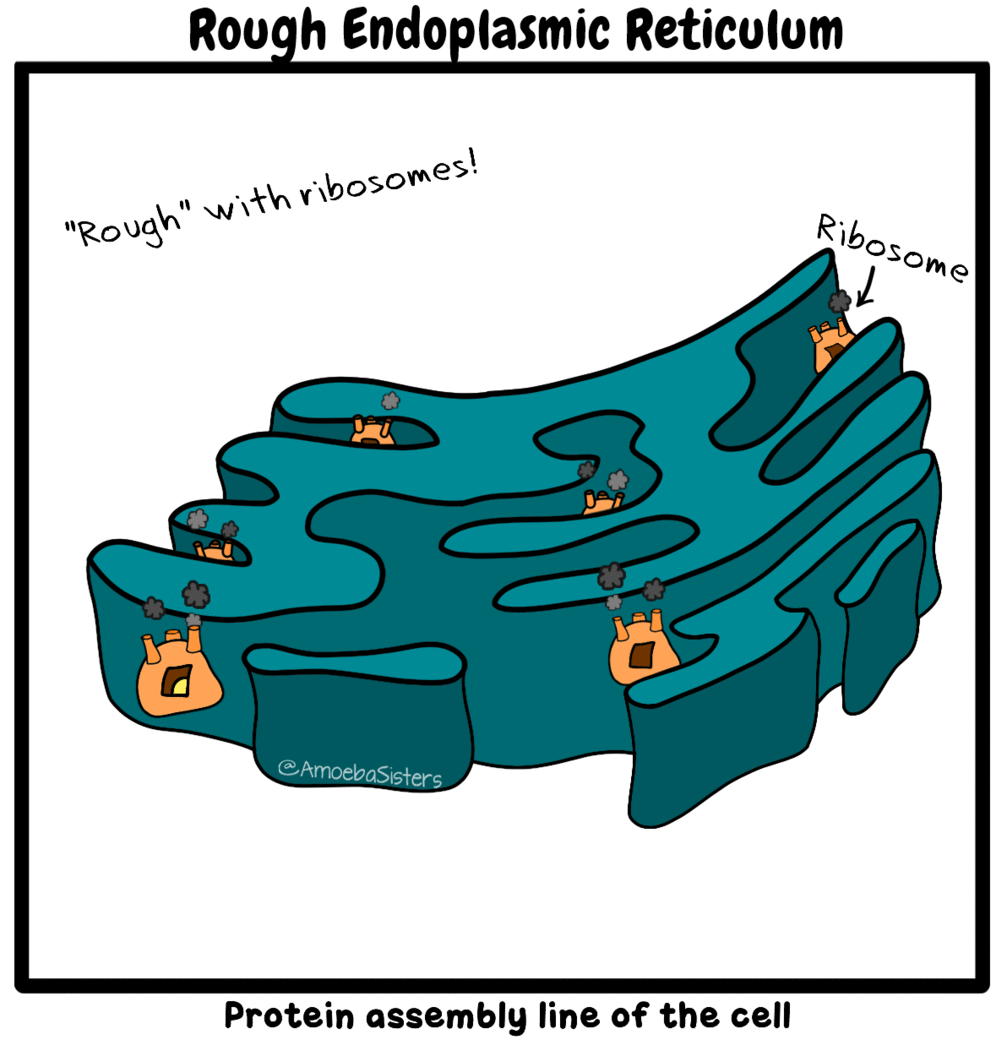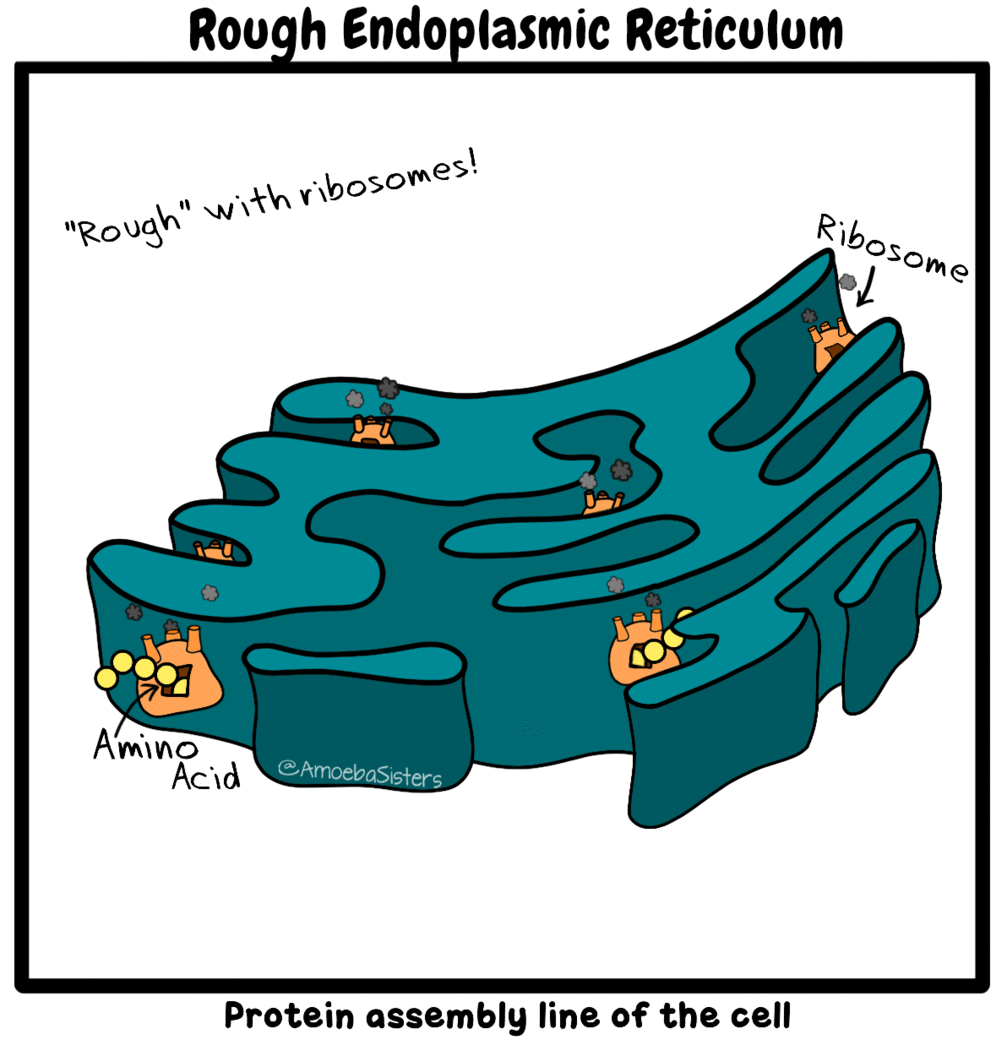