| envs_105_study_guide_midterm_3.pdf | |
| File Size: | 2087 kb |
| File Type: | |
|
|
|
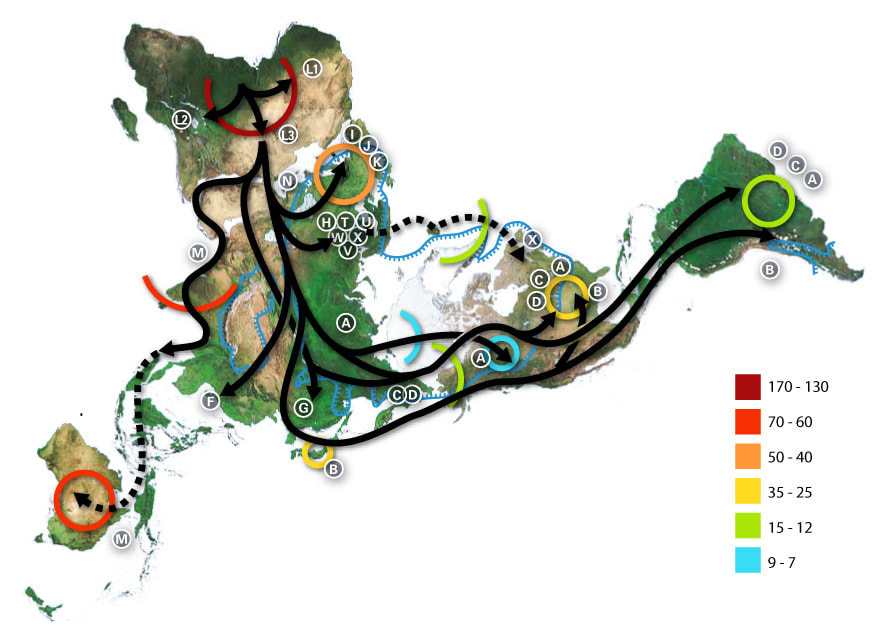
A History of the Human Population
- POPULATION ECOLOGY
worldpopulationhistory.org/map/1/mercator/1/0/25/
A SHORT TRIP
FROM 500,000 in 1650 TO 7.4 BILLION in 2015
PEOPLE ON EARTH
FROM 500,000 in 1650 TO 7.4 BILLION in 2015
PEOPLE ON EARTH
POPULATION ECOLOGY
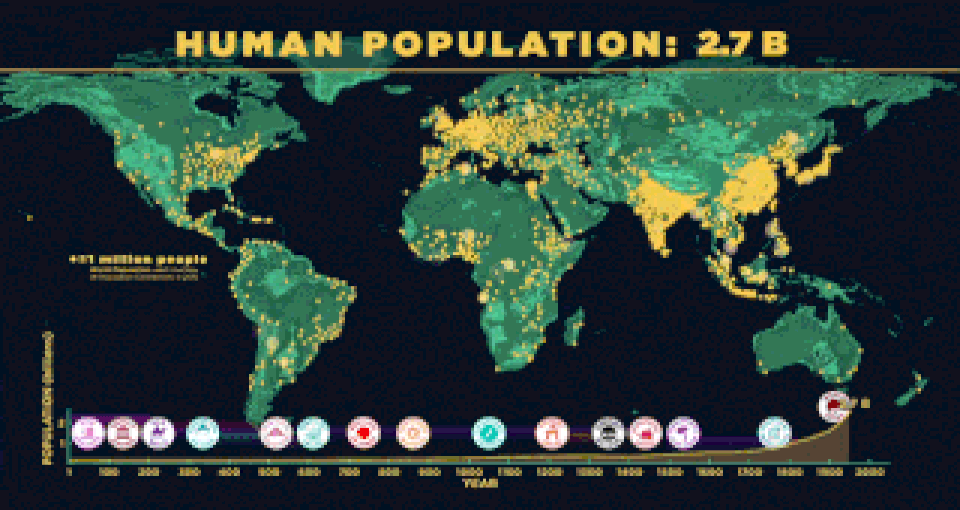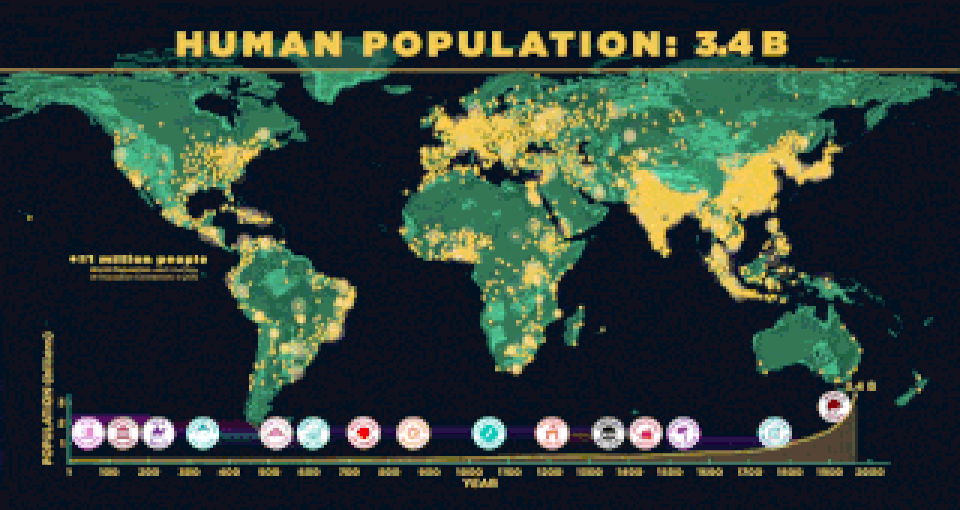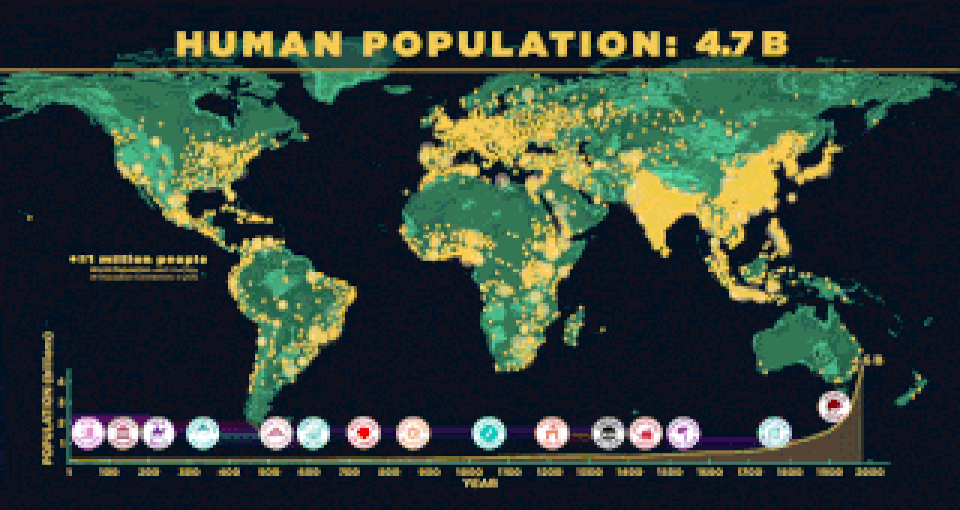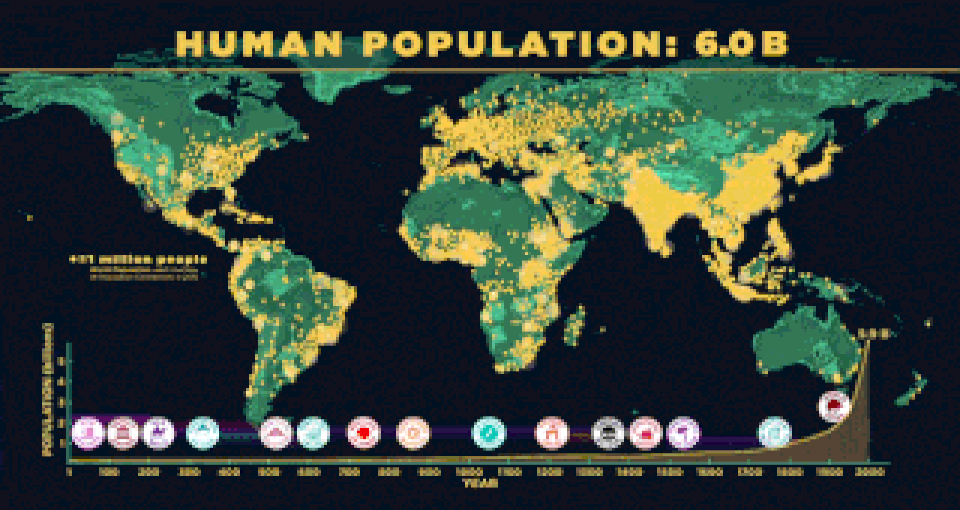
The world population was estimated to have reached 7.5 billion in April, 2017. The United Nations estimates it will further increase to 11.2 billion in the year 2100. |
A Look at the Events That Led to the Human Population Explosion
The Beginning of Modern Humans
- Homo Sapiens
The spread of humans and their rapidly increasing population has had a profound impact on the environment and millions of species worldwide.
|
|
Homo sapiens evolved in Africa around 200.000 years ago. These modern humans evolved from the Homo erectus which walked upright, had good manual dexterity and used fire.
