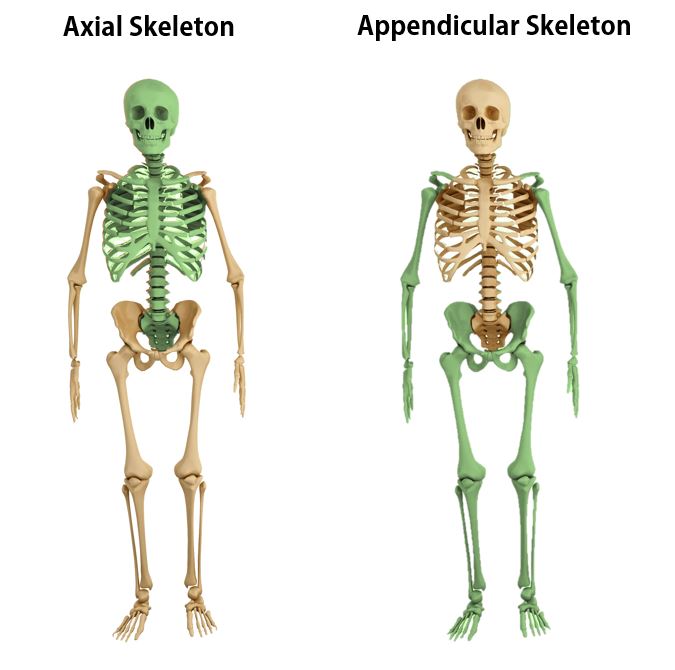
Our skeleton is divided into 2 main regions;
1) the axial skeleton
2) the appendicular skeleton
The axial skeleton has 80 named bones and consists of the skull, vertebral column, and rib cage.
The appendicular skeleton contains 126 named bones. It includes the the upper and lower limbs, pectoral (shoulder) girdle, and pelvic (hip) girdle.
The human body has 206 named bones total.
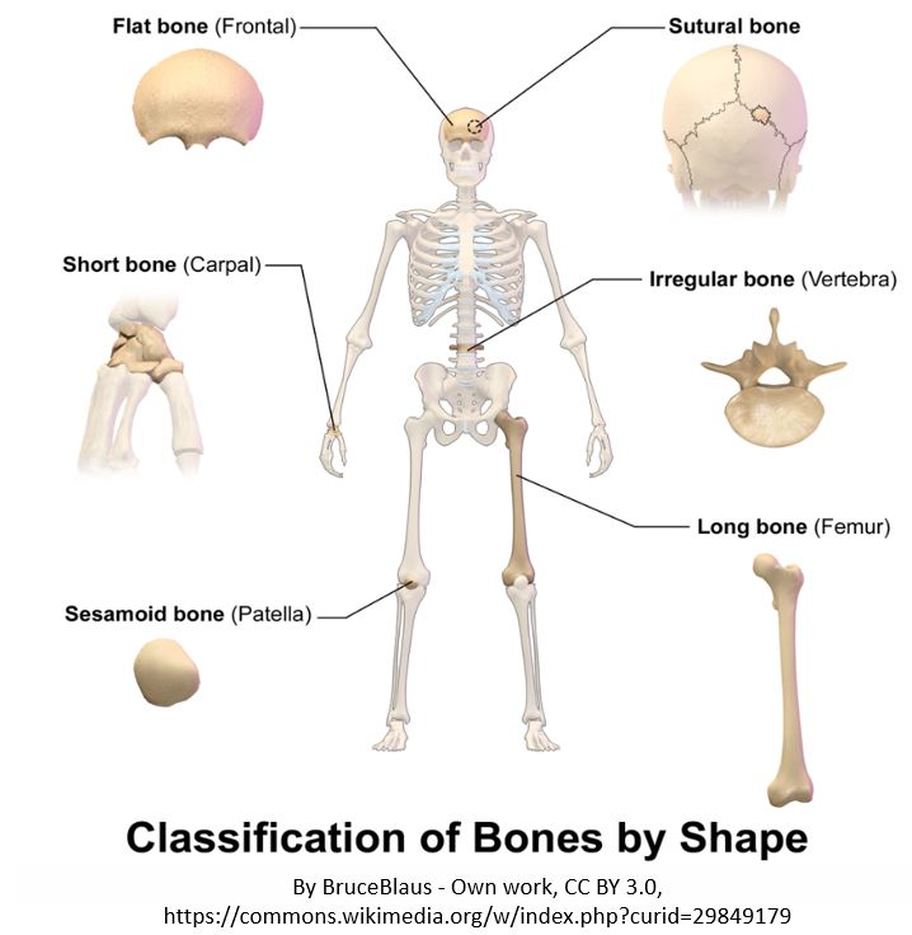
Classifications of Bones by Shape
Long Bones
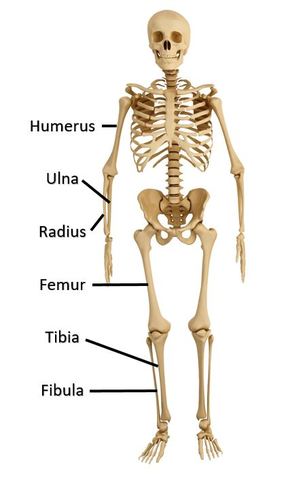
Long bones are longer than they are wide. Long bones string, dense bones that provide strength, structure, and mobility to the body.
