LEVELS OF ANATOMICAL ORGANIZATION
The Chemical Level
The story of biology begins in chemistry. We must have a basic understanding of chemistry to understand biology. This is because, everything that is made up of matter (from rocks to human beings) is made up of atoms.
The story of biology begins in chemistry. We must have a basic understanding of chemistry to understand biology. This is because, everything that is made up of matter (from rocks to human beings) is made up of atoms.
Hierarchical Levels of
Anatomy
|
There are six hierarchical levels of anatomy and physiology.
(1) Chemical level (2) Cellular level (3) Tissue level (4) Organ level (5) Organ system level (6) Organism level |
|
The Chemical Level
The Chemical Level Includes the Atomic Level and Molecular Level of our Bodies

The story of YOU is more beautiful and complex than you can ever image! Many scientists believe that our universe started with a "BIG BANG" or a "BIG BANG-LIKE" event. The universe we live in was created by some type of BANG that contained all of the subatomic particles needed to make matter. In the beginning, the early universe was too hot for atoms to form, but as the universe cooled the first atoms were able to form.
We are all made of stars!
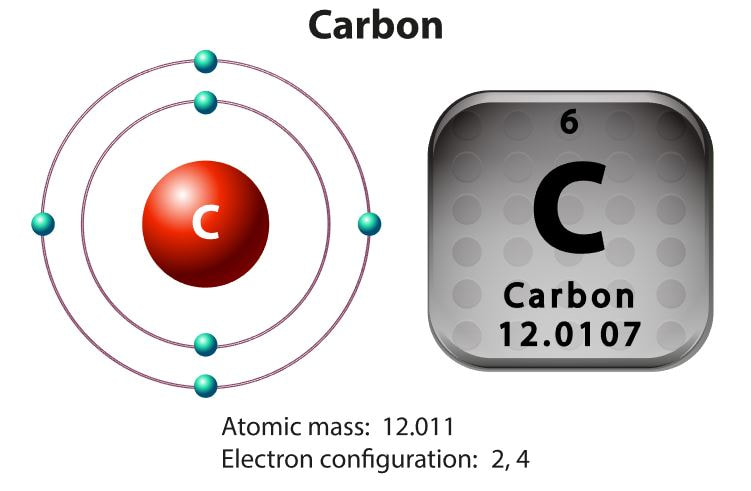
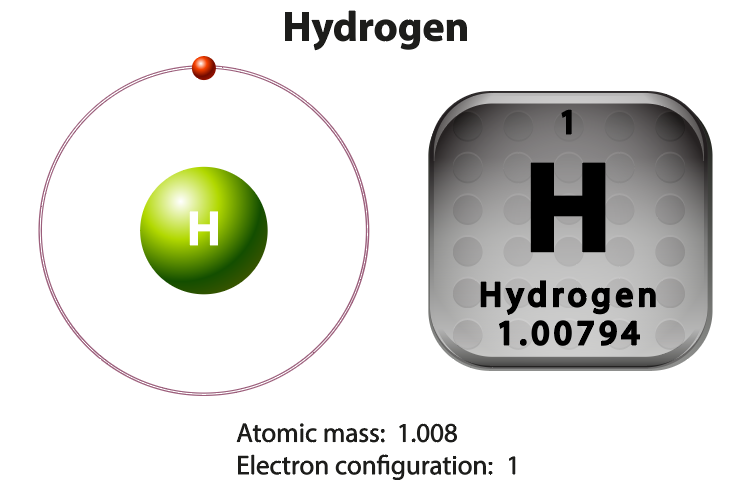
The first atoms to form were hydrogen and helium. Hydrogen is made up of only 1 electron and 1 proton. Helium is made up of 2 electrons and 2 protons. Stars are made up almost entirely of hydrogen and helium. All of the heavier elements are made when a star dies and explodes as a super nova.
The matter that you are made of has been around since the beginning of the universe 13 billion years ago. All of the heavier elements required for life like you and I to exist, were form in the cauldron of an exploding star.
The matter that you are made of has been around since the beginning of the universe 13 billion years ago. All of the heavier elements required for life like you and I to exist, were form in the cauldron of an exploding star.
The Atom
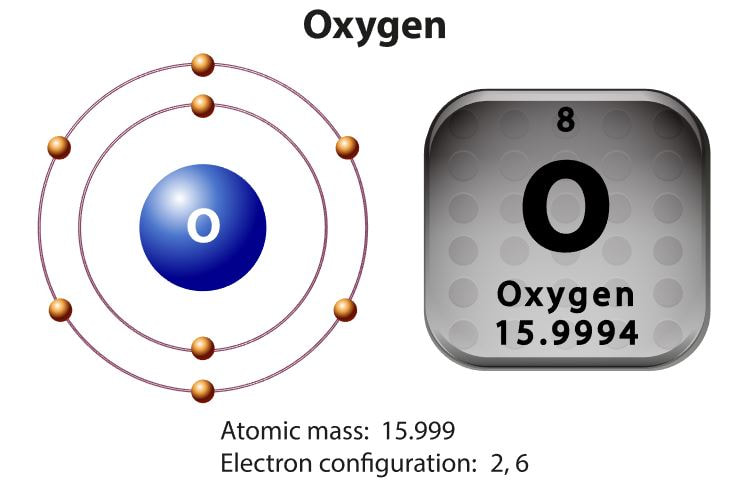
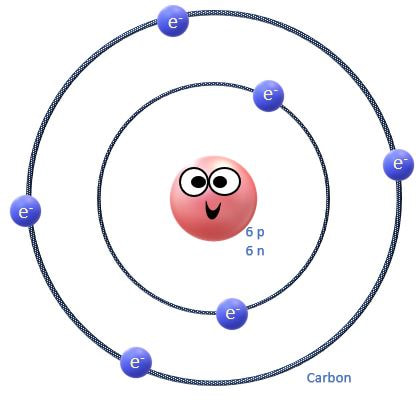
Atoms are the fundamental unit of matter. That means that all matter is composed entirely of atoms.Atoms are made up of a combination of subatomic particles, which are protons, electrons and neutrons.