The more modern traits we associate with modern humans evolved around 50.000 years ago. At this point in history, Homo sapiens ventured out of Africa and populated most of the world . Advantages that explain the evolutionary success of modern humans include
|
Curiosity and the human desire to understand and influence the environment and to explain and manipulate phenomena (or events) has provided the foundation for developing science, philosophy, religion, anthropology and numerous other fields of knowledge." |
|
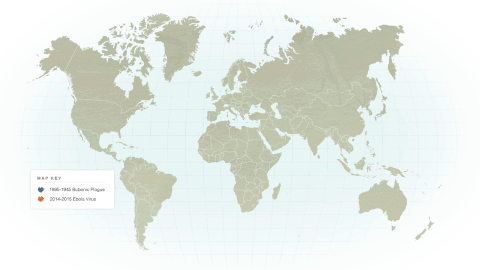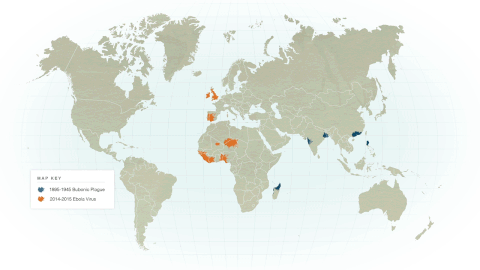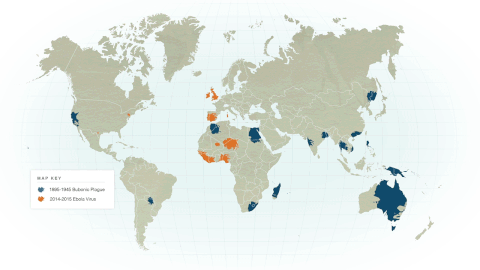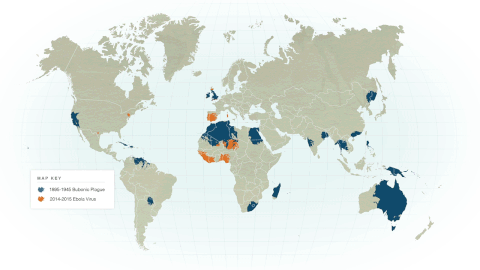
The world population peaks at ~ 384 million people around the mid 1300's, then quickly declines due to the Bubonic Plague (a.k.a. The Black Death). The Black Death that began in China in 1334 quickly spread along trade routs to Constantinople, Europe and finally Italy in 1347. It has been estimated that as many as 50% of the European population fell ill, killing most of the infected people within the short span of 1 week. The plague killed about (1/5) one-fifth of the entire world's population. This correlates to an estimated 42 million deaths.
|
|
The bubonic plague was carried by infected people, fleas and animals. This made the spread of the infection quick, deadly and difficult to control.

The depopulation of Europe caused by the plague led to changes in hygiene and heath awareness, as well as social and economic changes. The world's population had decreased to 342 million people by 1400 A.D.
In 1388, the English Parliament passes an act forbidding citizens from throwing garbage into ditches, rivers, and waterways.
In 1388, the English Parliament passes an act forbidding citizens from throwing garbage into ditches, rivers, and waterways.
Soon after, in the 1500's, Smallpox spread through the Americas killing at least one-third of the indigenous population.
|
In 1650, the world's population was 0.5 Billion people. The discovery of germs as the cause of disease occurs later that century due to the invention of the microscope.
The increased knowledge of bacteria, viruses and the spread of disease changes the sanitation and hygienic practices of people in society. |
Alexander Cummings patents the first flush toilet 1775. Thomas Crapper added widespread popularity and several refinements to this invention a hundred years later.
The discovery of "germ theory" and the invention of the microscope lead to the first Small Pox Vaccine in 1796 by the English physician Edward Jenner. |
The World Population Hits 1 Billion in 1800
|
The world population reaches 1 billion. Global life expectancy is only approximately 30 years, due to high child mortality rates.
Social reformer Edwin Chadwick starts the Public Health movement in 1843. Improvements in sanitation and awareness continued to combat diseases and increase the health and longevity of the human race. |
|
|
Farming and domestication of animals has been around since about 10,000 B.C. However, farming technologies such as irrigation, crop rotation and fertilizers only developed in the 1800's, beginning with the British Agricultural Revolution and spreading to developed nations since 1900. These new developments played a significant role in the growth of the human population.
Modern agriculture has had a negative impact on the environment.has raised social, political, and environmental issues including sequestering land and water, pesticide use and water pollution. |
|
Physician John Snow links the spread of cholera to contaminated water in 1854. Snow’s findings lead to changes in the water and sewage systems around the world.
In 1902, William Thompson Sedgwich published The Principles of Sanitary Science and Public Health.This book connected water pollution to the Lowell typhoid epidemic in 1890 and helped to raise awareness on the importance of sanitation. Interestingly, Jersey City (United States) becomes the first population center to chlorinate the water supply in 1908, drastically reducing typhoid rates. |
|
In 1927, the world population reaches 2 billion people. The global life expectancy is 39 years.
Population Ecology |
A hallmark of the last 150 years has been the ability of farmers to increase food production. The amount of grain harvested worldwide increased from 631 million tons in 1950 to 1.65 billion tons in 1984. However, the increase in food production was not met with equitable distribution due to poverty.
