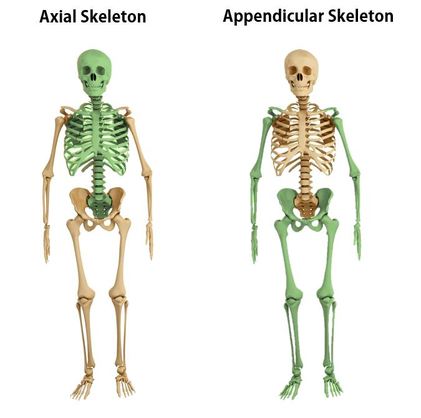
The human skeleton is divided into 2 categories; the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton.
The axial skeleton forms the long axis of your body. The axial skeleton is divided into 3 categories;
1) the skull,
2) the vertebral column, and
3) the thoracic cage.
The function of the axial skeleton is to support the head, neck, and trunk, and to protect the brain, spinal cord, and the thoracic organs.
The bones of the appendicular skeleton make up the rest of the skeleton, and are so called because they are appendages of the axial skeleton. The appendicular skeleton includes the bones of the shoulder girdle, the upper limbs, the pelvic girdle, and the lower limbs. The appendicular skeleton has 126 bones. The axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton make up the 206 named bones of your body!
The axial skeleton forms the long axis of your body. The axial skeleton is divided into 3 categories;
1) the skull,
2) the vertebral column, and
3) the thoracic cage.