Atoms are the fundamental unit of matter. That means that all matter is composed entirely of atoms.Atoms are made up of a combination of subatomic particles, which are protons, electrons and neutrons.
PROTONS are positively charged and are found at the nucleus (center) of the atom.
ELECTRONS are negatively charged and are found on the outer portions of the atom.
NEUTRONS have no charge and are found in the nucleus of the atom.
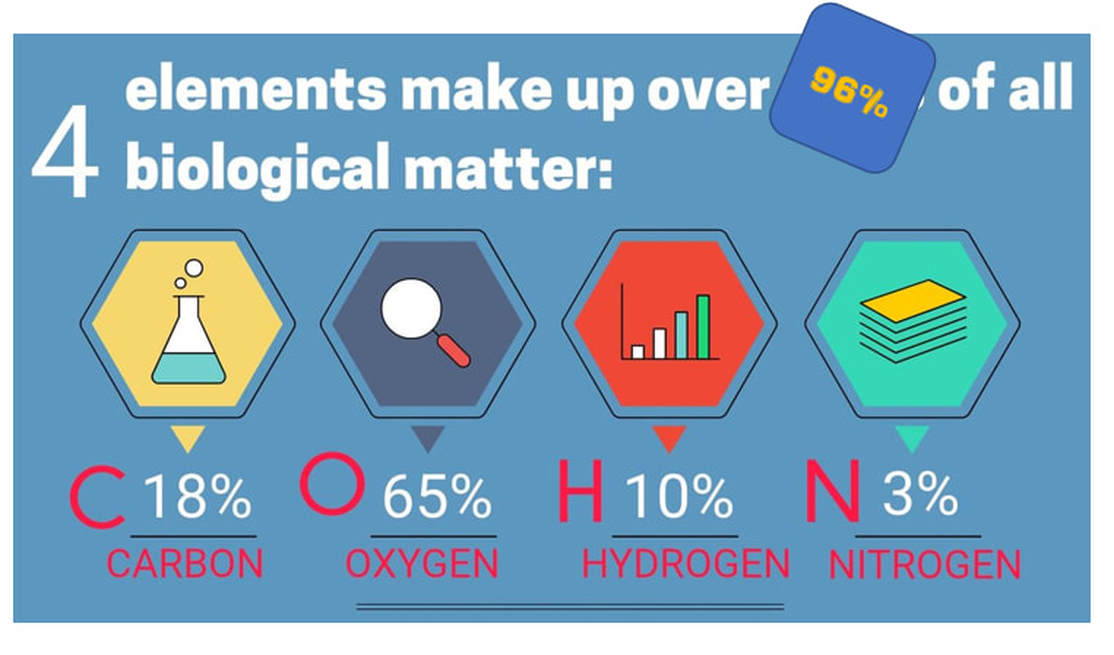
96% of all living matter is composed of only 4 atoms (elements)!
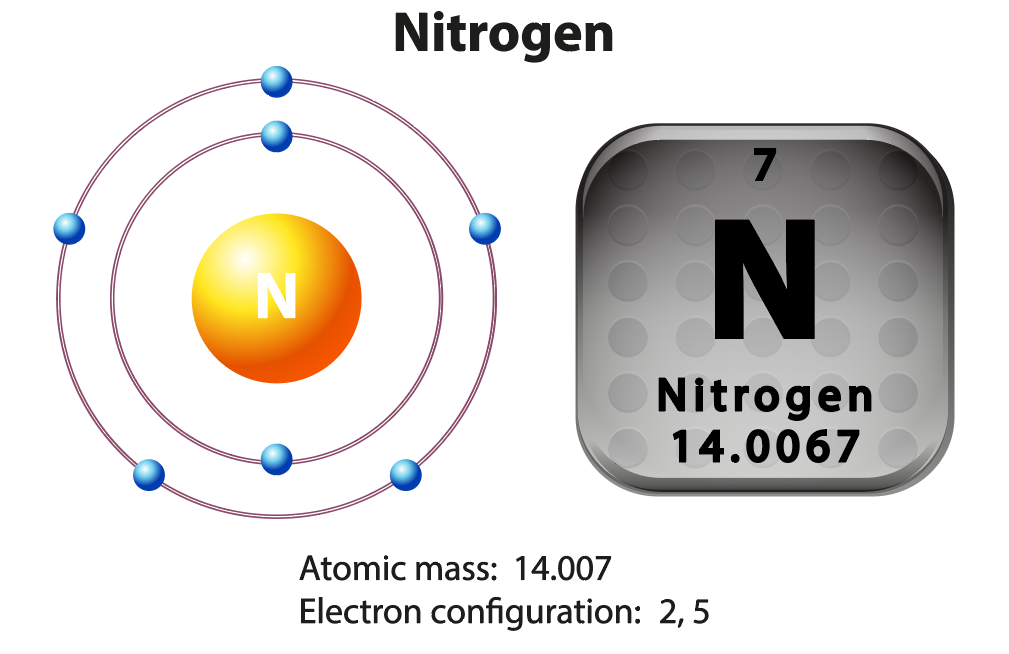
Hydrogen
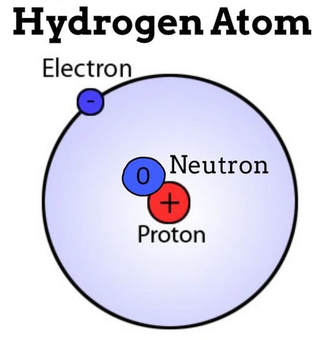
The simplest and most abundant atom is the hydrogen atom. The hydrogen atom contains only one electron and one proton.