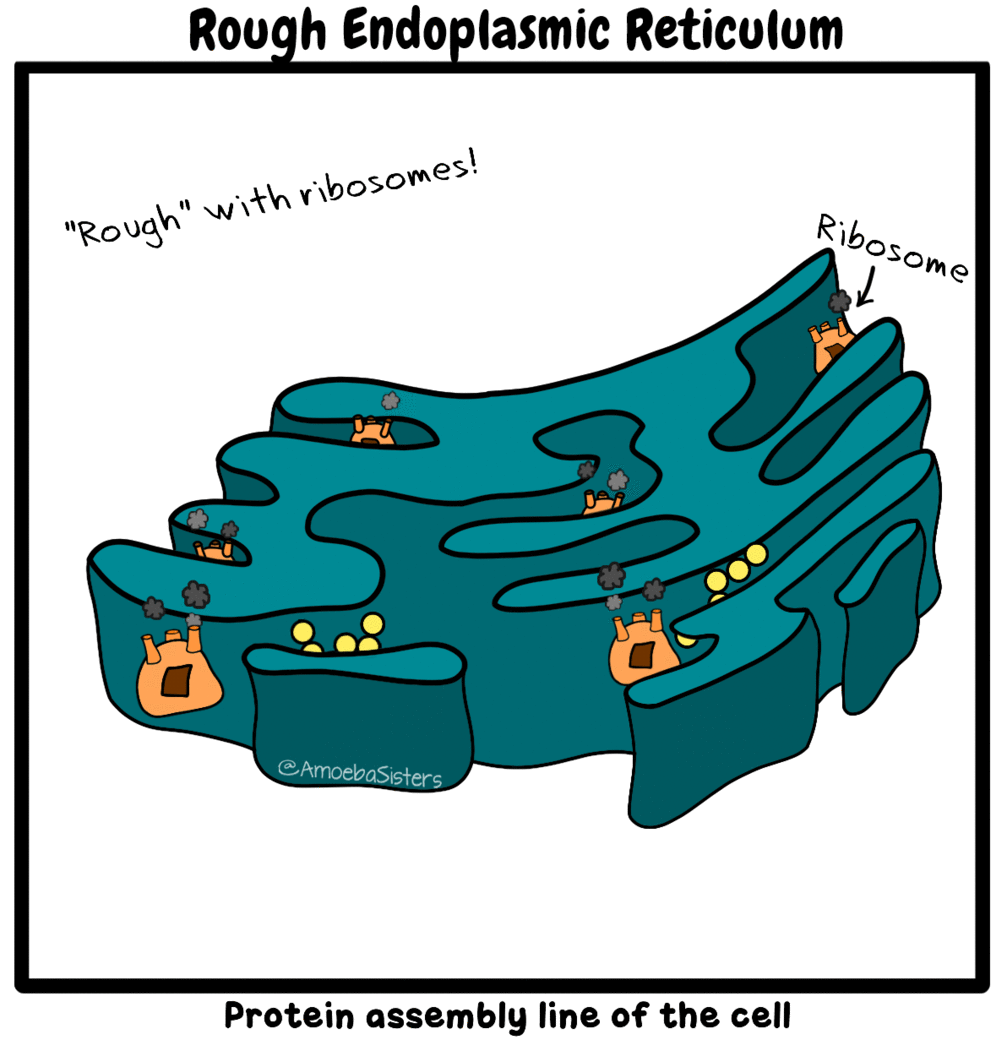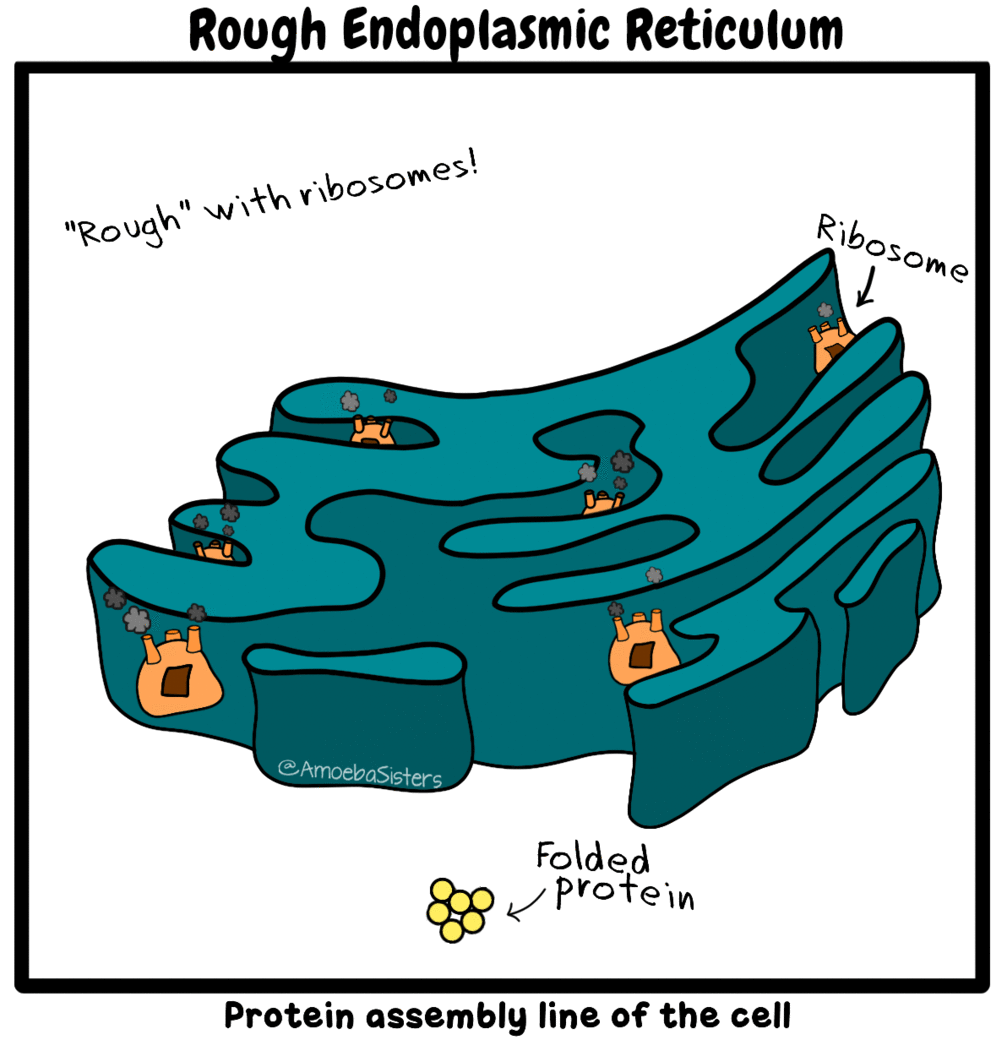