The function of the axial skeleton is to support the head, neck, and trunk, and to protect the brain, spinal cord, and the thoracic organs.
The bones of the appendicular skeleton make up the rest of the skeleton, and are so called because they are appendages of the axial skeleton. The appendicular skeleton includes the bones of the shoulder girdle, the upper limbs, the pelvic girdle, and the lower limbs. The appendicular skeleton has 126 bones. The axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton make up the 206 named bones of your body!
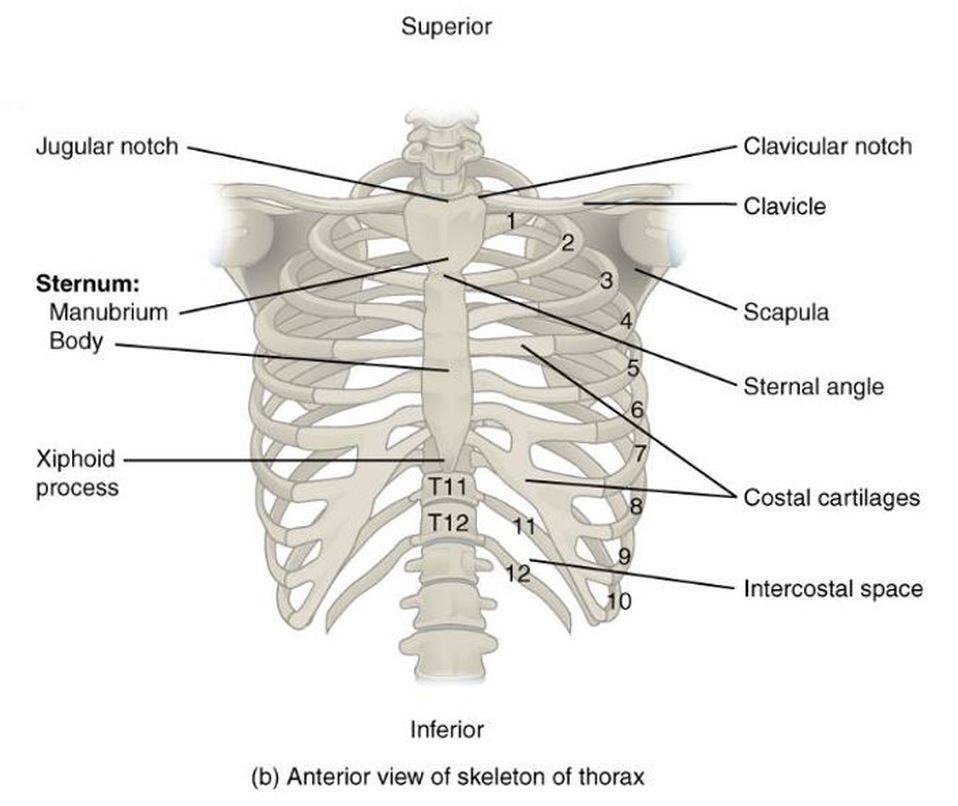
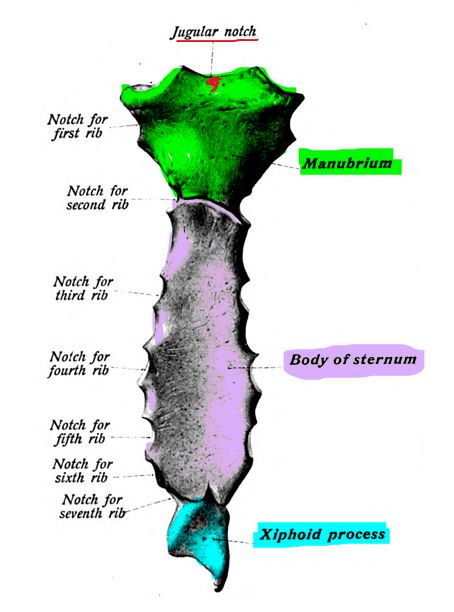
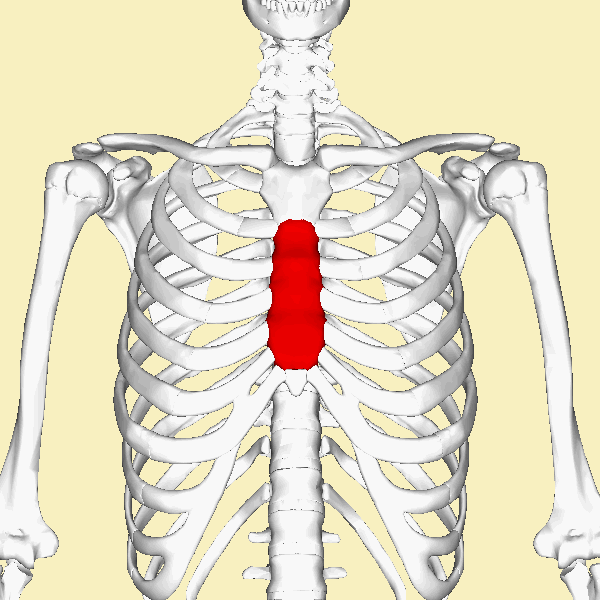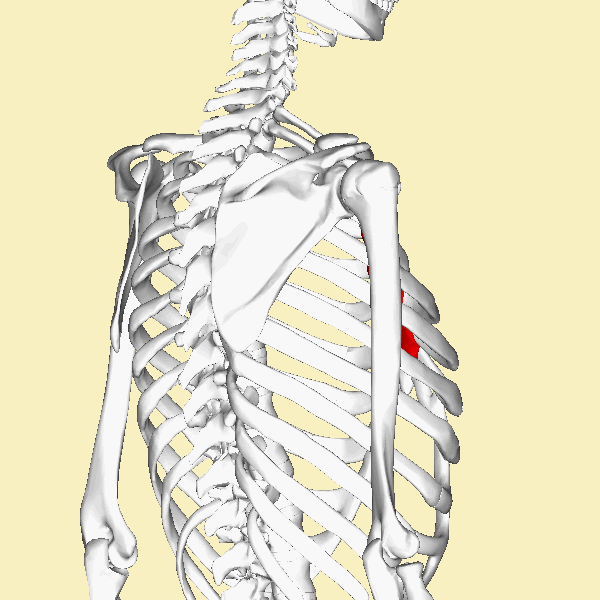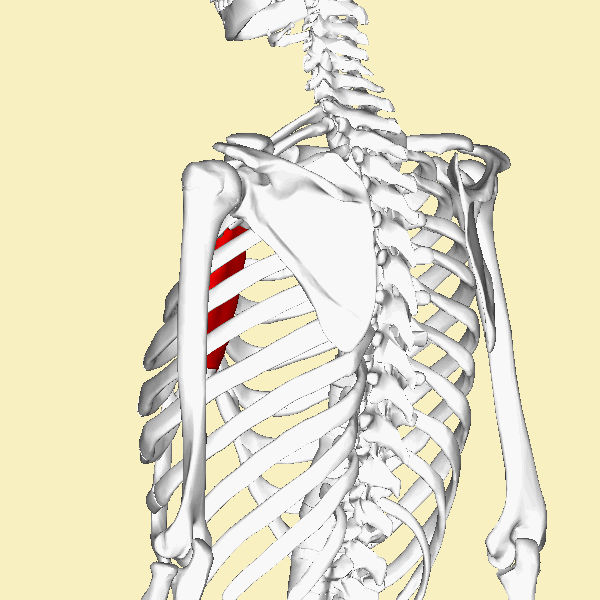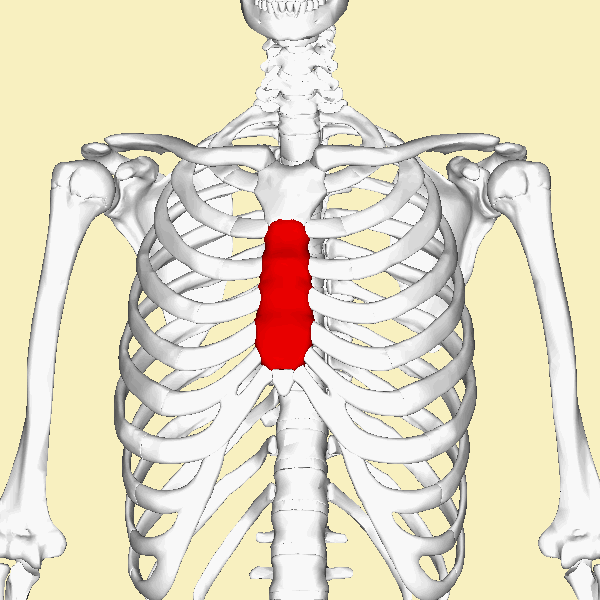
THE ANATOMY OF THE RIB CAGE AND STERNUM
The thoracic cage consists of the rib cage, the 12 thoracic vertebrae,
12 pairs of ribs (along with their associated costal cartilages) and the sternum.
The function of the thoracic cage is to support and protect the vital organs of the thorax.
12 pairs of ribs (along with their associated costal cartilages) and the sternum.
