|
|
|
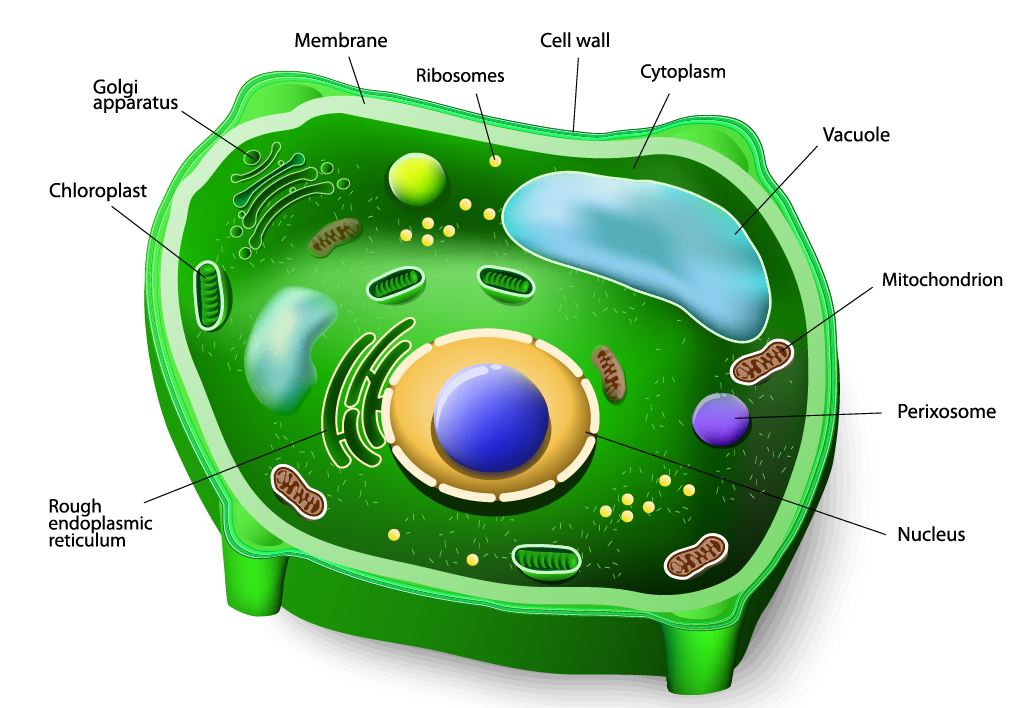
Plants are eukaryotic, multicellular organisms. that have the amazing ability to make their own food through the process of photosynthesis. |
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
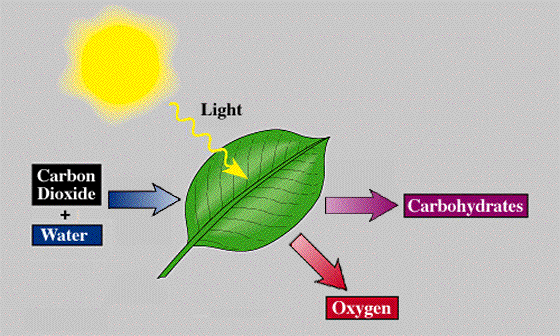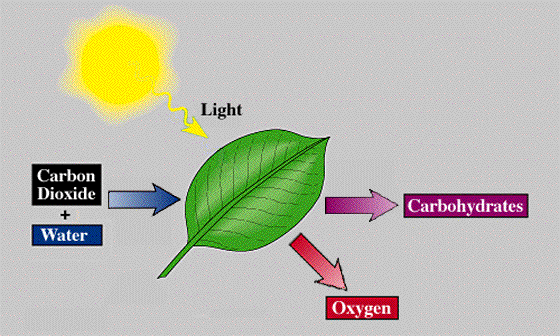
Photosynthesis is the process by which certain organisms are able to use sunlight (photons) to make their own food. These producers use carbon dioxide and water, in combination with light energy (photons), to create glucose and oxygen.
By definition, photosynthesis uses carbon dioxide and water, along with light energy, to form glucose and oxygen.
|
Plants house the bottom (and largest) tier of the food pyramid as producers.
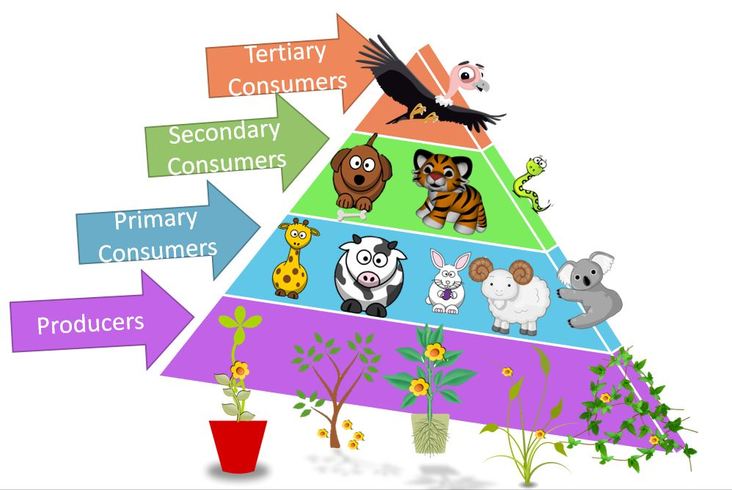 THE FOOD PYRAMID by Scientist Cindy
THE FOOD PYRAMID by Scientist Cindy
Because plants essentially “make their own food” they are also categorized as autotrophs. Autotrophic organisms are able to convert inorganic material into a form of energy that can, in turn, be used for biological functions. In contrast, heterotrophic organisms must consume other organisms in order to maintain their life processes. Because heterotrophs, such as animals, do not have the ability to make biologically-useful energy from light energy, they are required to consume other organisms to survive. In the food web, you will be able to trace any meal consumed by a heterotroph back to its origin, a producer. For example, a quaternary consumer would eat a tertiary consumer that ate a secondary consumer, who ate a primary consumer who ate a plant. No matter what tier of the food web pyramid the consumer is, its food source ultimately depends upon the producers.
