Summer 2018 BIO 101 Lecture Exam 1 1/2 Study Guide
I. The 7 characteristics of Life
I. The 7 characteristics of Life
- Order – Living things are made up of one or more cells. The cell is the fundamental unit of life.
- Reproduction – All living thing have the ability to make their own kind. This allows for propagation of the species.
- Growth and Development – Different parts of the organism’s DNA will the activated at different times points during development causing an increase in size and increase in number of cells (for multicellular organisms).
- Energy Processing – All living things acquire energy process thing energy in order to convert it into a form that can be used by the organism.
- Photosynthesis
- Metabolism
- Responds to the Environment – Living things respond to external stimuli (stimuli in the environment).
- Leaves will orient themselves so that they get the maximum amount of sunlight.
- Leaves will close their stomata (similar to pores in our skin) when it is too hot and they want to conserve water
- Animal use their senses to gather information from the environment about impending danger or food sources, etc.
- Regulation (Homeostasis) – Living things respond to changes in the internal and external environment in such a way to maintain its physiological factors and keep them within a narrow range. Failure in homeostasis results in illness or death.
- Adaptations that allow humans to regulate their temperature include shivering and sweating.
- Shivering when cold raises core body temperature.
- Sweating helps an organism stay cool. When it is hot, humans release liquids through sweat glands. The liquid accumulates on the surface of the skin so when the water evaporates, the skin is cooled.
- Adaptations that allow humans to regulate their temperature include shivering and sweating.
- Evolutionary Adaptation - is the process a living thing goes through in order to become accustomed to an environment.
- occurs over many generations over time
- example : the long neck of the giraffe is an adaptation that allowed them to reach leaves competitors could not reach.
Introduction to the CELL
- Earth is about 4.5 billion years old
- Cyanobacteria were among the first organisms to exist on planet Earth ~ 3.7 Billion Years Ago
Eukaryotic cells
- Do have membrane-bound organelles.
- Do have a true nucleus.
Prokaryotic cells
- Do NOT have membrane-bound organelles.
- Do NOT have a true nucleus.
Prokaryotic organisms belong to the Archaea and Bacteria domains of life, whereas eukaryotic organisms belong to the Eukarya domain.
Prokaryotic cells existed from about one-billion years before eukaryotic single-celled organisms evolved. Prokaryotic cells are almost always smaller than eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells lack membrane-bound organelles and do not have a nucleus. In contrast, eukaryotic cells do have a nucleus and do have membrane-bound organelles.
Organelles and Structures of the CELL
The Cell Membrane (Plasma Membrane)
- The Main Function of the Cell Membrane is TRANSPORT REGULATION -
The cell membrane is also called the plasma membrane. You can think of the membrane as the "skin" of the cell. Anything outside of the cell is considered "extracellular" and the contents inside the cell are considered "intracellular". The cell membrane protects the cell by creating a barrier between what is inside the cell and what is outside the cell.
The cell membrane surrounds the entire cell. You can think of the cell membrane as acting like our skin!
In addition to this, the cell membrane does something our skin can’t do... It regulates what comes into the cell and what goes out of the cell. For this reason, we consider the cell membrane to be “SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE” which means that it allows some substances to enter or exit the cell, but not others. This is a very important function.
The Cell Membrane is selectively permeable due to its structure. The cell membrane is made up of a phospholipid bilayer.
The phospholipid bilayer of the cell membrane has a unique structure. It is made up of an inner layer and an outer layer of phospholipids that are oriented with their 'tails' facing each other.
Phospholipids are considered amphiphilic, because they contain a polar, hydrophillic head that consists of a phosphate group and two nonpolar, hydrophobic fatty acid chains as 'tails'.
When the phospholipids form the cell membrane, the polar, hydrophillic (water-loving) heads are oriented towards the liquid outside the cells (extracellular fluid) and the liquid inside the cell (intracellular fluid). The tails of the phospholipids are oriented towards each other, away from the liquid, since they are made up of hydrophobic (water-fearing) fatty acid chains. This formation creates a barrier between the extracellular matrix and the intracellular fluid (cytoplasm).
VESICLES
Vesicles perform a variety of functions, including transport, metabolism, and temporary storage.
A vesicle is basically a small circular piece of the cell membrane. It may have come from the cell membrane directly, as in endocytosis, or can be generated from membranes of membrane-bound organelles. The function of vesicles in the cell is transportation.
