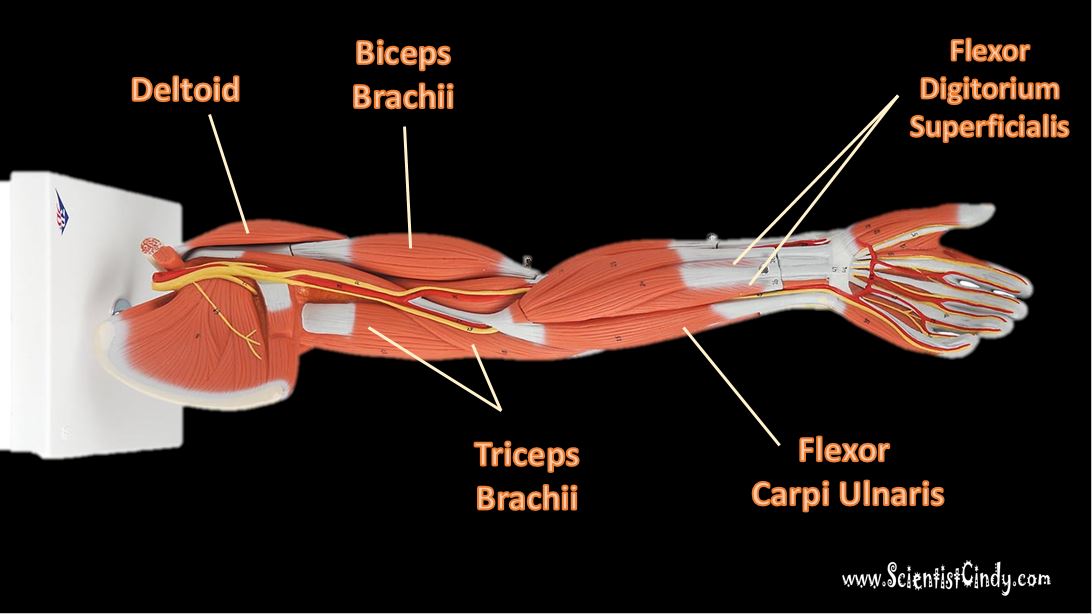
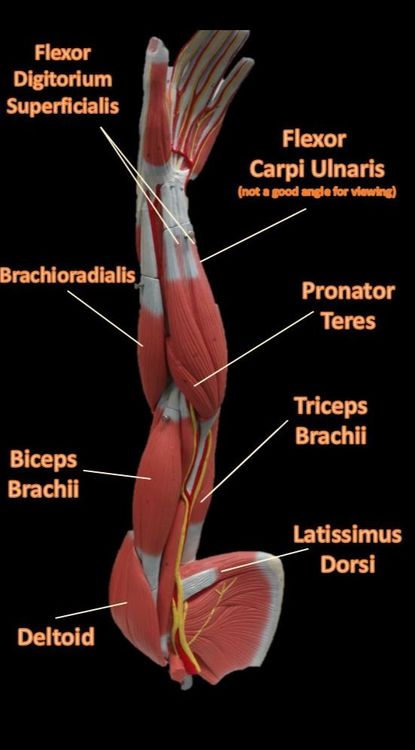
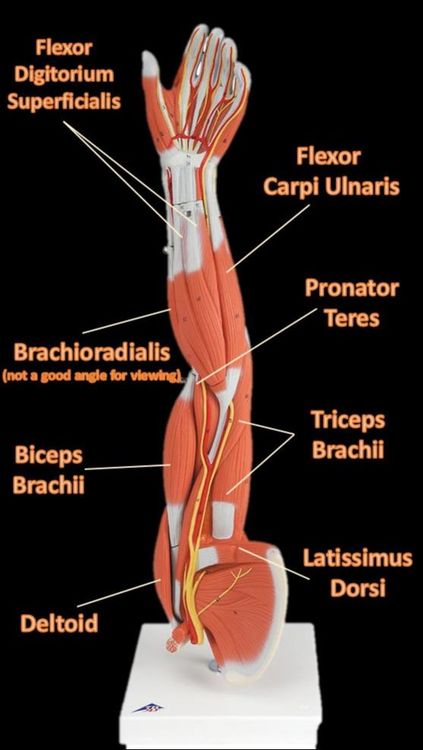
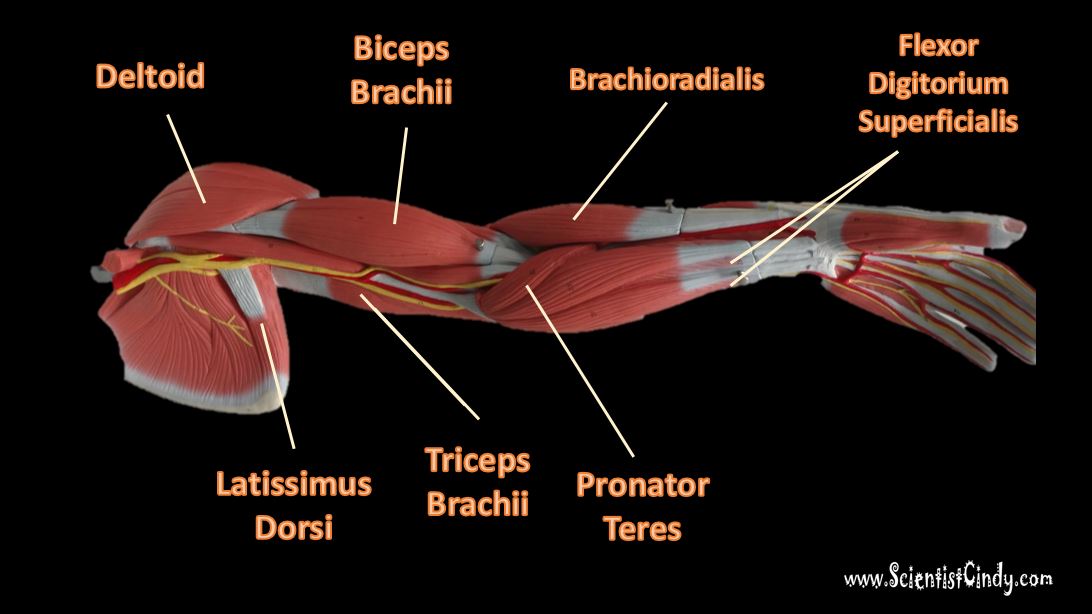
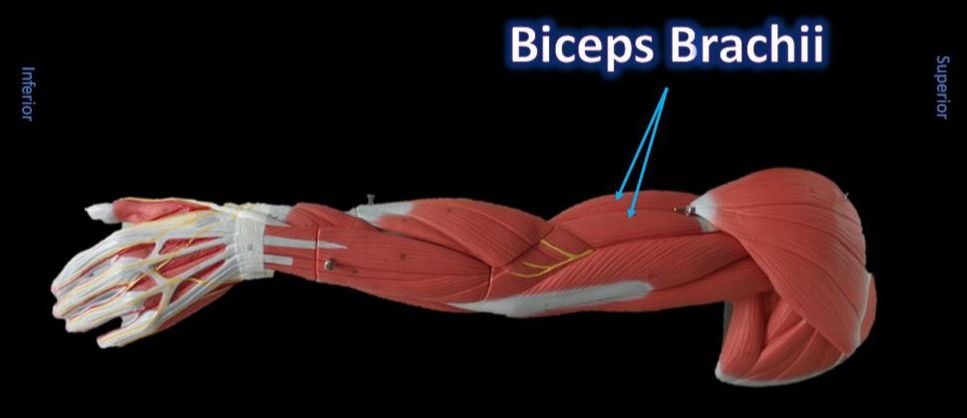
The Muscles of the Limbs
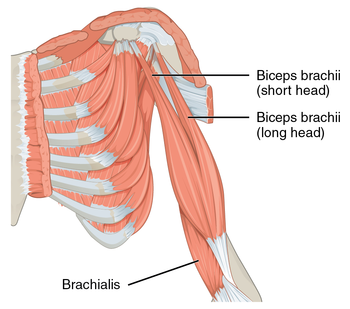
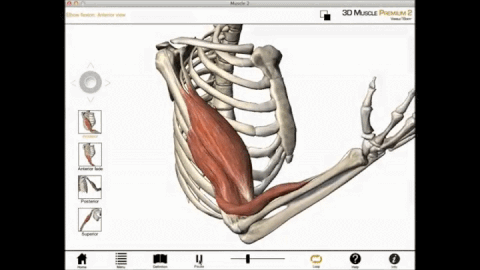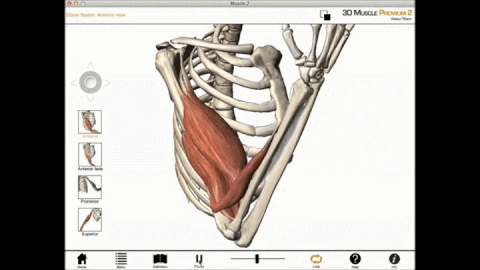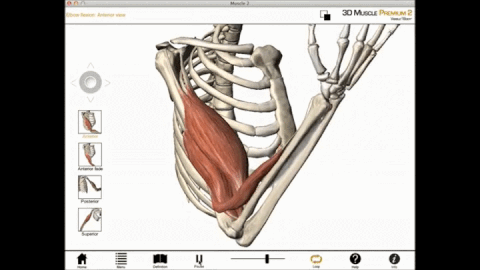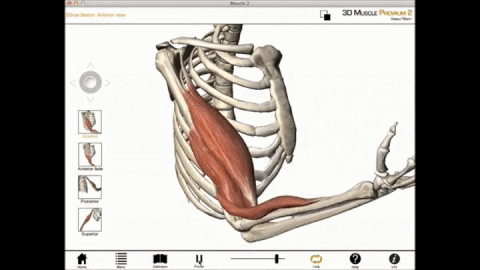
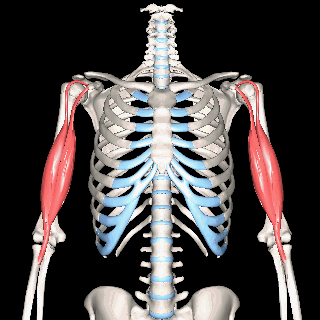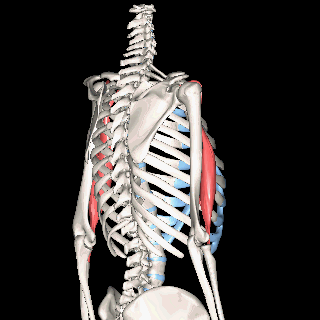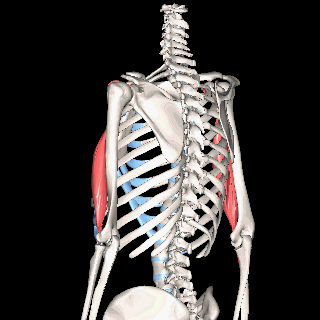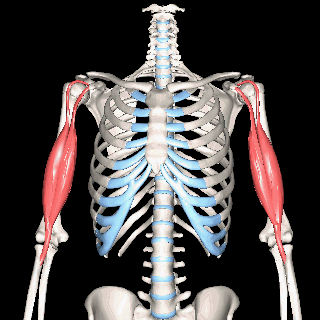