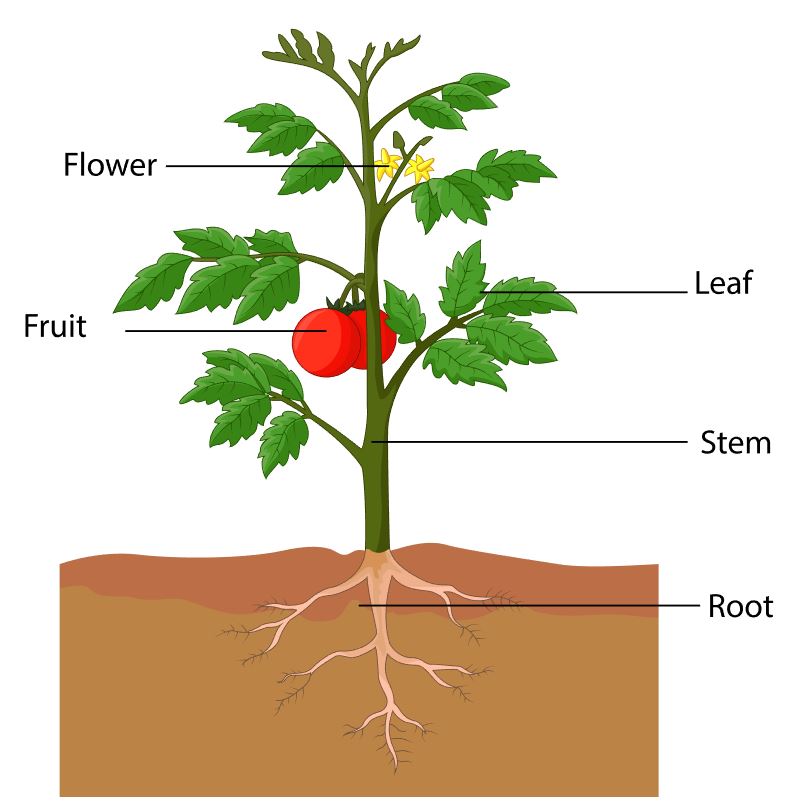
Anatomy of a Plant
Plants are made of three main parts.
|
STEMS
The 2 main functions of the STEMS are as follows:
|
XYLEM AND PHLOEM
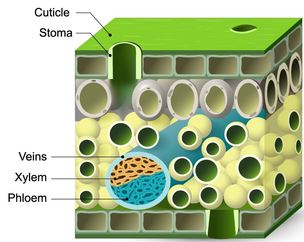
Xylem is a type of transport tissue found in vascular plants that allows for water to be transported from the roots of a plant to its shoots and leaves. An example of xylem tissue is "wood".
Phloem is a type of transport tissue found in vascular plants that allows for sugar (glucose) that is produces in the leaves through photosynthesis to be transported from the leaves of the plant to its roots and shoots.
ANATOMY OF A FLOWER
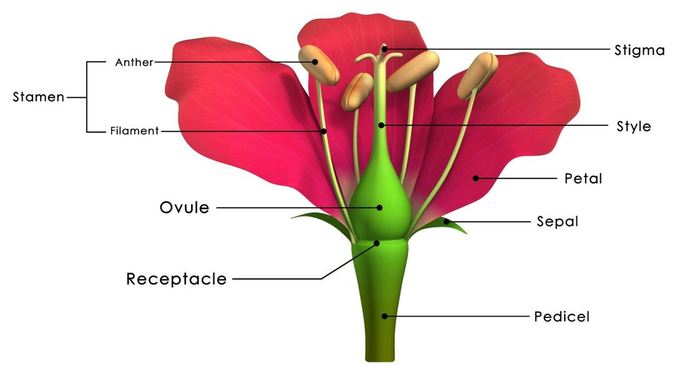
The flower is the reproductive structure of the plant. Flowers allow for the union of sperm with eggs. Flowers may reproduce using their own eggs and sperm, or they can be cross-bred by receiving sperm (pollen) from another plant. Many flowers have evolved to attractive to different insects and animals so that they essential "carry the seed" of reproduction to areas that the flower can't reach.
The 4 main parts of the flower are the 1) stamen, 2) carpel, 3) ovary, and 4) petals.
The 4 main parts of the flower are the 1) stamen, 2) carpel, 3) ovary, and 4) petals.
THE STAMEN
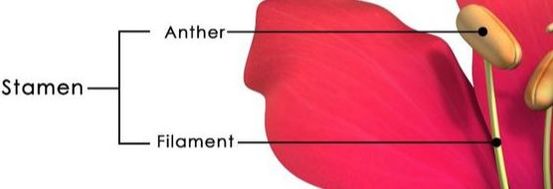
The main function of the stamen is to produce the pollen grains, which house male gametes (sperm), or sex cells, necessary for reproduction.