Public health advancements played a huge role in increasing the world population. Access to clean drinking water increased from 50% of the population before 1990 to 75%. The discovery of germs and creation of vaccines. The germ theory of disease of the 1870's led to water purification and nutritional education. As of this year, 2017, the world's population is now an astounding 7.5 Billion people. |
|
This principle in population ecology provides the basis for formulating predictive theories Population density Dispersion pattern - The way individuals are spaced within an area
|
|
|
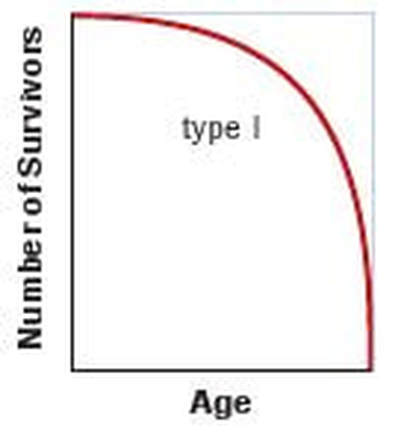
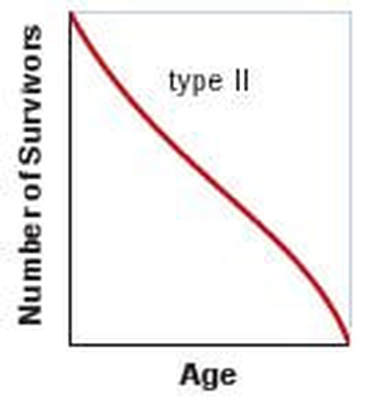
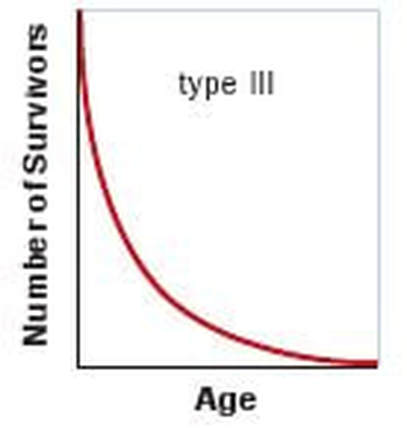
Survivorship curves
How do we make a survivorship curve? Plot the log of the percentage of survivors by the percent maximum lifespan to get the “survivorship curves”. There are 3 types of survivorship curves
1. Type I survivorship curve
2. Type II survivorship curve
3. Type III survivorship curve
|
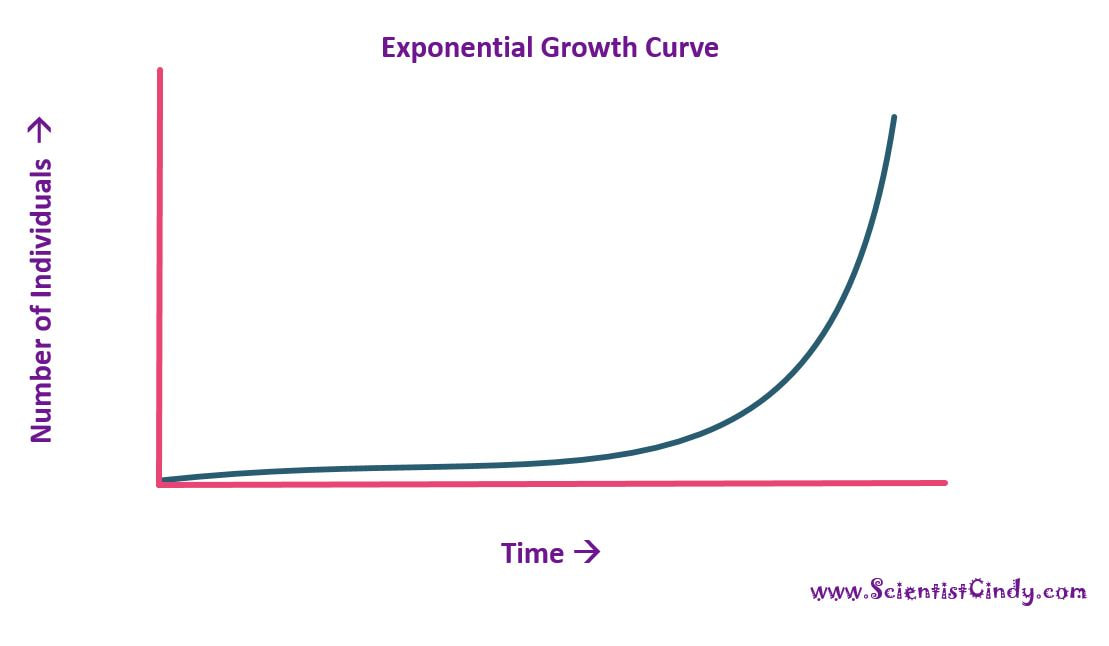
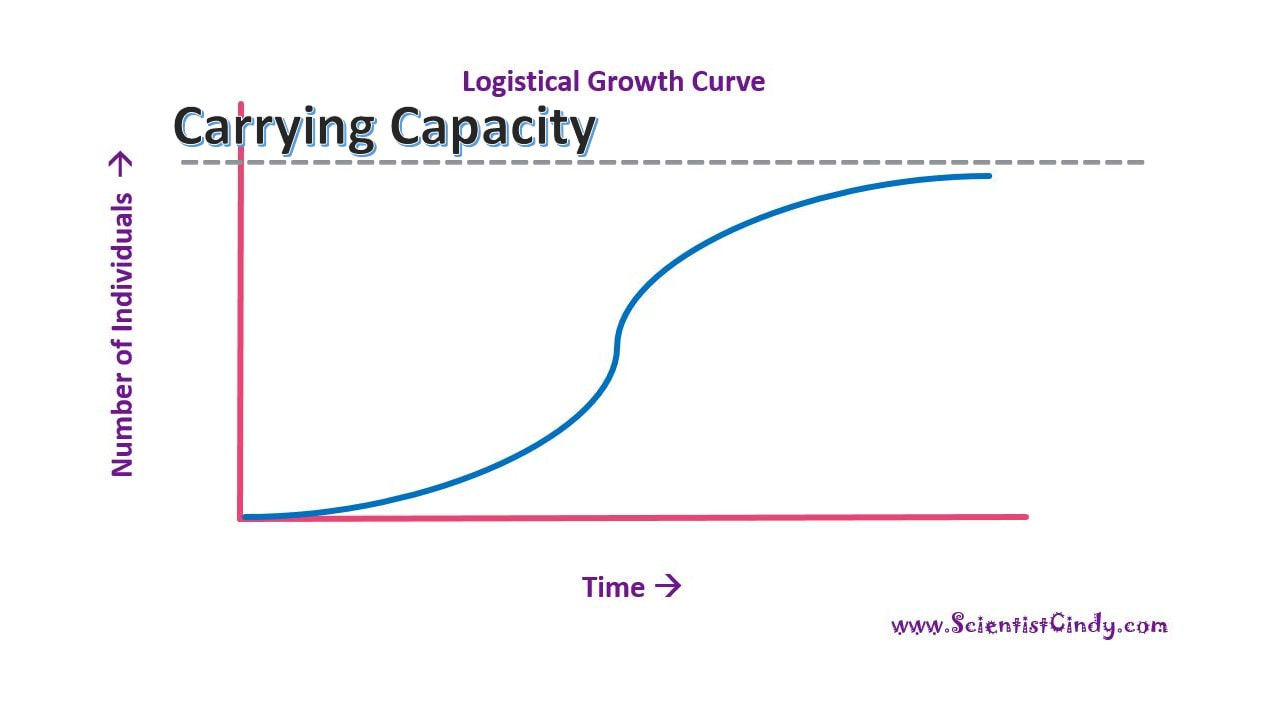
Two patterns of population growth:
- Exponential (J-shaped) - occurs when there are plenty of resources
- Logistic (s-shaped) - begins to occur when population gets too high and it is approaching the carrying capacity of the ecosystem.
Exponential Growth Model
•When a population is introduced to a new environment, it will often display Exponential Growth.
- In the exponential model of population growth, you do not see the effect of limiting factors.
- Population undergo rapid and explosive growth of population.
- This equation expresses rate of change
- the intrinsic rate of increase “r” is assumed to be constant
•When a population is introduced to a new environment, it will often display Exponential Growth.