An atom, by definition, is neutral (uncharged). That means in an atom, the number of protons will equal the number of electrons.
An atom, by definition, is neutral (uncharged). That means in an atom, the number of protons will equal the number of electrons.
ATOMS - What's the MATTER?
All matter in the universe as we know it, is made up of atoms. It is for this reason that we define the atom as the fundamental unit of matter. An atom is made up of subatomic particles. The nucleus (or center) of the atom is made up of one or more positively charged subatomic particles called protons and uncharged subatomic particles called neutrons. Almost all of the mass of the atom is located in the nucleus. Electrons "orbit" the nucleus of the atom. The electron(s) that are located on the outermost portion of the atom can participate in chemical reactions and can create bonds with other atoms.
All matter in the universe as we know it, is made up of atoms. It is for this reason that we define the atom as the fundamental unit of matter. An atom is made up of subatomic particles. The nucleus (or center) of the atom is made up of one or more positively charged subatomic particles called protons and uncharged subatomic particles called neutrons. Almost all of the mass of the atom is located in the nucleus. Electrons "orbit" the nucleus of the atom. The electron(s) that are located on the outermost portion of the atom can participate in chemical reactions and can create bonds with other atoms.
Molecules
WHAT IS A MOLECULE?
When an atom forms a bond with one or more other atoms, it is called a molecule. A molecule is made up of one or more atoms. Sometimes these molecules are small and simple. We can take oxygen as an example. Oxygen is a gas that is made up of simply 2 oxygen molecules that are bound together (02). Some molecules consist of thousands of atoms (macromolecules) like DNA and proteins.
When an atom forms a bond with one or more other atoms, it is called a molecule. A molecule is made up of one or more atoms. Sometimes these molecules are small and simple. We can take oxygen as an example. Oxygen is a gas that is made up of simply 2 oxygen molecules that are bound together (02). Some molecules consist of thousands of atoms (macromolecules) like DNA and proteins.
Proteins, lipids, carbohydrates and nucleic acids are the 4 most important molecules for the cell, and for life in general.
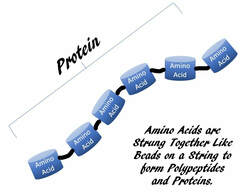
Proteins
Nucleic Acids
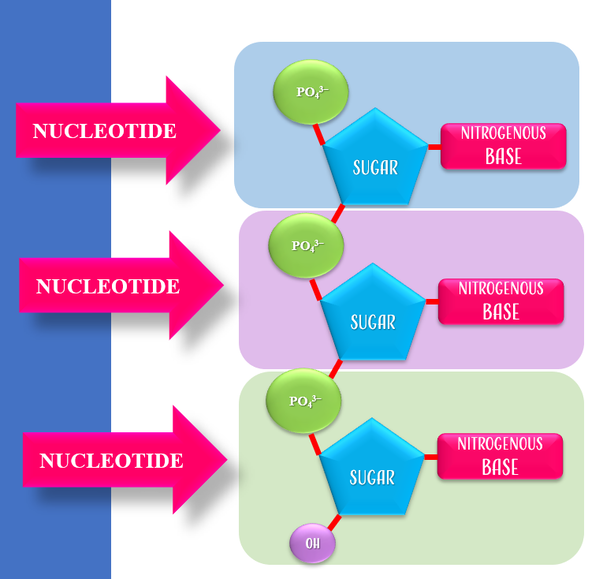
Nucleic Acids includes DNA and RNA.
|
Nucleic Acids are polymers that are formed from a long string composed of a single monomers, called nucleotides.
Nucleic acids includes our DNA and RNA. DNA stands for Deoxyribonucleic acid and RNA stands for Ribonucleic Acid. DNA and RNA function in coding and transferring genetic information. DNA functions as the master "instruction manual" that has all of the information on how that cell should develop and hold the instructions for making proteins which act out the various functions of the cell. |
|
Single Sugar Units (monosaccharides) Bond Together Forming Large Carbohydrate Molecules (polysaccharides)
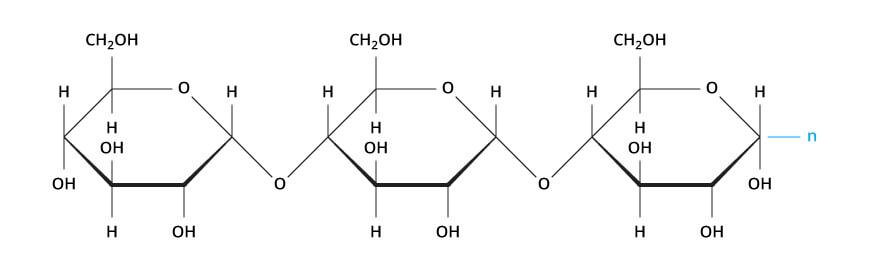 Polysaccharide Composed of Multiple Monosaccharides
Polysaccharide Composed of Multiple Monosaccharides
Carbohydrates get converted into energy in the body through our metabolism. Our metabolism breaks down the glucose molecule and creates ATP. ATP is the principle energy source for the cell. ATP is often called "the energy currency of the cell".