The anther is located within the stamen where these gametes are created. Pollen grains vary in size, shape, and surface structures based on the type of flower that produces them.
The anther is located within the stamen where these gametes are created. Pollen grains vary in size, shape, and surface structures based on the type of flower that produces them.
THE CARPAL AND THE OVARY

The carpal is the center part of the flower. It consists of the ovary (ovule), the stigma and the style. The carpel, the female reproductive structure that includes the ovary. The function of the carpel is to house the ovary which is the female reproductive portion of the flower. Inside the ovary is an ovule that, when fertilized, will develop into a seed. A seed contains an embryo (baby plant), the endosperm (food for the embryo), and a seed coat.
THE PETALS

Petals function to protect some parts of the flower and attract specific pollinators .
THE SEEDS
The function of a flower is to produce the reproductive cells of the plant (eggs and sperm (pollen)). A fertilized egg become a SEED, which is a dormant young plant. of the next generation.
THE FRUIT
The seeds of flowering plants are surrounded by a tissue called the FRUIT, which may be fleshy or dry. Animals eat the fruit and disperse the seeds.
THE SEEDS
The function of a flower is to produce the reproductive cells of the plant (eggs and sperm (pollen)). A fertilized egg become a SEED, which is a dormant young plant. of the next generation.
THE FRUIT
The seeds of flowering plants are surrounded by a tissue called the FRUIT, which may be fleshy or dry. Animals eat the fruit and disperse the seeds.
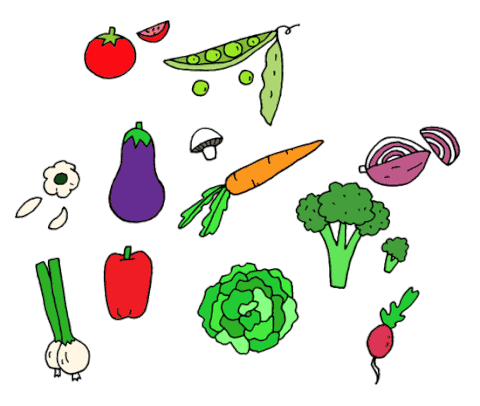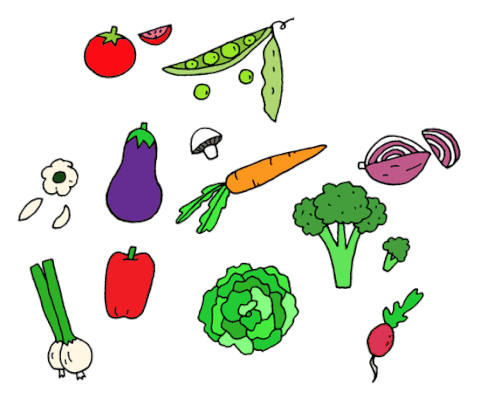
VEGETABLES
The term vegetable pertains specifically to plant parts that are edible such as leaves, roots, stems, flowers, etc. When we eat asparagus, we are eating the stem of the plant. When we eat spinach or lettuce, we are eating the plant's leaves. We eat the fruit of squash, cucumber and tomato plants. When we eat corn or peas we are eating seeds, and when we eat radish or carrot, we are eating roots.
|
KINGDOM ANIMALIA
Animal are an extremely diverse group of eukarytic organisms. They are heterotrophic, which means they must consume other organisms in order to stay alive.
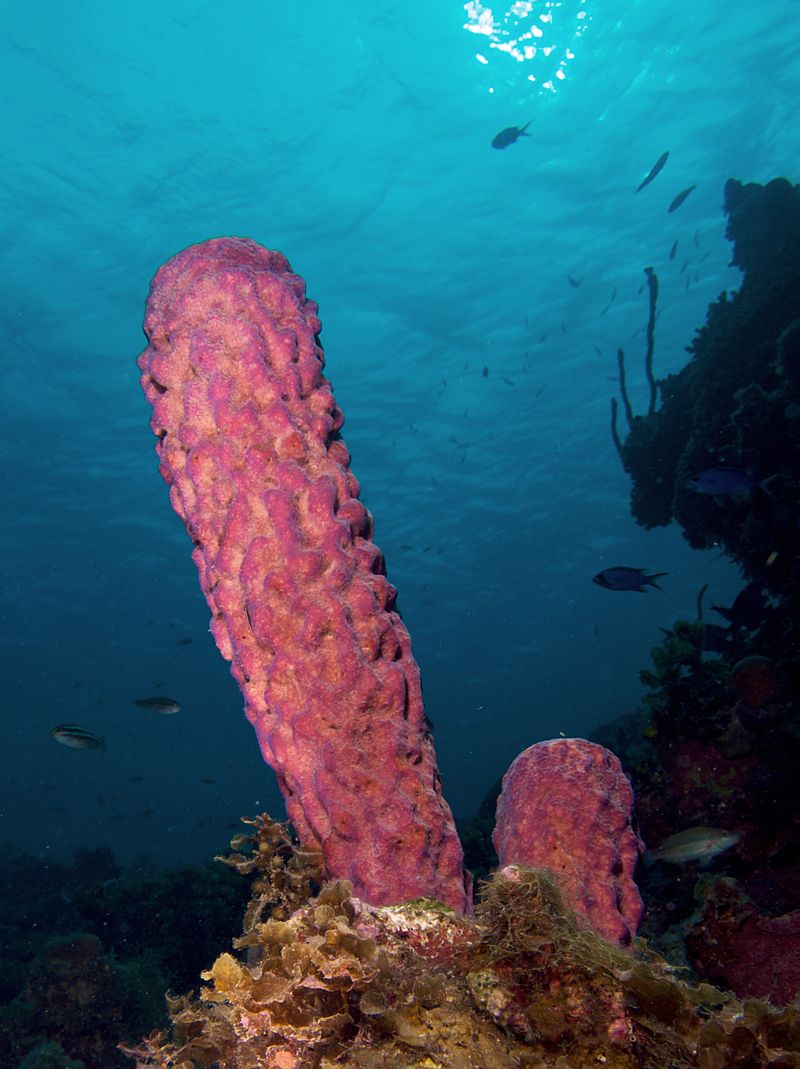
SPONGE
|
SPONGE - By Nhobgood (talk) Nick Hobgood - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=11448769
|
Sponges are among the first animals to evolve. They are extremely simplistic. The name "sponge" comes from the Latin word "pore bearer". Sponges have the unique ability to absorb large amounts of liquid through their pores. Sponges are used commercially as cleaning tools to soak up unwanted messes!