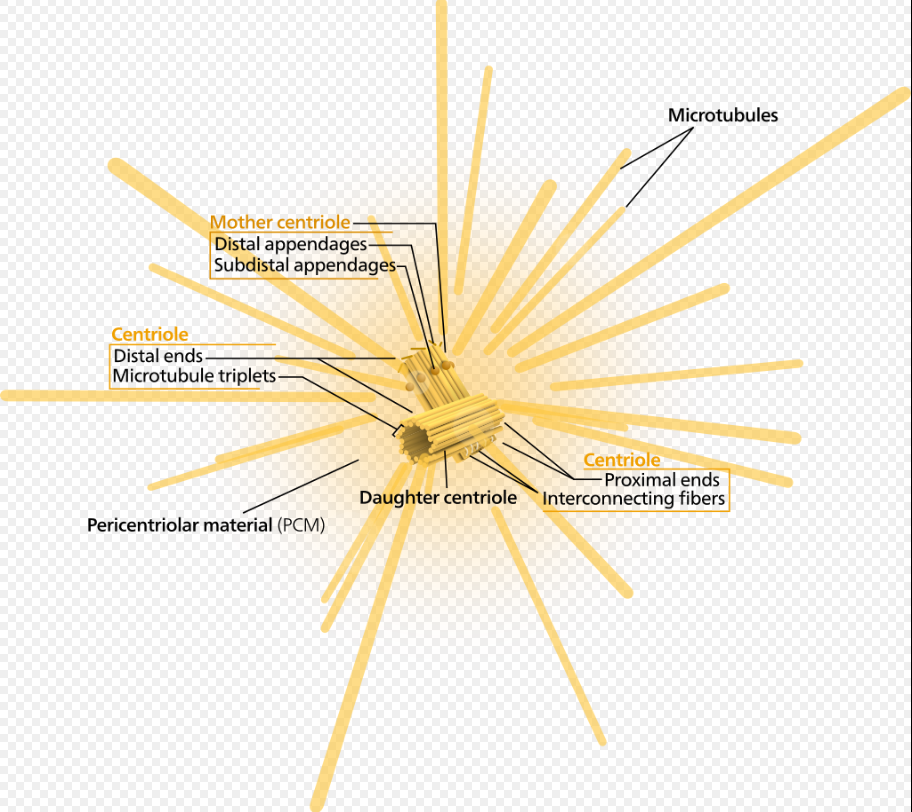
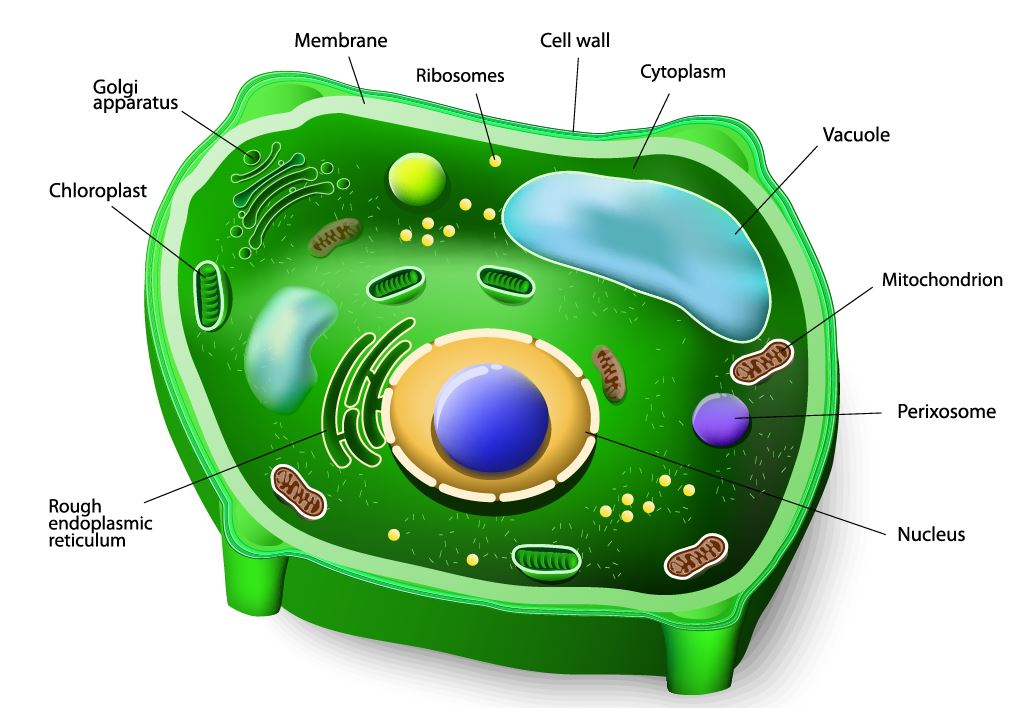
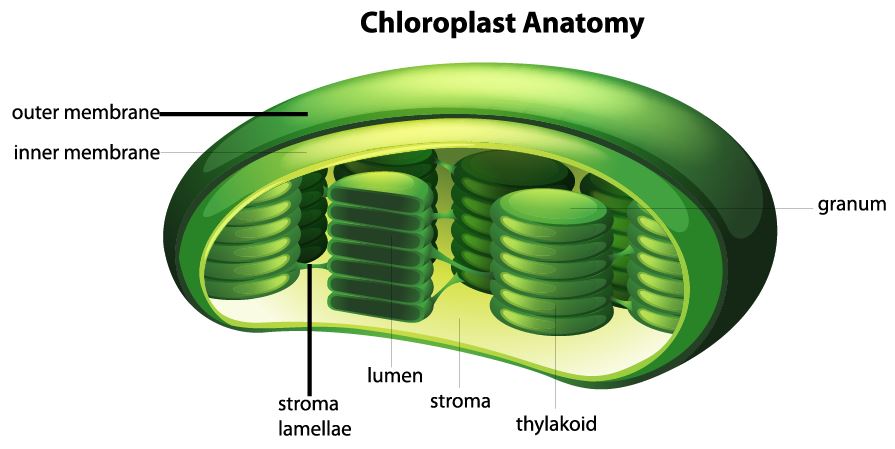
CELLS - BIO 111L
BIO 111L Lab 2
WHAT ARE THE FUNDAMENTAL UNITS OF LIFE?