The function of the thoracic cage is to support and protect the vital organs of the thorax.
THE RIB CAGE
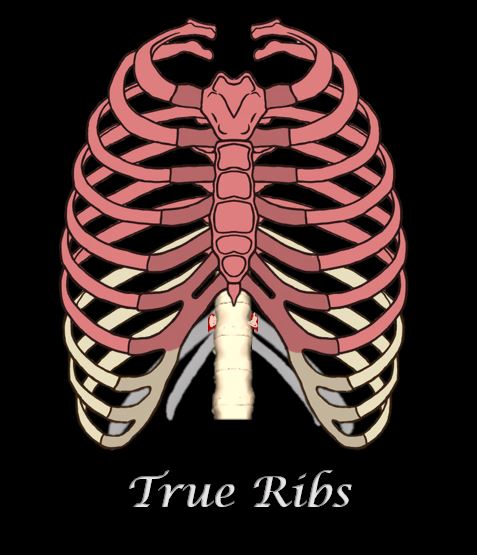
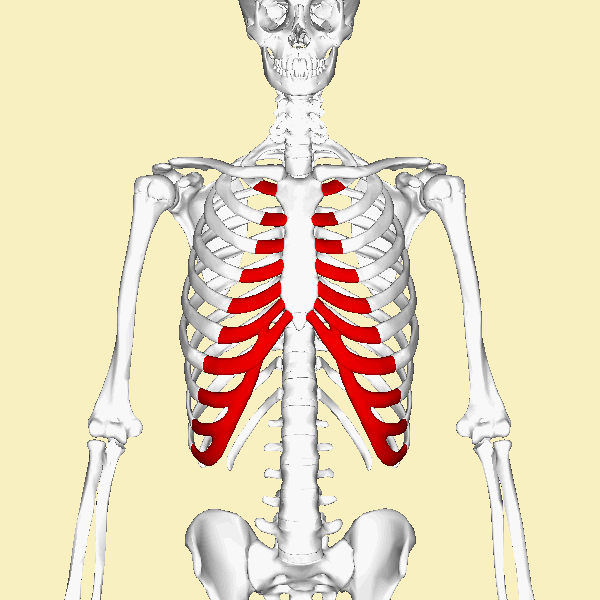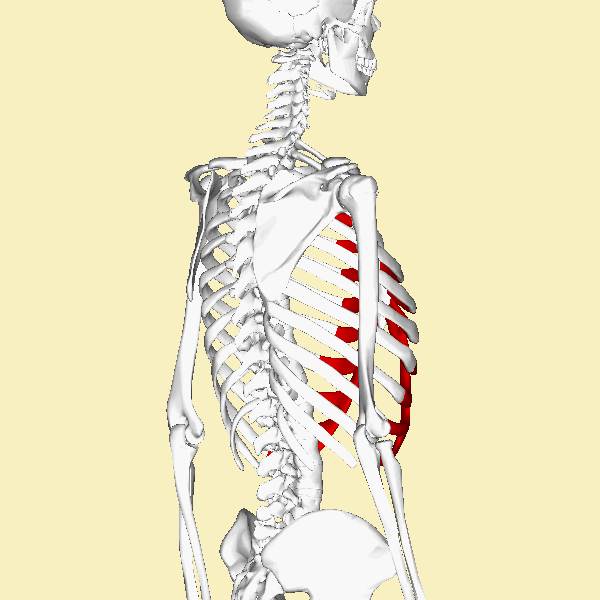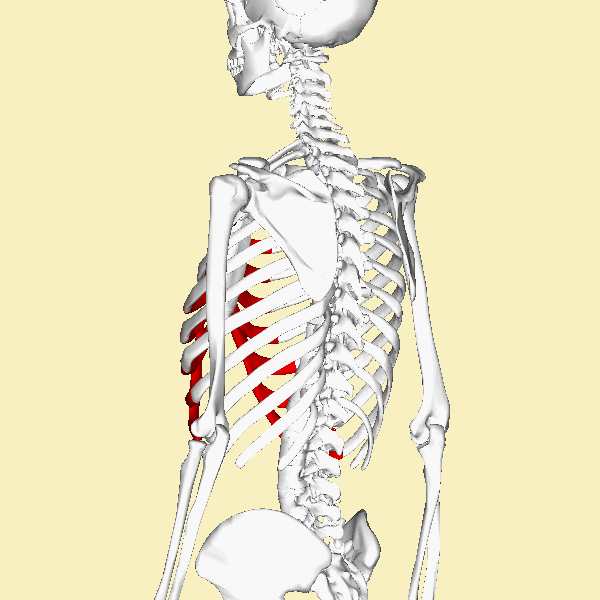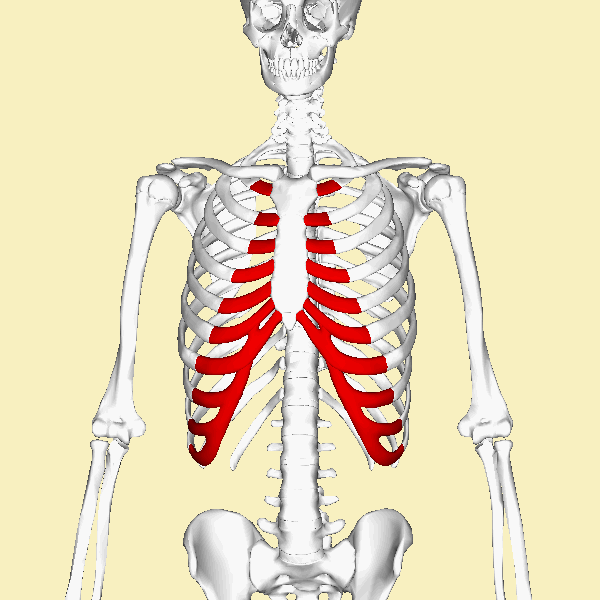
THE TRUE RIBS
|
The rib cage of most humans contains 12 total pairs of ribs. The ribs are numbered beginning with the 1st ribs being the superior-most pair of ribs., and proceeding inferiorly, with the 12th pair of ribs being the most inferior ribs.