Sponges do not have digestive or circulatory systems. Instead, they rely on maintaining a constant water flow through their bodies to obtain food and oxygen and to remove wastes. For this reason, sponges are called "filter-feeders". |
JELLYFISH
Jellyfish are very simple aquatic animals that have soft, gelatinous bodies with thin, trailing tentacles that contain stinging cells that can immobilize and capture prey.By Nhobgood (talk) Nick Hobgood - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=11448769
|
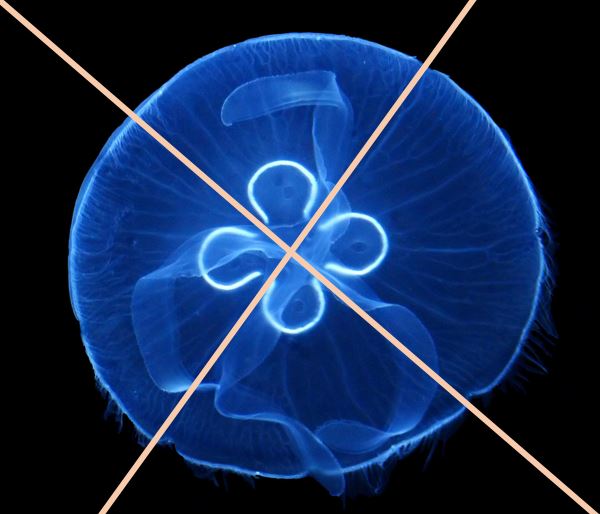
Jellyfish have radial symmetry. This means their "body plan" is organized in such a way that if you were to slice it like a pizza, each of the slices would be nearly identical. |
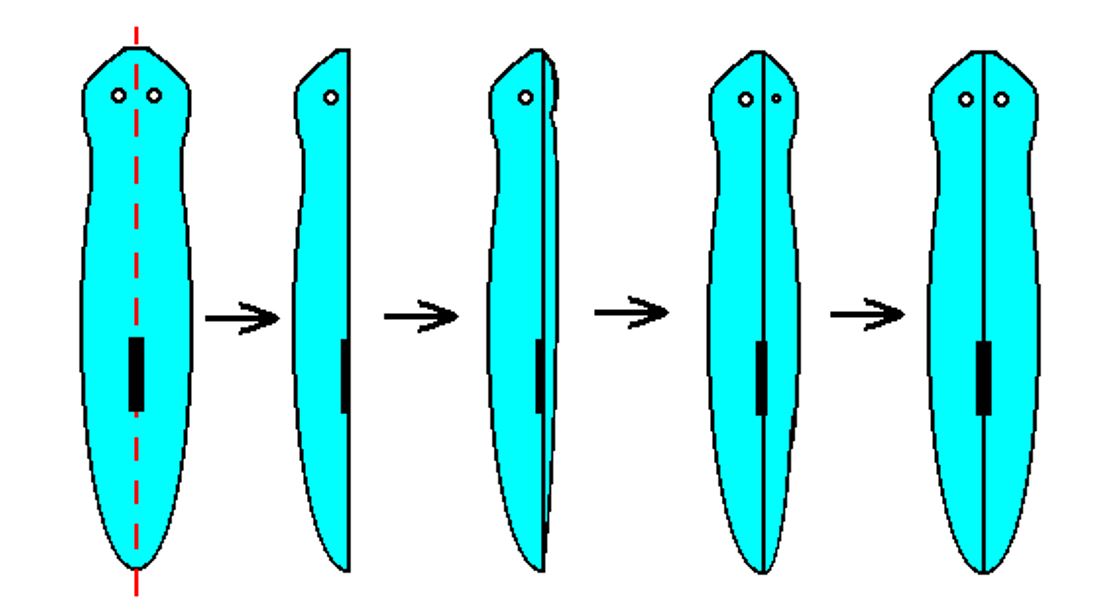
As organisms continued to evolve over time, the radial symmetry of simple organisms like the sea anemone, the sea star and the jellyfish, evolved to favor the more complex body plan of bilateral symmetry.
FLATWORMS
Flatworms are the most primitive animals with bilateral symmetry.
The tapeworm, is a type of flatworm that has very peculiar eating habits.
