Evolution - Our Beginning
We Are All Made of Stars.
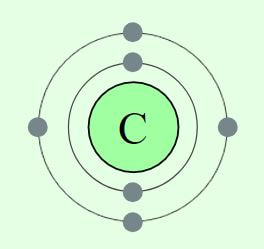
All of the elements heavier, including carbon, were formed in stars over 4.5 billion years ago. All life as we know it, is "carbon-based". So this means that the carbon that makes up a large portion of our bodies, and the carbon in all lifeforms living now or that have ever lived before, has been formed in stars billions of years ago.
In the Beginning...

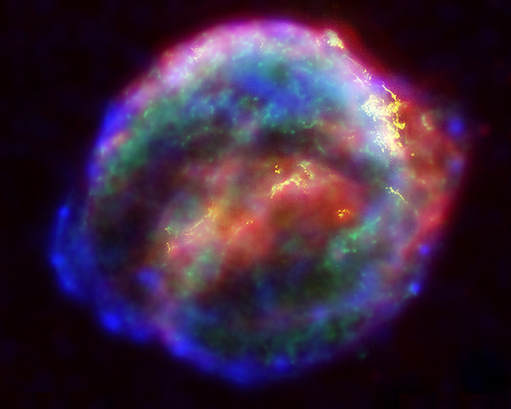
Stars have a life cycle. They are born, live for millions of years, and eventually die. Stars are composed of the 2 lightest atomic elements; hydrogen and helium. The hydrogen in stars undergo a continuous nuclear fusion reaction that transforms hydrogen (hydrogen has one electron and one proton) into helium (helium has two electrons and two protons). After billions of years, the star runs out of hydrogen and the fusion reaction ends along with the life of the sun. Some stars will explode at the end of their life-cycle. They literally go out with a BANG! These exploding stars are called a supernova.
The supernova explodes with a huge amount of energy that produces all of the heavier elements that we find in the universe. The supernova explodes with so much force that the matter formed in the explosion is pushed outward from the explosion in all directions. These heavier elements made life possible.
96% of the human body is composed 4 elements.
The carbon, oxygen and nitrogen were formed in stars that lived and dies billions and billions of years ago.
- Carbons
- Hydrogen
- Oxygen
- Nitrogen
The carbon, oxygen and nitrogen were formed in stars that lived and dies billions and billions of years ago.
THE EARTH'S BABY PICTURES!

The Earth formed over 4.5 billion years ago probably through a process of accretion. Accretion is the theory that gravity pulled matter together in our solar system. In space, matter attracts matter, so the more massive a celestial body became, the more matter it would attract. The atmosphere of the newly formed Earth did not contain oxygen and nitrogen. In fact, the Earth was so different, you probably would not recognize it as Earth at all!
|
There is good evidence that our moon was formed from an asteroid hitting the early Earth and breaking off a large amount of the Earth's mantle into space. This matter coalesced into what is now known as our precious moon.
The moon was able to shield early Earth from many of the asteroids that plagued the early Earth in what was called the Early and late Bombardment Periods. |

After the moon formed, the moon provided some protection for the early Earth as the Earth was able to cool and develop its protective atmosphere. When Earth first formed, it was a very different place than it is now. Even though the Earth had cooled some from its original ball of spewing magma, scientists believe the Earth consisted of massive rocks afloat a sea of molten lava.
The early atmosphere was oxygen-free, and was composed of carbon dioxide, nitrogen gas and water vapor.

