|
|
|
Lab 5 - How is Energy Acquired?
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
Energy Flow Through the Ecosystem
WATCH THE VIDEO!
WATCH THE VIDEO!
ENERGY
All living things need energy to power the processes of life. For example, it takes energy to grow. It also takes energy to produce offspring. In fact, it takes energy just to stay alive.
PLANTS are the base of all (or nearly all) food chains.

- Ecosystems get their energy from the Sun.
- Most use energy in the ecosystem comes from the sun (a little comes from chemotrophs).
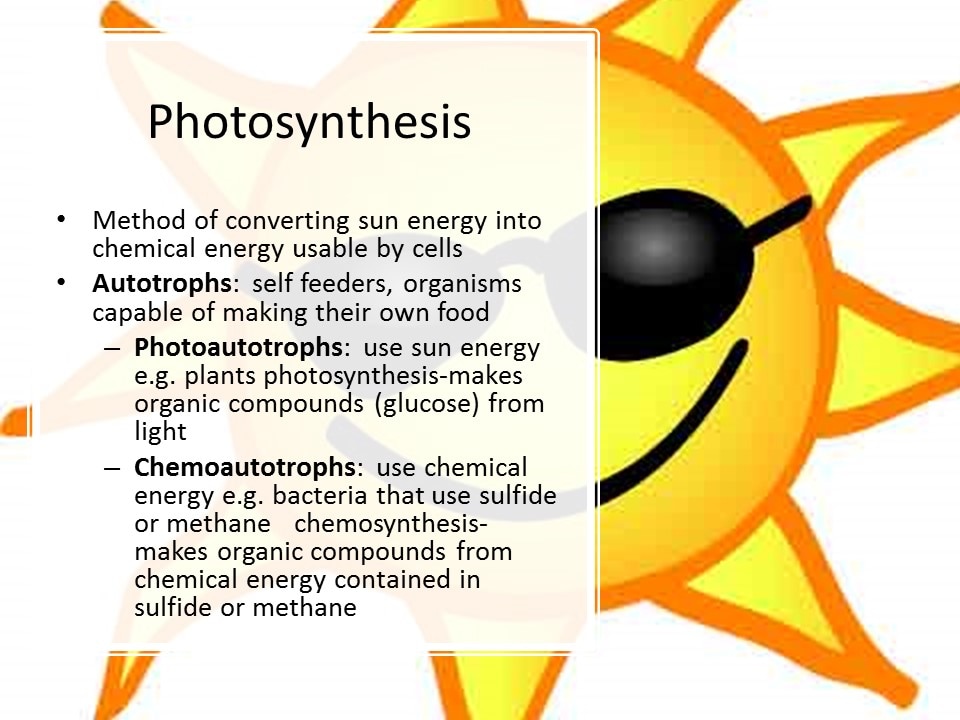
- Only producers can use sunlight to make usable energy.
- Producers convert the sunlight into glucose.
- For example: Plants create chemical energy from abiotic factors that include solar energy.
- The food energy created by producers is passed through the food chain.
- In this way, energy flows from one living thing to another.
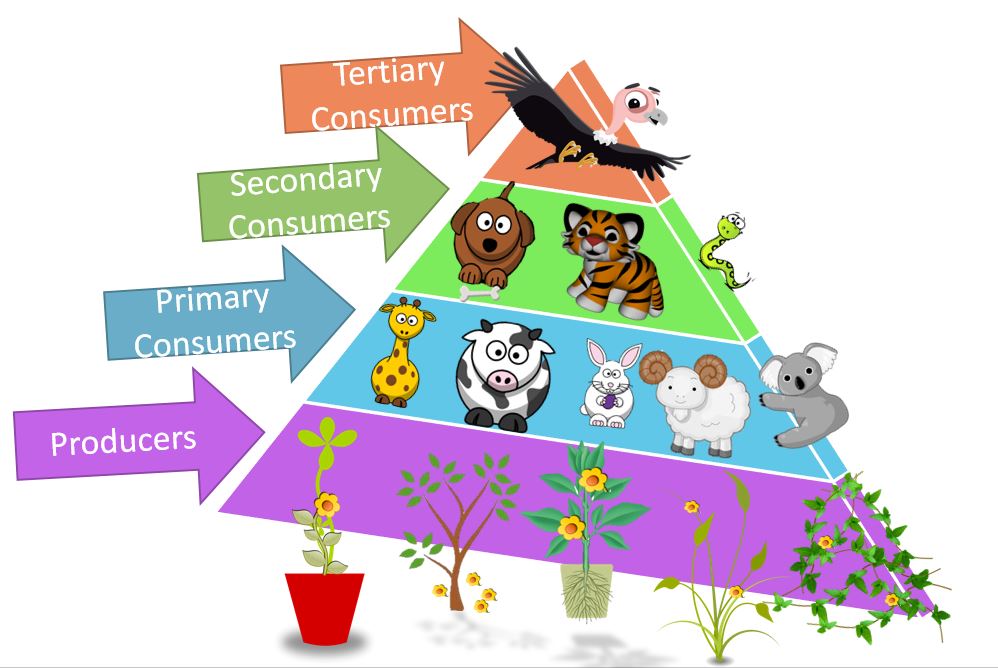
Food Pyramids - a series of steps depicted as a pyramid in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten. You can see the loss of energy at each trophic step in the pyramid since the area of the trophic steps gets smaller as you get away from the producers at the bottom. Pyramid diagrams show the relative amount of energy available at each trophic level.