Great examples of long bones can be seen in the arms (humerus, ulna and radius) and legs (femur, tibia and fibula) of your skeleton.
- Keep in mind, a bone can be considered a long bone, even if it is small. As long as it is much longer than it is wide, it qualifies as a "long bone"
For example, some bones in the fingers are small, but they are classified as long bones.
FUN FACT: The Femur is the Longest Bone of the Body.
Long bones are some of the longest bones in the body, such as the Femur, Humerus and Tibia but are also some of the smallest including the Metacarpals, Metatarsals and Phalanges.
Short Bones
Flat Bones
Flat bones appear as broad, and flat plates. Flat bones function to add a hard shield of protection for vital internal structures or to provide a large, broad surface for muscle attachment. Flat bones are especially strong. Some great examples of flat bone in your skeleton include the shoulder blade (scapula), the Sternum (breast bone), the cranium (skull), the pelvis and the ribs. The anterior and posterior surfaces of flat bones are composed of compact bone to provide strength and protection. The inner portion of long bones contains spongy bone which has the bone marrow. FUN FACT: In adults, the highest number of red blood cells are formed in flat bones.
Flat bones are wide and flat. We have flat bones that make up the cranial bones of the skull, the scapulae, the pelvis, the sternum and the rib cage.
Irregular Bones
Some bones are oddly shaped and do not fit into the other categories of bone ("Long", "Short" or "Flat"). These bones have a category all their own, called irregular bone. These bones have a non-uniform shape.
The irregular bones of your body includes your vertebrae, facial bones, the mandible, the sacrum and the hyoid bone (assists in swallowing). They primarily consist of cancellous bone, with a thin outer layer of compact bone.
Sesamoid Bones
|
Sesamoid bones are short or irregular bones that are embedded in a tendon. The best example of a sesamoid bone is the patella. The patella is not attached to the other bones in the joint. Instead, it is attached to the tendon. This allows your patella (known commonly as your knee cap) to glide along the distal edge of the femur. Other sesamoid bones can be found in your smallest carpel and metatarsals. Sesamoid bones function in the body to to protect the tendon by creating a strong surface that can better withstand friction.
|
Sutural Bones
Most textbooks leave out the category of "sutural bone", and for good reason. The other classifications of bones discussed on this page are based solely on the shape (or morphology) of the bone itself. The category or classification of sutural bone refers to bones in a specific location within the skeleton. Sutural bones (sometimes called Wormian bones) are the specific bones of the skull that come together and form extra bone pieces that occur within a suture (joint) in the cranium. These are irregular isolated bones that appear in addition to the usual centers of ossification of the cranium and, although unusual, are not rare.
Summary Table of Bone Classifications
Is a Bone a Tissue or an Organ?
The answer is... YES!
|
Bones are considered a tissue and an organ. Remember... An organ is made of different tissue types which come together to form a unit that has a specific function in the body. Even though our bones consist primarily of osseous tissue, they also contain nervous tissue in their nerves, fibrous tissue lining their cavities, and muscle and epithelial tissue in their blood vessels.
BONE AS A TISSUE: Bone tissue (or osseous tissue) is a type of connective tissue. Osseous tissue consists primarily of osteoblasts which makes the proteins and molecules needed to form the fibers and the ground substance which makes up the extracellular matrix. BONE AS AN ORGAN: When we refer to bones as an organ, we include not only the osseous tissue, but also the cartilage, nervous tissue, the epithelial tissue (in the form of blood vessels) and the fibrous connective tissue that functions together as a unit. A bone is an organ that makes up a large portion of the human skeleton. Bones function in your body to support and protect your internal organs and to allow for mobility. Bones also store vital minerals and produce red and white blood cells. |
|
The Functions of Our Bones
|
•Support – The bones of your body creates a rigid framework that provides structural support form the framework that supports the body.
•Protection – Your bones provide a protective casing around your brain, spinal cord, and vital organs •Movement – Your bones act as levers that are moved by your muscles to provide movement of body segments. •Mineral Storage – reservoir for minerals, especially calcium and phosphate •Blood Cell Formation – hematopoiesis occurs within the red marrow •Energy storage – yellow marrow stores fats |
Bones provide a lever that provides movement upon muscle contraction. In the animation below, contraction of the bicep muscle causes the forearm to move along the joint axis.