At some point in our early Earth's history, the Earth cooled enough for the water vapor to liquefy covering the Earth with precious life-giving water.
Somehow, out of this "primordial soup" of non-living molecules, the first building blocks of life formed. One of the biggest questions scientists have is how did life on our planet begin? It is hypothesized that life had evolved from non-living molecules through the 4 following stages.
- Small Organic Molecules Formed
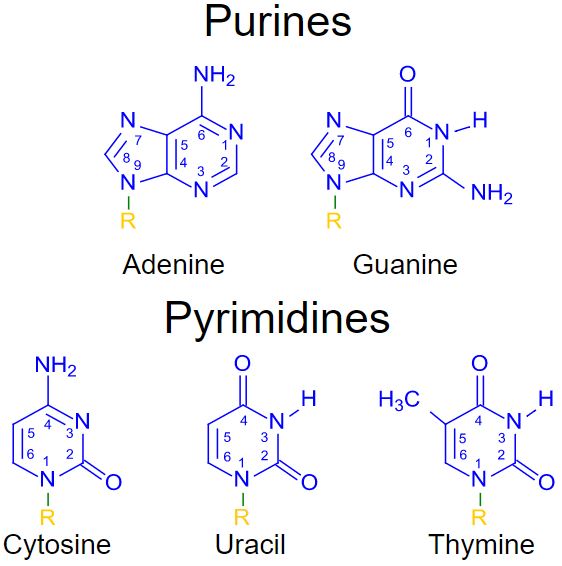
- Carbohydrates, Amino Acids that form Proteins and Nucleotides that make up DNA and RNA molecules.
- Small Organic Molecules (monomers) came together to form Larger Organic Molecules (polymers).
- Polymers Formed protobionts.
- The term "protobionts" literally means 'early form of life'.
- A protobiont is basically a cell membrane surrounding a liquid droplet.
- they can reproduce
- They do not contain genetic information (DNA)
- they metabolize
- they respond to their environment.
- they form easily and spontaneously
- Protobionts evolved to contain DNA and pass on their genetic information during reproduction.
Experiments that show that the hypothesis is possible, include a famous study performed by Stanley Miller and Harold Urey in the 1950's. Miller and Urey sought to test an idea hypothesized by Russian chemist, A.I. Oparin in 1920. Oparin hypothesis was that early life forms may have formed through a series of chemical reactions that made simple compounds evolve into increasingly more complex structures.
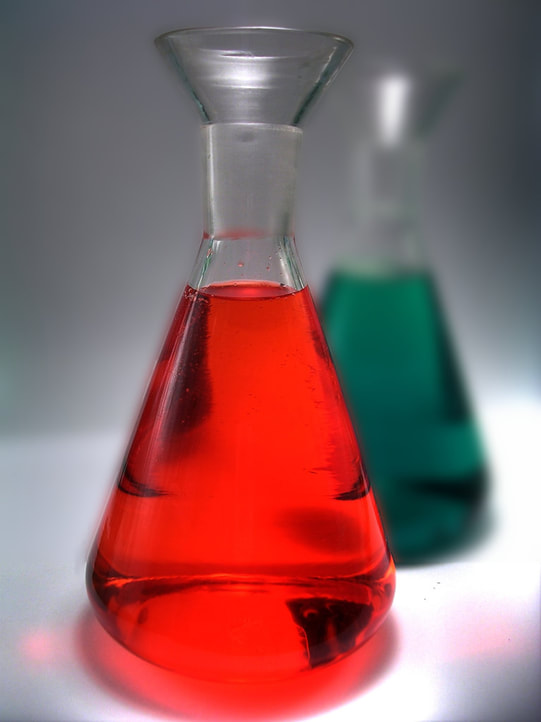
Stanley Miller and Harold Urey created a contraption that was able to simulate the oxygen-free atmosphere of the early Earth and adding a secret ingredient, LIGHTENING!
Stanley Miller and Harold Urey created a contraption that was able to simulate the oxygen-free atmosphere of the early Earth and adding a secret ingredient, LIGHTENING!

Scientists determine how old things are both relatively and specifically. In order to determine the specific age of rocks and fossils, radioactive dating is used. For most fossils of living things, carbon-14 is used.
Miller and Urey used sparks to simulate lightning that could have been a natural source of energy for these chemical reaction to occur. The Miller-Urey experiment created proteins and RNA. These are the building block of life. The experiment showed that it is possible that the conditions hypothesized by Oparin may indeed have produced early forms of life.
The Earth's history is divided into three major eons:
- Archean
- Proterozoic
- Phanerozoic