|
|
|
Energy From the Sun
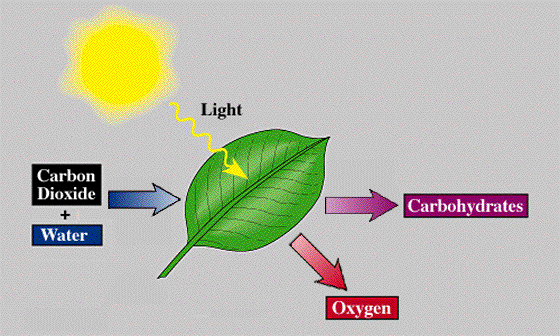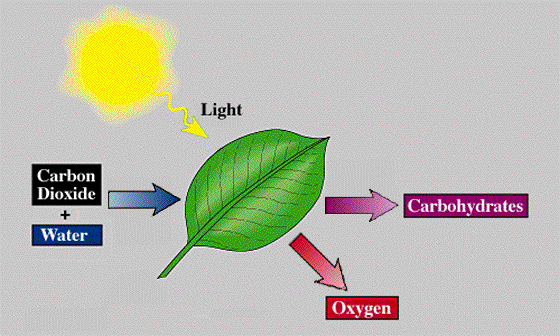
Photosynthesis uses light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and sugar (glucose). Photosynthesis takes CO2 from the air and adds O2 to the air.
Light energy comes in packets called PHOTONS.
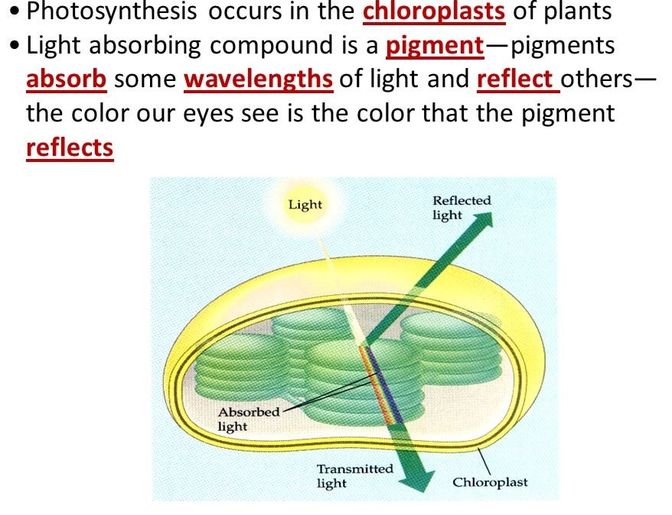
Photosynthesis when photons are absorbed by the photosensitive pigment, chlorophyll.
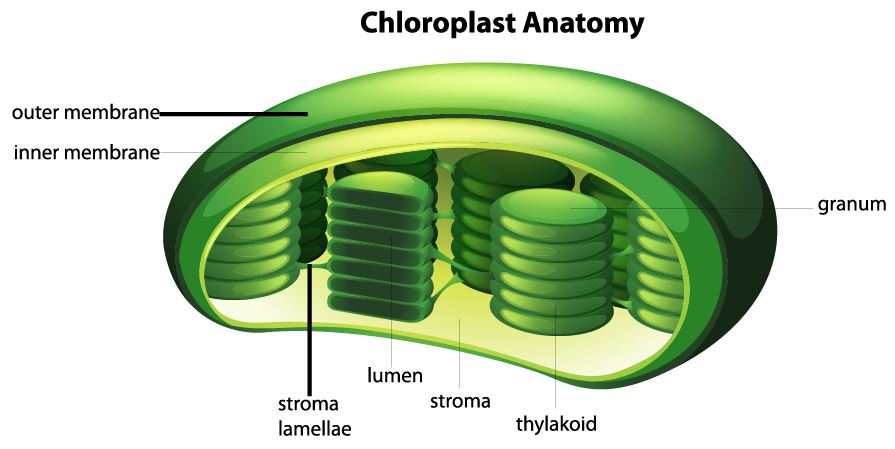
CHLOROPHYLL exists inside of specialized structures called CHLOROPLASTS which are in the leaves of plants.
Chlorophyll reflects green light and gives plants their green color.
Photosynthesis when photons are absorbed by the photosensitive pigment, chlorophyll.
CHLOROPHYLL exists inside of specialized structures called CHLOROPLASTS which are in the leaves of plants.
Chlorophyll reflects green light and gives plants their green color.