Your bones act as levers that are moved by your muscles to allow for mobility of different parts of your body. |
Bone Remodeling
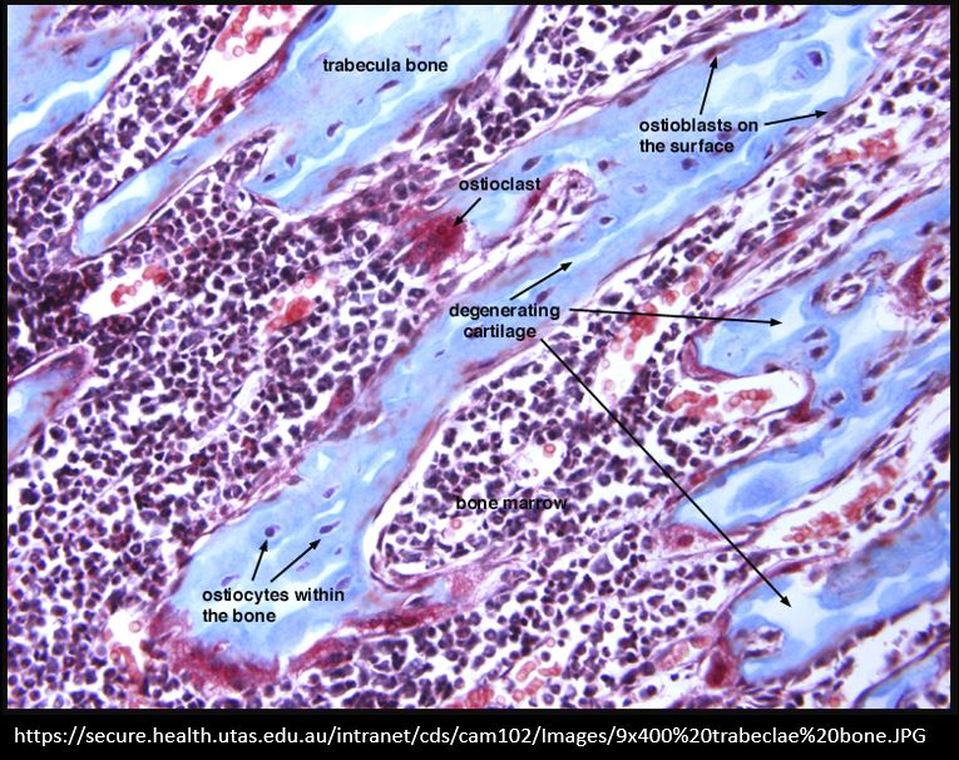
The trabeculae have three types of bone cells: osteoblasts (immature osteocytes), osteocytes and osteoclasts.
Osteoblasts function to build new bone for growth and repair by producing layers of new bone tissue composed largely of calcium and phosphate. Osteoblasts become osteocytes when they mature and they remain embedded in the bone tissue.
Osteoclasts are large cells that act to breakdown bone tissue. They destroy old or damaged bone so that it can be repaired and replaced. This breakdown / buildup cycle is referred to as bone remodeling.
Osteoblasts function to build new bone for growth and repair by producing layers of new bone tissue composed largely of calcium and phosphate. Osteoblasts become osteocytes when they mature and they remain embedded in the bone tissue.
Osteoclasts are large cells that act to breakdown bone tissue. They destroy old or damaged bone so that it can be repaired and replaced. This breakdown / buildup cycle is referred to as bone remodeling.
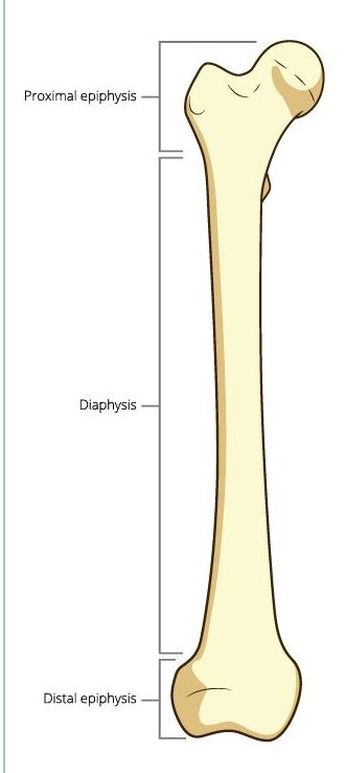
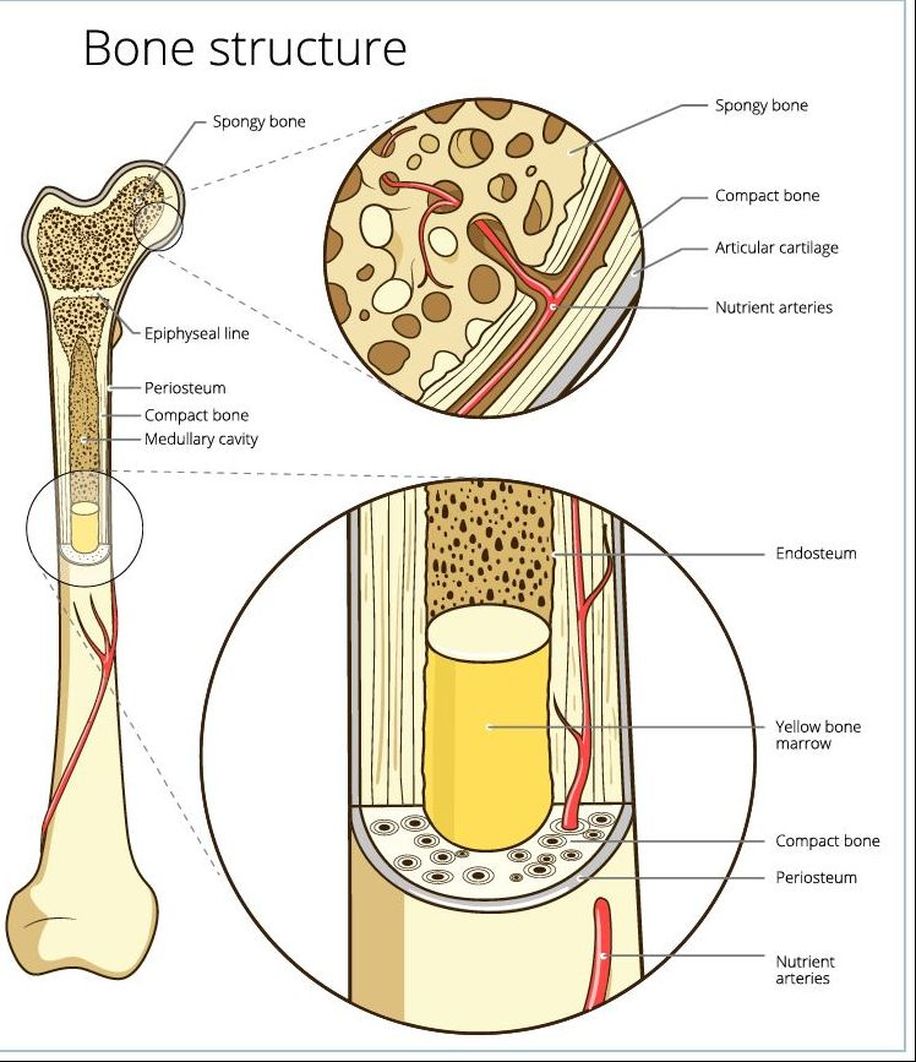
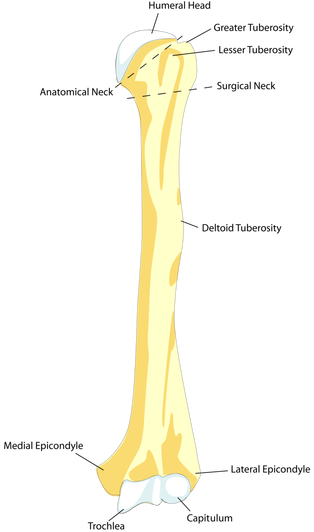
The Anatomy of a Bone
The bones of the arms and legs in humans are the largest in the body and are known as long bones. Long bones are made up of two types of bone tissue. The diaphysis (central part) of a long bone is composed of compact (cortical) bone. Spongy (cancellous) bone is found at the epiphysis (ends) of long bones and is also found in the pelvic bones, ribs, skull, and the vertebrae. it contains the red bone marrow that makes red blood cells and the yellow bone marrow which stores fats.
Be able to Locate and Identify Each of the Following Structures on a Long Bone