- Monosaccharides are simple sugars composed of one sugar molecule. Glucose is an example of a monosaccharide.
- Disaccharides are composed of 2 sugar molecules bound to each other. Sucrose (table sugar) is an example of a disaccharide.
- Polysaccharide are sugar (or carbohydrates) that are formed from long chain of monosaccharides bound together, Starch is an example of a polysaccharide.
Fatty Acids
|
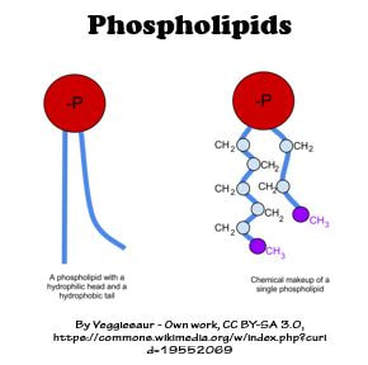
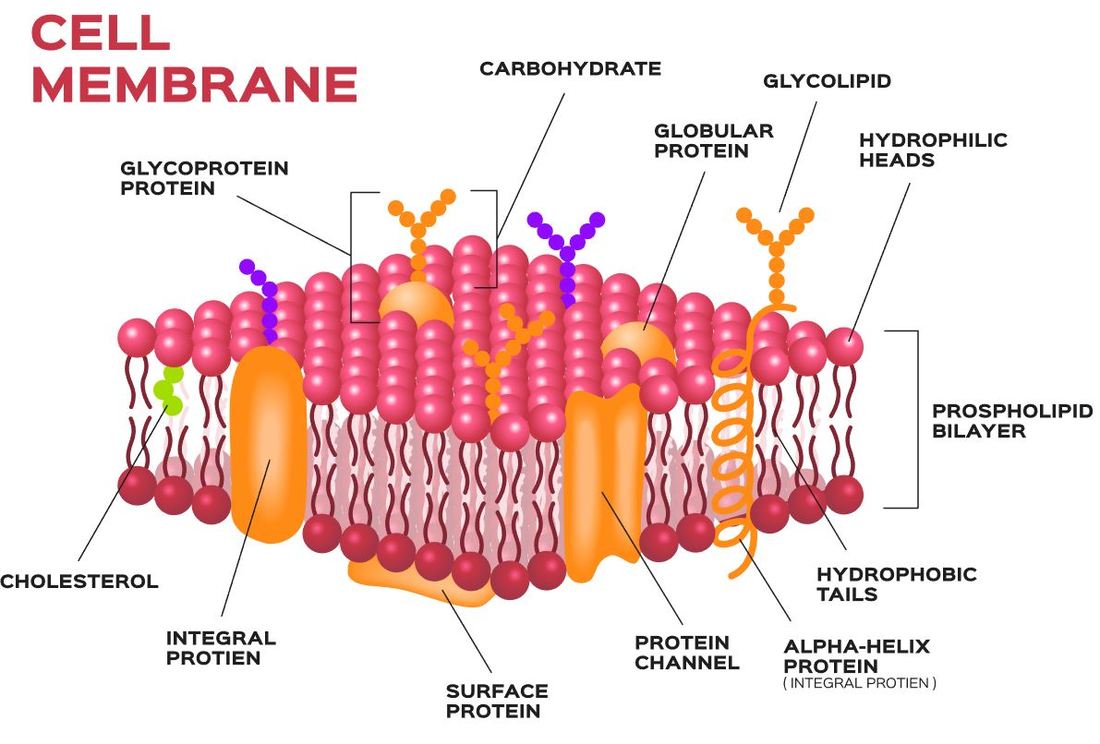
Phospholipids are made up of two fatty acids, and a phosphate group. The phosphate group hydrophilic (water-loving), whereas the 2 fatty acid chains (tails) are hydrophobic (water fearing).
In the cell membrane, the hydrophobic tails face each other creating a barrier of impermeability ro many substances. The phosphate heads are hydrophilic and face the intracellular and extracellular fluid. Phospholipids are considered amphiphilic, because that contain q hydrophobic region, as well as a hydrophilic groups. |
|
The Cellular Level
|
|
The cell is the fundamental unit of life. All living things are made up of one or more cells.