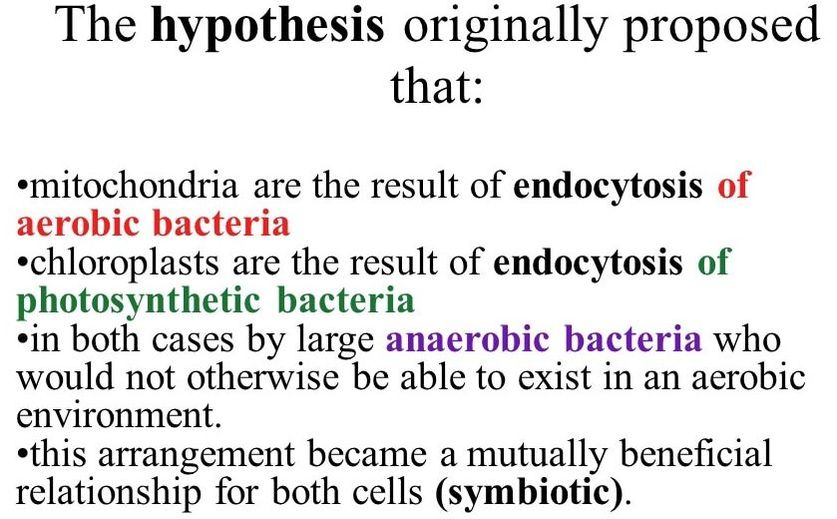
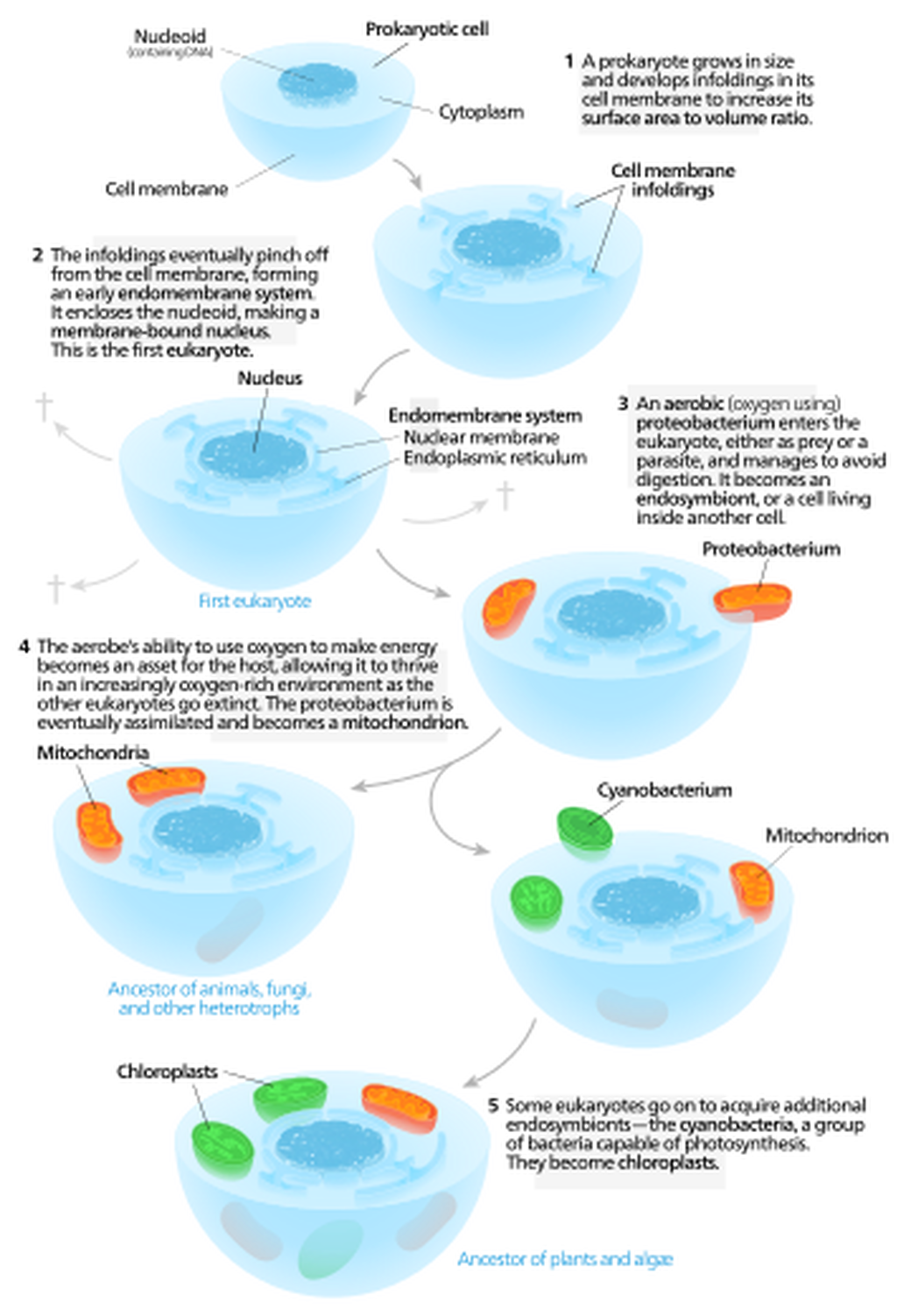
ChloroplastsChloroplasts most likely evolved as a result of a larger prokaryotic cell engulfing a photosynthesizing bacteria.