Vesicular transport is a vital part of the cell's function.
The vesicle consists of a small amount of fluid (and sometimes particles) surrounded by a phospholipid bilayer. This bilayer is made up of the same phospholipids that are found in the cell membrane of the plasma membrane. this is due to the fact that vesicles are actually made from the cell membrane itself!
Vesicular Transport
exocytosis = secretion = from inside to outside
endocytosis = uptake = from outside to inside
Endocytosis
Brings Things INTO the Cell.
"Endo-" means "inside". "Cyto-" means "cell". The suffix (or the last part of the term) is "-osis" which means "a process". So, the word endocytosis, is literally the process by which the cell takes contents from the extracellular fluid and brings it INSIDE the cell.
TIP: By breaking scientific terms down into their Greek and Latin roots, the name gives us the function! This is a great thing to know when you 'blank out' on that exam question! Endocytosis is the process by which contents from the extracellular fluid are taken up INTO the cell through a mechanism that involves the cell membrane essentially "pinching off" part of itself to form a vesicle that surrounds the particles being transported into the cell.
Exocytosis
Moves Things OUT OF the Cell.
"Exo-" means "outside". "Cyto-" means "cell". The suffix (or the last part of the term) is "-osis" which means "a process". So, the word exocytosis, is literally the process by which the cell transports contents from the inside to OUTSIDE the cell. Exocytosis is when a vesicle from inside the cell fuses with the membrane and the contents are released into the extracellular fluid.
Nucleus
The Main Function of the Nucleus is to Hold the DNA.
The nucleus is like the "brain" or the "command center" of the cell. This is due to the fact that the nucleus holds the DNA. The DNA acts as the cell's "instruction manual" which has the instructions for all of the functions of the cell, as well as the instructions for growth, development and cellular reproduction!
The structure of the nucleus - The nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear envelope, which is essentially a membrane (a phospholipid bilayer) that compartmentalizes (or separates) the nucleus from the rest of the cell. The liquid inside of the nucleus is called the nucleoplasm.
DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. It is the "instruction manual" for the cell. The primary function of the DNA is to provide the instructions for protein synthesis to the cell through the processes of transcription and translation.
Nucleolus
The Main Function of the Nucleolus is to Make/Assemble Ribosomes
The nucleolus is located inside of the nucleus. It is the largest structure residing inside of the nucleus. Its primary function is to make ribosomes.
Ribosomes
The Main Function of a Ribosome is to Be the Site of Protein Synthesis.
After the ribosome is assembled (made) in the nucleolus, it leaves the nucleus. Some ribosomes will end up as "free ribosomes" that remain unattached in the cytosol. Other ribosomes will attach to the nearby Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum.
All ribosomes function as "the site of protein synthesis". Free ribosomes are used as the site for making water-soluble proteins, whereas the ribosomes that are attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum act as the site for making proteins that will either be incorporated into the cell membrane or will be transported out of the cell (via exocytosis).
ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM
There are 2 types of endoplasmic reticulum (ER); the rough endoplasmic reticulum and the smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
The Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (The Rough ER)
The Main Functions of the rough ER is to hold the Ribosomes and act as a passageway for proteins to go from the ribosomes to the Golgi Body/Apparatus..
The rough ER gets its name from its 'bumpy' or 'rough' appearance due to ribosomes that are attached to it. In the rough ER, ribosomes are assembled in the nucleolus and then exit the nucleus. Some of these ribosomes then attach themselves to the rough endoplasmic reticulum, where they will act as a "site of protein synthesis" for the cell.
The Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (The Smooth ER)
The smooth ER's main function is to make lipids. and hormones..
The smooth endoplasmic reticulum (Smooth ER) appears smooth in comparison to the rough ER. This is because the smooth ER does not have ribosomes bound to it.
Lysosomes
The lysosomes digest and recycle the non-harmful materials in the cell.
Lysosomes contain enzymes that break down macromolecules such as nucleic acids, proteins, and polysaccharides.
Peroxisomes
The peroxisomes detoxify the cell by breaking down toxins and other potentially harmful materials in the cell.
Cytoskeleton - acts as bones of the cell. Provides structure and separates chromosomes during cellular division.
CYTOSOL / Intracellular Fluid / Cytoplasm - LIQUID OF THE CELL THAT LIES INSIDE OF THE CELL MEMBRANE, AND OUTSIDE THE NUCLEUS
Cell Wall
All plant cells have a cell wall which gives them an added layer of protection. The cell wall protects plant cells from environmental conditions, most importantly, osmotic pressure.