You came from just one cell! You started out as a zygote, which is a fertilized egg. From there you began to undergo rapid cellular division (see GIF) which lead to the exponential growth that made the cute, bouncing baby that was YOU! Pretty amazing! Cells and their surroundings are made up of molecules. It takes about 100 trillion atoms to make a typical cell. |
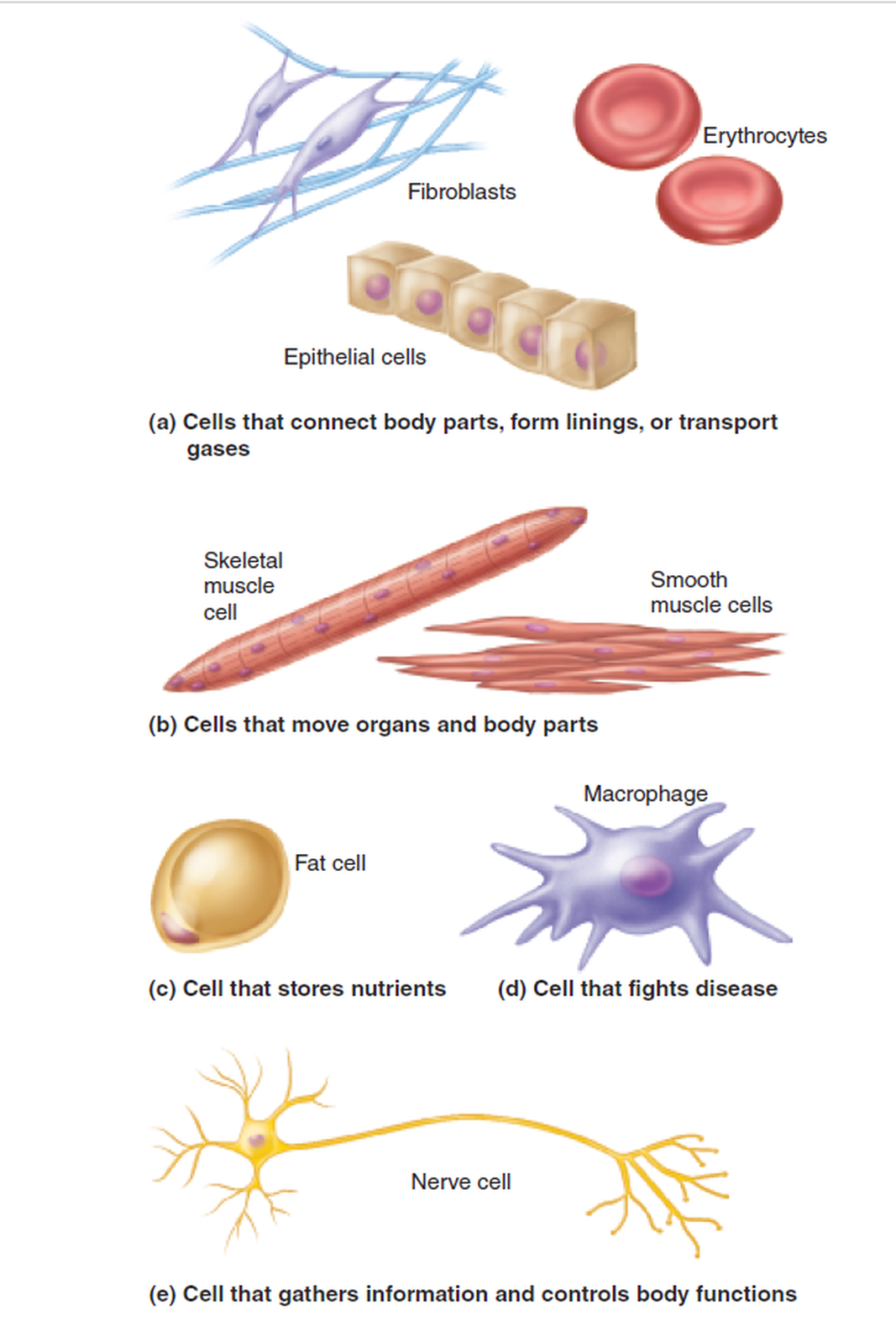
There Are More Than 200 Types of Cells in the Human Body
|
HERE IS A LIST OF SOME OF THE MOST COMMON CELLS
|
|
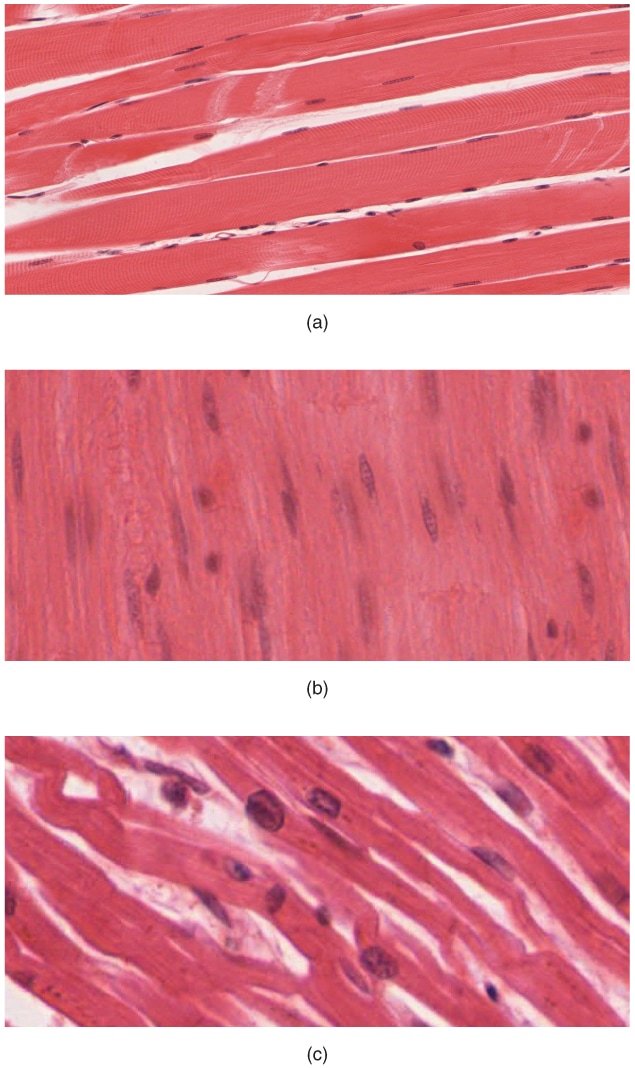
The Tissue Level
|
Tissue level:
There are 4 types of tissues
|
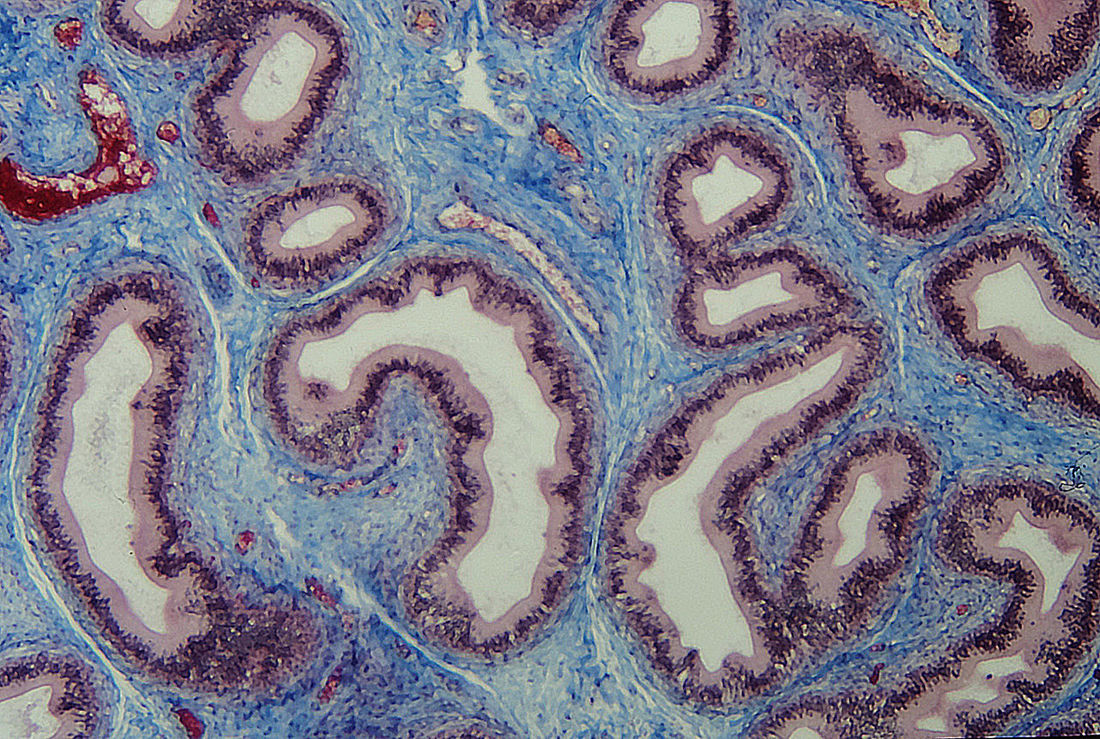
Cells of similar types come together to form tissues. A TISSUE is a group of two or more cells (of similar function or origin) that come together to perform a common function. |
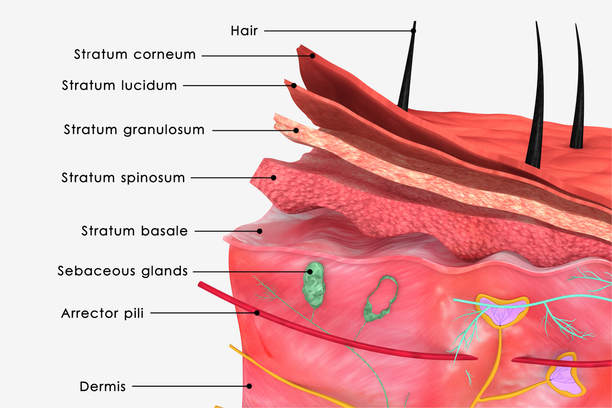
Epithelial cells come together to form epithelial tissue.
The Organ Level
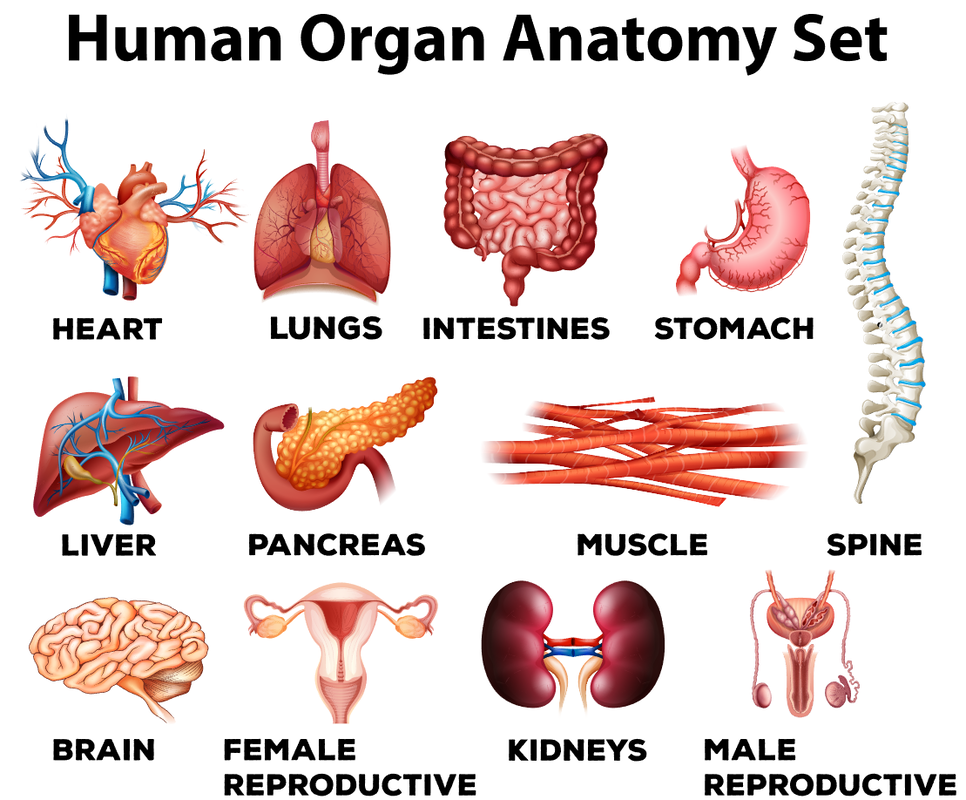
An organ is a discrete structure made up of more than 2 different tissue types that work together as a functional unit for the body. The major organs of the human body are listed and illustrated here.