|
Vocabulary
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
|
|
|
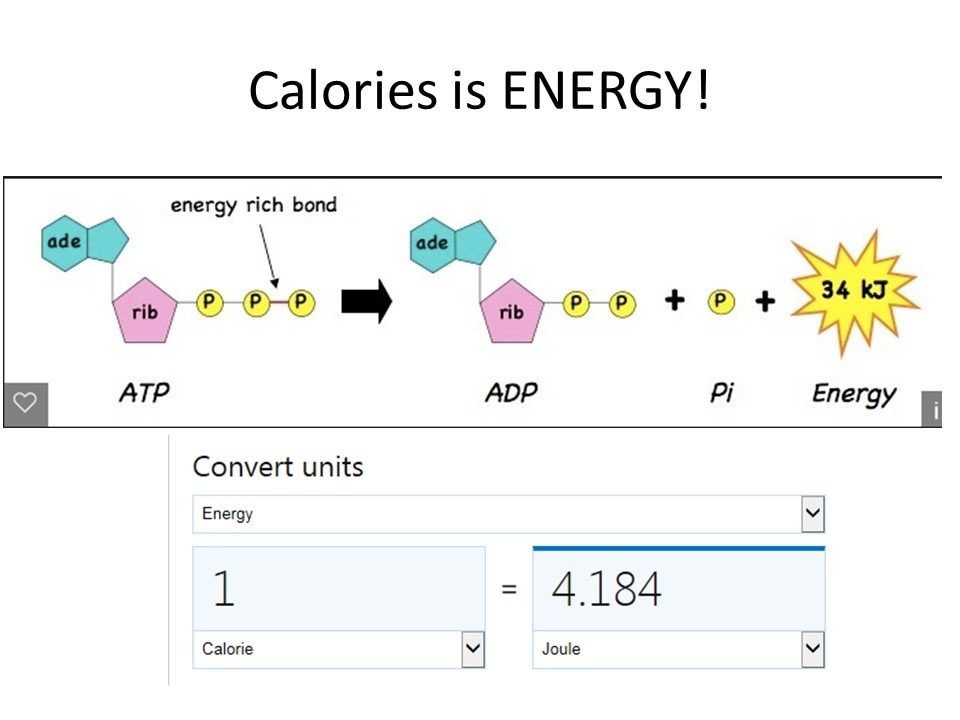
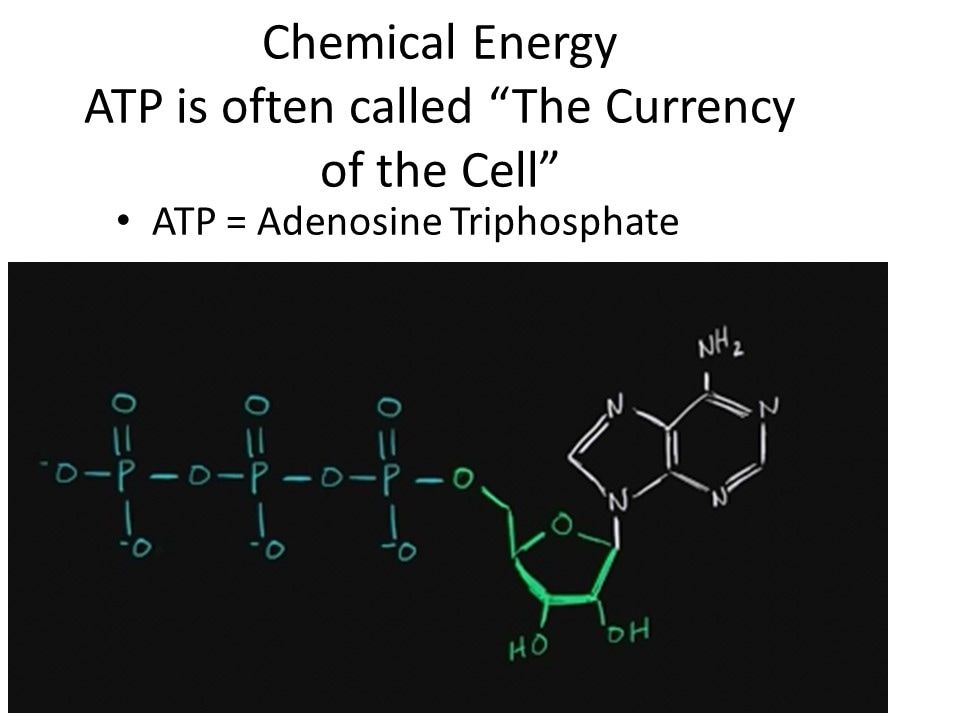
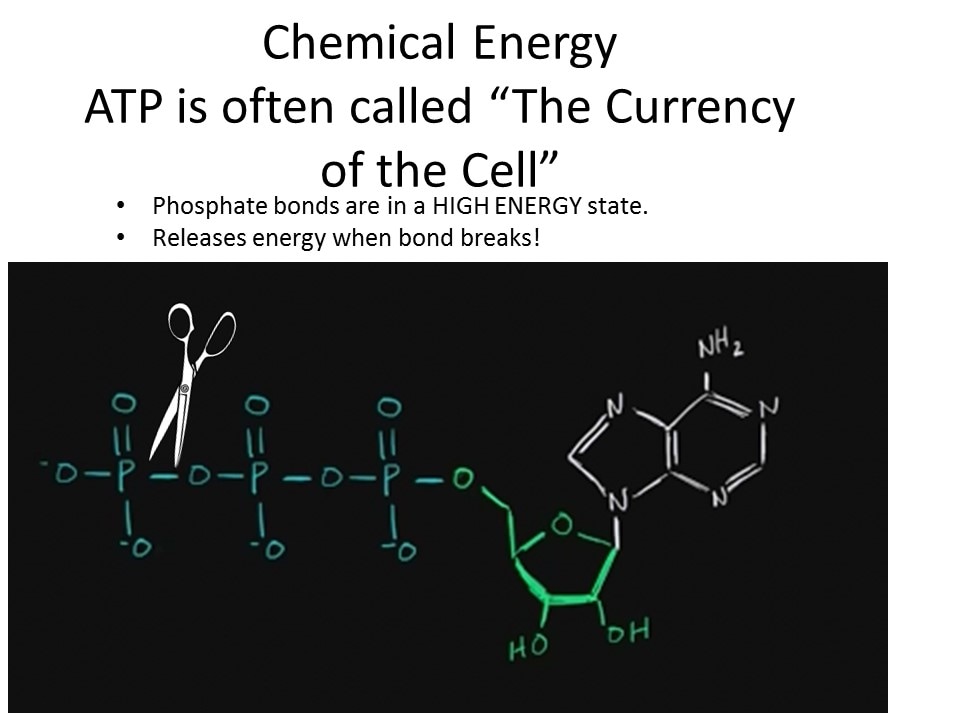