•After some time, this will change to a logistic growth model. WHY? This is because as the population increases, there is competition for resources. The population approaches the carrying capacity of the ecosystem.
Logistic Growth Model
• The carrying capacity is the limit of the individuals of a certain species that a particular ecosystem can support.
Limiting factors that contribute to the logistical growth model are …
- Limited Food
- Limited Space
- Limited water
- Illness
- Intraspecific competition – when members of the same species compete for limited resources. This leads to a reduction in fitness for both individuals.
- Interspecific competition - when members of different species compete for a shared resource.
“Boom-and-bust” population cycles
- These are dramatic fluxuations in population
Boom-and-Bust cycles occur when the population growth of one species is closely tied to a limiting factor that may be expended.
- The predator populations increase and decrease as the prey numbers change.
- Predation may be an important cause of density-dependent mortality for some prey.
- Boom-and-bust cycles: Prey populations rapidly increase.
The Boom-and-Bust cycle has two-phases:
- Boom – rapid population increase is followed by a…
- BUST – population falls back to minimal levels
Example of Boom-and-Bust cycle - Lynx and snowshoe hare population cycles
- Lynx and snowshoe hare population cycles have a period of rapid population increase followed by a sudden precipitous decline in numbers.
- The increase is prey is then followed by an increase in the predator population.
- As predators eat the prey, the prey population goes down.
- As the predator’s food source becomes scarce, the predator population decreases.