Long Bones
|
Bone Marrow - The two types of bone marrow are "red marrow" and "yellow marrow"(
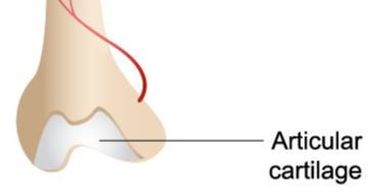
Red Marrow - Located within the medullary cavity, it consists mainly of hematopoietic cells that give rise to red blood cells, platelets, and most white of the blood cells of the body. Yellow Marrow - Located within the medullary cavity, it consists mainly of fat cells. Articular Cartilage - Articular cartilage is the smooth, white tissue that covers the ends of bones where they come together to form joints.
|
You should be able to identify the following structure in long bones:
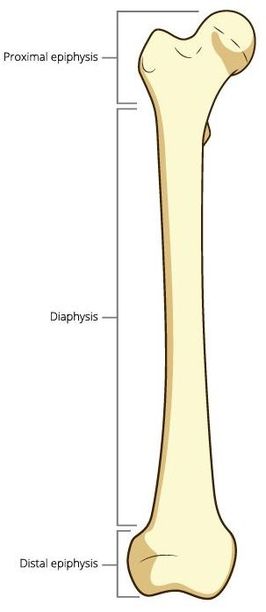
The Diaphysis - the middle section of the long bone (also called the shaft). The Epiphysis - the ends of the long bones The Epiphyseal Line - created by a plate of hyaline cartilage (found in children and adolescents) that permits growth and lengthening of the bone, as the cartilage reproduces and ossifies.
The Medullary Cavity - (Sometimes referred to as the Marrow Cavity) makes up part of the central cavity within the diaphysis (bone shaft) and houses red bone marrow (blood cells creation) and/or yellow bone marrow (adipose tissue) is stored; hence, the medullary cavity is also known as the marrow cavity.
The Periosteum - The layer of dense irregular connective tissue that contains osteoblasts. These osteoblasts are responsible for increasing the width of a long bone and the overall size of the other bone types. Osseous tissue does not contain any nerve endings and it does not have its own blood supply, except for the layer of the periosteum. Nutrient Foramen - All bones possess foramina (openings) for the entrance of the nourishing blood-vessels. In long bones, the nutrient foramen is located at the shaft and leads into a nutrient canal, which extends into the medullary cavity.