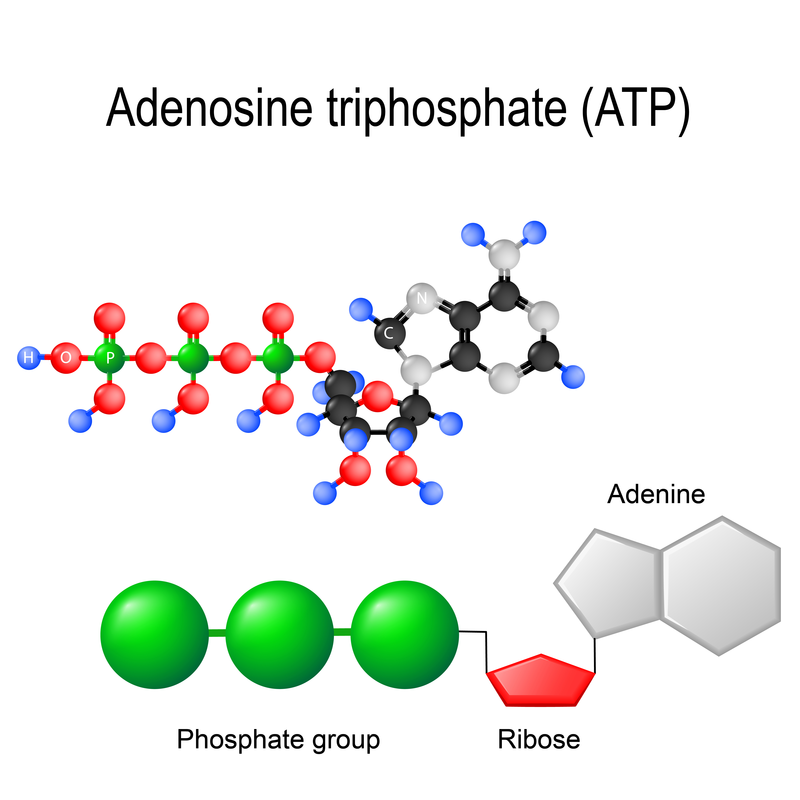
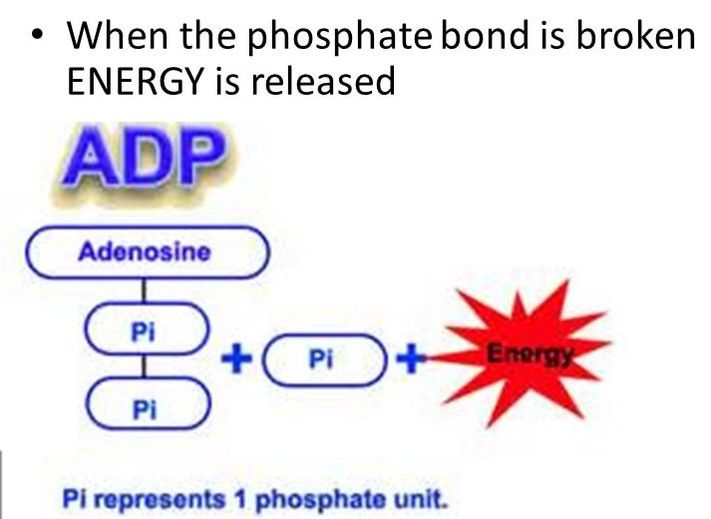
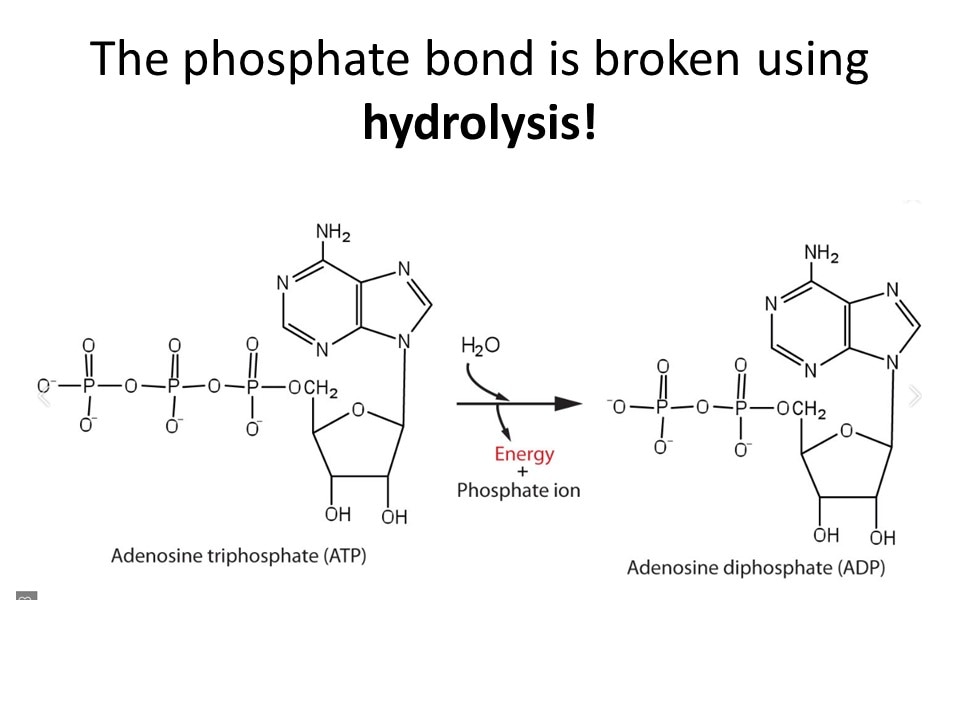
- - ATP is an energy-carrying molecule that cells use