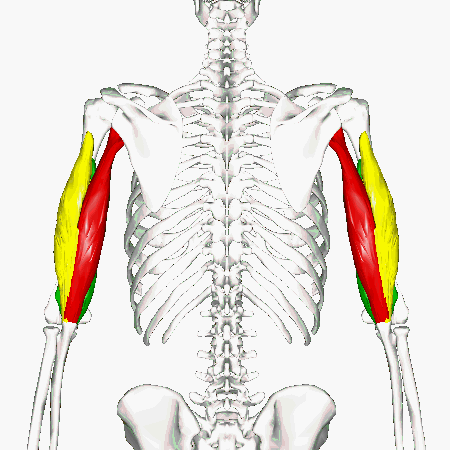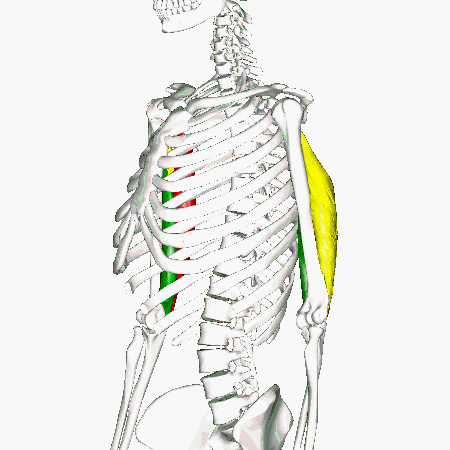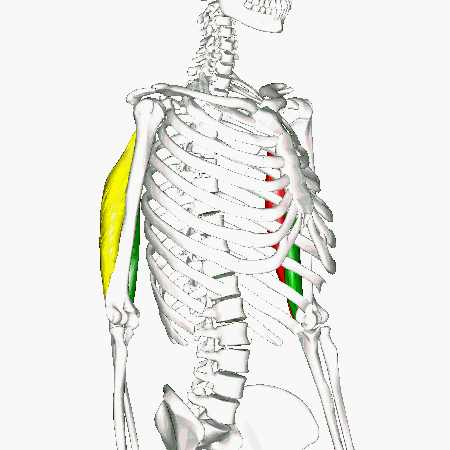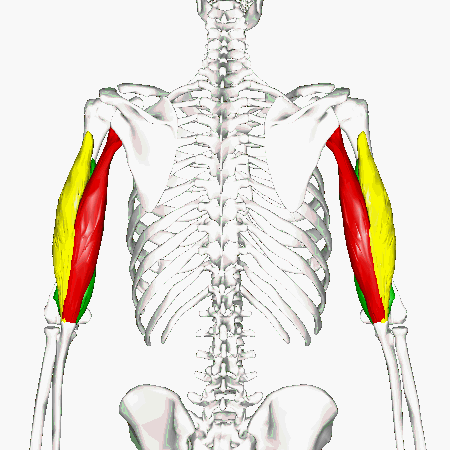
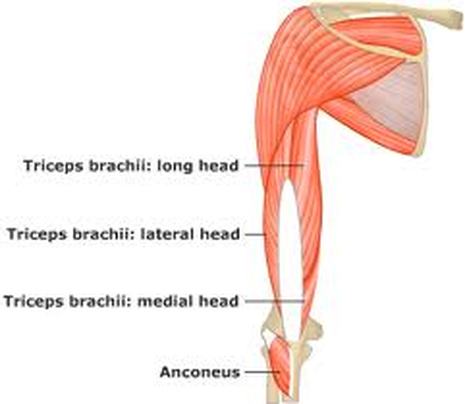
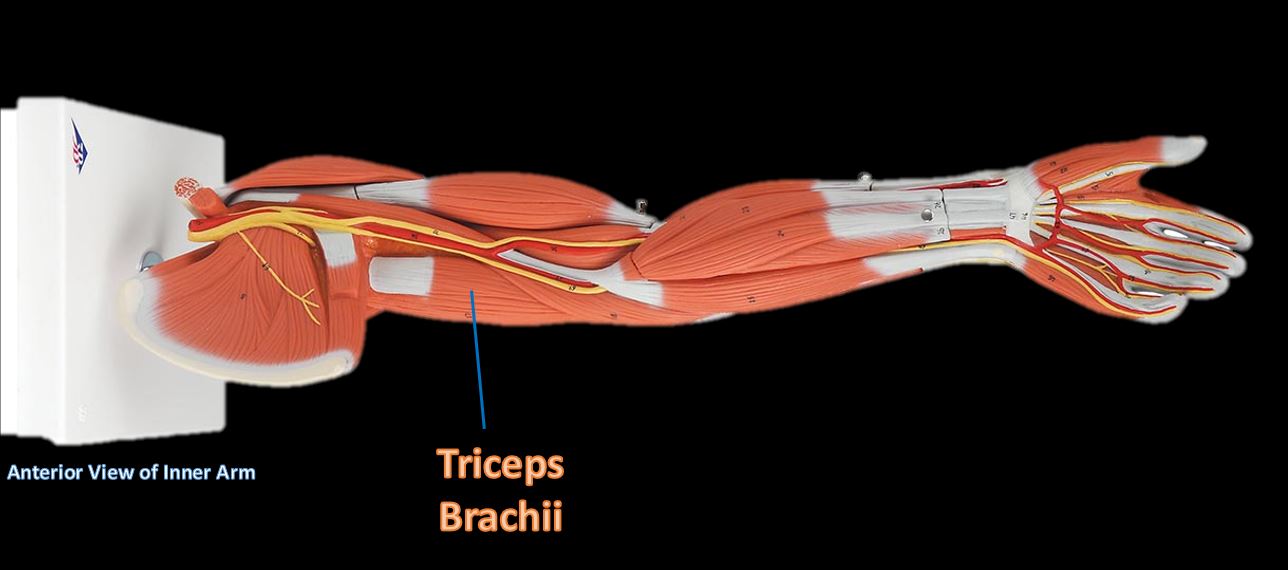
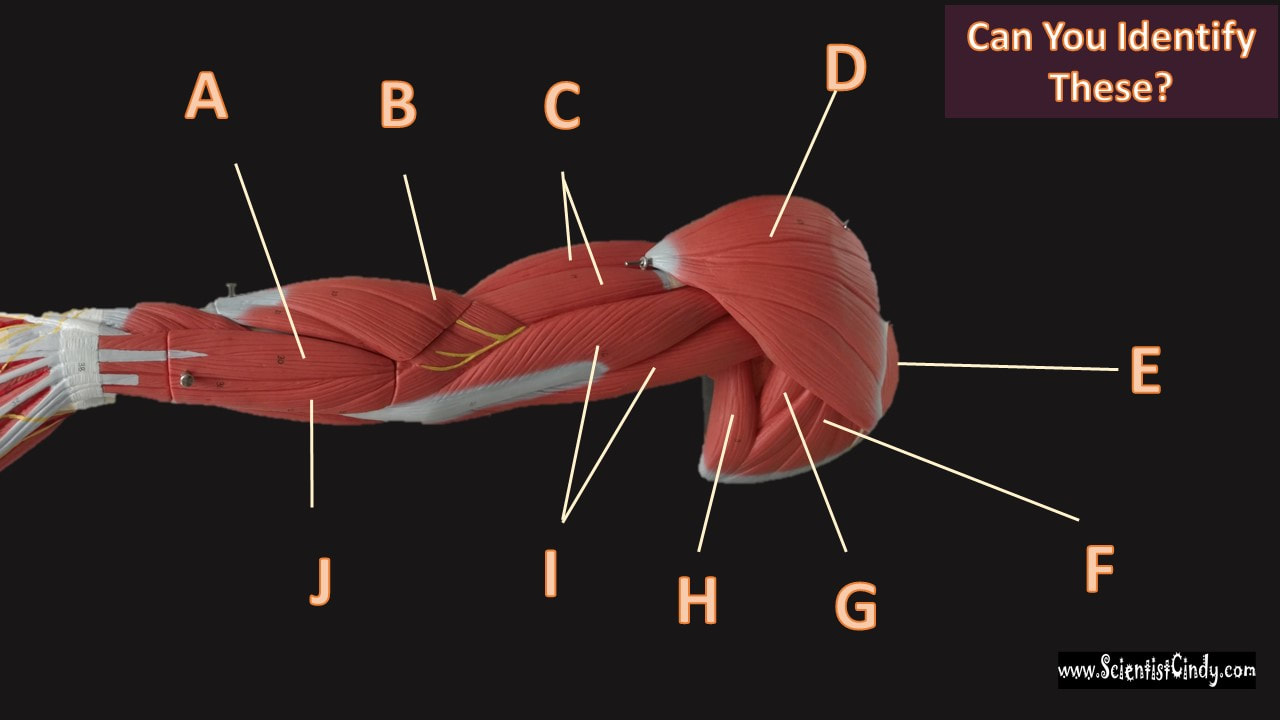
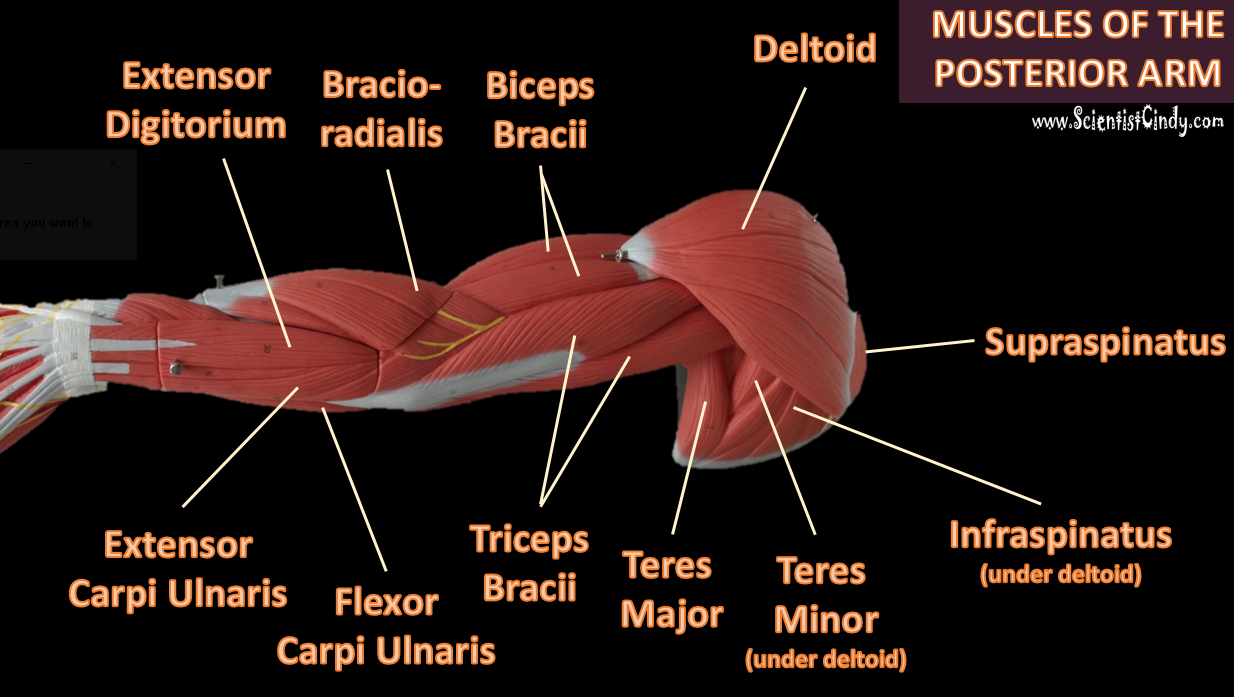
The muscles of the brachial region span the elbow joint. The muscle of the brachial region have their origin in the brachial region (upper arm area) and attach to the antebrachial region (lower arm area) on the forearm bones (radius and ulna).