The ribs are categories according to how they articulate with the sternum through the costal cartilage.
|
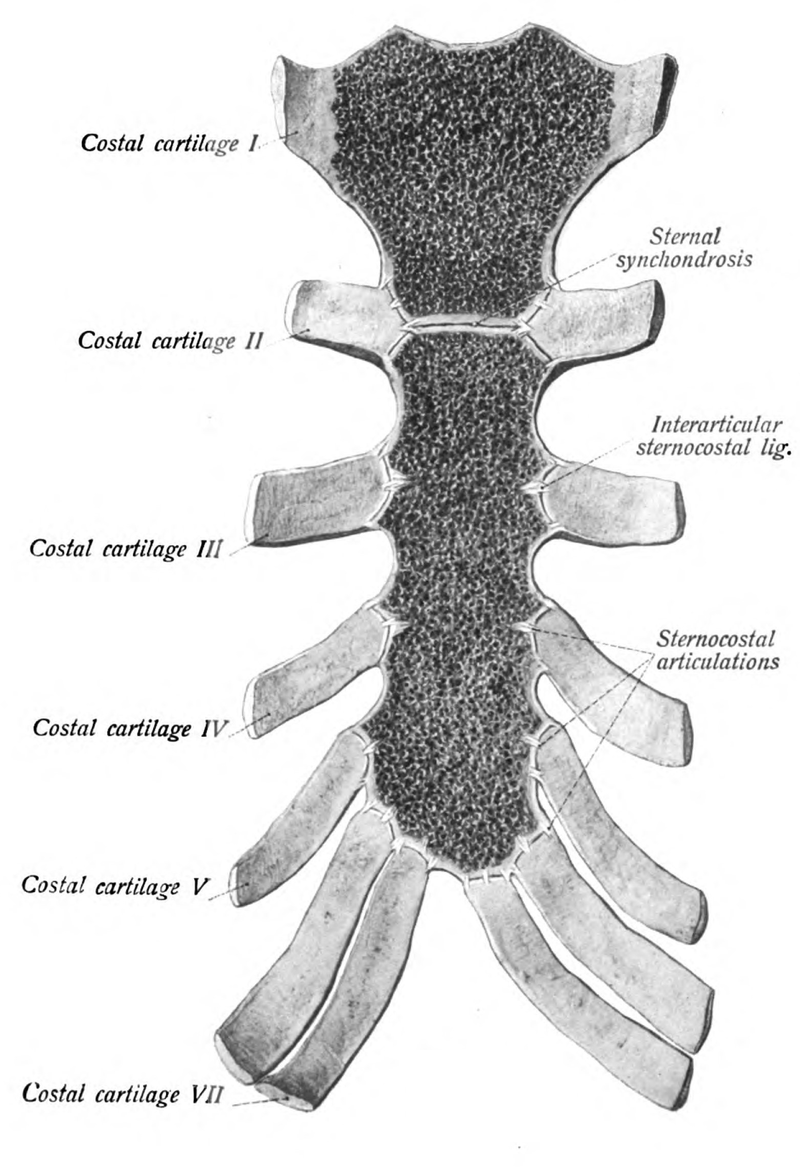
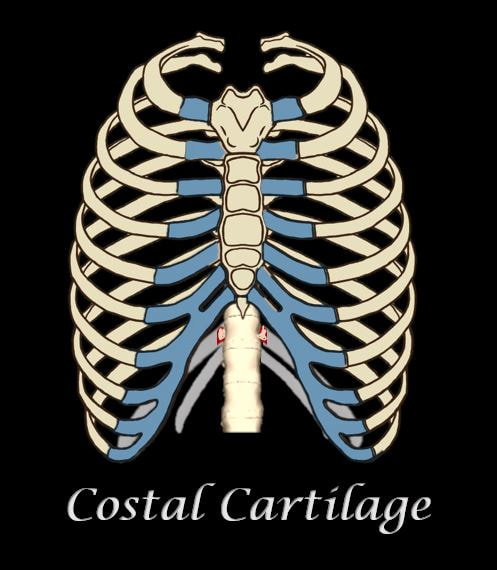
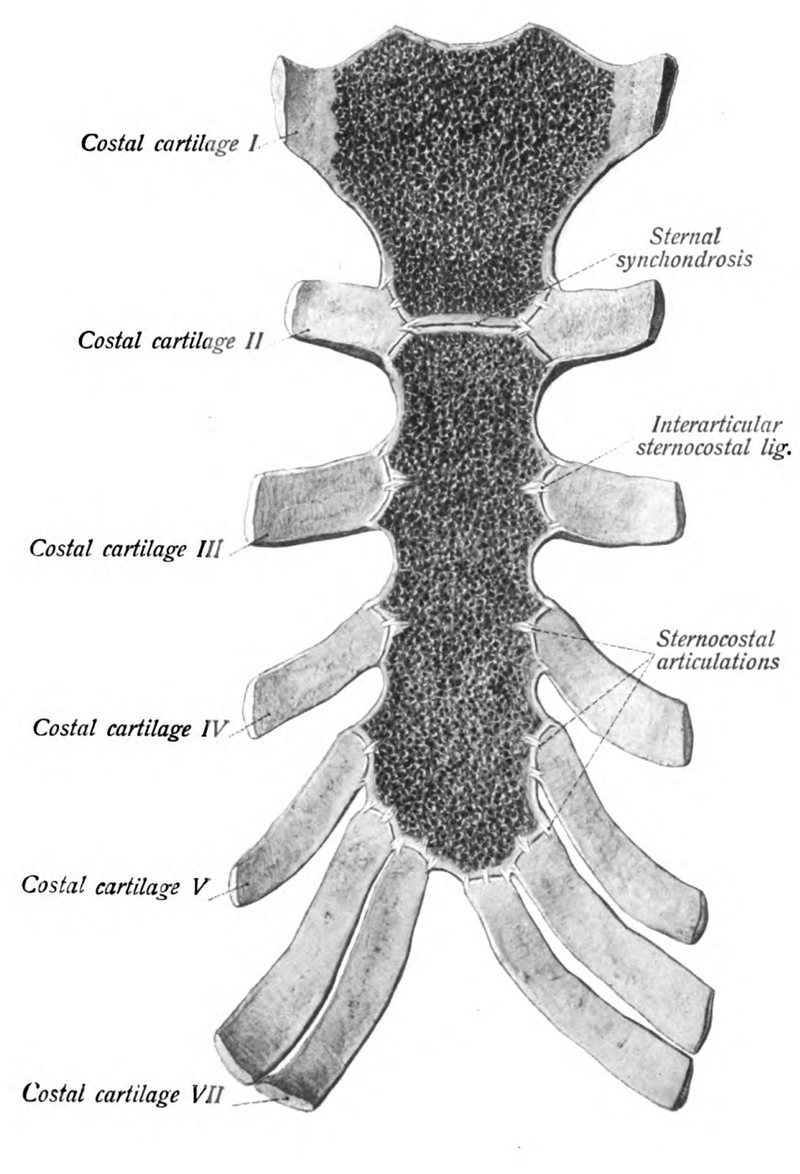
COSTAL CARTILAGE
The ribs are connected to the sternum through the costal cartilage. There are 7 sections of costal cartilage on each side for the superior 7 ribs.