Organs that are found anywhere in the ventral cavity, can be referred to as visceral organs. The word "visceral" or "viscera" refers specifically to the internal organs that lie in the thoracic or abdominal regions of the body, such as the heart, lungs, liver, stomach or intestines. In a figurative sense, something "visceral" is felt "deep down."
Organs that are found anywhere in the ventral cavity, can be referred to as visceral organs. The word "visceral" or "viscera" refers specifically to the internal organs that lie in the thoracic or abdominal regions of the body, such as the heart, lungs, liver, stomach or intestines. In a figurative sense, something "visceral" is felt "deep down."
The Organ System Level
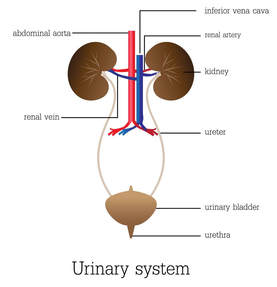
There 1 Organ Systems of the Human Body. An organ system is a group of organs and associated structures that perform a specific function in the body.
|
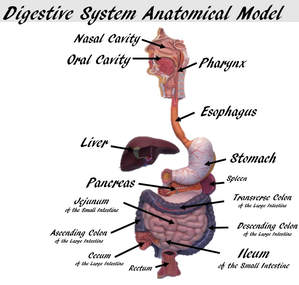
The digestive system includes the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus. There are also accessory digestive organs like the liver and pancreas that assist the digestive system. The function of the digestive system is to break down food, absorb nutrients, and eliminate waste as feces.
|
The immune system is the body's defense against disease. The immune system includes the includes, the thymus and the leukocytes (white blood cells) of the body.
The lymphatic system includes lymph nodes, lymph ducts and lymph vessels, and also plays a role in the body's defenses. Its main job is to make is to make and move lymph, a clear fluid that contains white blood cells, which help the body fight infection. The lymphatic system also removes excess lymph fluid from bodily tissues, and returns it to the blood.
The lymphatic system includes lymph nodes, lymph ducts and lymph vessels, and also plays a role in the body's defenses. Its main job is to make is to make and move lymph, a clear fluid that contains white blood cells, which help the body fight infection. The lymphatic system also removes excess lymph fluid from bodily tissues, and returns it to the blood.
|
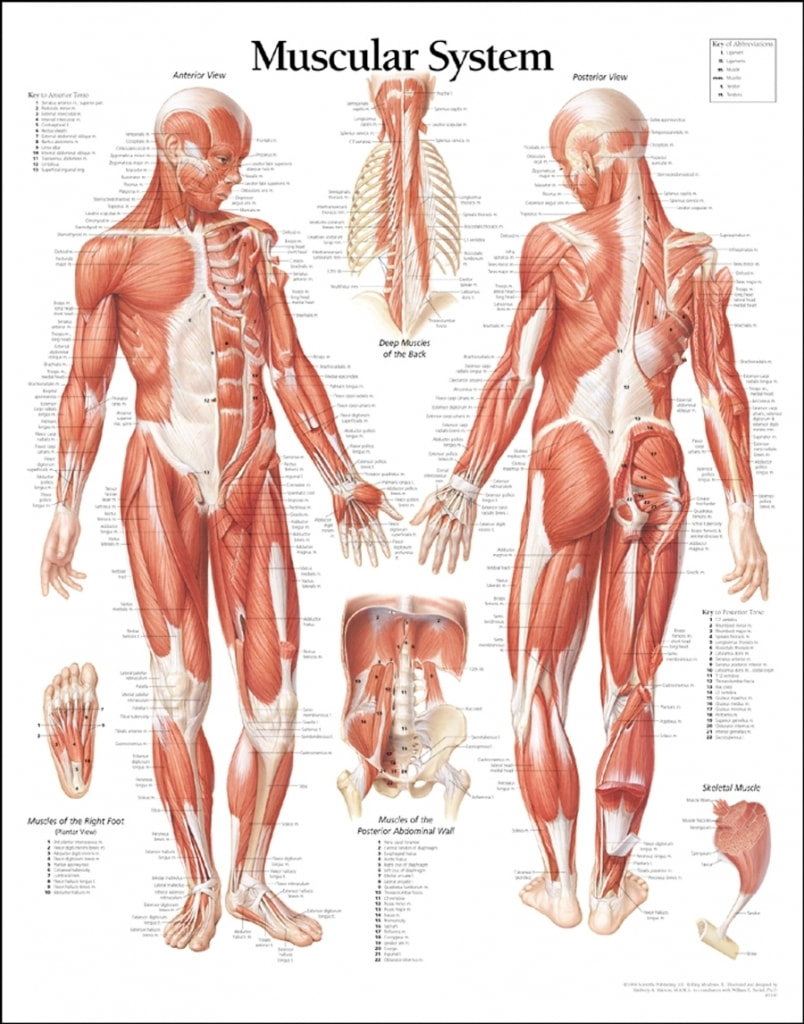
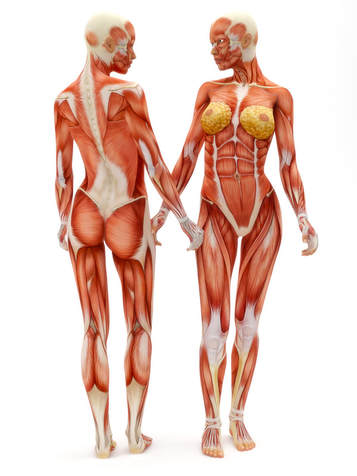
The muscular system includes all of the muscles in the body. This includes the skeletal muscles which allow us to move parts of our body at will, and the smooth muscles which moves substances through the body, and the cardiac muscle which lies exclusively in the heart. Smooth muscle and cardiac muscle are involuntary and are not under conscious control.