Watch the Video!
The CELL is the Fundamental Unit of LIFE!
|
All Living Organisms Are Made Up of One or More CELLS.
|
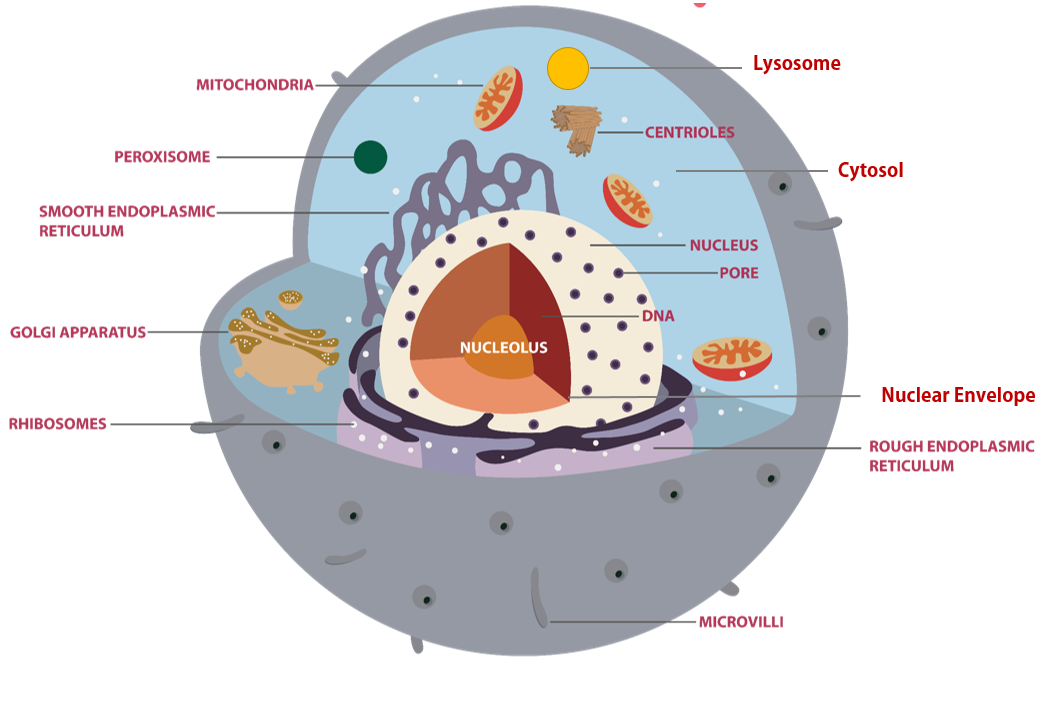
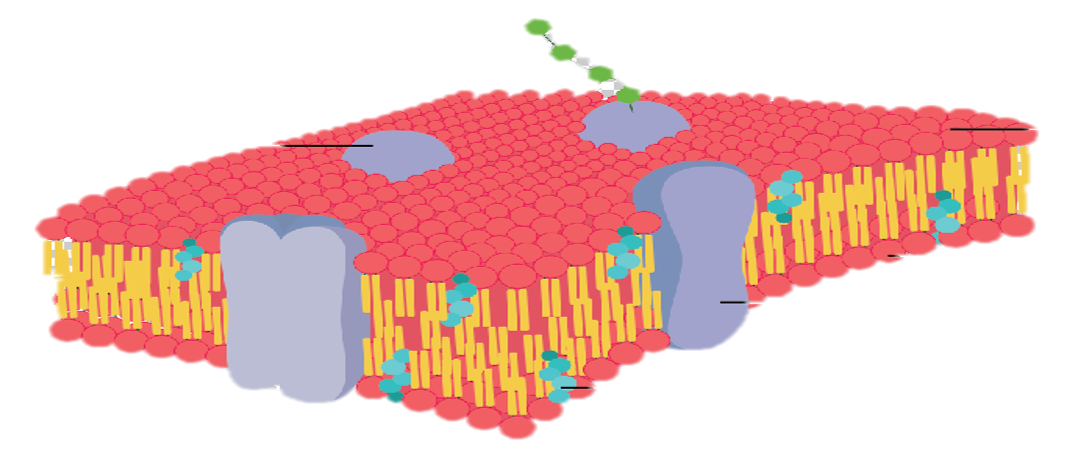
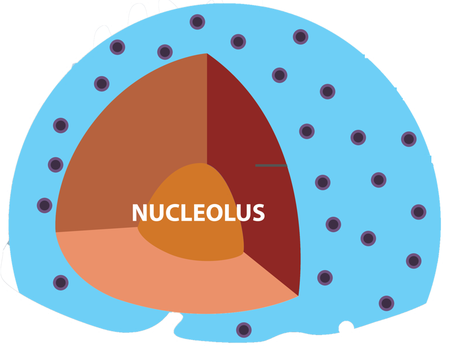
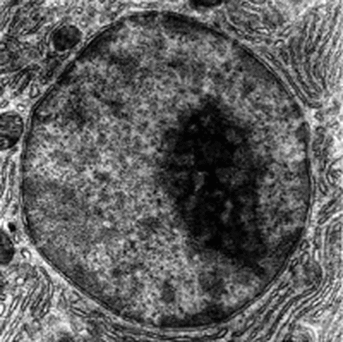