The POSTERIOR brachial muscles function to EXTEND the elbow.
THE ANTERIOR brachial muscles function to FLEX the elbow.
|
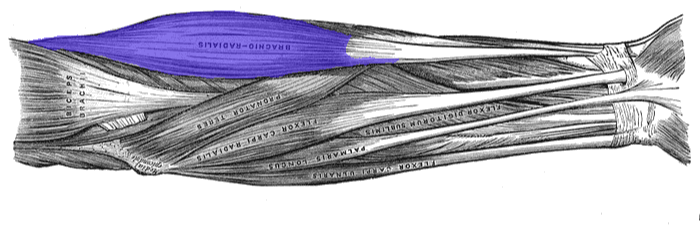
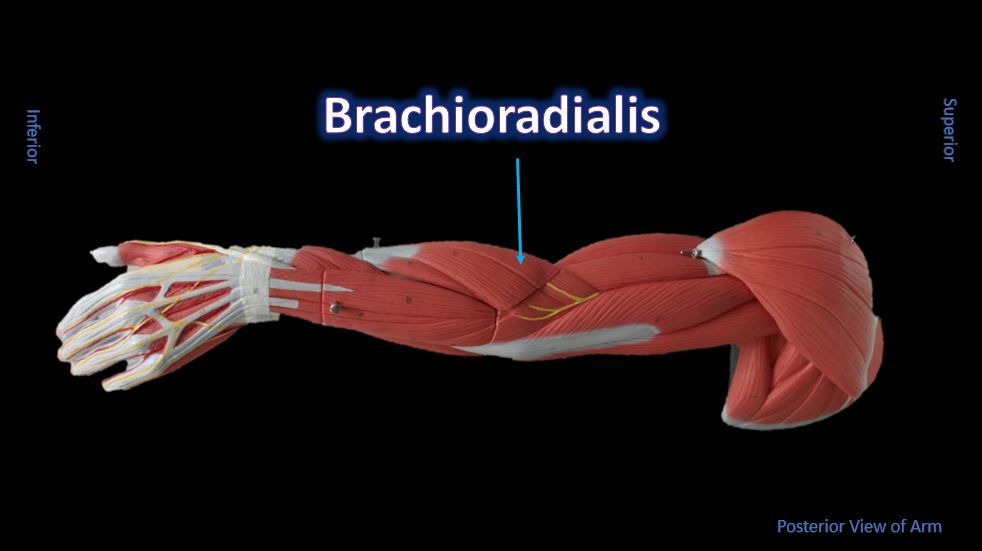
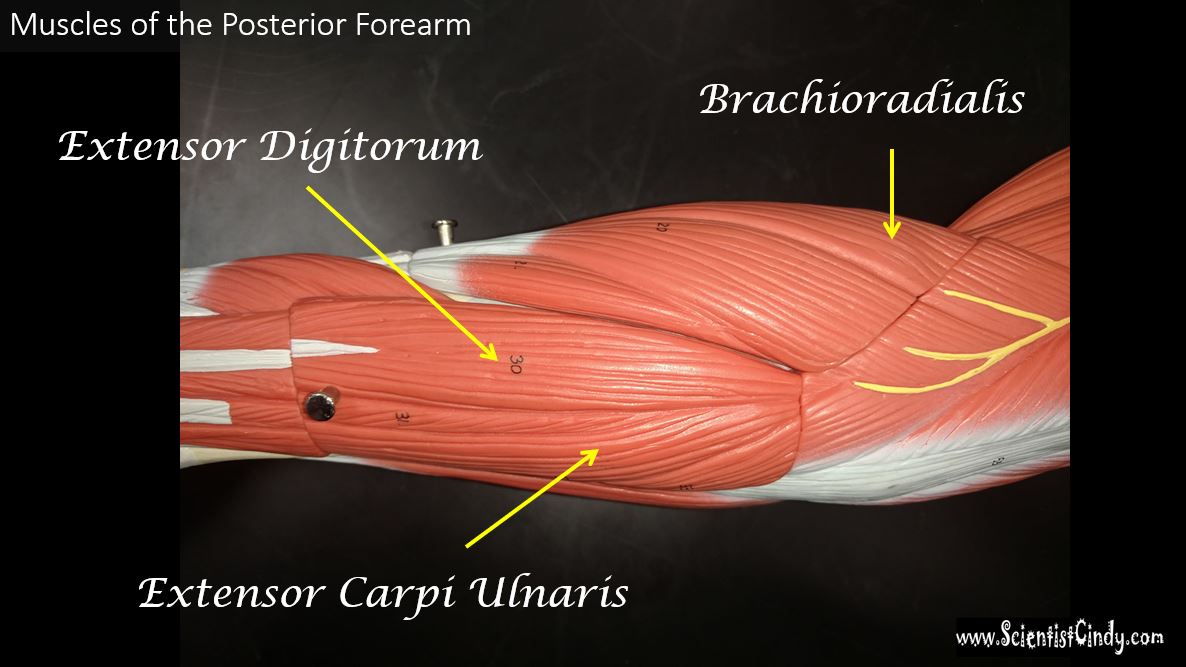
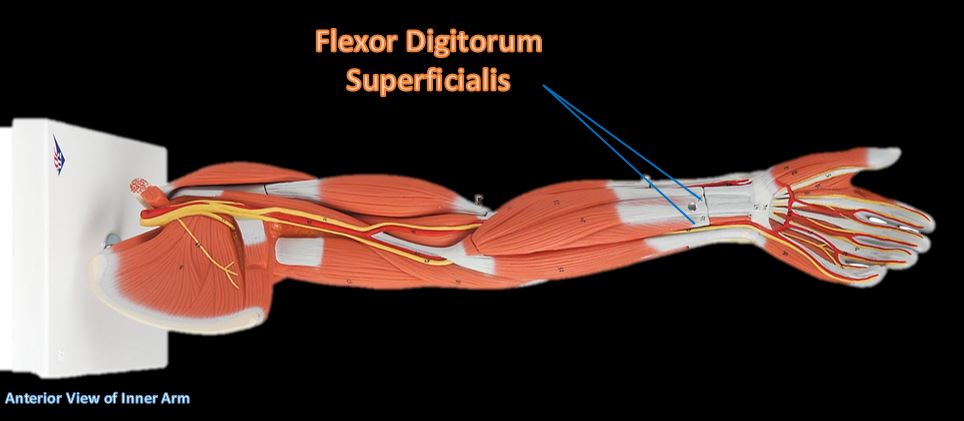
The Brachioradialis
|
|
Function = Flexes forearm at the elbow
The brachioradialis lies at the radial side of the proximal antebrachial region. On the anatomical model, this muscle is found by following the lateral most nerve (yellow) at the elbow region.
|
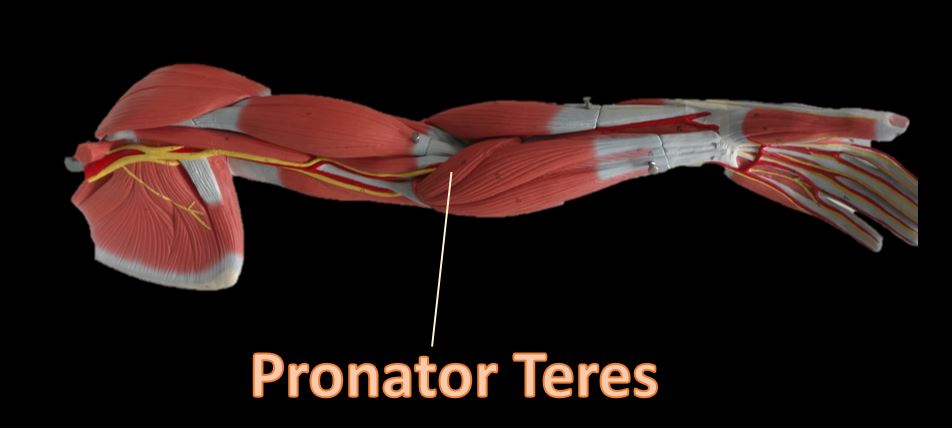
Pronator Teres
Function = Pronation of forearms and hands
The pronator teres is a muscle of the human body (located mainly in the forearm) that assists in the pronation of the forearm. The pronator teres muscle is located on the anterior portion of the forearm just below the antecubital region (inner elbow area).
