What Do We Mean By "Body Cavity"?
Before we begin our discussion of body cavities and membranes, it is important to know what a cavity is in the first place! (These are not the cavities in your teeth that you dread getting filled by your friendly neighborhood dentist. )
In anatomy you learn that the human body is, in a sense, a glorified tube. ( I can almost hear you GASP! ) OK, a tube is an over simplification, but the premise holds true. The inside and the outside of your tube is covered with epithelial tissue. This tube has some specialized regions that are made up of concave regions (also lined with epithelium) that are connected to the outside. You also have fluid-filled chambers inside of your body that is NOT connected to the outside. All of these regions are considered CAVITIES. The definition of a body cavity - a body cavity is considered to be any fluid-filled space in the body, other than vessels (blood and lymph).
The human body has 2 main body cavities.
They are called the dorsal (or posterior) cavity and a ventral (or anterior) cavity (see illustration).
They are called the dorsal (or posterior) cavity and a ventral (or anterior) cavity (see illustration).
BACK |
FRONT |
The Dorsal (or Posterior) Cavity
|
The Ventral (or Anterior) Cavity
|
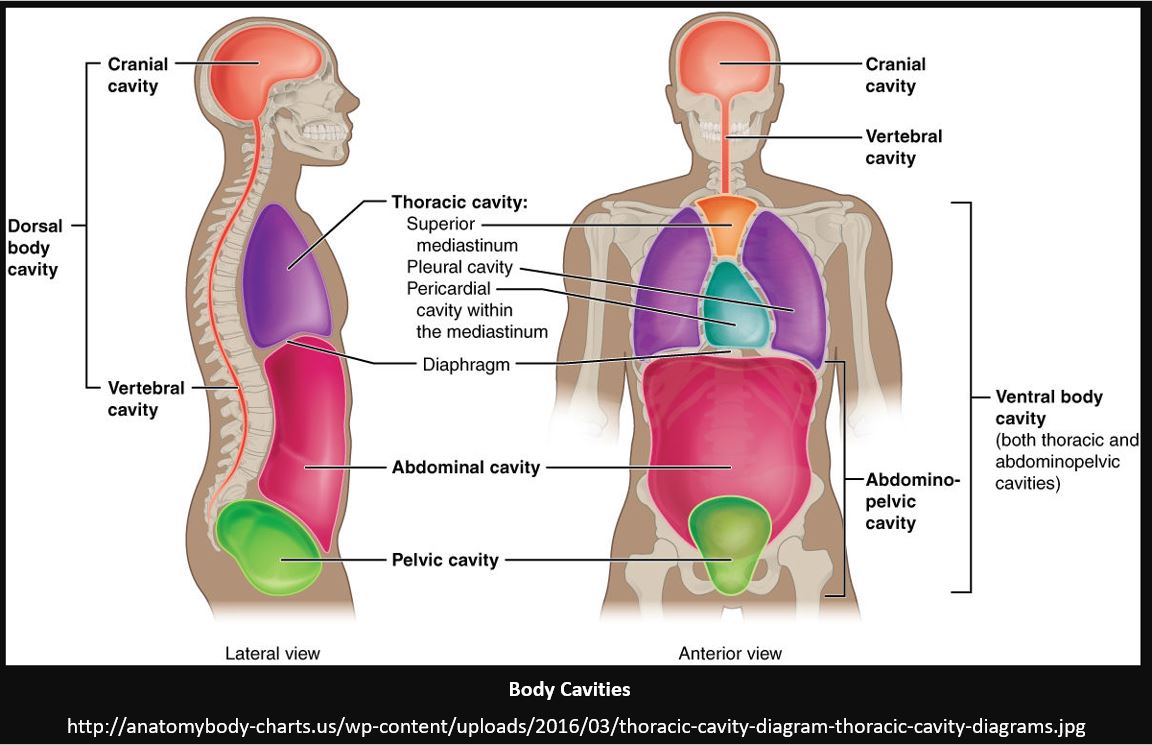
IMAGE: By NCI (original) / Mysid (SVG) - Vectorized by Mysid in Inkscape, based on http://training.seer.cancer.gov/module_anatomy/unit1_3_terminology3_cavities.html. Image renamed from File:Body cavities.svg, Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=5678872
The Dorsal Cavity |
The Ventral Cavity |
|
The dorsal cavity consists of the cranial cavity that houses the brain and the vertebral (or spinal) cavity which contains the spinal cord.