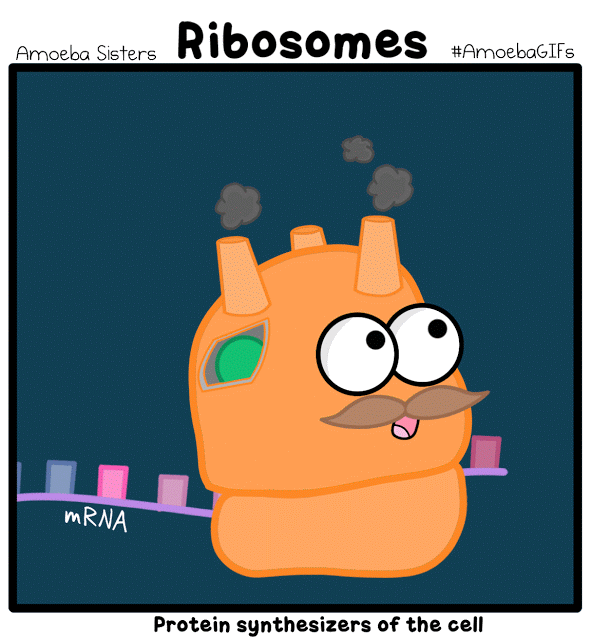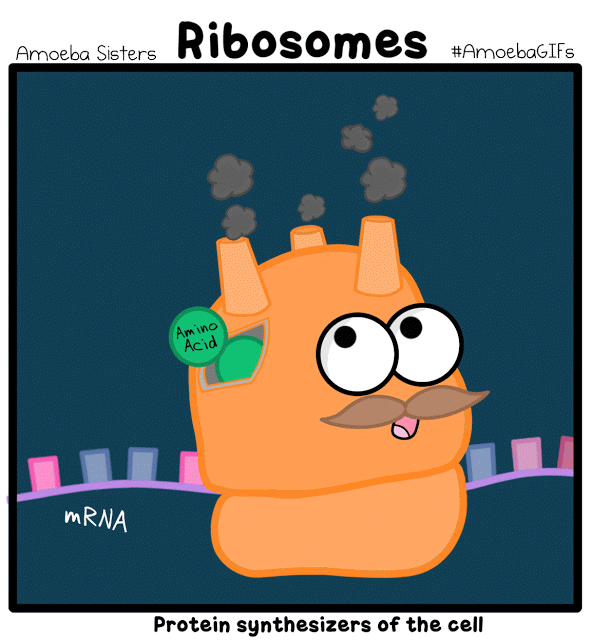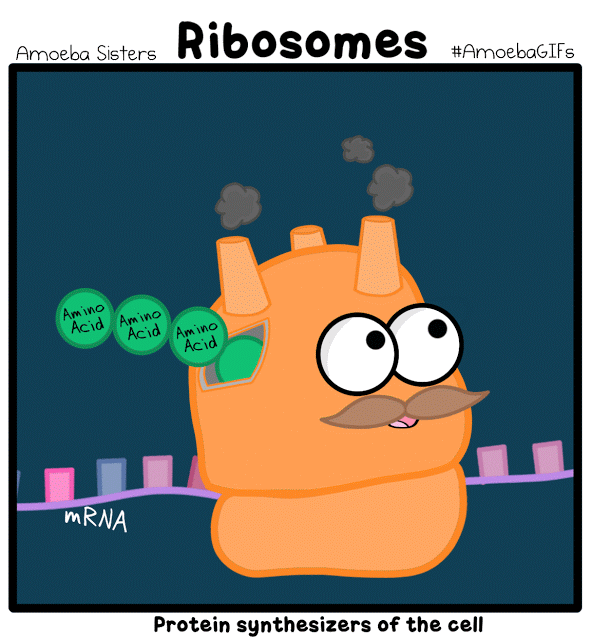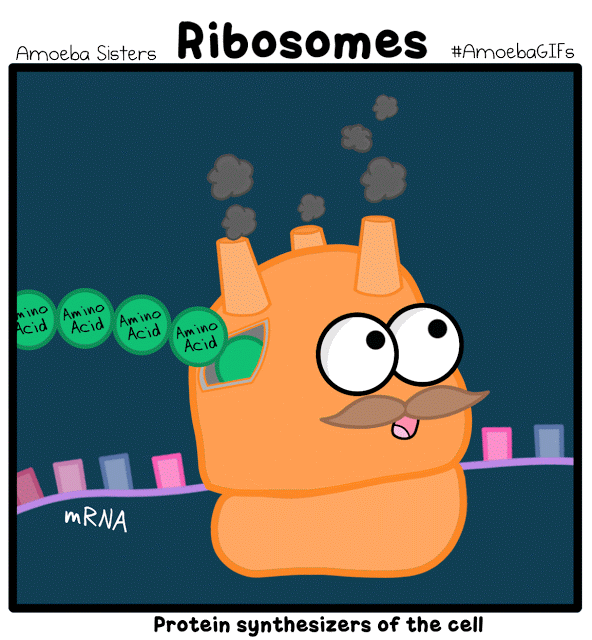
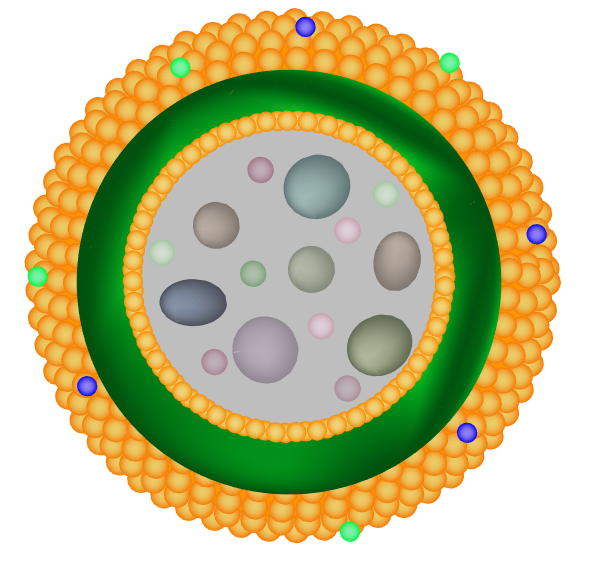
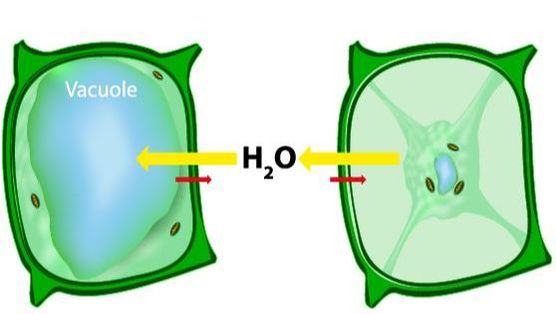