|
|
|
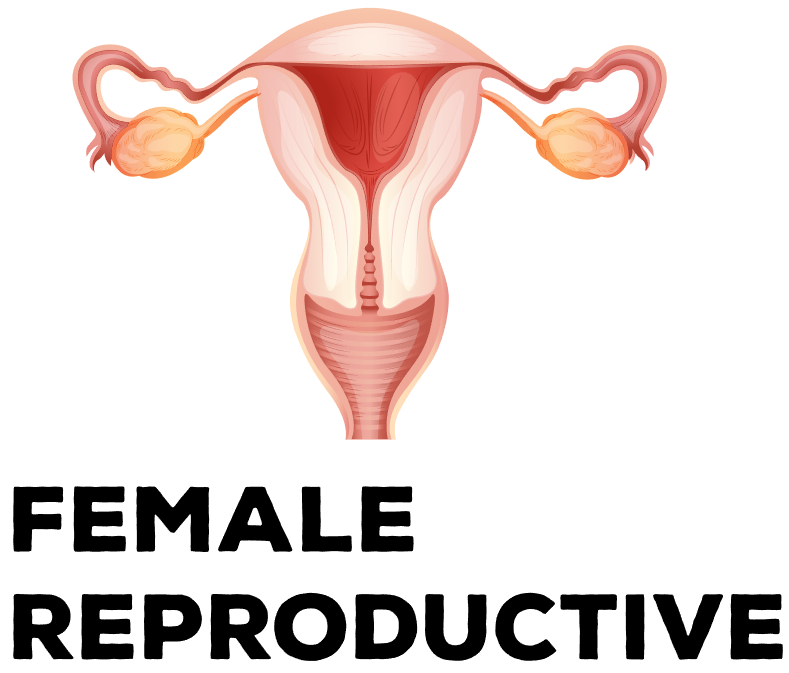
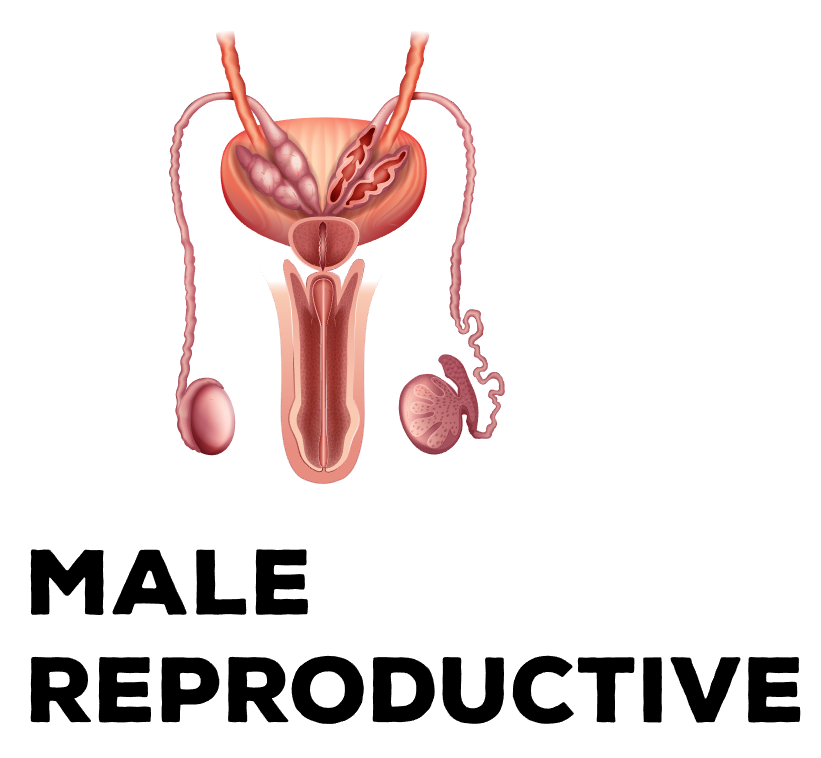
The reproductive system allows humans to reproduce. The male reproductive system includes the penis and the testes, which produce sperm. The female reproductive system consists of the vagina, the uterus and the ovaries, which produce eggs. During conception, a sperm cell fuses with an egg cell, which creates a fertilized egg that implants and grows in the uterus. v
|
The Organism Level
The level of the organism looks at how all of the anatomical structure of body work together to provide all of the necessary function for life.