Compact Bone - In long bones, compact bone is found at the diaphysis (shaft_ region of the bone.
Spongy Bone - In long bones, spongy bone is found at the epiphysis (ends) of the bone. |
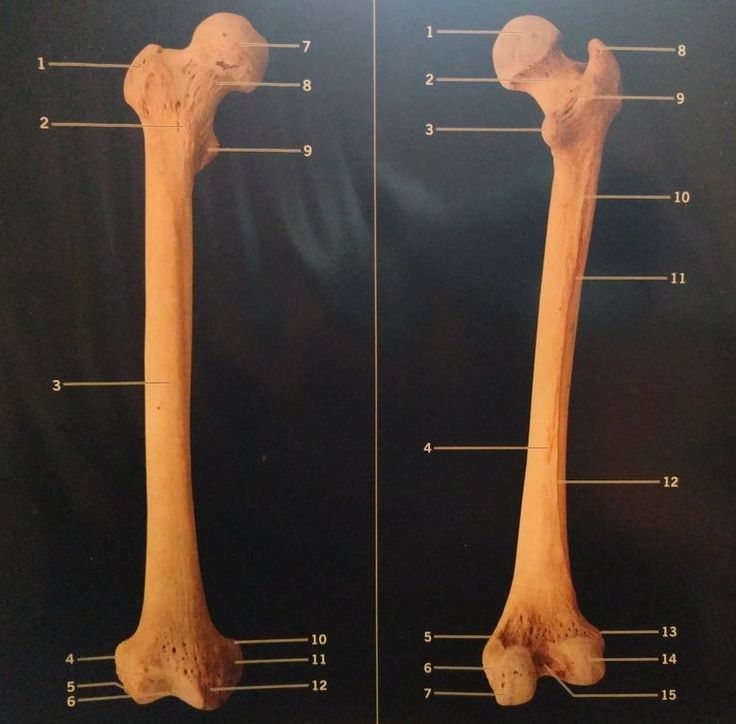
Identify the Structures of a Femur
For the practical exam, you will be expected to locate and identify the following structures of the femur. The femur will not be attached to a skeleton. You should be able to recognize the the anterior and the posterior of the femur by looking at its structure (morphology).
In the diagram below, the anterior and posterior view of the human femur is of the RIGHT LEG of the skeleton as shown. Keep in mind that due to anatomical positioning rules, "right" and "left" refer to the right and left side of the patient or the subject, and not of the observer.
|
FEMUR - ANTERIOR VIEW
|
FEMUR - POSTERIOR VIEW
|
|
Femur Anterior View KEY
|
Femur Posterior View KEY
|
THE EPIPHYSEAL LINE (PLATE)
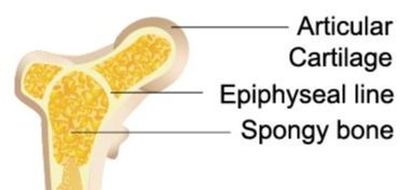
The epiphyseal line exists at the ends of adult long bones, between the diaphysis and the epiphysis. The epiphyseal plate is a disc-like structure composed of hyaline cartilage. Once your bones have fully formed, the epiphyseal line remains as a remnant of the epiphyseal plate that existed as your bones were still growing.
The epiphyseal line is the point at which the epiphysis and the diaphysis meet. This is an important anatomical landmark that defines where the diaphysis ends and the epiphysis begins.
The epiphyseal line is the point at which the epiphysis and the diaphysis meet. This is an important anatomical landmark that defines where the diaphysis ends and the epiphysis begins.
MEDULLARY CAVITY
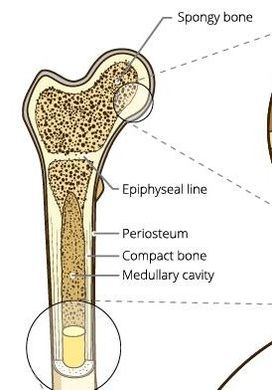
Medullary means "middle". So the medullary cavity (sometimes called the marrow cavity) is the cavity that lies at the center of the diaphysis of your long bones. In adults, the medullary cavity contains yellow bone marrow that stores energy in the form of fat. You also have yellow bone marrow in the spaces between the trabeculae of spongy bone.
YELLOW MARROW
Yellow bone marrow stores energy in the form of fats (triglycerides). Yellow bone marrow is found in the medullary cavities of adults and in the spaces between the trabeculae of spongy bone. The yellow bone marrow that is in the medullary cavities starts out as red marrow. Once a child reaches about 5 years of age, the marrow of the medullary cavity changes to yellow.
RED MARROW
In adults, red marrow is found primarily in the flat bones, which includes the hip bone, sternum (breast bone), skull, ribs, vertebrae and scapulae (shoulder blades).