|
|
|
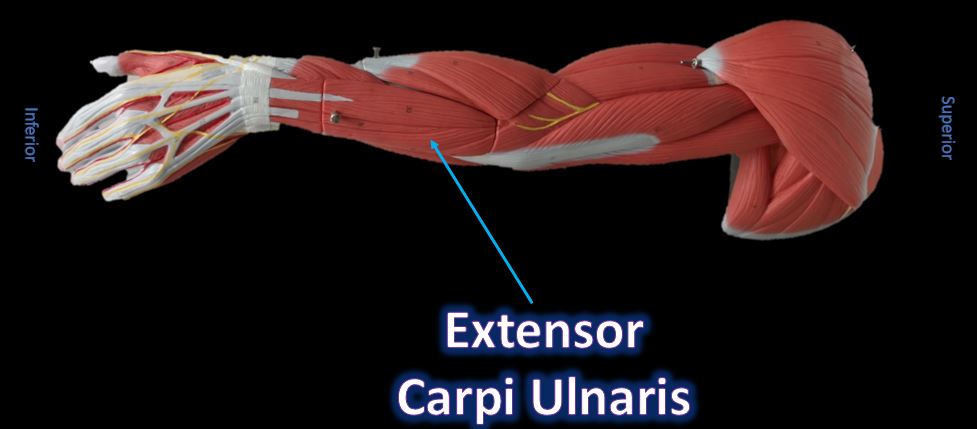
Extensor Carpi Ulnaris
Function = Flexes and adducts wrist/hand
|
|
The extensor carpi ulnaris is a skeletal muscle located on the "ulnar side" of the forearm (this is the portion of the arm that is "under" the radius when you do a "thumb up"). It is visible on the posterior aspect of the forearm. It acts to extend and adduct at the carpus/wrist from anatomical position. Being an extensor muscle, extensor carpi ulnaris is on the posterior side of the forearm.
|
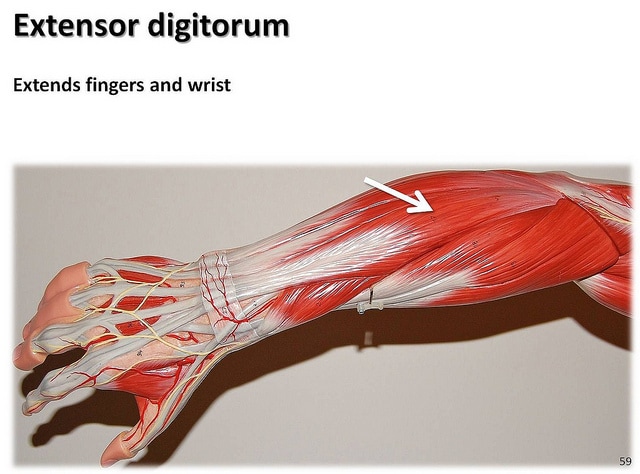
Extensor Digitorium
Function = Extends wrist and medial digits (phalanges)
All wrist extensors are located on the back of the forearm. The extensor digitorum muscle is located at the posterior forearm. It extends the medial four digits of the hand, the wrist, and the elbow. It tends to separate the fingers as it extends them. |
The extensor digitorum acts principally on the proximal phalanges.
|
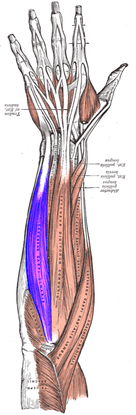
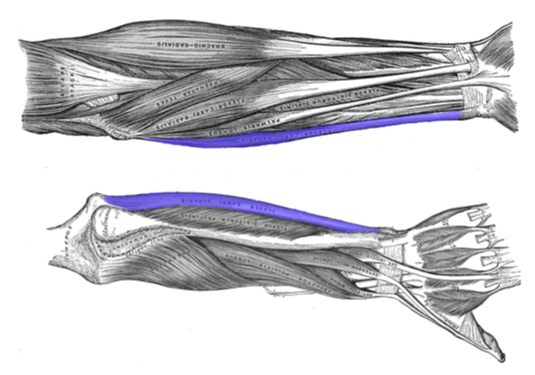
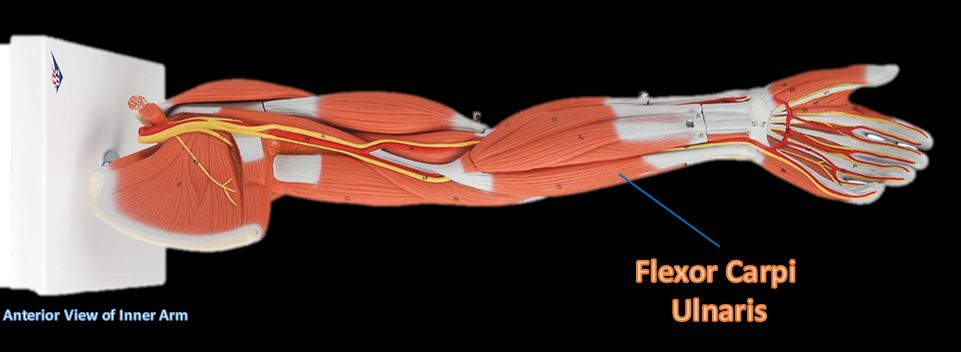