to power their metabolic processes
- Producer organism that makes its own food
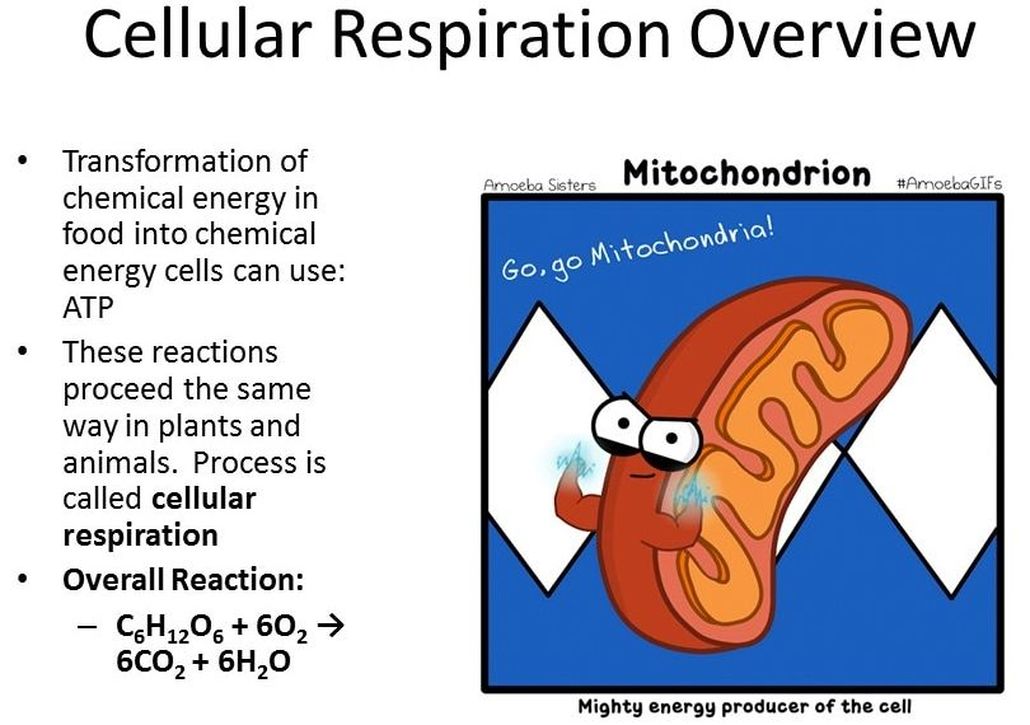
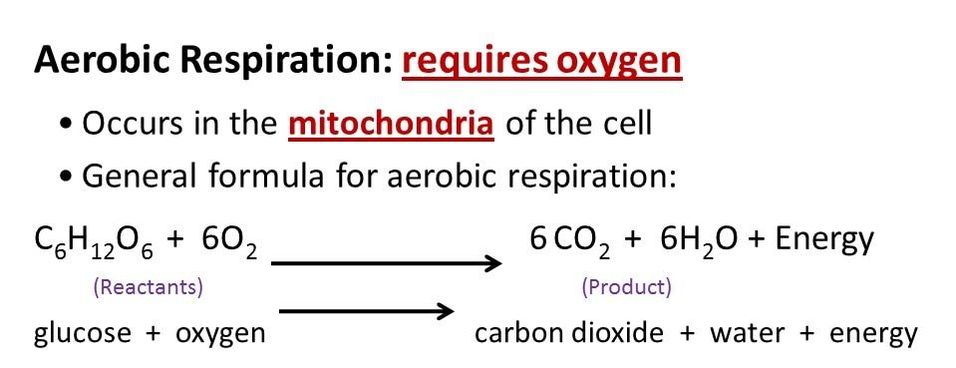