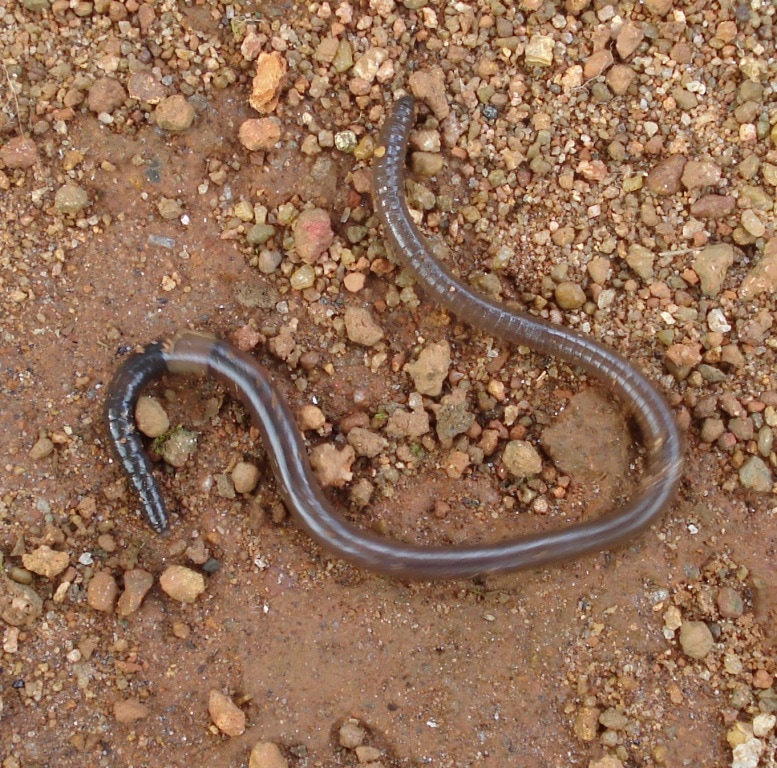
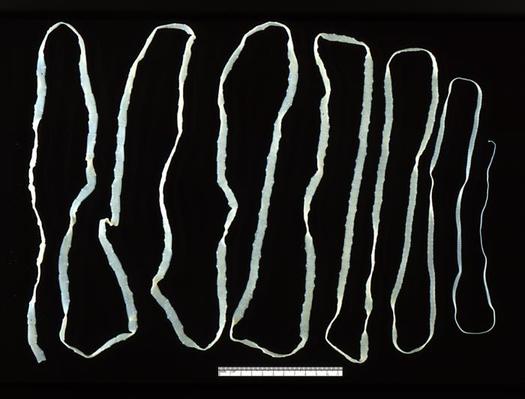
ROUNDWORMS (Nematodes)
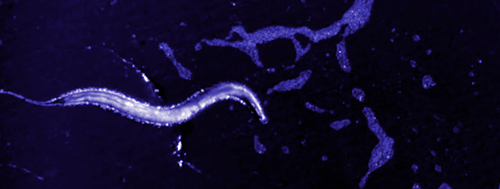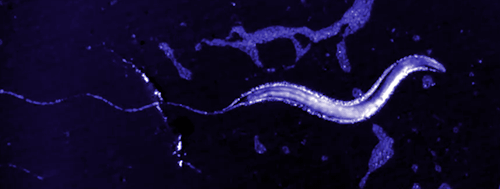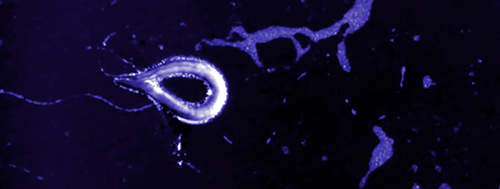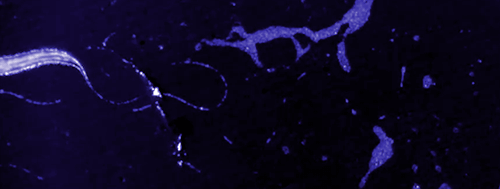 A Roundworm
A Roundworm
Roundworms (also known as nematodes) include over 25,000 known species belonging to the phylum Nematoda. Roundworms differ from flatworms (like the tapeworm) in that they do have a digestive system. Their digestive system consists of a tube with openings at both ends.
Roundworms are extremely diverse and resilient; inhabiting just about every climate and environment on earth. Roundworms are found in all different habitats including salt water, fresh water, soil, mountain tops, sea floors, tropic rain forests and even polar ice caps! If this impresses you, just wait! Roundworms have been discovered buried beneath more than 2 miles of dirt below the surface of the Earth! In addition to being diverse, they are strong in numbers. Approximately 90% of all animal species on the ocean floor are roundworms. And, it is estimated that roundworm may constitute upwards of 80% of all animals on Earth!
Roundworms are extremely diverse and resilient; inhabiting just about every climate and environment on earth. Roundworms are found in all different habitats including salt water, fresh water, soil, mountain tops, sea floors, tropic rain forests and even polar ice caps! If this impresses you, just wait! Roundworms have been discovered buried beneath more than 2 miles of dirt below the surface of the Earth! In addition to being diverse, they are strong in numbers. Approximately 90% of all animal species on the ocean floor are roundworms. And, it is estimated that roundworm may constitute upwards of 80% of all animals on Earth!