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris
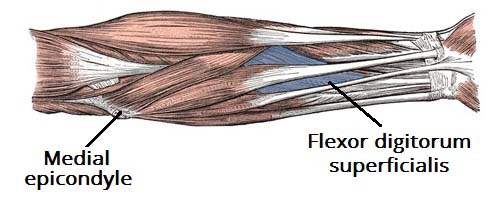
Extensor Digitorium Superficialis
GOT SKILLS?
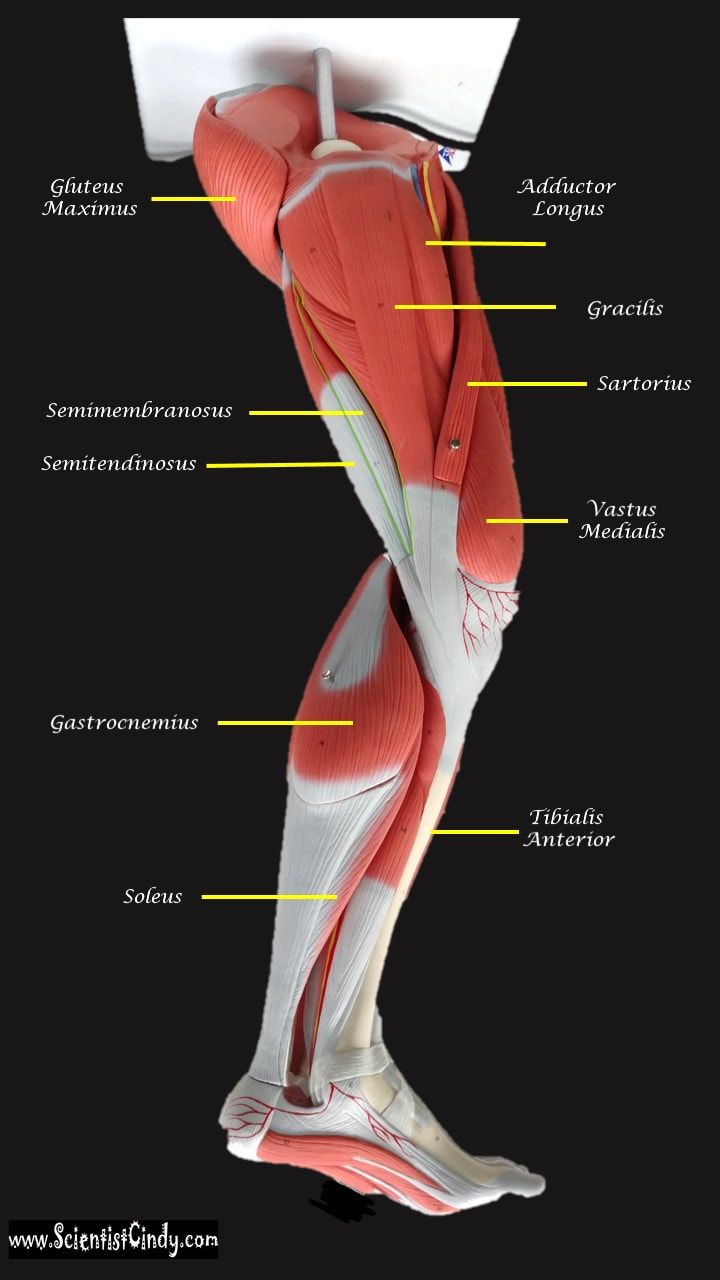
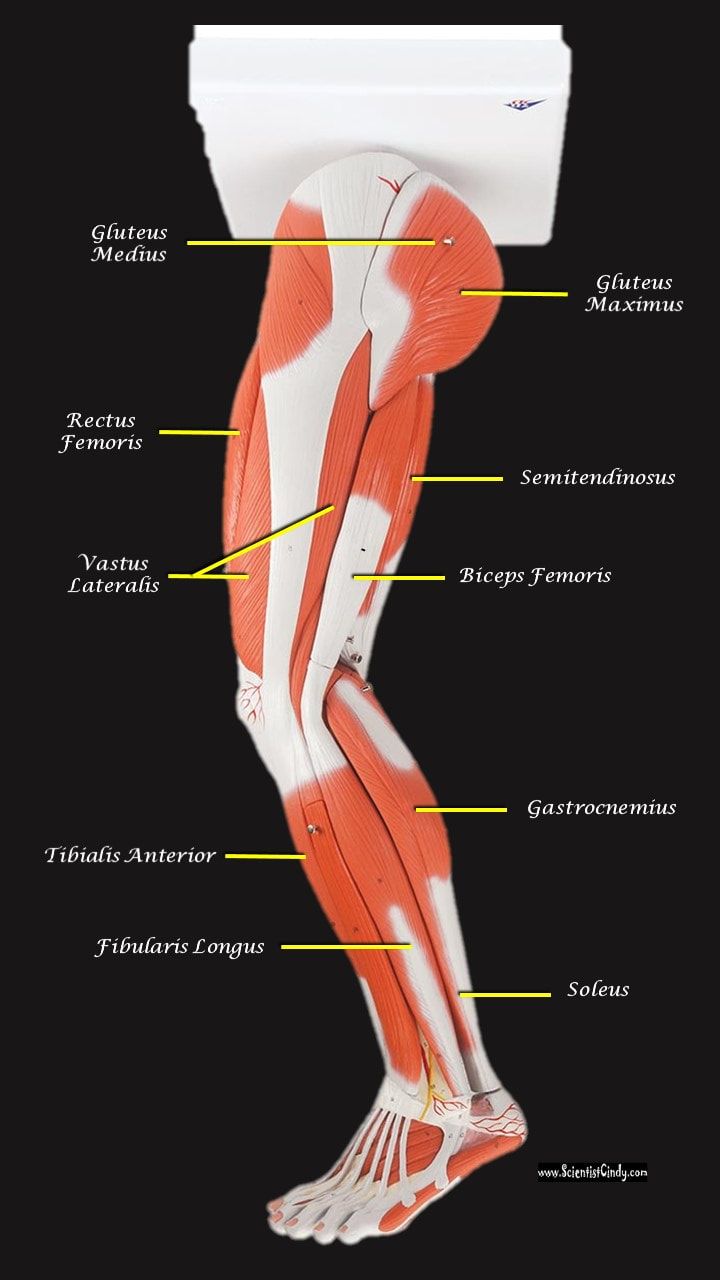
Muscles of the Legs
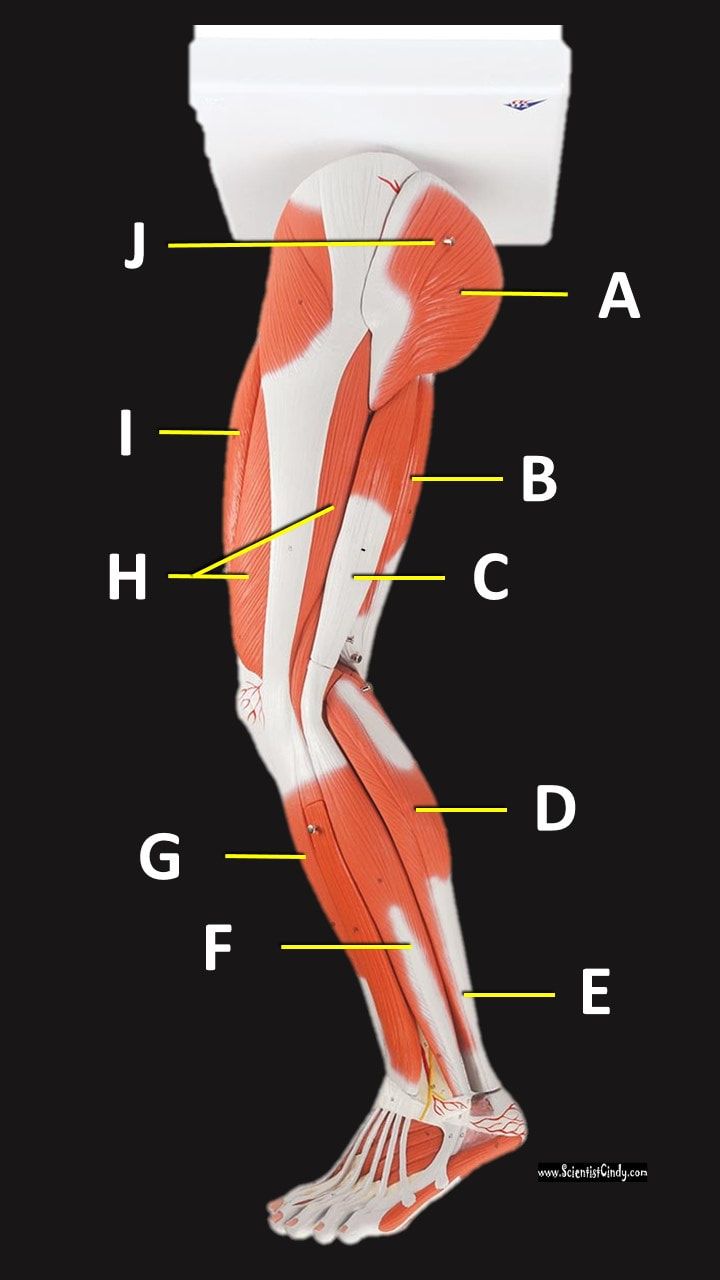
Supporting, balancing, and propelling the body is the work of the muscular system of the legs and feet. From the large, strong muscles of the buttocks and legs to the tiny, fine muscles of the feet and toes, these muscles can exert tremendous power while constantly making small adjustments for balance – whether the body is at rest or in motion.
GOT SKILLS??
IMAGE GALLERY
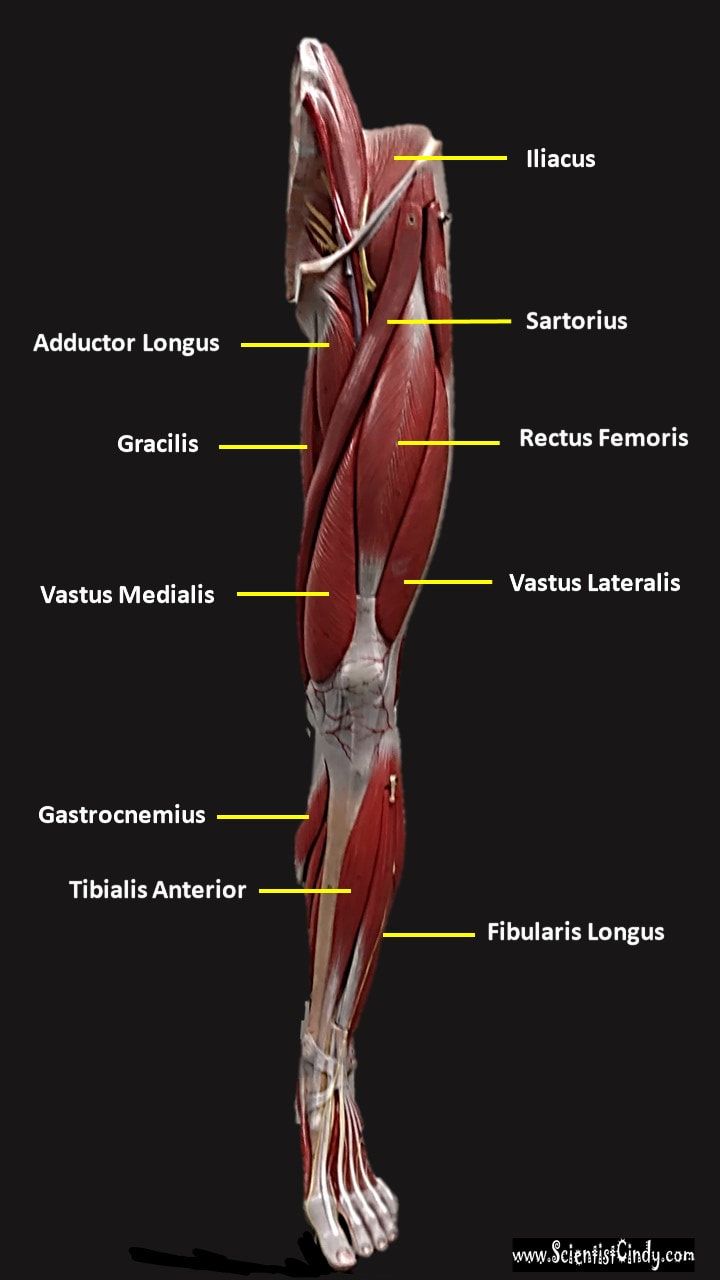
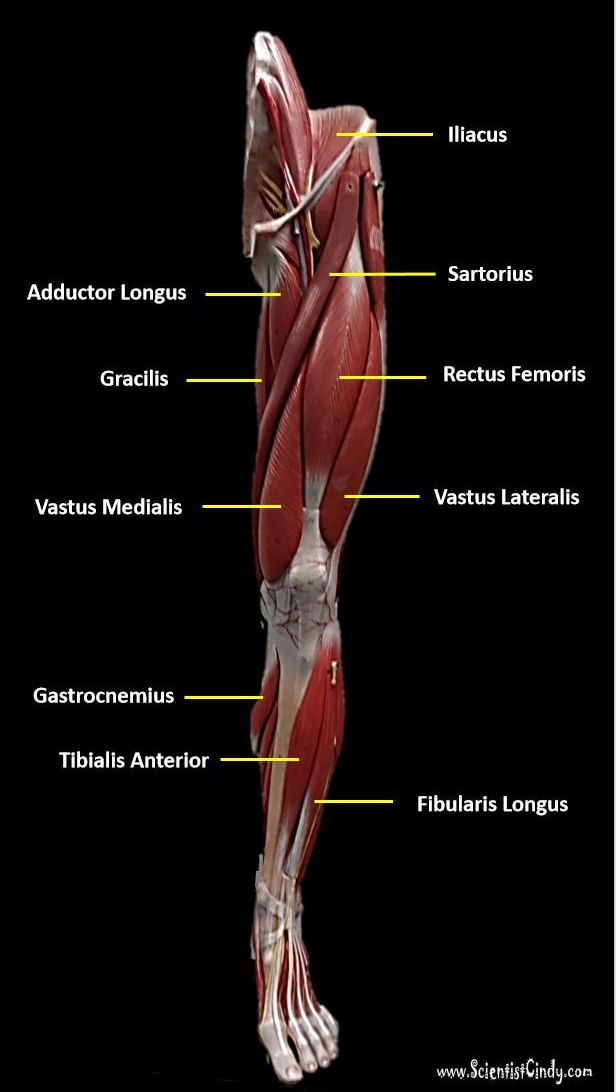
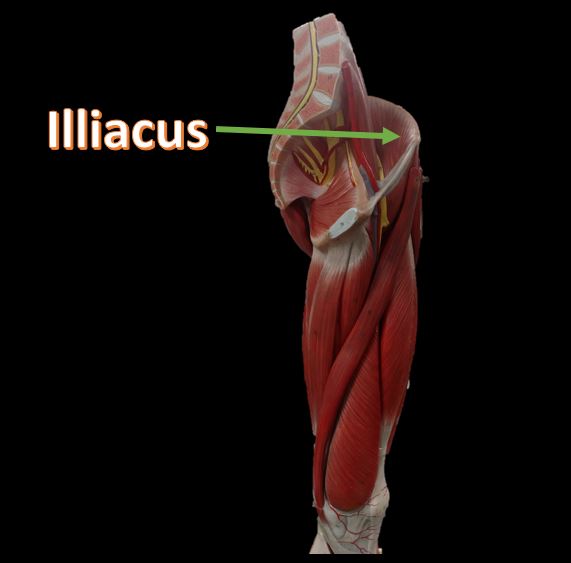
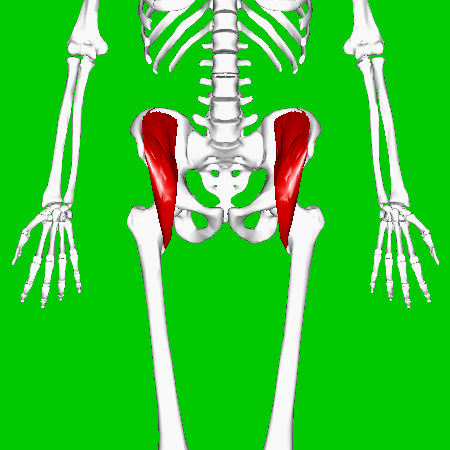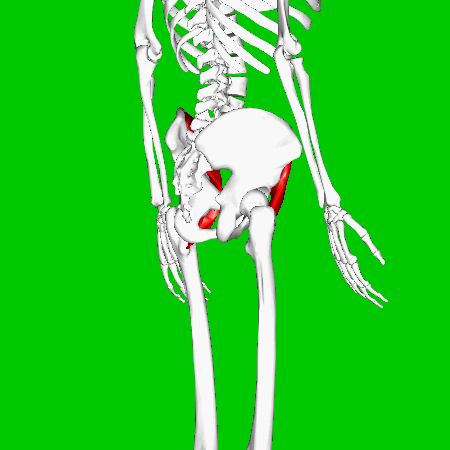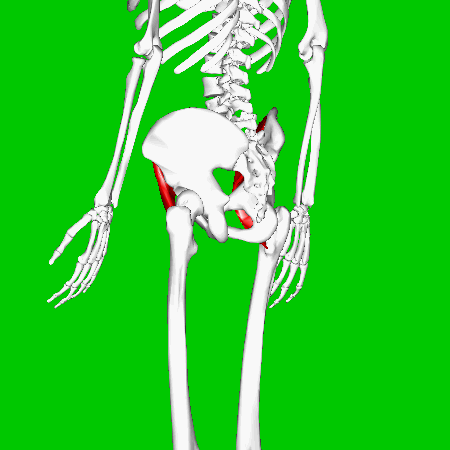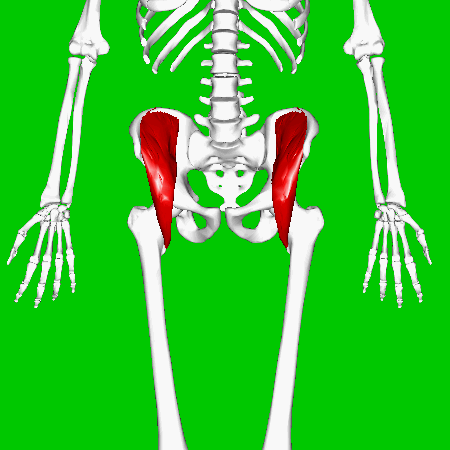
Iliacus Muscles
Function = flexes the thigh (femur) at the hip, adducts thigh, medially rotates thigh.