- The Main Function of the Cell Membrane is TRANSPORT REGULATION -
The cell membrane is also called the plasma membrane. You can think of the membrane as the "skin" of the cell. Anything outside of the cell is considered "extracellular" and the contents inside the cell are considered "intracellular". The cell membrane protects the cell by creating a barrier between what is inside the cell and what is outside the cell.
The cell membrane surrounds the entire cell. You can think of the cell membrane as acting like our skin!
In addition to this, the cell membrane does something our skin can’t do... It regulates what comes into the cell and what goes out of the cell. For this reason, we consider the cell membrane to be “SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE” which means that it allows some substances to enter or exit the cell, but not others. This is a very important function.
The Cell Membrane is selectively permeable due to its structure. The cell membrane is made up of a phospholipid bilayer.
The phospholipid bilayer of the cell membrane has a unique structure. It is made up of an inner layer and an outer layer of phospholipids that are oriented with their 'tails' facing each other.
Phospholipids are considered amphiphilic, because they contain a polar, hydrophillic head that consists of a phosphate group and two nonpolar, hydrophobic fatty acid chains as 'tails'.
When the phospholipids form the cell membrane, the polar, hydrophillic (water-loving) heads are oriented towards the liquid outside the cells (extracellular fluid) and the liquid inside the cell (intracellular fluid). The tails of the phospholipids are oriented towards each other, away from the liquid, since they are made up of hydrophobic (water-fearing) fatty acid chains. This formation creates a barrier between the extracellular matrix and the intracellular fluid (cytoplasm).
VESICLES
Vesicles perform a variety of functions, including transport, metabolism, and temporary storage.
A vesicle is basically a small circular piece of the cell membrane. It may have come from the cell membrane directly, as in endocytosis, or can be generated from membranes of membrane-bound organelles. The function of vesicles in the cell is transportation.
Vesicular transport is a vital part of the cell's function.
The vesicle consists of a small amount of fluid (and sometimes particles) surrounded by a phospholipid bilayer. This bilayer is made up of the same phospholipids that are found in the cell membrane of the plasma membrane. this is due to the fact that vesicles are actually made from the cell membrane itself!
Vesicular Transport
exocytosis = secretion = from inside to outside
endocytosis = uptake = from outside to inside
Endocytosis
Brings Things INTO the Cell.
"Endo-" means "inside". "Cyto-" means "cell". The suffix (or the last part of the term) is "-osis" which means "a process". So, the word endocytosis, is literally the process by which the cell takes contents from the extracellular fluid and brings it INSIDE the cell.
TIP: By breaking scientific terms down into their Greek and Latin roots, the name gives us the function! This is a great thing to know when you 'blank out' on that exam question! Endocytosis is the process by which contents from the extracellular fluid are taken up INTO the cell through a mechanism that involves the cell membrane essentially "pinching off" part of itself to form a vesicle that surrounds the particles being transported into the cell.
Exocytosis
Moves Things OUT OF the Cell.
"Exo-" means "outside". "Cyto-" means "cell". The suffix (or the last part of the term) is "-osis" which means "a process". So, the word exocytosis, is literally the process by which the cell transports contents from the inside to OUTSIDE the cell. Exocytosis is when a vesicle from inside the cell fuses with the membrane and the contents are released into the extracellular fluid.
Nucleus
The Main Function of the Nucleus is to Hold the DNA.
The nucleus is like the "brain" or the "command center" of the cell. This is due to the fact that the nucleus holds the DNA. The DNA acts as the cell's "instruction manual" which has the instructions for all of the functions of the cell, as well as the instructions for growth, development and cellular reproduction!
The structure of the nucleus - The nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear envelope, which is essentially a membrane (a phospholipid bilayer) that compartmentalizes (or separates) the nucleus from the rest of the cell. The liquid inside of the nucleus is called the nucleoplasm.
DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. It is the "instruction manual" for the cell. The primary function of the DNA is to provide the instructions for protein synthesis to the cell through the processes of transcription and translation.
Nucleolus
The Main Function of the Nucleolus is to Make/Assemble Ribosomes
The nucleolus is located inside of the nucleus. It is the largest structure residing inside of the nucleus. Its primary function is to make ribosomes.