The Archean and Proterozoic eons together are also referred to as the Precambrian eon. These eons saw the gradual appearance of life on Earth, followed by the gradual evolution of simple organisms.The Phanerozoic eon started with the Cambrian explosion, which was a massive increase in the number and diversity of life on Earth.
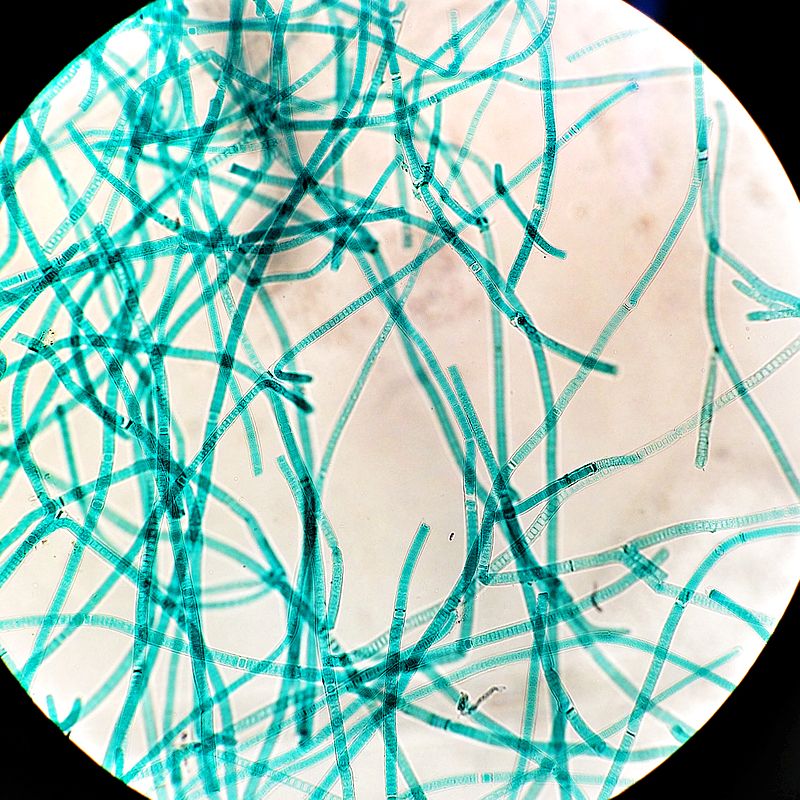
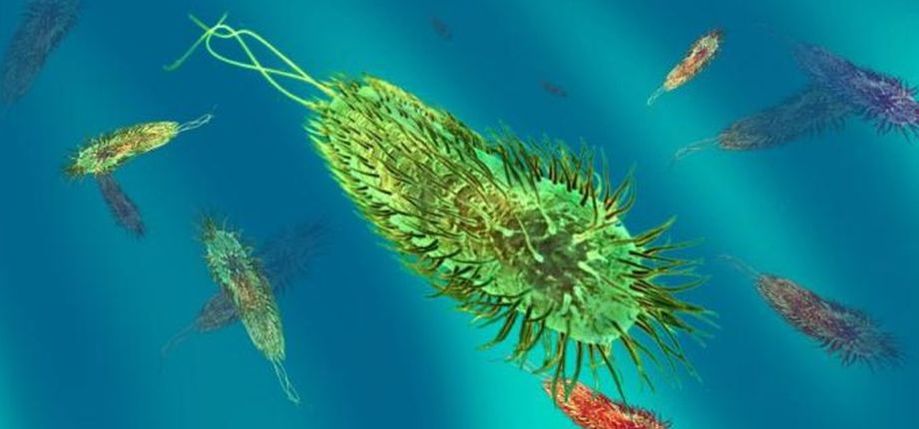
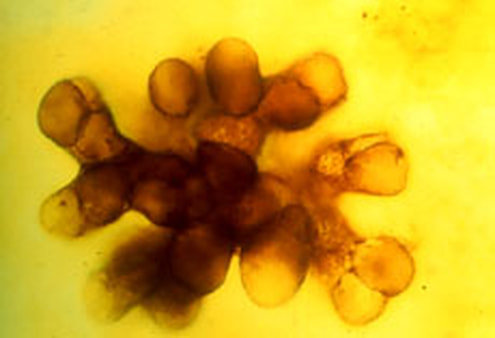 Crystallized Fossil of Cyanobacteria
Crystallized Fossil of Cyanobacteria
The earliest fossil evidence that we have of life on our planet is over 3.5 billion years old. The earliest known life-form was a single-celled organism called cyanobacteria. Cyanobacteria are able to undergo both photosynthesis and chemosynthesis to meet their energy needs. Both of these processes use up carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and release oxygen as a waste product.
Over the course of hundreds of millions of years, trillions of cyanobacteria transformed the atmosphere to contain the oxygen. The addition of oxygen to the atmosphere paved the way for new life forms to evolve that depended on oxygen, like humans do.
Over the course of hundreds of millions of years, trillions of cyanobacteria transformed the atmosphere to contain the oxygen. The addition of oxygen to the atmosphere paved the way for new life forms to evolve that depended on oxygen, like humans do.
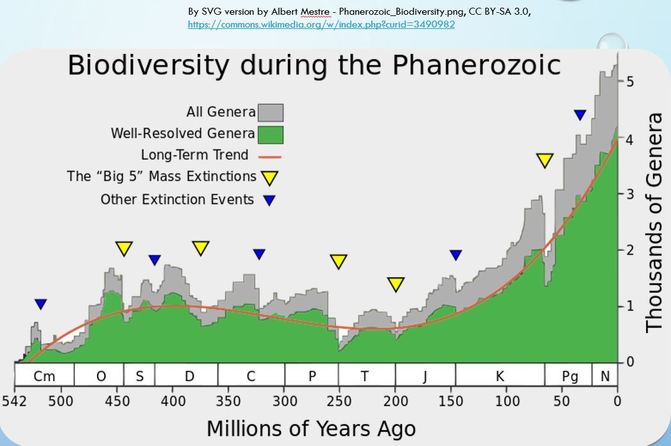
Over time, life moved from water to land. More species evolved. More complex species evolved. This trend continues until mass extinction occurs. The Mesozoic Era is best known as the age of the dinosaurs. These reptiles ruled the Earth until there was a mass extinction ending the era. There were actully 5 mass extinction events in our Earth's history.