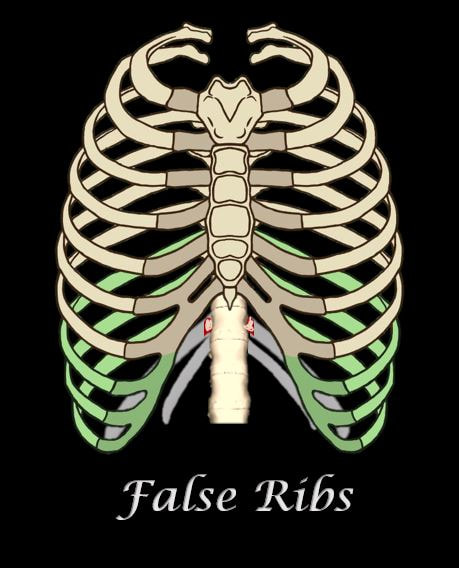
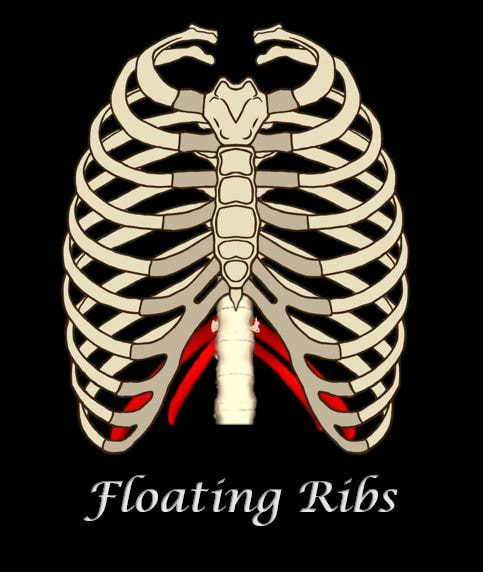
FALSE RIBS
|
Unlike the "true ribs" which articulate directly to the sternum through the costal cartilage. the "false ribs" do not articulate directly to the sternum through costal cartilage. Instead, the "false ribs" connect to the 7th ribs through cartilage.