Ribosomes
The Main Function of a Ribosome is to Be the Site of Protein Synthesis.
After the ribosome is assembled (made) in the nucleolus, it leaves the nucleus. Some ribosomes will end up as "free ribosomes" that remain unattached in the cytosol. Other ribosomes will attach to the nearby Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum.
All ribosomes function as "the site of protein synthesis". Free ribosomes are used as the site for making water-soluble proteins, whereas the ribosomes that are attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum act as the site for making proteins that will either be incorporated into the cell membrane or will be transported out of the cell (via exocytosis).
ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM
There are 2 types of endoplasmic reticulum (ER); the rough endoplasmic reticulum and the smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
The Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (The Rough ER)
The Main Functions of the rough ER is to hold the Ribosomes and act as a passageway for proteins to go from the ribosomes to the Golgi Body/Apparatus..
The rough ER gets its name from its 'bumpy' or 'rough' appearance due to ribosomes that are attached to it. In the rough ER, ribosomes are assembled in the nucleolus and then exit the nucleus. Some of these ribosomes then attach themselves to the rough endoplasmic reticulum, where they will act as a "site of protein synthesis" for the cell.
The Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (The Smooth ER)
The smooth ER's main function is to make lipids. and hormones..
The smooth endoplasmic reticulum (Smooth ER) appears smooth in comparison to the rough ER. This is because the smooth ER does not have ribosomes bound to it.
Lysosomes
The lysosomes digest and recycle the non-harmful materials in the cell.
Lysosomes contain enzymes that break down macromolecules such as nucleic acids, proteins, and polysaccharides.
Peroxisomes
The peroxisomes detoxify the cell by breaking down toxins and other potentially harmful materials in the cell.
Cytoskeleton - acts as bones of the cell. Provides structure and separates chromosomes during cellular division.
CYTOSOL / Intracellular Fluid / Cytoplasm - LIQUID OF THE CELL THAT LIES INSIDE OF THE CELL MEMBRANE, AND OUTSIDE THE NUCLEUS
Cell Wall
All plant cells have a cell wall which gives them an added layer of protection. The cell wall protects plant cells from environmental conditions, most importantly, osmotic pressure.
Summary of Structure and Function of ORGANELLE or STRUCTURE
NUCLEUS - HOLDS THE DNA, which acts as the INSTRUCTION MANUAL of the cell
NUCLEOLUS - MAKES RIBOSOMES
CELL/PLASMA MEMBRANE - PROTECTION and REGULATION OF MEMBRANE TRANSPORT
MITOCHONDRIA - MAKES ATP WHICH IS THE ENERGY FOR THE CELL
ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM - Holds RIBOSOMES and acts as pathway fro proteins
SMOOTH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM - functions in LIPID PRODUCTION
PEROXISOME - DETOXIFIES CELL
LYSOSOME - DIGESTS or recycles UNWANTED SUBSTANCES
RIBOSOMES - THE SITE OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
NUCLEOPLASM - LIQUID OF THE NUCLEUS
NUCLEAR ENVELOPE - MEMBRANE AROUND THE NUCLEUS/"SKIN" OF NUCLEUS
VESICLES - TRANSPORTATION VEHICLES
CYTOSOL/Intracellular Fluid/Cytoplasm - LIQUID OF THE CELL THAT LIES INSIDE OF THE CELL MEMBRANE, AND OUTSIDE THE NUCLEUS
CELL WALL - added protection surrounding all plant cells and some other organisms as well.
NUCLEOLUS - MAKES RIBOSOMES
CELL/PLASMA MEMBRANE - PROTECTION and REGULATION OF MEMBRANE TRANSPORT
MITOCHONDRIA - MAKES ATP WHICH IS THE ENERGY FOR THE CELL
ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM - Holds RIBOSOMES and acts as pathway fro proteins
SMOOTH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM - functions in LIPID PRODUCTION
PEROXISOME - DETOXIFIES CELL
LYSOSOME - DIGESTS or recycles UNWANTED SUBSTANCES
RIBOSOMES - THE SITE OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
NUCLEOPLASM - LIQUID OF THE NUCLEUS
NUCLEAR ENVELOPE - MEMBRANE AROUND THE NUCLEUS/"SKIN" OF NUCLEUS
VESICLES - TRANSPORTATION VEHICLES
CYTOSOL/Intracellular Fluid/Cytoplasm - LIQUID OF THE CELL THAT LIES INSIDE OF THE CELL MEMBRANE, AND OUTSIDE THE NUCLEUS
CELL WALL - added protection surrounding all plant cells and some other organisms as well.