ILLNESSES CAUSED BY ROUNDWORMS
Over half of the known species of roundworms are considered parasitic, because they benefit from invading a host, while the host suffers illness and disease! The best way to prevent infection is to practice good hygiene be washing your hands often and by making sure that any meat you eat is cooked thoroughly, especially pork and poultry.
Ascariasis is the most common roundworm infection. About 10 percent of the developing world is infected with intestinal worms, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). Ascariasis is most common in places without modern sanitation. It’s transmitted through unsafe food and water. The infection usually causes no symptoms, but heavier infestations can lead to problems in the lungs or intestines. |
Trichinosis is a disease caused by a parasitic roundworm called Trichinella spiralis. The Trichinella spiralis is sometimes referred to as the "pork worm", because it likes to live in pigs! Humans typically become infected when eating undercooked pork products. Trichinosis also can affect other mammals that may ingest an infected animal.
EARTHWORMS
|
An earthworm is a tube-shaped, segmented worm belonging to the phylum Annelida. Earthworms are commonly found living in soil, feeding on live and dead organic matter. An earthworm's digestive system is in the form of a tube that is open at both ends (similar to the roundworm). Earthworms are hermaphrodites. That means that each individual carries both male and female sex organs.
Earthworms assist the environment by creating healthier dirt and soil to grow crops. This is due to the fact that the holes created by the earthworms allow for more air and water to reach the down into the soil. The worms also breakdown organic materials like leaves and grasses into a form that is more useful for other organisms.
By Aruna at ml.wikipedia - Transferred from ml.wikipedia by User:Sreejithk2000 using CommonsHelper., CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=12602652
|
LEECHES
|
|
Leeches are still used today in some medical situations and alternative medicine therapies. Leeches are segmented worms that belong to the phylum Annelida. Leeches eat by attaching themselves to a host and sucking their blood. The leech secretes an anticoagulant agent that prevents the blood from clotting during the leech's feast. Leeches are used frequently in the reattachment of fingers and toes to help the flow of blood through the tissues that were reattached. Leeches have also been used to drain blood clots and treat other conditions, like psoriasis.
|
CEPHALIZATION
Along with the evolutionary advancement of the bilaterally symmetric body plan, the evolutionary trend of cephalization had begun.
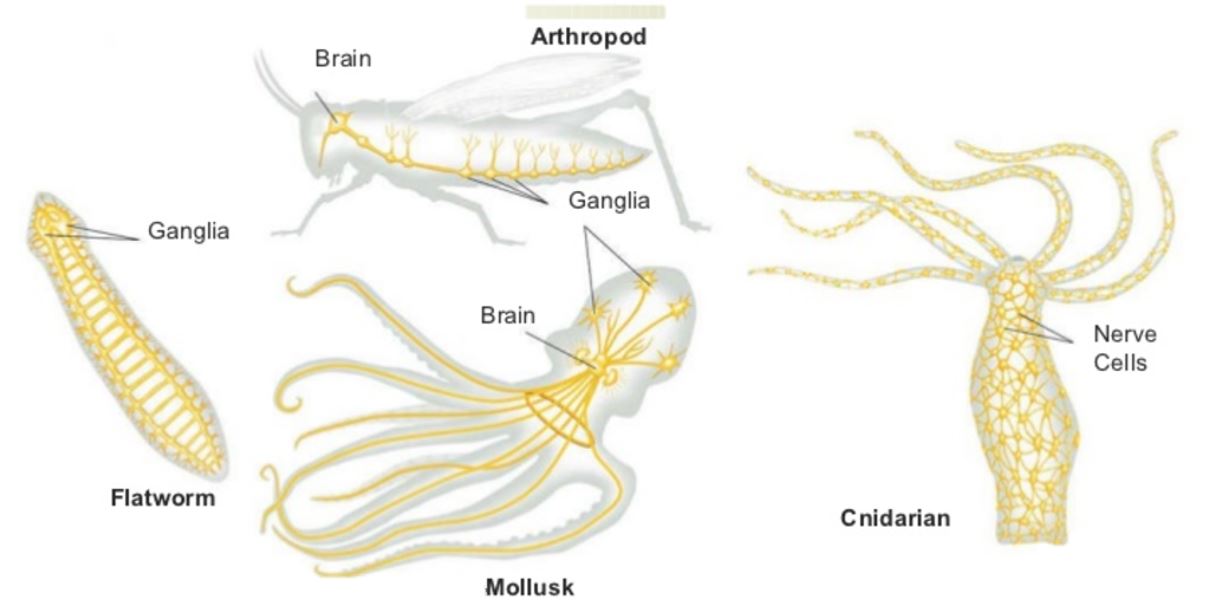
According to wikipedia, "Cephalization is considered an evolutionary trend, whereby nervous tissue, over many generations, becomes concentrated toward one end of an organism."
- en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cephalization
Cephalization the is the gradual process of evolution that led to the development of the head and brain. In evolution, organisms evolve from being simple to being more complex. Organisms that are more complex, are considered to be more evolved and have developed (or evolved) later here on Earth.
- en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cephalization
Cephalization the is the gradual process of evolution that led to the development of the head and brain. In evolution, organisms evolve from being simple to being more complex. Organisms that are more complex, are considered to be more evolved and have developed (or evolved) later here on Earth.
MOLLUSCS
|
The molluscs are organisms belonging to the phylum Mollusca. They are largely composed of marine species and include cuttlefish, octopuses and squids. In fact, an estimated 23% of all marine organisms are thought to be mollusks! However, some mollusk species can be found on land, such as the snail.