- As the predator population decreases, The prey population can increase again
- —the cycle repeats; for example, the snowshoe hare and lynx have a 10-year cycle.
|
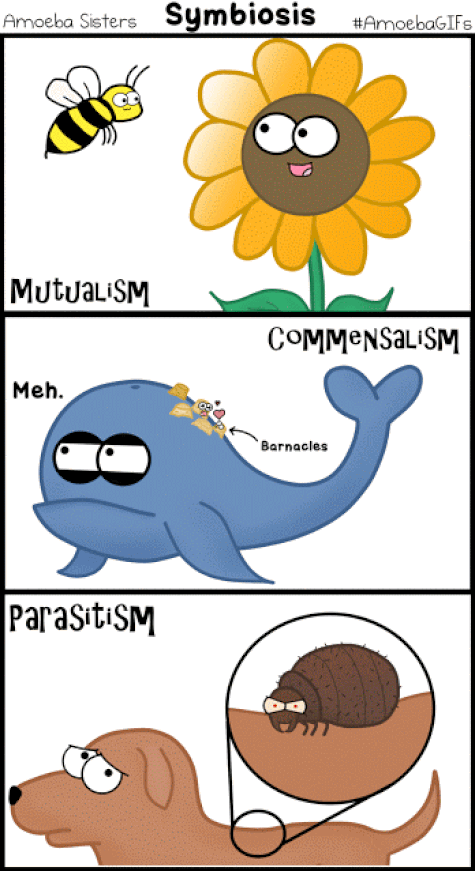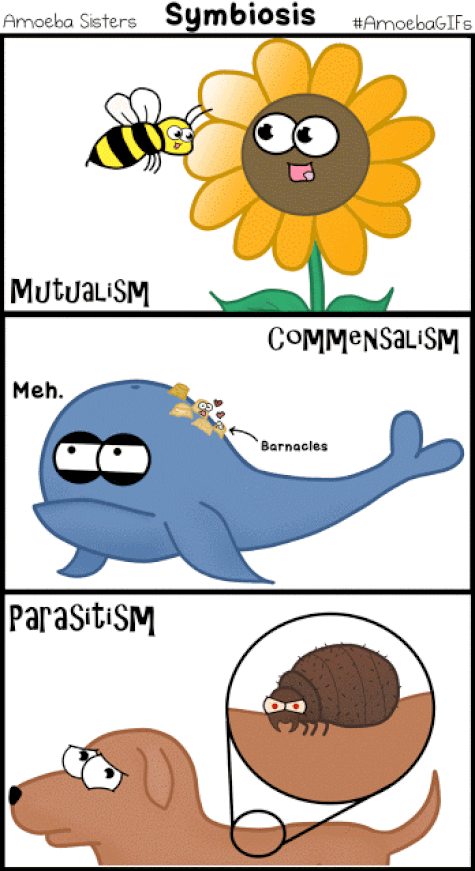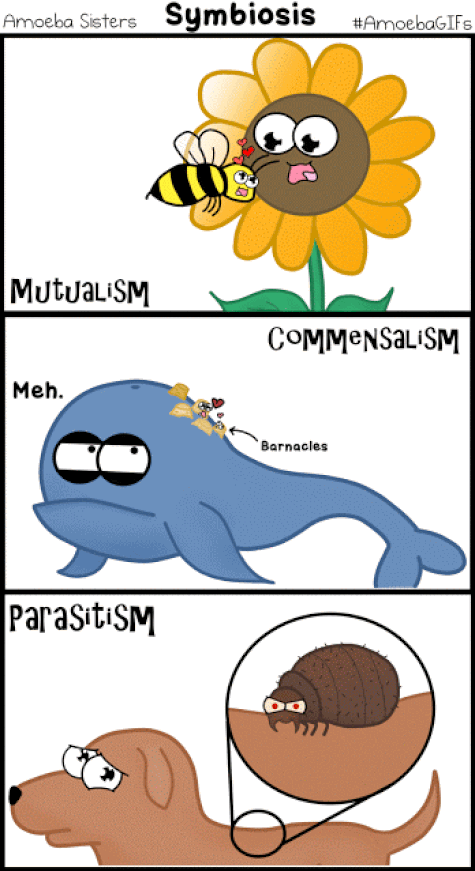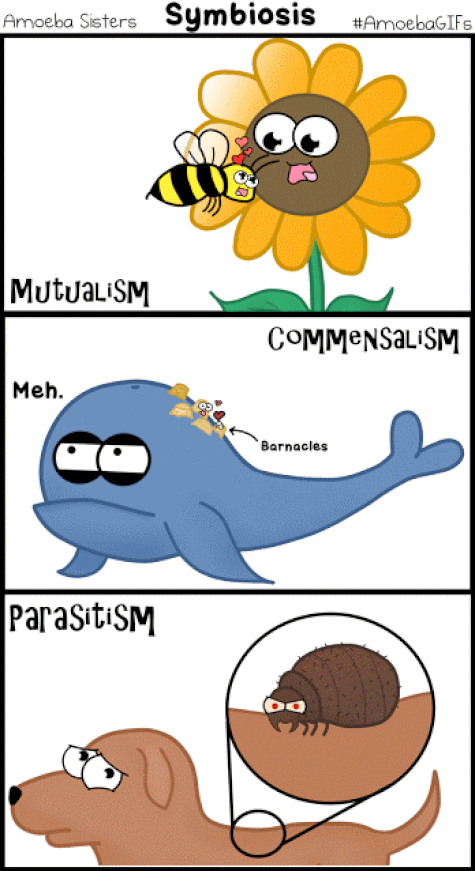
What is Symbiosis?