Endosymbiotic Theory
Eukaryotic cells may have evolved through the process of a smaller prokaryotic cell being engulfed by by a larger prokaryotic cell, without killing it. This theory is known as the endosymbiotic theory.
Mitochondria make the majority of ATP, which is used as energy for the cell. In eukaryotic photosynthetic organisms, chloroplasts hold chlorophyll and structures needed for photosynthesis.
The Endosymbiotic Theory in a nut shell
Mitochondria make the majority of ATP, which is used as energy for the cell. In eukaryotic photosynthetic organisms, chloroplasts hold chlorophyll and structures needed for photosynthesis.
The Endosymbiotic Theory in a nut shell
- The mitochondria and the chloroplasts may have evolved from independent prokaryotic organisms that had the abilities to undergo cellular respiration and photosynthesis, respectively.
- These prokaryotic cells were likely engulfed by another prokaryotic cell in the ancient past.
- Instead of the larger cell digesting and killing the engulfed prokaryotic cell, the host cell and the engulfed cell had a mutually-beneficial (symbiotic) relationship.
- Prokaryotes can be engulfed by other prokaryotes through a process called phagocytosis..
- The host cell provided protection while the engulfed cell (the symbiont) made energy for the host cell.
- Over time, the host cell and symbiont evolved together, becoming the first eukaryotic cells.
Evidence that Supports Endosymbiotic Theory
- Mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own DNA that is completely different and separate from the DNA of the cell.
- The DNA found in mitochondria and chloroplasts exists in the form of a single circular chromosome.
- Only prokaryotic cells have DNA in the form of the a single circular chromosome. which is in a circular form like we seen in prokaryotic cells only.
- Mitochondria and chloroplasts reproduce independently inside the cell using a process called binary fission, which only occurs in prokaryotic cells.
- Mitochondria and chloroplasts have a double lipid bilayer surrounding them. This would make since if the mitochondria and chloroplasts were engulfed!
All the mitochondria in your body was maternally inherited!
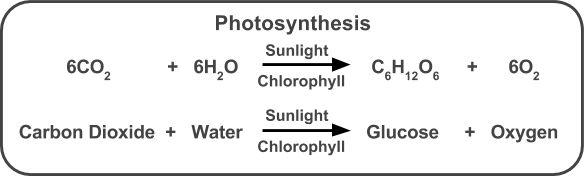
Photosynthesis
Energy From the Sun
Photosynthesis uses light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and sugar (glucose). Photosynthesis takes CO2 from the air and adds O2 to the air.
Chemosynthesis - Energy from inorganic molecules In the process called chemosynthesis, bacteria harness chemical energy from inorganic molecules (such as hydrogen sulfide) to produce carbohydrates. Chemosynthesizers often live in extreme environments = deep ocean vents, hot springs, etc.
Light energy comes in packets called PHOTONS. Photosynthesis occurs when photons are absorbed by the photosensitive pigment, chlorophyll.
CHLOROPHYLL exists inside of specialized structures called CHLOROPLASTS which are in the leaves of plants.
Chlorophyll reflects green light and gives plants their green color. Chloroplasts most likely evolved as a result of a larger prokaryotic cell engulfing a photosynthesizing bacteria. This is the endosymbiotic theory. Some of the evidence that supports this theory is...
1) Chloroplasts have their own bacterial DNA in the form of a circular plasmid.
2) Chloroplasts have a double membrane.
3) Chloroplasts reproduce independently with the plant cell.
Photosynthesis uses light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and sugar (glucose). Photosynthesis takes CO2 from the air and adds O2 to the air.
- Most use energy in the ecosystem comes from the sun (a little comes from chemotrophs).
- Only producers can use sunlight to make usable energy.
- Producers convert the sunlight into glucose.
- For example: Plants create chemical energy from abiotic factors that include solar energy.
- The food energy created by producers is passed through the food chain.
- In this way, energy flows from one living thing to another.
Chemosynthesis - Energy from inorganic molecules In the process called chemosynthesis, bacteria harness chemical energy from inorganic molecules (such as hydrogen sulfide) to produce carbohydrates. Chemosynthesizers often live in extreme environments = deep ocean vents, hot springs, etc.