The iliacus muscle originates at the illium, which is located on the inside of the hip (coxal) bones (at the anterior aspect). The function of the iliacus muscles are to lifting (flex) the femur forward. The iliacus muscle is part of the Iliopsoas which is the prime mover in thigh flexion and in flexing trunk (as when bowing).
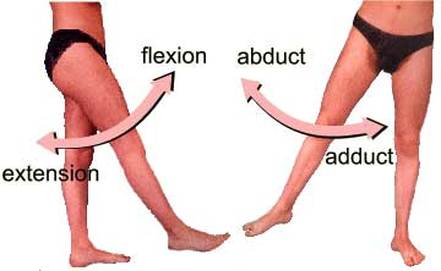
The hip is a ball-and-socket joint that permits flexion, extention, adduction, abduction, and rotation of the thigh. The muscles that flex the thigh at the hip originate from the vertebral column and pelvis and pass anterior to (in front of ) the hip joint. These muscles include the illiacus muscles and the rectus femoris.
The hip is a ball-and-socket joint that permits flexion, extention, adduction, abduction, and rotation of the thigh. The muscles that flex the thigh at the hip originate from the vertebral column and pelvis and pass anterior to (in front of ) the hip joint. These muscles include the illiacus muscles and the rectus femoris.
Animated GIF By Anatomography - en:Anatomography (setting page of this image), CC BY-SA 2.1 jp, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=27547285
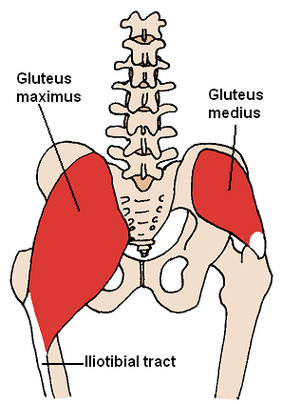
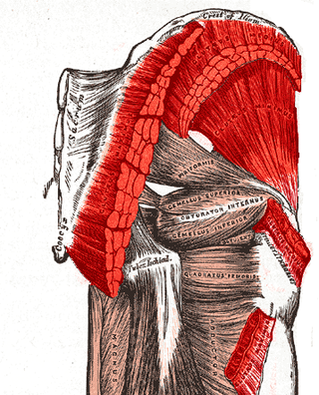
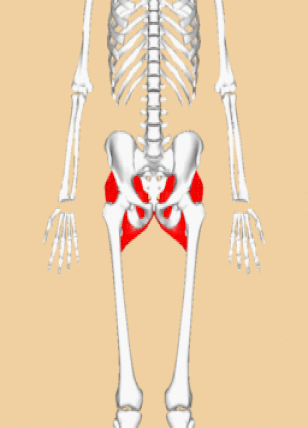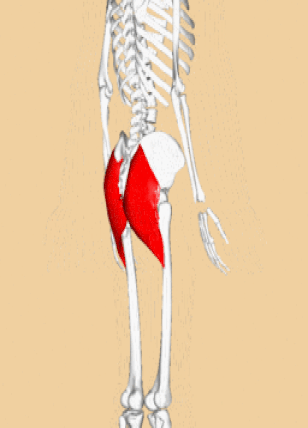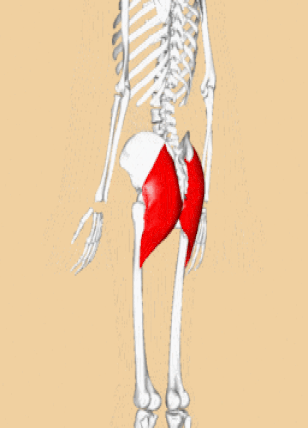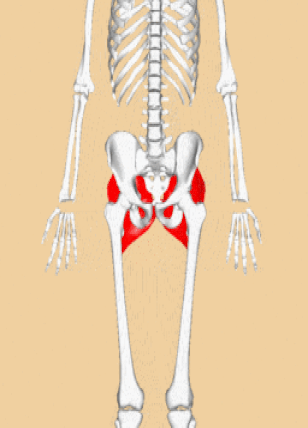
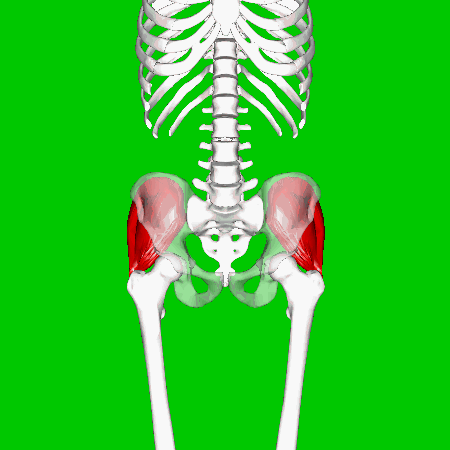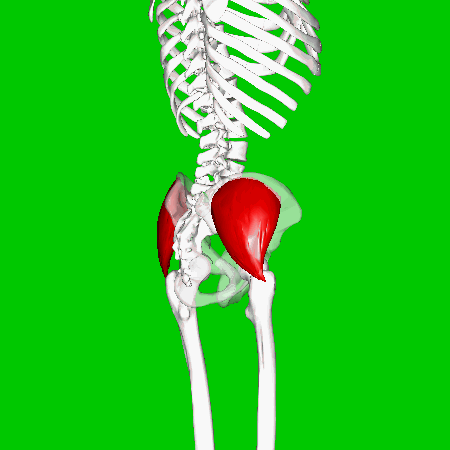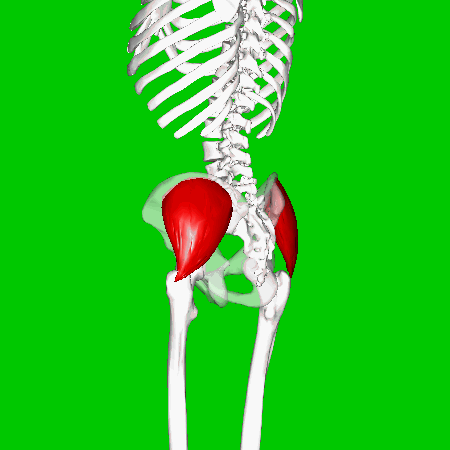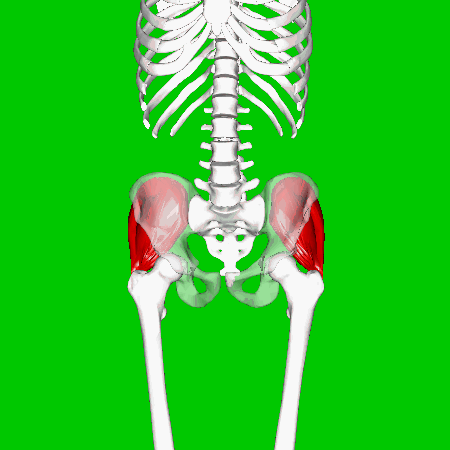
GLUTEAL MUSCLES
|
CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=545381
Each of these muscles originate at the ilium and the sacrum and insert at the femur. The gluteal muscles allow for the extension of the thigh (femur) and abduction of the thigh (femur), as well as the external rotation and internal rotation of the hip joint.
|
The muscles of the buttocks (gluteal muscles) include.