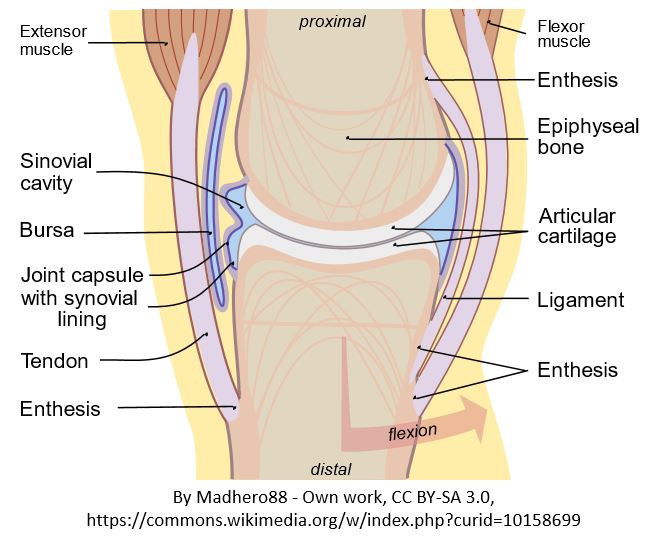
PERIOSTEUM
The periosteum is the membrane of connective tissue that surrounds the entire outside of the a bone, except for areas that are covered with articulate cartilage. This periosteal membrane has two sublayers. The superficial layer of the periosteum consists of dense irregular connective tissue which adds strength and resilience to the bone. The deep layer of the periosteum contains osteoblasts which function to produce new bone, and osteoclasts that act to break down bone in preparation for the bone's remodeling. As the osteoblasts form new layers of bone tissue, ring-like formations called lamellae form. The periosteum is the only portion of the bone that contains nerves and blood vessels. The deep layer contributes to the thickness of the bone, but not the length, since new material is being added to the surface. This type of growth is considered appositional growth.
YELLOW MARROW
Yellow bone marrow stores energy in the form of fats (triglycerides). Yellow bone marrow is found in the medullary cavities of adults and in the spaces between the trabeculae of spongy bone. The yellow bone marrow that is in the medullary cavities starts out as red marrow. Once a child reaches about 5 years of age, the marrow of the medullary cavity changes to yellow.
RED MARROW
In adults, red marrow is found primarily in the flat bones, which includes the hip bone, sternum (breast bone), skull, ribs, vertebrae and scapulae (shoulder blades).
PERIOSTEUM
The periosteum is the membrane of connective tissue that surrounds the entire outside of the a bone, except for areas that are covered with articulate cartilage. This periosteal membrane has two sublayers. The superficial layer of the periosteum consists of dense irregular connective tissue which adds strength and resilience to the bone. The deep layer of the periosteum contains osteoblasts which function to produce new bone, and osteoclasts that act to break down bone in preparation for the bone's remodeling. As the osteoblasts form new layers of bone tissue, ring-like formations called lamellae form. The periosteum is the only portion of the bone that contains nerves and blood vessels. The deep layer contributes to the thickness of the bone, but not the length, since new material is being added to the surface. This type of growth is considered appositional growth.
ARTICULATE CARTILAGE
Articulate Cartilage is found at the epiphysis of long bones, where it functions to provide a smooth surface for the gliding motion of the joint. Almost every joint in our bodies contains articulate cartilage.
NUTRIENT FORAMEN
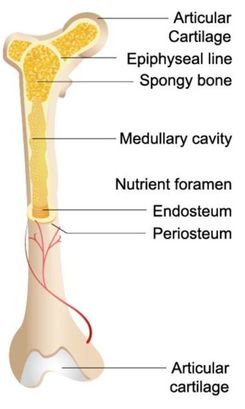
The word "foramen" means "hole" In anatomy, the nutrient foramen refers to a hole in the surface of a bone that allows blood vessels and nerves to reach the medullary cavity. All of your bones have foramina (plural of foramen), but the long bones have a particularly large nutrient foramen which is located on the diaphysis (shaft) of the bone.
You may recall that cartilage tissue does not have nerves or blood vessels, but don't think that bone tissue is the same way, because it is not. Unlike cartilage, your bones are have their own blood supply. In fact, you can have up to 11% of your blood in your bones at any given time.
The nutrient foreamen allows for the nutrient artery to enter the medullary cavity through the diaphysis, and it allows the nutrient vein to exit the interior of the bone. The
nutrient artery functions to supply nutrients to the areas of spongy bone and bone marrow that lie within the bone.