- - Cellular Respiration - process in which cells break down glucose and make ATP for energy
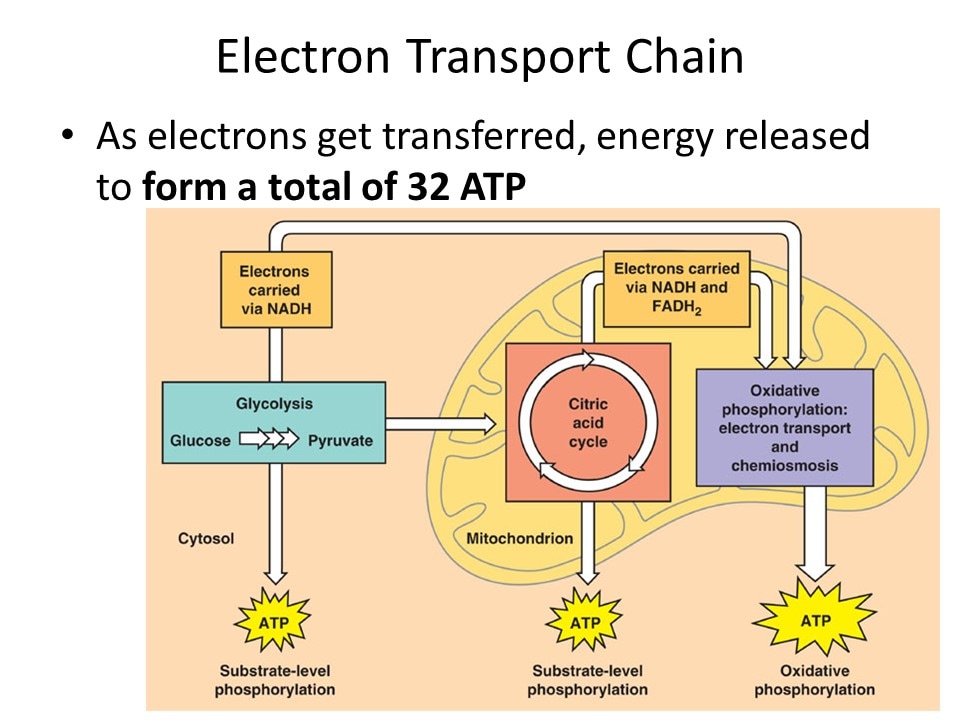
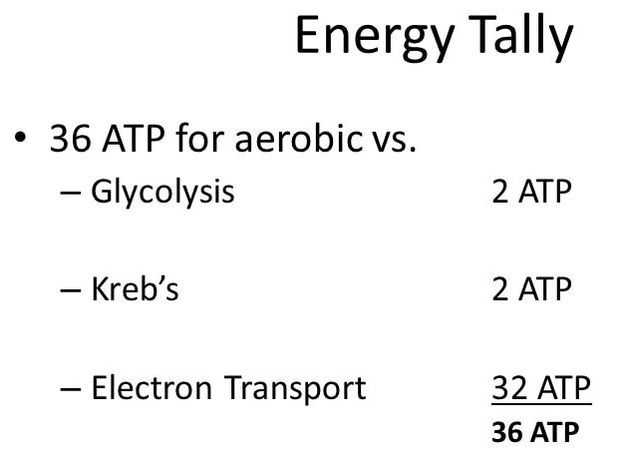
Cellular respiration has 3 parts.