|
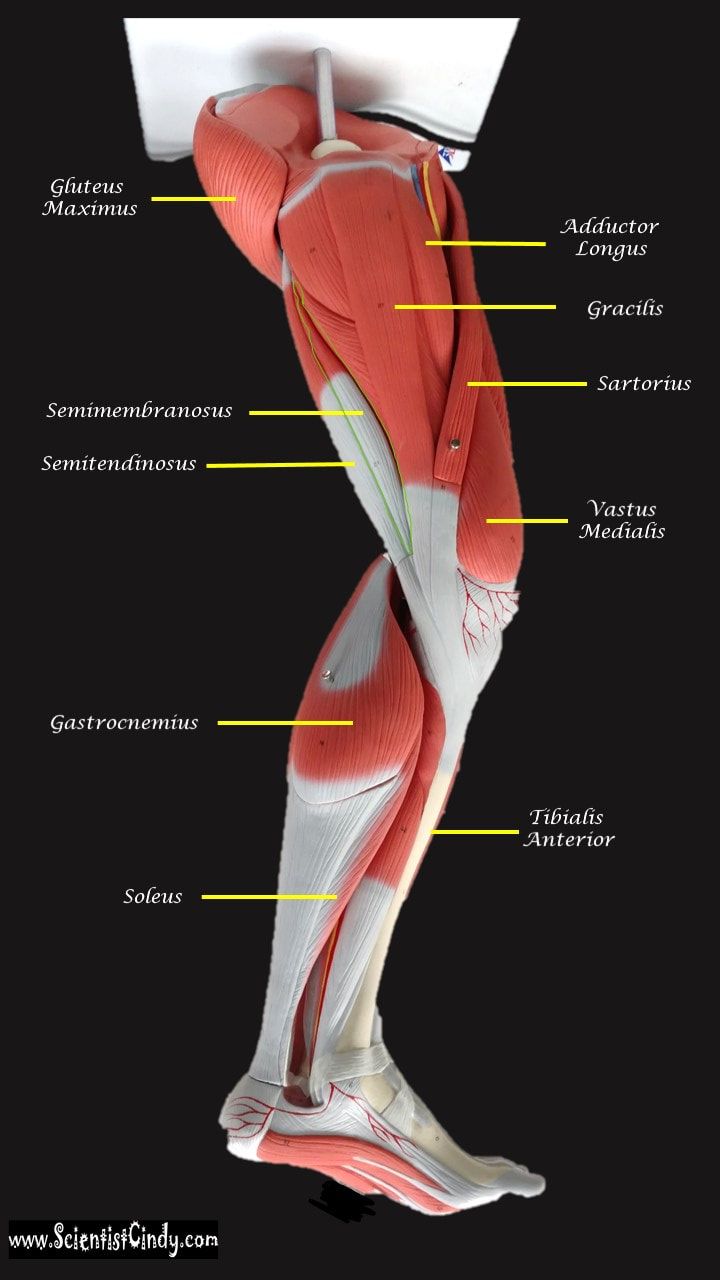
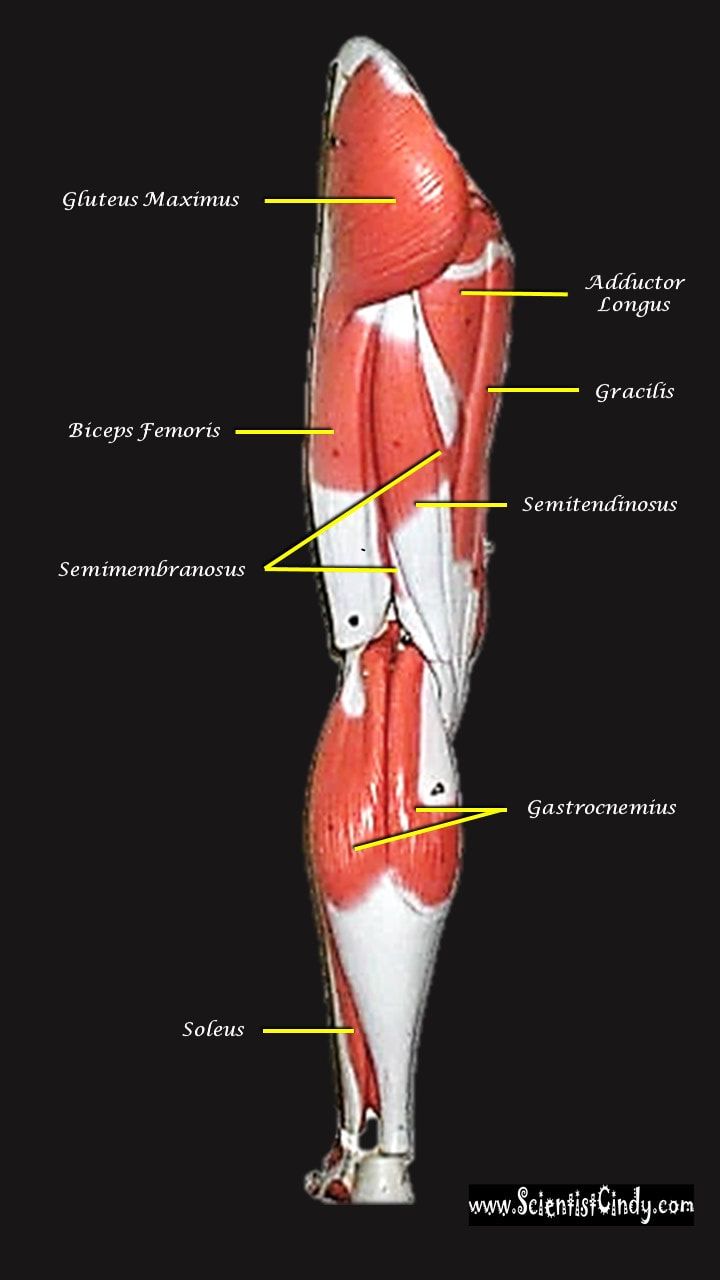
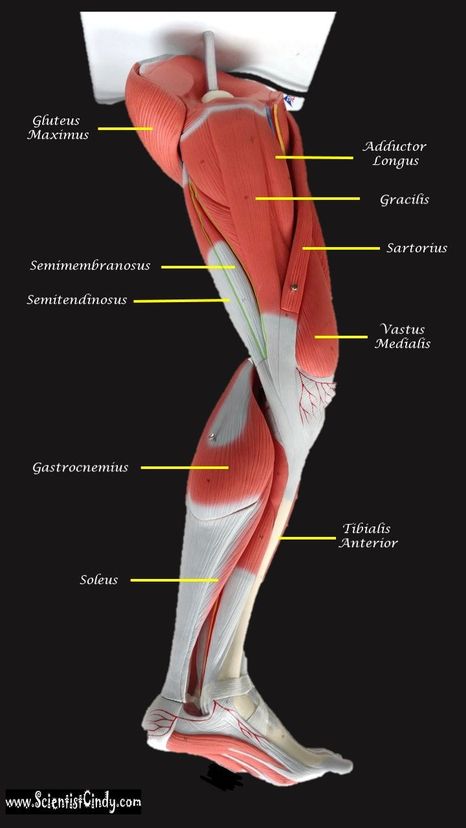
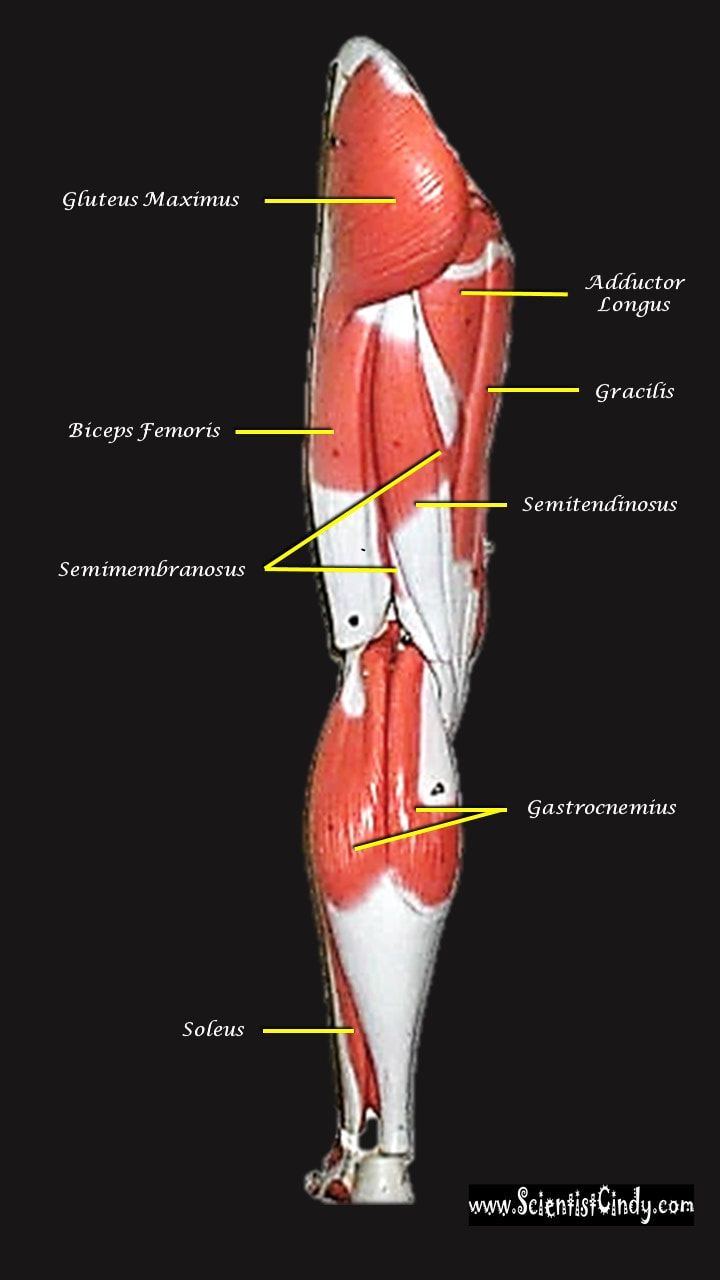
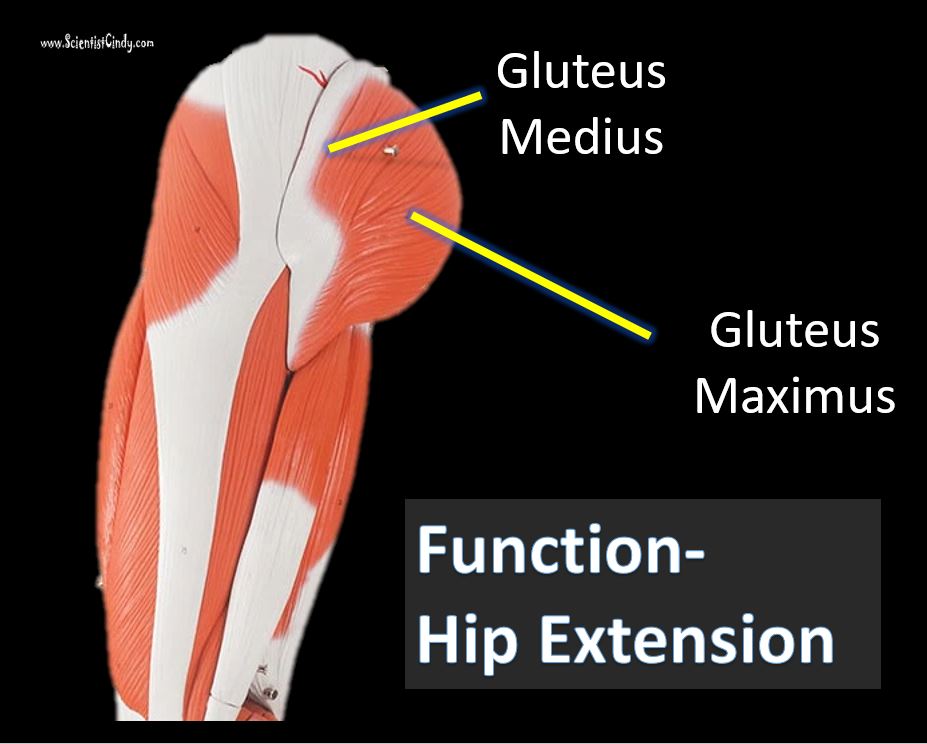
Gluteus Maximus The thigh extensors arise posterior to the hip joint and include the gluteus maximus and hamstrings. It is the largest and most superficial of gluteus muscles. This muscle forms most of the mass of the buttocks. The gluteus maximus is the main extensor of thigh. It functions to assist in stair climbing and is able to laterally rotate and adduct the thigh.