Symbiosis is the result of coevolution, the interdependent evolution of two interacting species. In symbiosis, individuals of one species usually live in or on or around the individuals of another species. At least one of the species—and sometimes both—uses its partner’s resources. Types of Symbiosis There are 3 types of symbiotic relationship
|
MUTUALISTIC SYMBIOTIC RELATIONSHIPS –
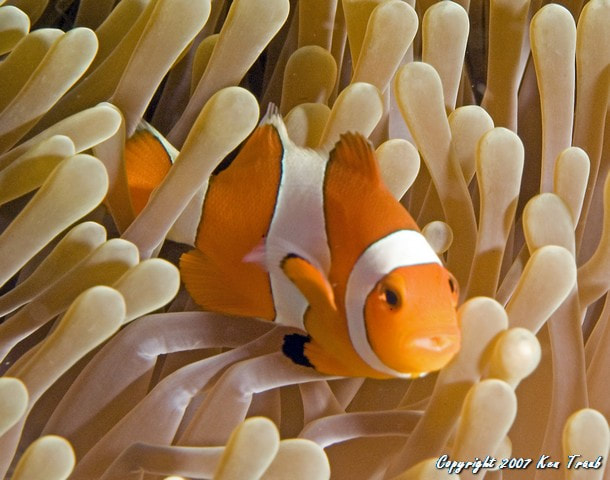
Sea Anemone and the Clown Fish
Clownfish are one of the only species that can survive the deadly sting of the Sea Anemone. By making the anemone their home, clownfish become immune to its sting.
These fish will gently touch every part of their bodies to the anemone’s tentacles until it no longer affects them. A layer of mucus then forms on the clownfish’s body to prevent it from getting stung again.
These fish will gently touch every part of their bodies to the anemone’s tentacles until it no longer affects them. A layer of mucus then forms on the clownfish’s body to prevent it from getting stung again.
Parasitic Relationships

The tongue louse
The tongue louse is a parasite that replaces the tongue of its victims. Tongue lice are all born as males. Each louse searches for a host. When they find a fish, they enter the fish. If there is no other louse infesting the fish, the louse will turn into a female and wait for a male to join it inside the fish host. If he finds there is already a female infesting the fish, he will remain male and mate with her. As this transformation takes place, the female’s body grows enormously and anchors itself firmly inside the mouth of the unlucky fish.
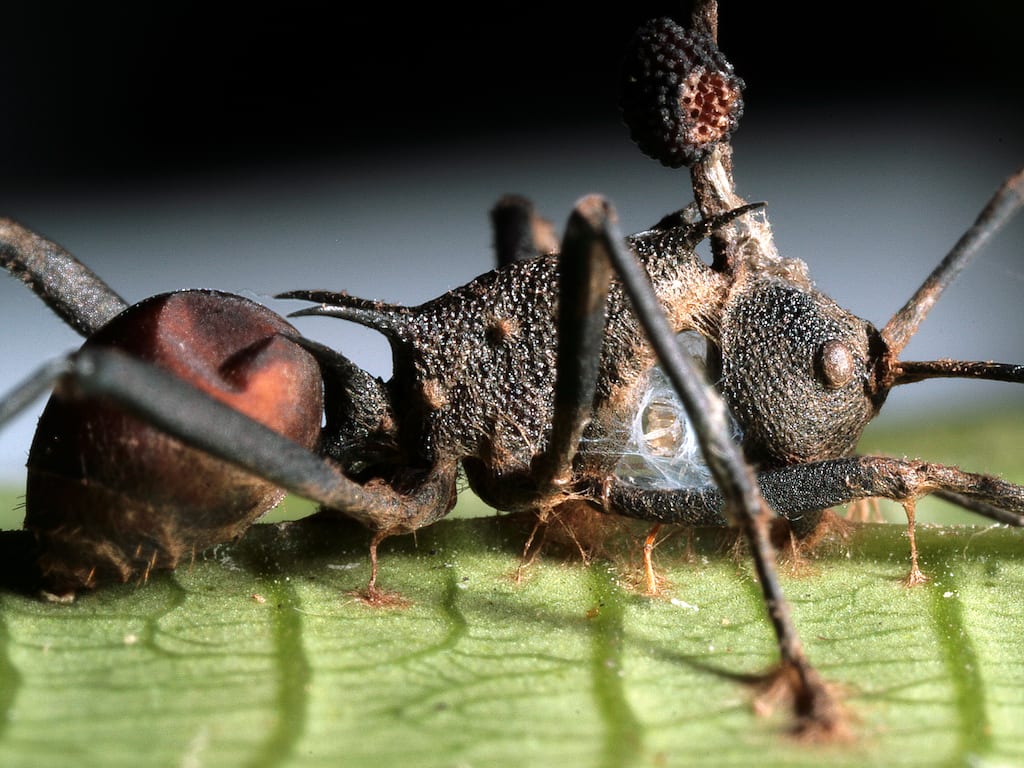
ZOMBIE ANTS

A parasitic fungus is known to manipulate the brains of ants turning them into slavelike "zombies". The fungus releases its mind-controlling chemical cocktail on its host.