There is no physical separation between the cranial cavity and vertebral cavity. This cavity is a continuous chamber filled with cerebrospinal fluid that surrounds the brain and the spinal cord. "Cerebro-" means "brain" and "spinal" means "of the spine", so the liquid cerebrospinal fluid is named after what it essentially bathes, which is the brain and spine. |
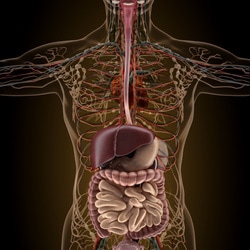
The ventral (or anterior) cavity contains the body's visceral organs. The visceral organs are your body's internal organs, including the heart, the lungs, the liver, the pancreas and the intestines.
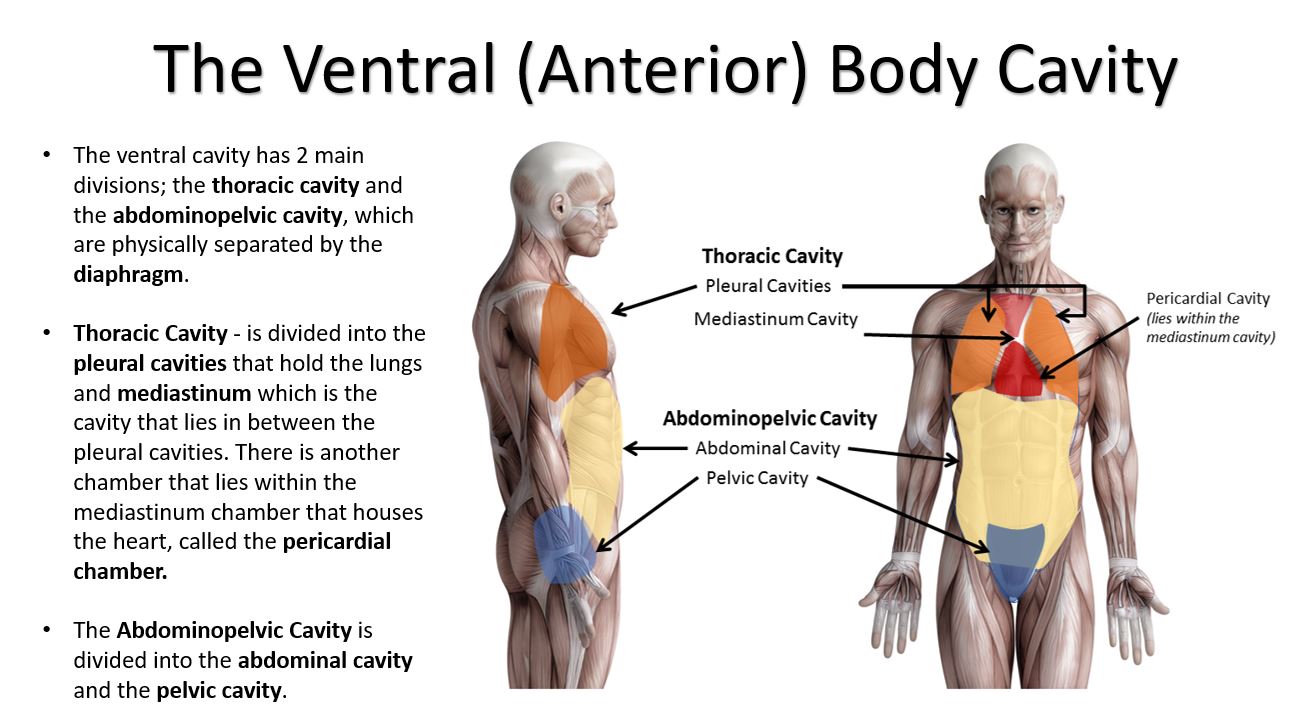
The ventral cavity of the human body is divided into two main regions; the thoracic cavity, and the abdominopelvic cavity, each of which have additional subdivisions. The thoracic cavity and the abdominal cavity are separated by the diaphragm. |
Subdivisions of the Thoracic Cavity
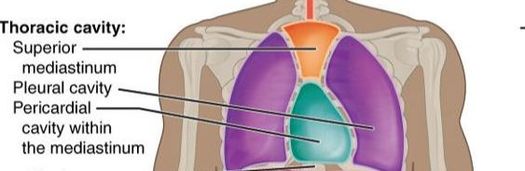
The Thoracic Cavity
The thoracic cavity is separated into three chambers; the left and right pleural cavities and the mediastinum. The thoracic cavity is the cavity of the chest area. This cavity lies underneath the rib cage and houses many important organs and structures of cardiovascular, respiratory and lymphatic systems. The two arguably most notable organs of the thoracic cavity are the heart and the lungs.
The Pleural Cavity
The left lung is in the left portion of the pleural cavity and the right lung is in the right portion of the pleural cavity.
The Mediastinum Cavity
The space between the 2 pleural cavities is the mediastinum, which holds the pericardial cavity which contains the heart (see illustration).
The thoracic cavity is separated into three chambers; the left and right pleural cavities and the mediastinum. The thoracic cavity is the cavity of the chest area. This cavity lies underneath the rib cage and houses many important organs and structures of cardiovascular, respiratory and lymphatic systems. The two arguably most notable organs of the thoracic cavity are the heart and the lungs.
The Pleural Cavity
The left lung is in the left portion of the pleural cavity and the right lung is in the right portion of the pleural cavity.
The Mediastinum Cavity