Light energy comes in packets called PHOTONS. Photosynthesis occurs when photons are absorbed by the photosensitive pigment, chlorophyll.
CHLOROPHYLL exists inside of specialized structures called CHLOROPLASTS which are in the leaves of plants.
Chlorophyll reflects green light and gives plants their green color. Chloroplasts most likely evolved as a result of a larger prokaryotic cell engulfing a photosynthesizing bacteria. This is the endosymbiotic theory. Some of the evidence that supports this theory is...
1) Chloroplasts have their own bacterial DNA in the form of a circular plasmid.
2) Chloroplasts have a double membrane.
3) Chloroplasts reproduce independently with the plant cell.
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
1) Glycolysis
2) The Kreb's Cycle / The Citric Acid Cycle
3) The Electron Transport Chain / Oxidative Phosphorylation
1) Glycolysis
2) The Kreb's Cycle / The Citric Acid Cycle
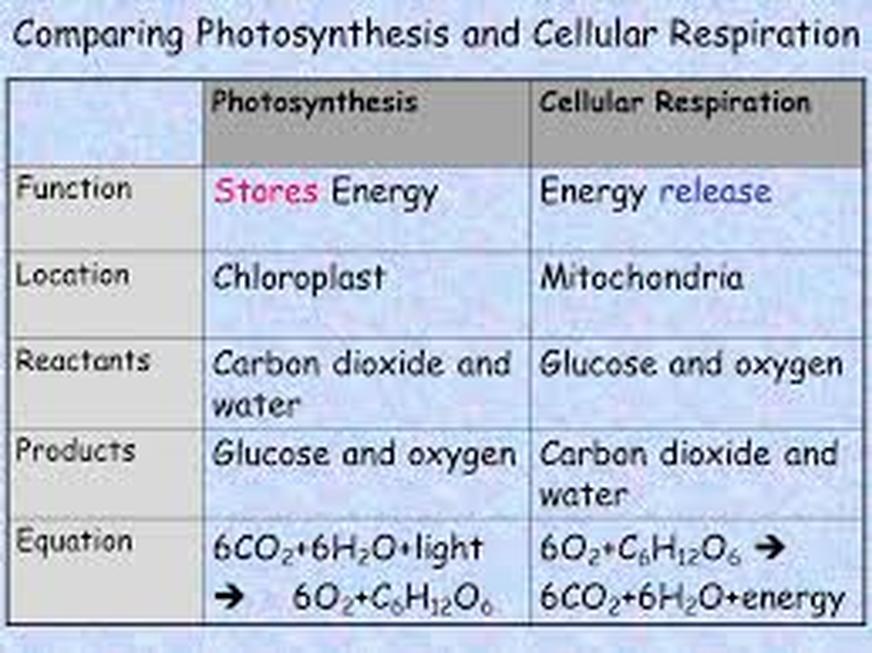
Plants undergo both photosynthesis and cellular respiration Plants take in CO2 during photosynthesis and make glucose. The glucose is then used by the plants or organisms that consume the plants for the process of cellular respiration to make ATP. Photosynthesis releases oxygen into the atmosphere Cellular respiration produces carbon dioxide ( CO2 ) which is released back into the atmosphere.
- - ATP is an energy-carrying molecule that cells use to power their metabolic processes
- - Cellular Respiration - process in which cells break down glucose and make ATP for energy.
1) Glycolysis
2) The Kreb's Cycle / The Citric Acid Cycle
3) The Electron Transport Chain / Oxidative Phosphorylation
1) Glycolysis
- Glycolysis literally means "to cut something sweet". Glycolysis comes from the Latin words "Glyco-" = "sweet" and "Lysis" = "to cut"
- Glycolysis is the process of breaking down 1 glucose molecule into pyruvate.
- the NET YIELD of ATP in glycolysis is 2 ATP
- The process of glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell.
2) The Kreb's Cycle / The Citric Acid Cycle
- The Kreb's cycle is the 2nd step in cellular respiration
- The Kreb's cycle takes place inside of the mitochondria
- Mitochondria exist in both plant and animal cells
- The Kreb's cycle starts with the pyruvate molecule product from glycolysis getting transferred from the cytoplasm of the cell into the mitochondria.
- Pyruvate is then broken down (pyruvate is the remaining portion of the glucose molecule we started with).
- The Kreb's cycle creates 2 additional ATP.