Molluscs include many species that are wonderful food sources for us! These include clams, squid (calamari), scallops, oysters, abalone, mussels and snails (escargot).
|
|
INSECTS
Insects rule the world, making up more than half of all living organisms on this planet.
Insects are important for food production in agriculture. The insects function as decomposers in the ecosystem. They break down large organic materials (like decaying plants and animals) into smaller molecules that become nutrients for the soil. The nutrient-rich soil allows plants to grow.
Burrowing insects, such as ants and beetles, dig tunnels into the ground which allows water to reach the deeper layers of soil. This helps the soil maintain the moisture it needs to cultivate plant growth.
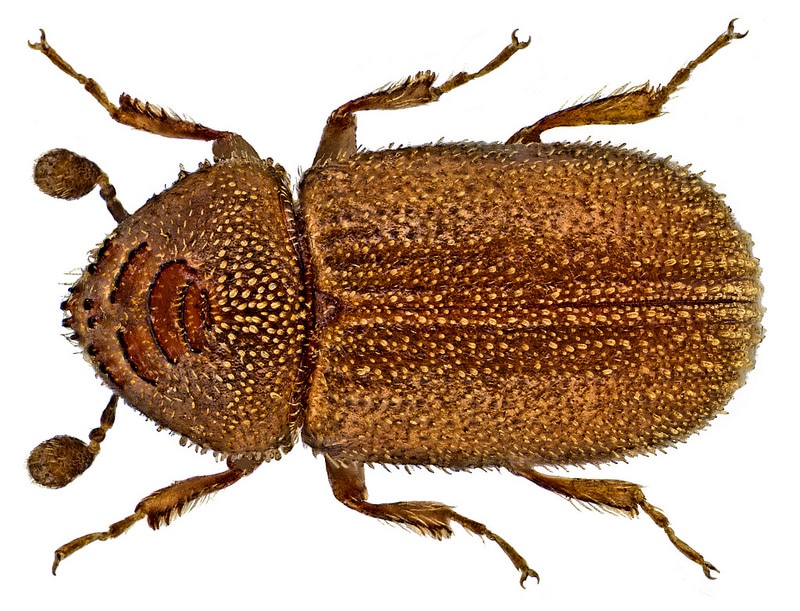
ARTHROPODS
Arthropds have jointed legs, an exoskeleton and a segmented body.
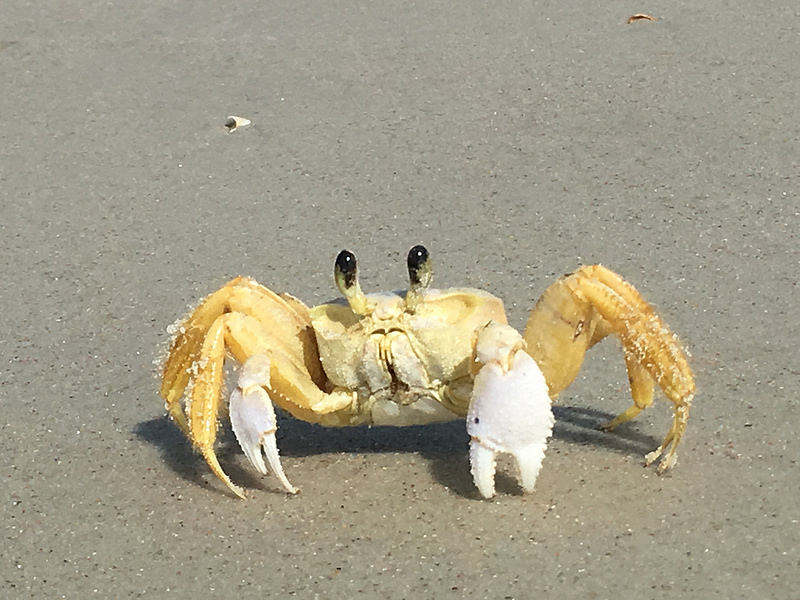
Crustaceans are arthropods. Crustaceans include things we like to eat like shrimp lobster and crab!
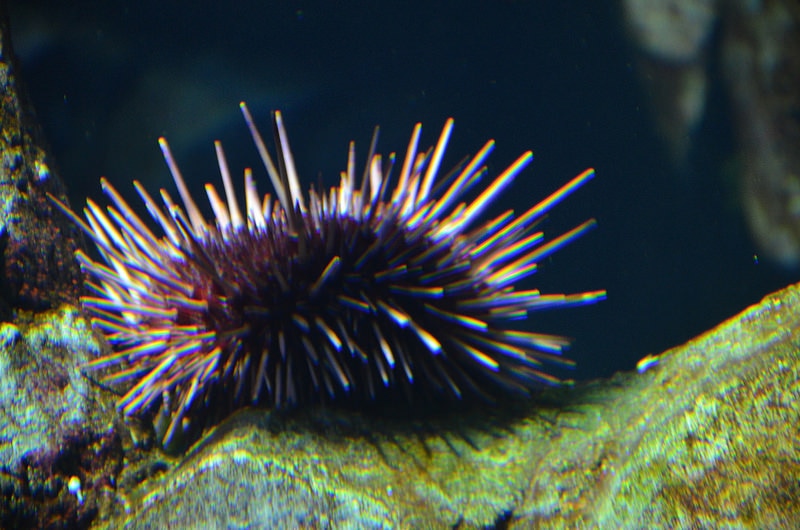
Sea Urchins
Sea urchins are spiky and small organisms of the Echinoderm phylum. An interesting story about the sea urchin is that they were seen as pests by fishermen and were routinely destroyed or discarded as "unwanted". Nowadays, these sea urchins are harvested for their roe which is considered a rare delicacy and is believed to enhance sex drive as an aphrodisiac. If you are wondering what the roe of the sea urchin is, it is the gonads of the sea urchin itself (not the eggs like in cavier). 100,000 tons of sea urchin roe, which is sold under the name "uni", are gobbled up by people in places like Japan and France. In Japan, uni is a popular and coveted gift during New Year celebrations. |
Chordates
Animals in the phylum Chordata share four key features: 1) a notochord, 2) a dorsal hollow nerve cord, 3) pharyngeal slits, and a 4) post-anal tail.