The space between the 2 pleural cavities is the mediastinum, which holds the pericardial cavity which contains the heart (see illustration).
Subdivisions of the Abdominopelvic Cavity
|
The Abdominopelvic Cavity The abdominopelvic cavity is divided into 2 areas; the abdominal cavity and the pelvic cavity. The Abdominal Cavity The abdominal cavity contains digestive organs., including the stomach, the liver, the kidneys, the small intestines, etc. The Pelvic Cavity The pelvic cavity contains the internal reproductive organs, the urinary bladder and the rectum. |
Other Body Cavities
There are other body cavities in addition to the dorsal and ventral cavities. These other cavities, however, are accessible from the outside of the body.
This includes the oral cavity, the nasal cavity and the orbital cavity. The word oral means "of the mouth".
Membranes
It is important to also know about the membranes that line the body's cavities, as well. The body's cavities are lined with a specialized membrane, called the serous membrane (serosa). The serous membrane supplies the cavity with a constant supply of serous fluid that is secretes.
The serous membrane (serosa) is a thin membrane that covers the walls and organs of the ventral cavity (which is made up of the thoracic cavity and the abdominopelvic cavity). The portion of the serous membrane that covers the walls of the cavity is called the parietal serosa. The definition of the word parietal is "of, relating to, attached to, or denoting the wall of the body or of a body cavity or hollow structure" according to the Merriam-Webster online dictionary (https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/parietal). The portion of the serous membrane that covers the internal organs (or viscera) is referred to as the visceral serosa.
Some areas of the serous membrane (serosa) have special names. For example, the serosa of the pericardial cavity that houses the heart is called the pericardial membrane, and the serosa that lines the peritoneal cavity that surrounds most of the organs of the abdomen, is called the peritoneum.
Some areas of the serous membrane (serosa) have special names. For example, the serosa of the pericardial cavity that houses the heart is called the pericardial membrane, and the serosa that lines the peritoneal cavity that surrounds most of the organs of the abdomen, is called the peritoneum.