Cells are Living Compartments. Organisms can even exist as a single cells. Cells vary in size and shape.
|
What are the Different Cell Types?
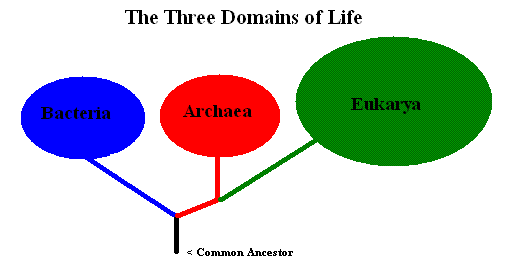
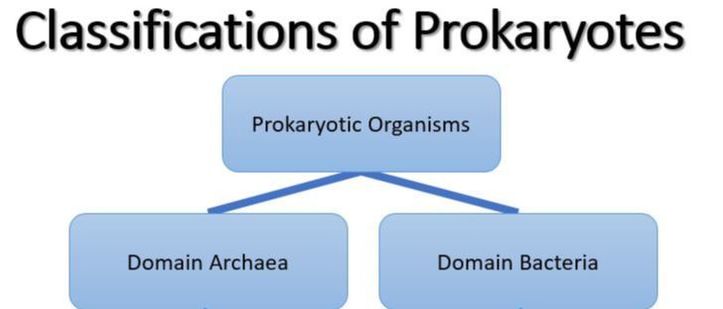
The domains “Archaea” and “Bacteria” are made up entirely of prokaryotic organisms.