BONE MARKINGS
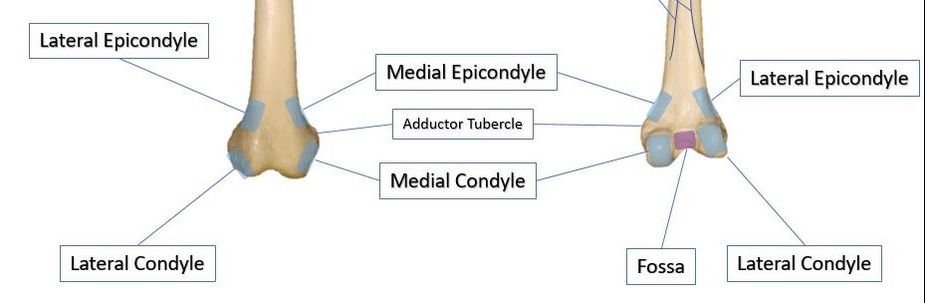
THE CONDYLE

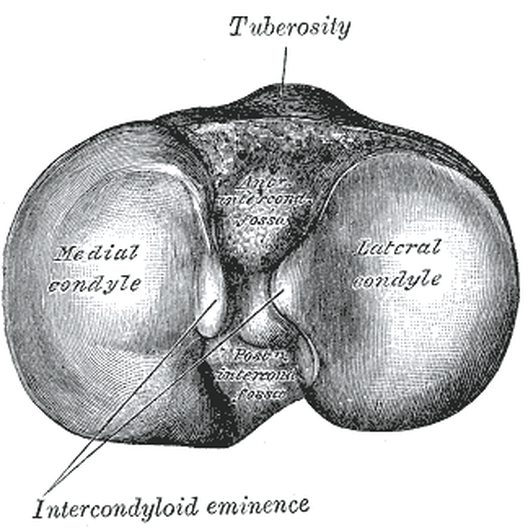
The Condyle
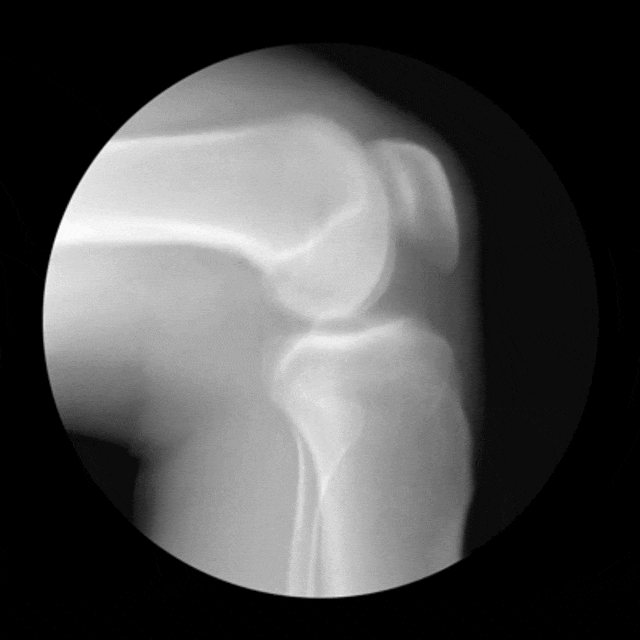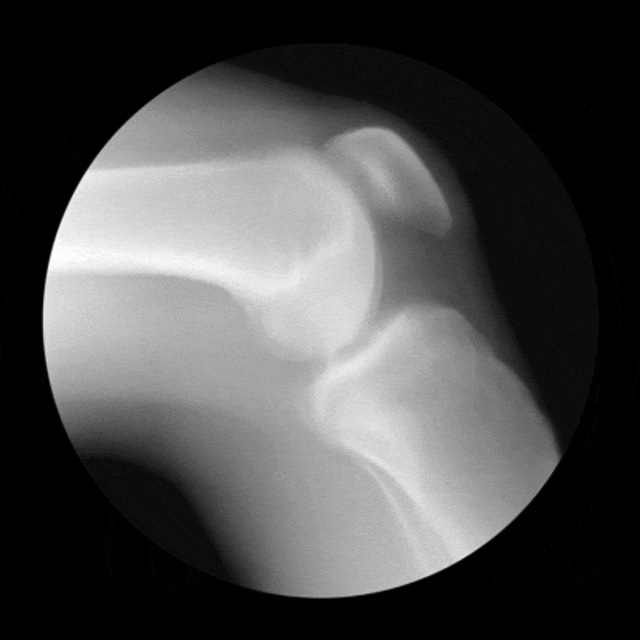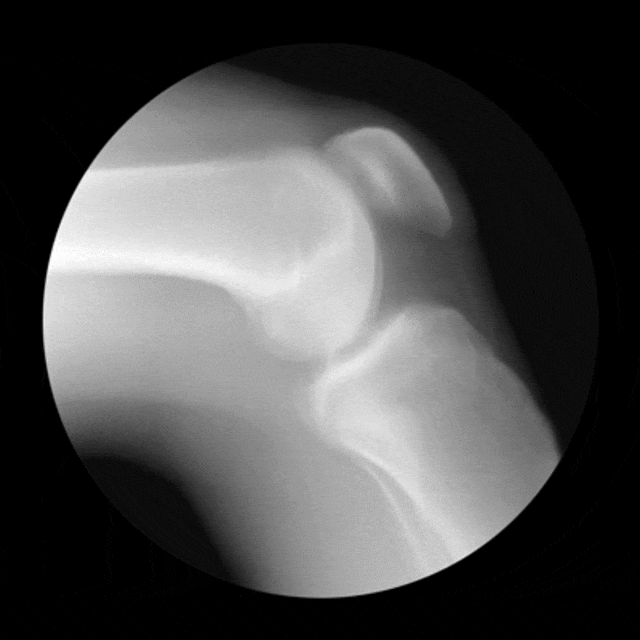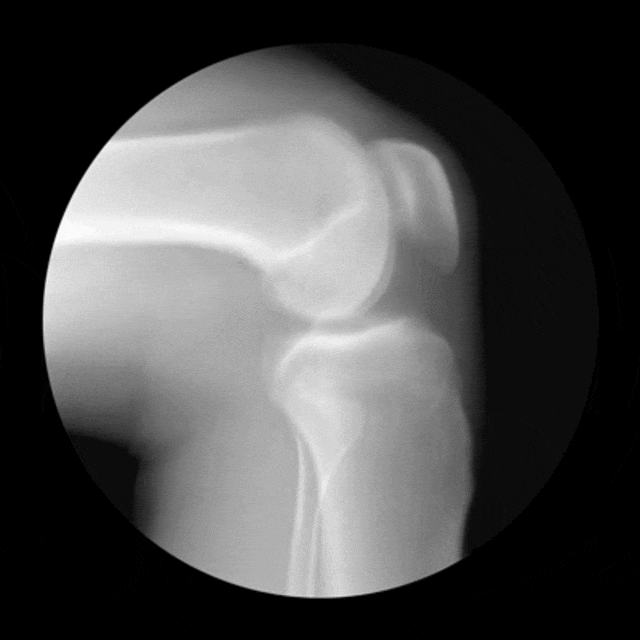
The term condyle is Greek for "knuckle". It refers to the round "knuckles" at the end of specific bone (usually around a joint) that fit together, like the pieces of a jigsaw puzzle. Condyles can be seen on at the ends of the femur and the tibia where they come together to form the knee joint. Each of these bones has a medial condyle and a lateral condyle.