Fish have gills which allow them to breath under water. A gill is a respiratory organ found in fish which functions to extract dissolved oxygen from the water passing over the gill and to excrete unwanted carbon dioxide.

Amphibians
|
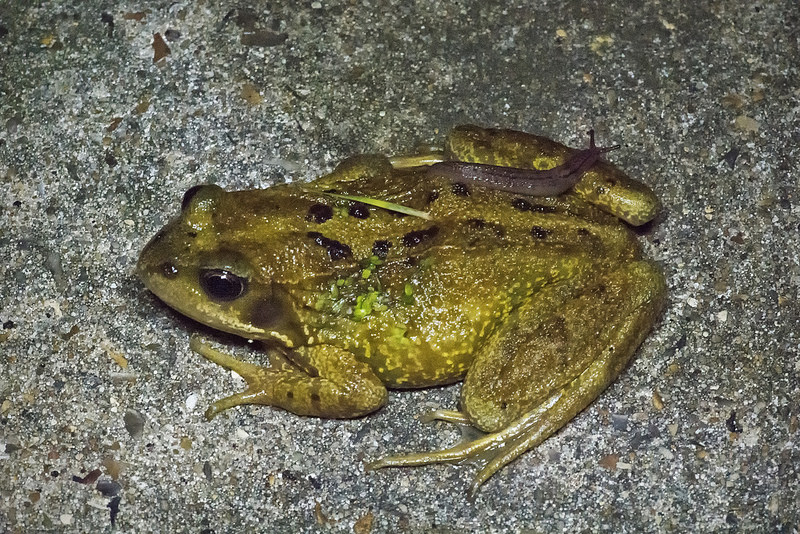
Amphibians live most of their lives in and around fresh water. Amphibians begin life as a larvae that have gills and are restricted to the water. As the amphibian develops, it will undergo a formidable physical change (called metamorphosis) in which the gills develop into lungs capable of breathing air. This metamorphosis allows the adult amphibian to leave the water and travel on land to search for food and mates. Amphibians also breath through their skin. They use their skin as a secondary respiratory surface. Some species of small frogs and salamanders don't have have lungs at all and only use their skin to breath. and some small species of salamanders and frogs lack lungs and rely entirely on their skin.
|
Reptiles

Reptiles include animals such as turtles, crocodiles, snakes, and lizards. Reptiles are closely related to birds. The earliest known reptiles evolved 312 million years ago. Reptiles are better suited to live on dry land. Reptiles have several adaptations which allows them to live on dry land.
ADAPTATION 1 - They do not need to lay their eggs in fresh water, like amphibians do. Laying eggs that can survive on land is a major adaptation allowing reptiles to live away from aquatic environments.
ADAPTATION 2 - Reptiles developed thick, scaly skin that helps conserve moisture inside their bodies. This waterproof skin holds water inside of the reptile so it can live on dry land.
ADAPTATION 3 - Reptiles do not need to breath through their skin. Living on land means reptiles can't rely on absorbing oxygen through their skin like amphibians. They rely on their lungs solely for respiration. Lungs allow reptiles to live in dryer climates instead of being tied to an aquatic environments.
ADAPTATION 1 - They do not need to lay their eggs in fresh water, like amphibians do. Laying eggs that can survive on land is a major adaptation allowing reptiles to live away from aquatic environments.
ADAPTATION 2 - Reptiles developed thick, scaly skin that helps conserve moisture inside their bodies. This waterproof skin holds water inside of the reptile so it can live on dry land.
ADAPTATION 3 - Reptiles do not need to breath through their skin. Living on land means reptiles can't rely on absorbing oxygen through their skin like amphibians. They rely on their lungs solely for respiration. Lungs allow reptiles to live in dryer climates instead of being tied to an aquatic environments.
BIRDS
The next evolutionary leap was thermoregulation. Birds evolved from reptiles and are able to regulate their body temperature. This was a great advantage over the reptiles, because this ability allowed birds to inhabit areas with a wide range of temperatures.
|
Birds maintain their body temperature by increasing their Respiration Rate, Exposing areas of bare skin (like legs) and dispelling excess heat with their bills. When the temperature gets colder, birds alter their blood flow away from their colder, more exposed legs, which keeps more heat concentrated at their body.
|
MAMMALS
Humans are mammals, too. Humans, like all mammals have the following characteristics. 1) All mammals have fur or hair growing out of their skin. 2) All female mammals have mammary glands which produce milk for their young. 3) All mammals have a neocortex (region of the brain). 4) All mammals have sweat glands.