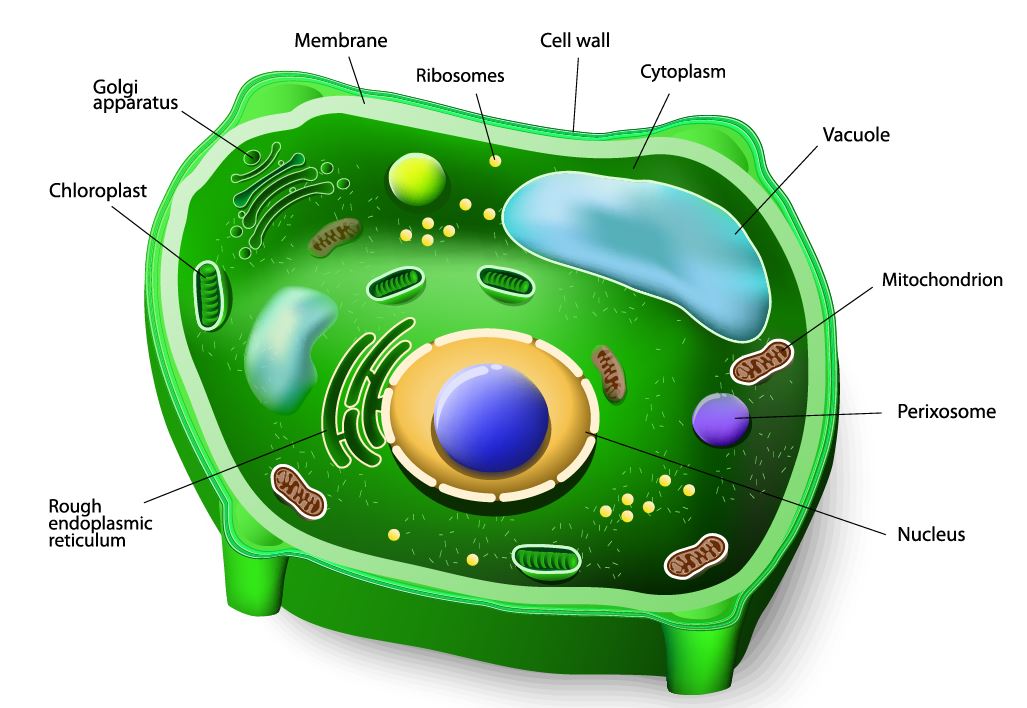
The domain “Eukarya” is made up entirely of eukaryotic organisms.
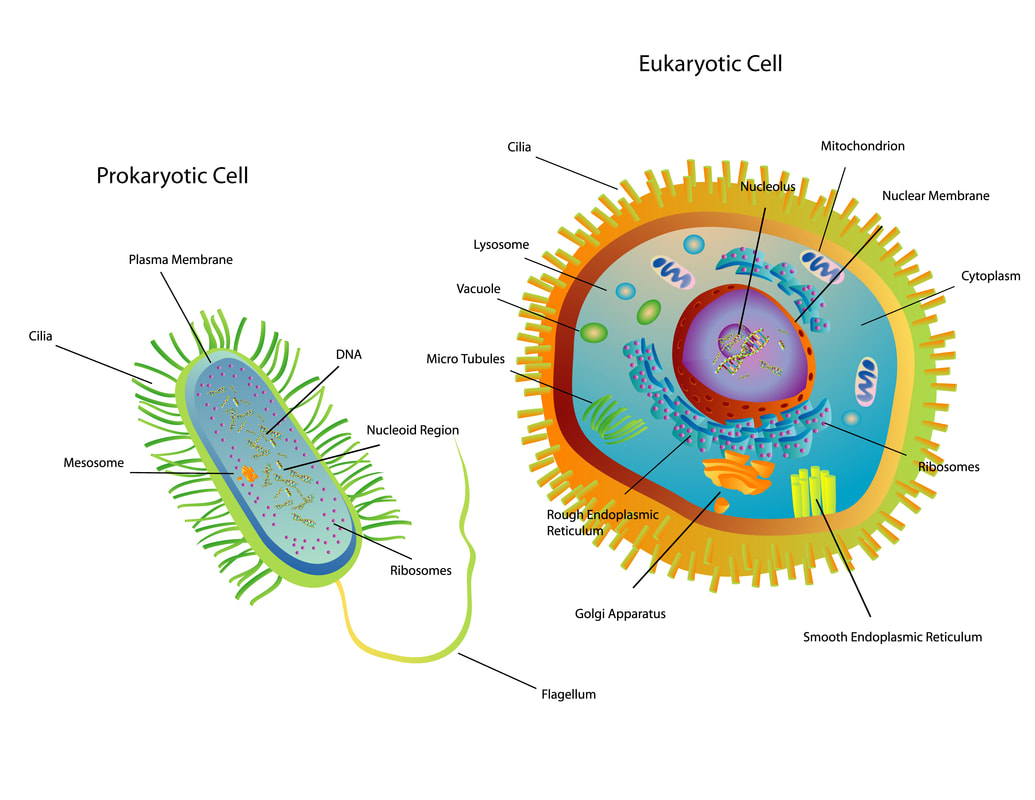
Prokaryotic organisms are made up of prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic organisms are made up of eukaryotic cells.
The domain “Eukarya” is made up entirely of eukaryotic organisms.
Prokaryotic organisms are made up of prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic organisms are made up of eukaryotic cells.