The false ribs are the 8th, 9th, and 10th pairs of ribs. |
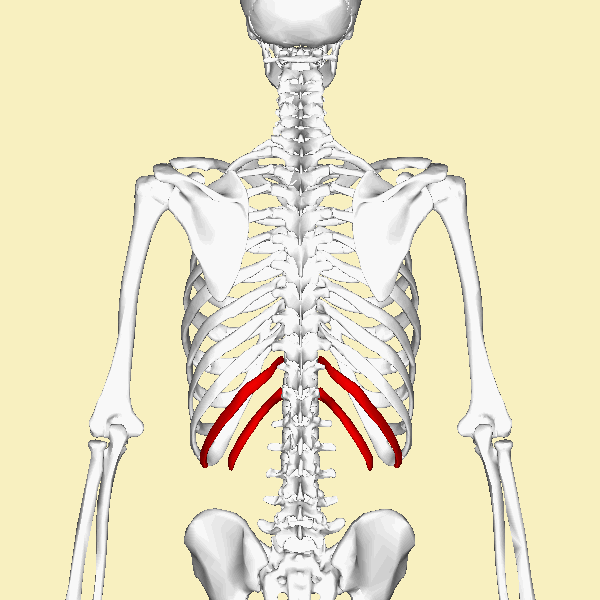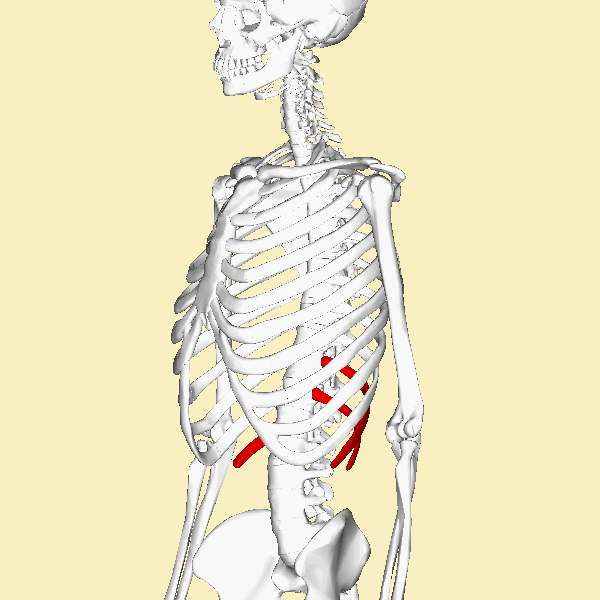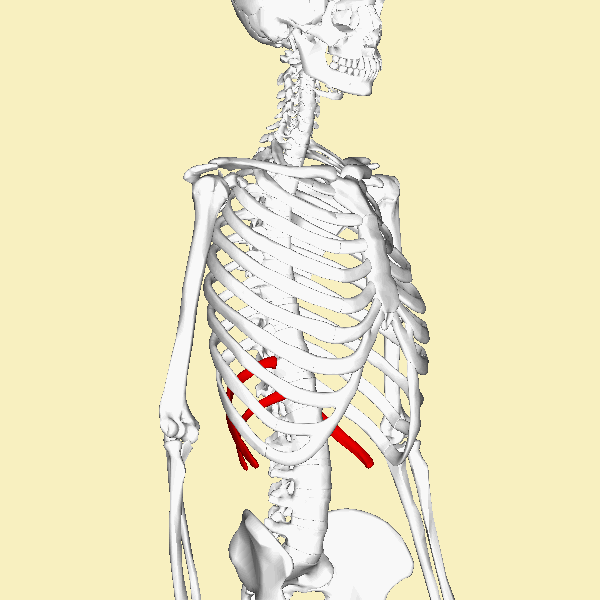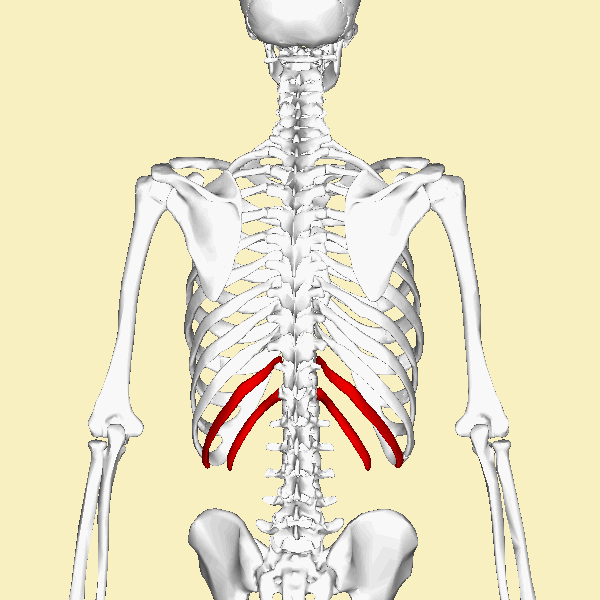
FLOATING RIBS
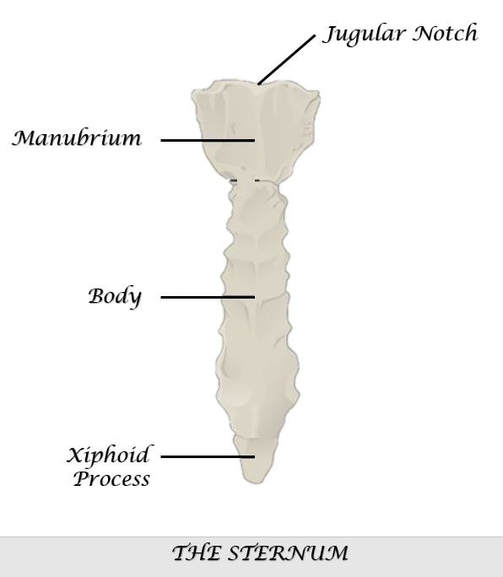
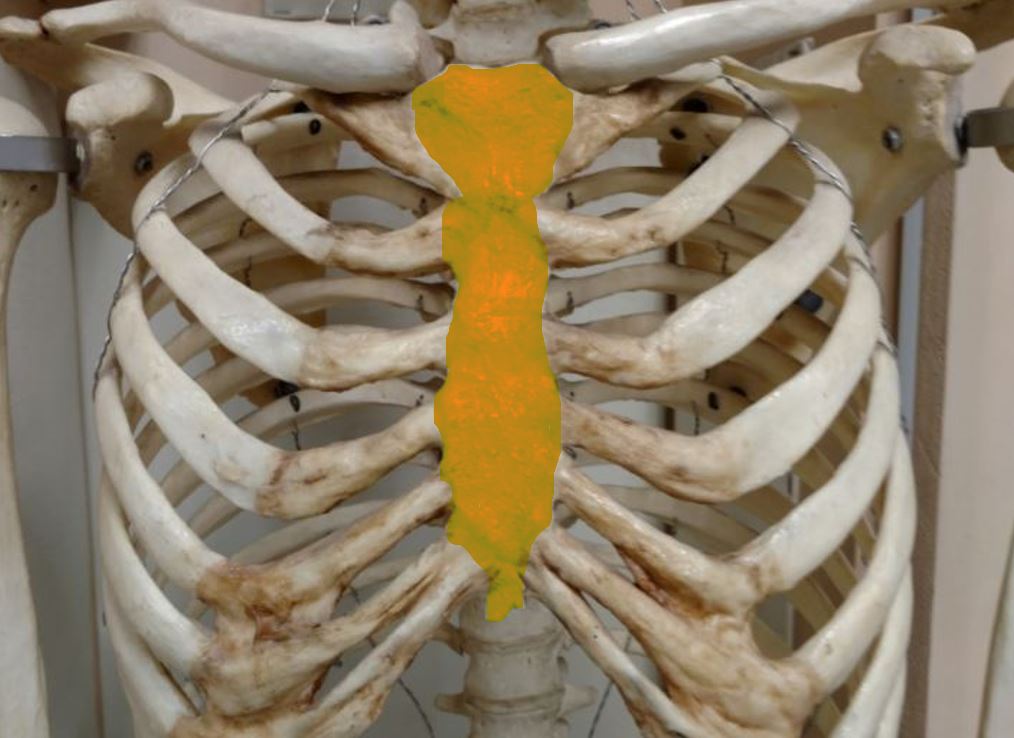
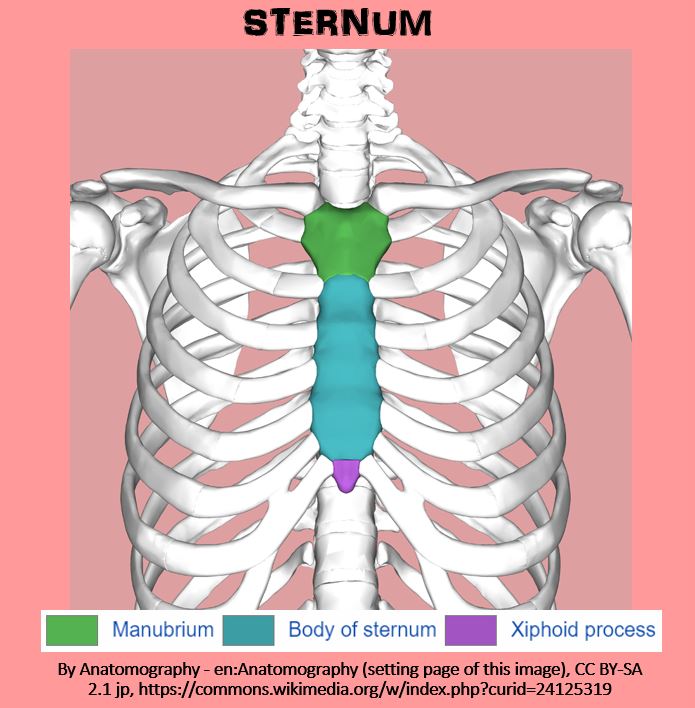
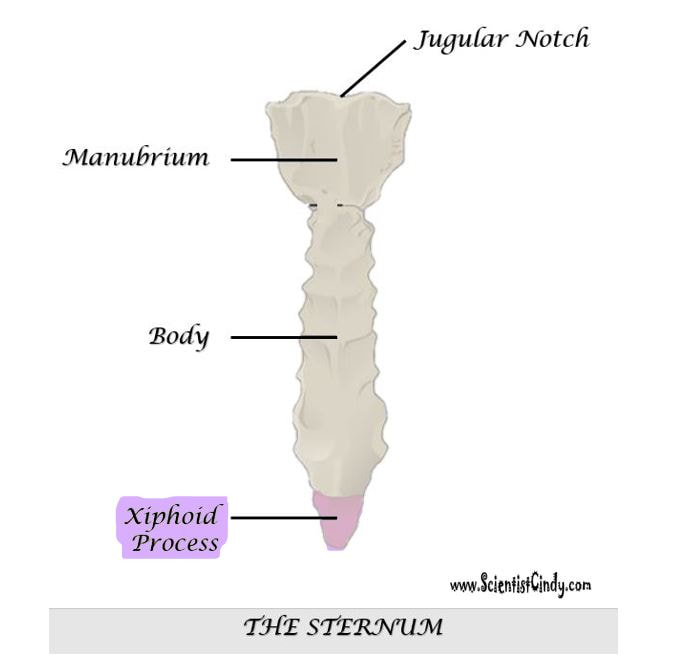
THE STERNUM
|
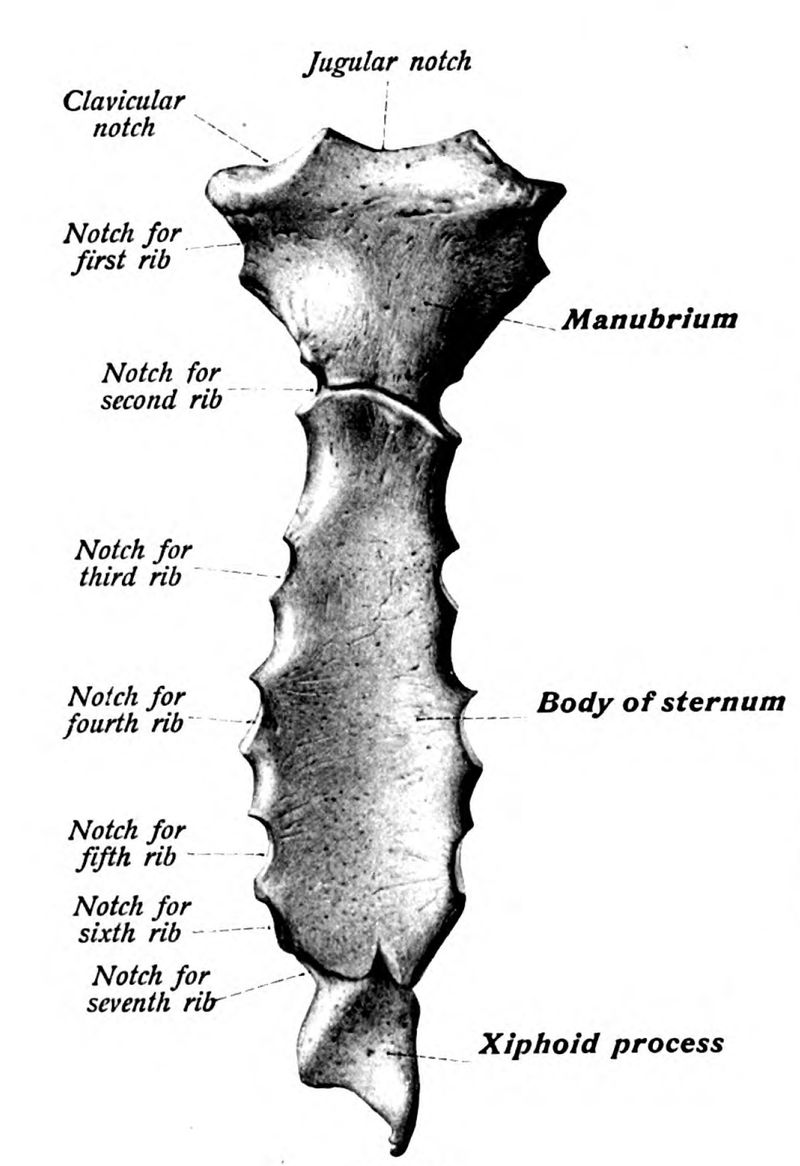
The sternum articulates with the superior 7 ribs through the costal cartilage. The manubrium part of the sternum articulates