Plants undergo both photosynthesis and cellular respiration Plants take in CO2 during photosynthesis and make glucose. The glucose is then used by the plants or organisms that consume the plants for the process of cellular respiration to make ATP. Photosynthesis releases oxygen into the atmosphere Cellular respiration produces carbon dioxide ( CO2 ) which is released back into the atmosphere.
Notice that the reactants of cellular respiration are the products of the photosynthesis and the reactants of photosynthesis are the products of the cellular respiration. Cellular respiration is basically photosynthesis in reverse.
The main point of cellular respiration is to create ATP which is used as a source of energy within the cell.
The main point of cellular respiration is to create ATP which is used as a source of energy within the cell.
III. Chemistry of Life – Inorganic
- Atoms are the fundamental unit of matter
- All matter is made up of atoms, this includes you
- Atoms are made up of a combination of 3 subatomic particles
- Protons – are positively charges
- Electrons – are negatively charged
- Neutrons – are neutral , have no charge, charge = 0
- Protons – are positively charges
- The nucleus of the atom
- is the center of the atom
- The nucleus of the atom is made up of protons and neutrons
- Essentially all of the mass of the atom is in the nucleus
- Since the nucleus of the atom has one or more protons, the nucleus is positively charged
- is the center of the atom
- Electrons
- are on the outer portion of the atom
- Electrons are extremely small and far less massive than the protons and neutrons that make up the nucleus
- Only the electrons that are at the outermost shell of the atom are able to form bonds (react)
- Electrons on the outermost shell have a special name – VALENCE ELECTRONS
- are on the outer portion of the atom
- Atoms
- An atom (by definition) has no chargeb.
- An atom will always have equal numbers of protons and electrons
- Example - If the atom has 3 protons, it must have 3 electrons
- Example - If the atom has 5 electrons, it must have 5 electrons
- Example - If the atom has 3 protons, it must have 3 electrons
- An atom (by definition) has no chargeb.
- Ions
- Charged atoms are not called atoms, they are called ions
- Ions form when atoms can gain or lose electrons that are on the outer shell and become charged
- Electrons are negatively charged so...
- If an atom gains 1 electron, it becomes an ion with a -1 charge2.
- If an atom gains 2 electrons, it becomes an ion with a -2 charge… and so on3.
- If an atom loses 1 electron, it becomes an ion with a +1 charge4.
- If an atom loses 2 electrons, it becomes an ion with a +2 charge… and so on7.
- If an atom gains 1 electron, it becomes an ion with a -1 charge2.
- Electrons are negatively charged so...
- Charged atoms are not called atoms, they are called ions
- Hydrogen
- Was the first atom in the universe to form
- Hydrogen is the most abundant atom in the universe
- Is the simplest atom
- It is made up of 1 proton and 1 electron
- It is made up of 1 proton and 1 electron
- Was the first atom in the universe to form
- Helium
- Was the second atom in the universe to form
- Hydrogen is the second-most abundant atom in the universe
- Is the second-most simplest atom
- It is made up of 2 protons and 2 electrons
- It is made up of 2 protons and 2 electrons
- Was the second atom in the universe to form
- Stars
- Stars are almost entirely made up of Hydrogen (H) and Helium (He)
- All of the heavier elements (all elements besides H and He) were formed when a star exploded (this is called a super nova).
- We are all made of “star stuff”
- Stars are almost entirely made up of Hydrogen (H) and Helium (He)
- Carbon
- Carbon is the single most important element for life
- All life as we know it is carbon-based (has one or more carbons)
- Carbon atoms have 4 electrons in outer shell (these are known as valence electrons)
- Carbon can accept an additional 4 electrons in its outer shell (since the shell can hold up to 8 electrons total)
- Carbon is able to form 4 bonds.
- Carbon is the only element that is able to form 4 very strong covalent bonds
- This is because the other elements that can form 4 bonds, are forming those bonds using electrons that are further away from the nucleus so they are not as strong.
- This is because the other elements that can form 4 bonds, are forming those bonds using electrons that are further away from the nucleus so they are not as strong.