Fungi of the genus Ophiocordyceps — so-called zombie ant fungi — need ants to complete their life cycle. When an ant comes across fungal spores while foraging, the fungus infects the insect and quickly spreads throughout its body.
A carpenter ant infected with a zombie ant fungus in the genus Ophiocordyceps. Once the fungus kills its hapless drone it grows a spore-releasing stalk from the ant's head in order to infect more ants.
Fungal cells in the ant's head release chemicals that hijack the insect's central nervous system. The fungus forces the ant to climb up vegetation and clamp down onto a leaf or twig before killing its hapless drone. It then grows a spore-releasing stalk out of the back of the victim's head to infect more ants on the ground below.
Fungi of the genus Ophiocordyceps — so-called zombie ant fungi — need ants to complete their life cycle. When an ant comes across fungal spores while foraging, the fungus infects the insect and quickly spreads throughout its body.
A carpenter ant infected with a zombie ant fungus in the genus Ophiocordyceps. Once the fungus kills its hapless drone it grows a spore-releasing stalk from the ant's head in order to infect more ants.
Fungal cells in the ant's head release chemicals that hijack the insect's central nervous system. The fungus forces the ant to climb up vegetation and clamp down onto a leaf or twig before killing its hapless drone. It then grows a spore-releasing stalk out of the back of the victim's head to infect more ants on the ground below.
LIFE CYCLE OF A BOTFLY

Botflies, or Dermatobia hominis for humans and the genus Gasterophilus for other mammals, are a bumble bee-like fly that require a human or mammal host in order to complete their life cycle. The life cycle of the botfly is comprised of four stages.
Egg Transmission
Adult female botflies lay their eggs on blood-sucking insects, such as mosquitoes or ticks, that they capture during flight. This practice is known as phoresy. After a period of 10 to 140 days, the host insect consumes a blood meal. This transfers the mature botfly eggs from the flying insect to the warm-blooded animal, which then hatch upon feeling the temperature increase. Adult females can also attach their eggs directly onto the hairs of mammal hosts. Egg hatching and larvae movement may cause the mammal to bite or scratch at the area.
It's a Grub Life
The mammal may consume some of the first instar larvae by licking them. Alternatively, the larvae may travel down hair follicles or through bite wounds and burrow into the mammal's skin. From here, the larvae undergo their final two instars, or molt periods, in the skin of the mammal or in the digestive tract during the winter. Larvae developing in the digestive tract attach to the system's walls and feed on tissue. In early spring, they detach as third instars and are expelled through the mammal's feces. Third instar larvae growing in the skin drop from the mammal host after a period of 30 days.
Rest and Renewal
Mature larvae expelled through feces or dropped down from skin in early spring burrow into soil and begin to pupate within two or three days. Pupae do not feed. Instead, they use this time to transform into adults. For a period of one month, the pupae develop adult features, such as wings and antennae. Once fully transformed, sexually mature adult botflies emerge and begin the life cycle over again.
Life Cycle Completion
Like pupae, adult botflies do not feed. Newly emerged from their pupal cases, the adult botflies have sensitive antennae to make up for their poor vision. Male and female adults depend on their sensitive antennae to find each other and mate. During summer and fall, adult females seek hosts for their eggs, whether they catch a fly or mosquito and transfer their eggs to them, or directly attach their eggs to warm-blooded mammals such as cattle, rabbits, sheep and horses.
Egg Transmission
Adult female botflies lay their eggs on blood-sucking insects, such as mosquitoes or ticks, that they capture during flight. This practice is known as phoresy. After a period of 10 to 140 days, the host insect consumes a blood meal. This transfers the mature botfly eggs from the flying insect to the warm-blooded animal, which then hatch upon feeling the temperature increase. Adult females can also attach their eggs directly onto the hairs of mammal hosts. Egg hatching and larvae movement may cause the mammal to bite or scratch at the area.
It's a Grub Life
The mammal may consume some of the first instar larvae by licking them. Alternatively, the larvae may travel down hair follicles or through bite wounds and burrow into the mammal's skin. From here, the larvae undergo their final two instars, or molt periods, in the skin of the mammal or in the digestive tract during the winter. Larvae developing in the digestive tract attach to the system's walls and feed on tissue. In early spring, they detach as third instars and are expelled through the mammal's feces. Third instar larvae growing in the skin drop from the mammal host after a period of 30 days.
Rest and Renewal
Mature larvae expelled through feces or dropped down from skin in early spring burrow into soil and begin to pupate within two or three days. Pupae do not feed. Instead, they use this time to transform into adults. For a period of one month, the pupae develop adult features, such as wings and antennae. Once fully transformed, sexually mature adult botflies emerge and begin the life cycle over again.
Life Cycle Completion
Like pupae, adult botflies do not feed. Newly emerged from their pupal cases, the adult botflies have sensitive antennae to make up for their poor vision. Male and female adults depend on their sensitive antennae to find each other and mate. During summer and fall, adult females seek hosts for their eggs, whether they catch a fly or mosquito and transfer their eggs to them, or directly attach their eggs to warm-blooded mammals such as cattle, rabbits, sheep and horses.