with the 1st rib, the clavicles (collar bones). The manubrium has an indentation at the superior end called the jugular notch (also called the suprasternal notch) which lies over the trachea (windpipe).
|
The Jugular Notch (Suprasternal Notch)
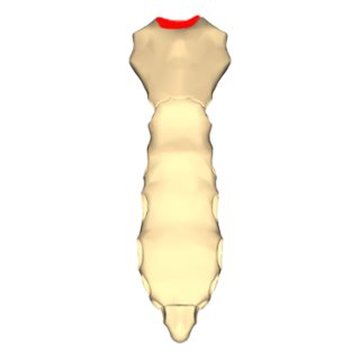
The jugular notch is clinically used to quickly diagnose intrathoracic pressure. The procedure involves placing either the index or middle finger at the indentation point of the jugular notch and feeling for the patient's pulse. The pulse is only felt at the jugular notch when a patient is experiencing an increase in intrathoracic pressure. If a prominent pulse is felt, the patient should undergo additional tests to rule out the following illnesses:
- Dissecting aneurysm
- Hypertension
- Aneurysm
- Atherosclerosis
STERNUM
THE BODY OF THE STERNUM
Xiphoid Process
|
The xiphoid process covers the solar plexus which is a bundle of nerves. The xiphoid process is at significant risk of being broken off during CPR chest compressions or other similar force. When the xiphoid process breaks off, the diaphragm or liver can be cut leading to internal bleeding.
|