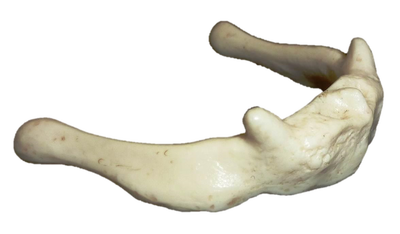
- Condyles can also be seen on the humerus at the elbow joint. This particular condyle is called the condyle of the humerus or condylus humeri. In a similar fashion, you have a mandibular condyle which in on the mandible (jaw bone) at the temporomandibular joint, and an occipital condyle on the occipital bone (bone at back of the skull) at the atlanto-occipital joint.
THE EPICONDYLE
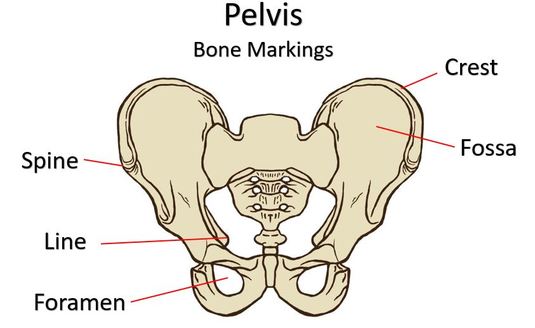
THE CREST
|
FISSURE
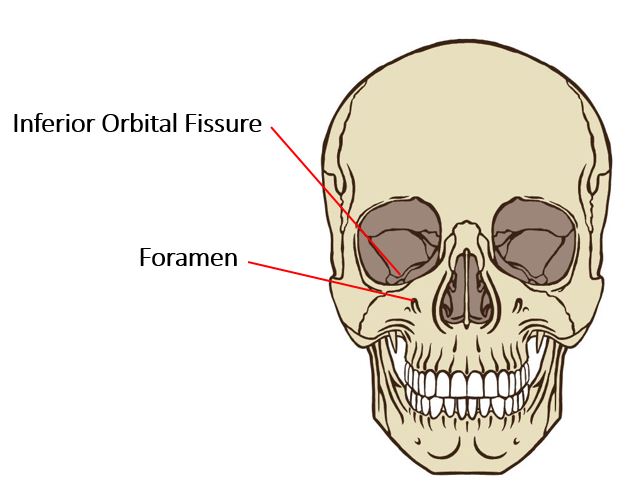
The word "fissure" means "groove" in Latin. In bone, a fissure is a thin slit-like opening that allows for the passage of vessels and nerves. FORAMEN
The word "foramen" means "opening". Each of your bones has one or more foramina, which are round or oval openings that allow vessels and nerves to enter the bone.
|
Table of Bone Marking Terminology
Bone Marking |
Definition |
Tuberosity |
Projection: Large rounded projection of bone; may be roughened |
Crest |
Narrow ridge of bone; usually prominent |
Trochanter |
Very large, blunt, irregularly shaped process (the only examples are on the femur) |
Line |
Narrow ridge of bone; less prominent than a crest |
Tubercle |
Small rounded projection or process |
Spine |
Sharp, slender, often pointed projection |
Process |
Any bony prominence |
Condyle |
Rounded articular projection, often articulates with a corresponding fossa |
Foramen |
|
Fissure |
Narrow slit-like opening |
Fossa |
Shallow basinlike depression in a bone, often serving as an articular surface |
Meatus |
Canal-like passageway |
Sinus |
Cavity within a bone, filled with air and lined with mucous membrane |
Notch |
Indentation at the edge of a structure |
Epicondyle |
Raised area on or above a condyle |