|
|
|
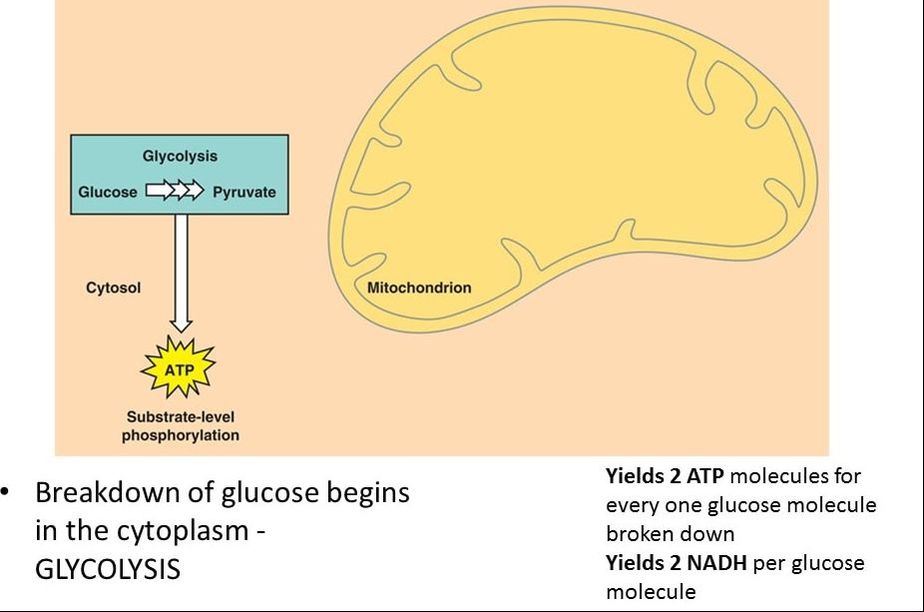
1) Glycolysis
|
|
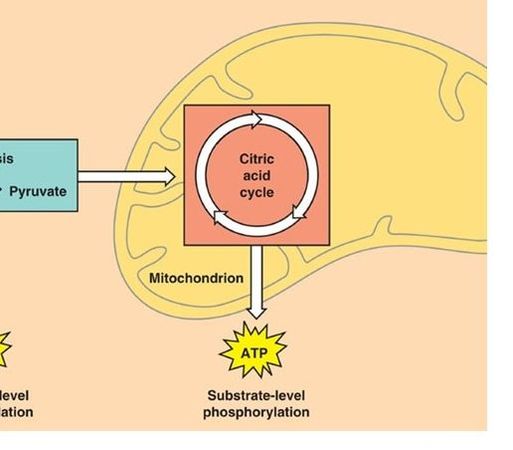
2) The Kreb's Cycle / The Citric Acid Cycle
|
Plants undergo both photosynthesis and cellular respiration
Plants take in CO2 during photosynthesis and make glucose. The glucose is then used by the plants or organisms that consume the plants for the process of cellular respiration to make ATP. Photosynthesis releases oxygen into the atmosphere Cellular respiration produces carbon dioxide ( CO2 ) which is released back into the atmosphere.
Notice that the reactants of cellular respiration are the products of the photosynthesis and the reactants of photosynthesis are the products of the cellular respiration. Cellular respiration is basically photosynthesis in reverse.
The main point of cellular respiration is to create ATP which is used as a source of energy within the cell. |
|
VOCABULARY
- Autotroph: (auto = by itself; trophikos = to feed) – a self feeder. Does not need to eat other organisms for food.
- Carnivore: kills and eats other animals (vore=eater; carne = meat) meat-eaters
- Omnivore (omni = all; vore = eater) = eats both plants and animals
- Herbivore (Herb= plant vore = eater) = eats only plants
- Chemosynthesis: when an organism can harness chemical energy from inorganic molecules (such as hydrogen sulfide) to produce glucose
- Consumer: Organisms that rely on other organisms for energy and nutrients.
- Food chain: a series of steps in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten.
- Food web: a network of feeding interactions. Food web: The complex eating relationships among species within an ecosystem. In a diagram of a food web organisms are connected to the organisms they consume by arrows representing the direction of energy transfer.
- Heterotroph: consumers - must acquire energy from other organisms, typically by ingesting them.
- Photosynthesis: uses light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and energy-rich carbohydrates
- Primary producer: (autotrophs) – are the first producers of energy-rich compounds that are later used by other organisms.
- Scavenger: consume the carcasses of other animals that are already dead.
- Secondary Consumer: An organism that eats primary producers. (example: A grasshopper eats a leaf.)
- Trophic level: Each step in a food chain or a food web
- Glucose – a simple carbohydrate with the chemical formula C6H12O6 that is the nearly universal food for life
- Heterotroph/ Consumer - organism that consumes other organisms for food
- Photosynthesis process of using the energy in sunlight to make food (glucose)