- Carbon is the single most important element for life
- Organic molecules are carbon-based, inorganic bonds are NOT carbon-based
- Water – H20
- Water is known the “universal solvent”
- called the universal solvent because it is able to dissolve (or pull apart) more substances than any other liquid
- When substances are dissolved, they can change and react to create new substances
- When substances are dissolved, they can change and react to create new substances
- called the universal solvent because it is able to dissolve (or pull apart) more substances than any other liquid
- Water is a requirement for life
- It is a polar molecule
- It has a partial negative charge on the oxygen (O)
- It has a partial positive charge on each of the hydrogens (H)
- It has a partial negative charge on the oxygen (O)
- The bonds within the water molecule (between the (H) and the (O) ) are called POLAR COVALENT BONDS
- Water is known the “universal solvent”
- Atomic bonding
- Ionic bond – one atom steals one or more electrons from another, resulting in 1 positively charged ion and one negatively charged ionb.
- Covalent bond – electrons are equally (or almost equally) shared between 2 atoms
- Very strong bond
- When carbon binds to carbon, it forms a covalent bond that is very strong
- When carbon binds to hydrogen…
- the carbon and hydrogen form a strong covalent bond that releases energy when it is broken
- These are called hydrocarbons
- Used for energy in biology
- Used for energy in the world – gas oil etc
- the carbon and hydrogen form a strong covalent bond that releases energy when it is broken
- Very strong bond
- Polar covalent bonds – electrons are unequally shared
- Hydrogen bonds
- Occurs between water molecules
- Short-lived
- Very weak
- Occurs between water molecules
- Ionic bond – one atom steals one or more electrons from another, resulting in 1 positively charged ion and one negatively charged ionb.
IV. Chemistry of Life – Organic
- Organic molecules evolved from inorganic molecules
- In 1950’s demonstrated in lab that we can get organic molecules from inorganic molecules with the assistance of lightening
- In 1950’s demonstrated in lab that we can get organic molecules from inorganic molecules with the assistance of lightening
- Carbon likes to bind to other carbon atom to form long chains that become a carbon backbone for a molecule
- RNA world hypothesis
- RNA evolved first (before DNA)
- DNA evolved from RNA
- 1st life forms may have used RNA as their genetic material instead of DNA
- RNA evolved first (before DNA)
- There are 4 classes (or categories) of organic molecules [Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins and Nucleic Acids]
- Carbohydrates (also known as sugars or saccharides)
- Monosaccharides – 1 unit sugar
- These are known as simple sugars
- Includes glucose, fructose and galactose
- Considered unhealthy
- Glucose is only molecule that your brain can use for feul
- These are known as simple sugars
- Dissacharides – sugar made up of 2 sugar monomers
- example - Sucrose (table sugar)
- example - Sucrose (table sugar)
- Polysaccharides
- Healthy
- These are called complex carbohydrates
- Example – starch (found in pastas)
- Healthy
- Monosaccharides – 1 unit sugar
- Lipids
- Fats and oils
- Are hydrophobic (don’t like water)
- Fatty acids, fatty acid chains
- Saturated fats
- Unhealthy
- Have the maximum number of hydrogens bound
- Unhealthy
- Unsaturated fats
- Have at least 1 double bond
- Healthy
- Have at least 1 double bond
- Polyunsaturated fats
- Healthiest fats (fish oil, avocado, etc.)
- Have many double bonds
- Healthiest fats (fish oil, avocado, etc.)
- Trans Fats
- Unnatural / Made in a lab (processed)
- They are a fatty acid chain that has a “TRANS” double bond
- A trans double bond has hydrogens on opposite sidesb. Natural (non-trans) fats have a cis double bond which means the hydrogens are on the same side.
- A trans double bond has hydrogens on opposite sidesb. Natural (non-trans) fats have a cis double bond which means the hydrogens are on the same side.
- Unnatural / Made in a lab (processed)
- Phospholipids
- Are polar
- The head group is a phosphate group that is positively charged and loves water (hydrophilic)
- Has 2 fatty acid tails that are not charged and hate water (hydrophobic)
- Make up cell membranes
- Will spontaneously form a membrane-like structure when placed in water
- In water, phospholipids will orient themselves so that the fatty acid tails face inward, toward each other with the phosphate heads facing outward toward the water molecules.
- The head group is a phosphate group that is positively charged and loves water (hydrophilic)
- Are polar
- Fats and oils
- Proteins
- Proteins are made up of amino acids
- The monomer (single unit of a protein is an amino acid)
- Proteins are made up of amino acids
- Nucleic Acids
- Includes RNA and DNA
- You do not get nucleic acids from the food you eat
- Includes RNA and DNA
- Carbohydrates (also known as sugars or saccharides)