|
Gluteus Medius
|
A portion of the gluteus medius lies superior to gluteus maximus. The inferior portion of the gluteus medius lies underneath (deep to) the gluteus maximus. The gluteus medius is one of the three gluteal muscles which lie on the outer portion of the pelvis at the posterior aspect.
By Anatomography - en:Anatomography (setting page of this image), CC BY-SA 2.1 jp, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=27657573
|
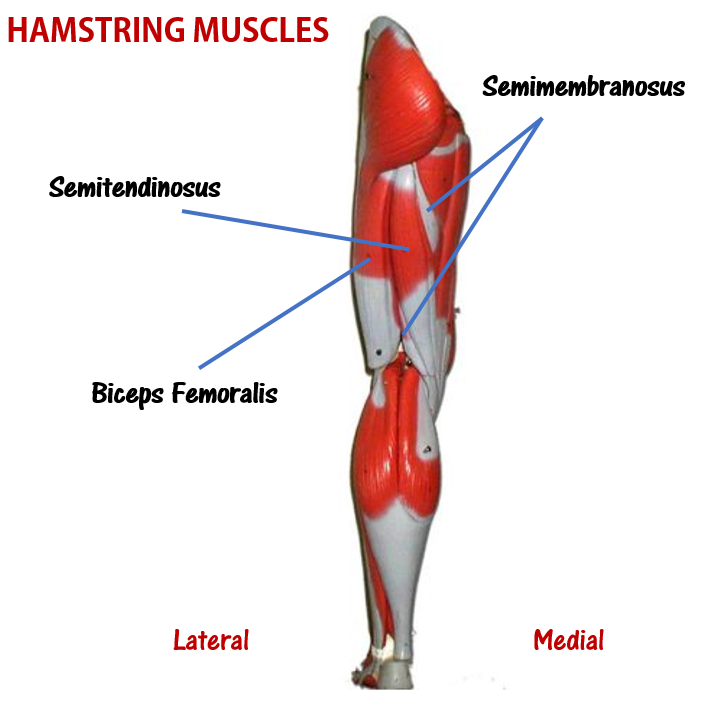
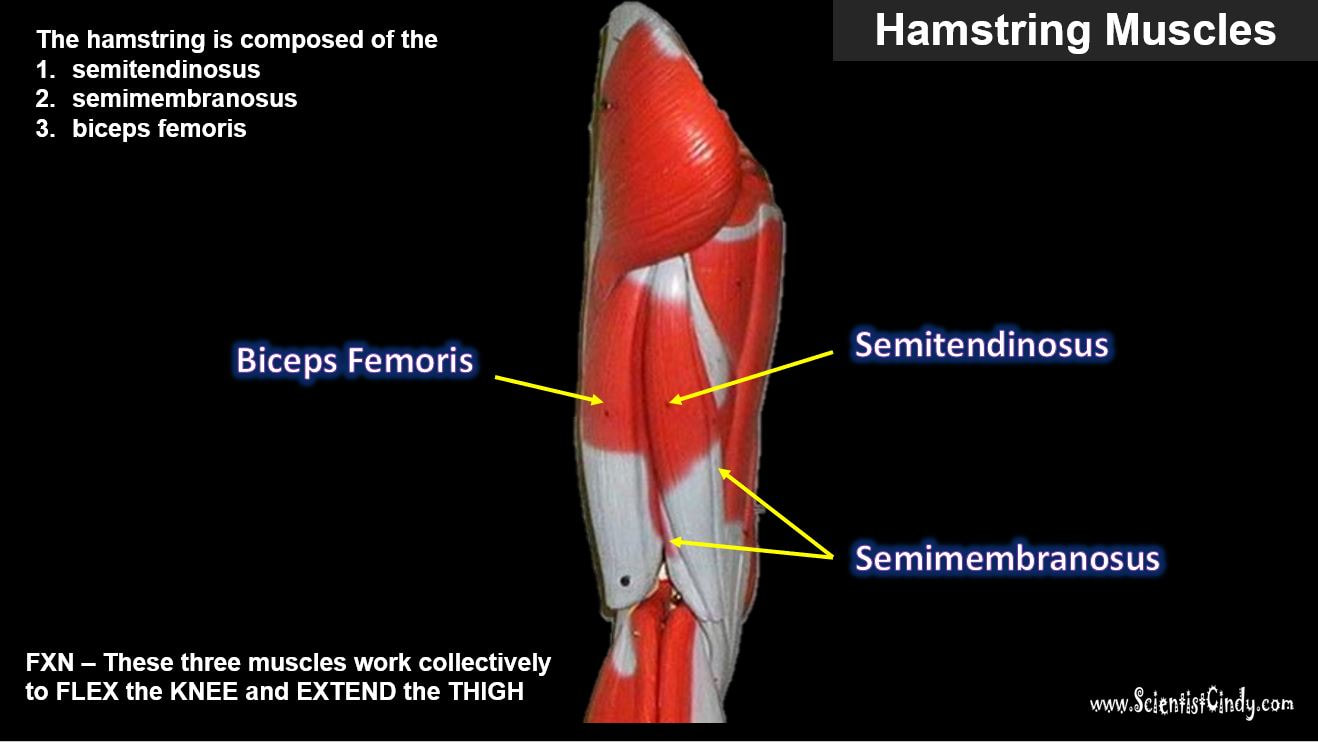
Hamstring Muscles

The hamstring refers to a group of muscles that lie at the posterior aspect of the thigh. The hamstring muscles cross (and therefore act upon) both the hip joint and the knee joint. The hamstring is the single large tendon found behind the knee or comparable area.The hamstrings include the following muscles from medial to lateral:
- The semimembranosus
- The semitendinosus
- The biceps femoris
The hamstring muscle function in the flexion of the knee joint and extension of the hip joint.
IMAGE courtesy of http://bodybuilding-wizard.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/08/machine-hip-flexor-1-3.jpg
IMAGE courtesy of http://bodybuilding-wizard.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/08/machine-hip-flexor-1-3.jpg
The Semimembranosus Muscle
Function = Extends thigh; flexes leg; medially rotates leg.
The semimembranosus muscle is medial hamstring muscle, lying toward the posterior portion of the inner thigh, underneath (deep) to the semitendinous muscle.
Function = Extends thigh; flexes leg; medially rotates leg.
The semimembranosus muscle is medial hamstring muscle, lying toward the posterior portion of the inner thigh, underneath (deep) to the semitendinous muscle.
|
The Semitendinosus Muscle
Function = Extends thigh; flexes leg; medially rotates leg.
The semitendinosus muscle lies medial to biceps femoris. It is superficial, and has a long, slender tendon at the posterior aspect of the thigh.
The Biceps Femoris
Function = Extends thigh; flexes leg; medially rotates leg.
|
The biceps femoralis gets its name because it has "two heads"; a long head and a short head. The long head of the biceps femoris extends the hip, as when beginning to walk; both short and long heads flex the knee and laterally (outwardly) rotate the lower leg when the knee is bent.
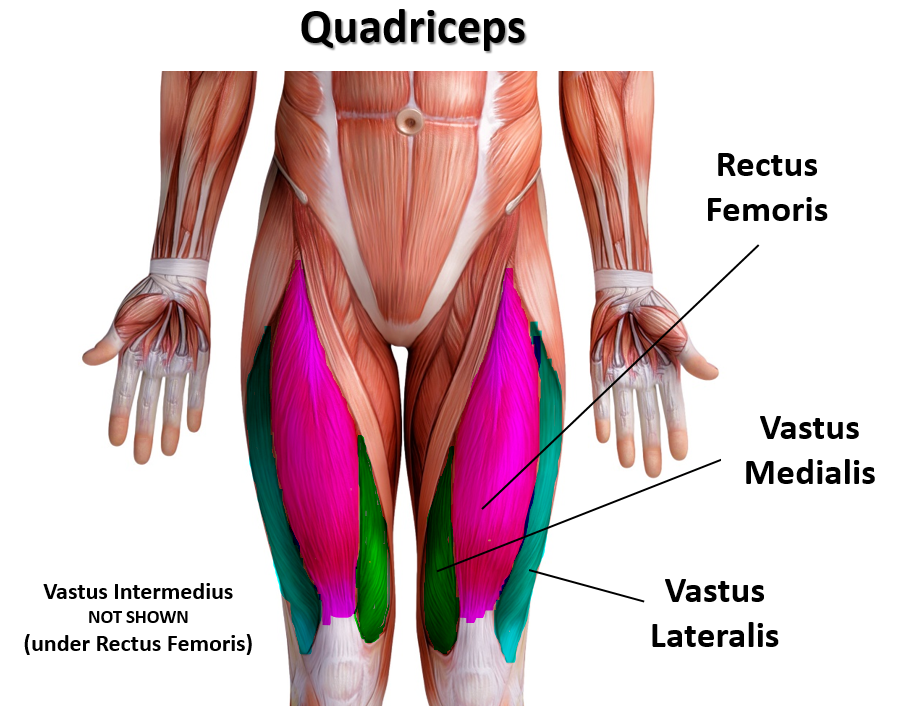
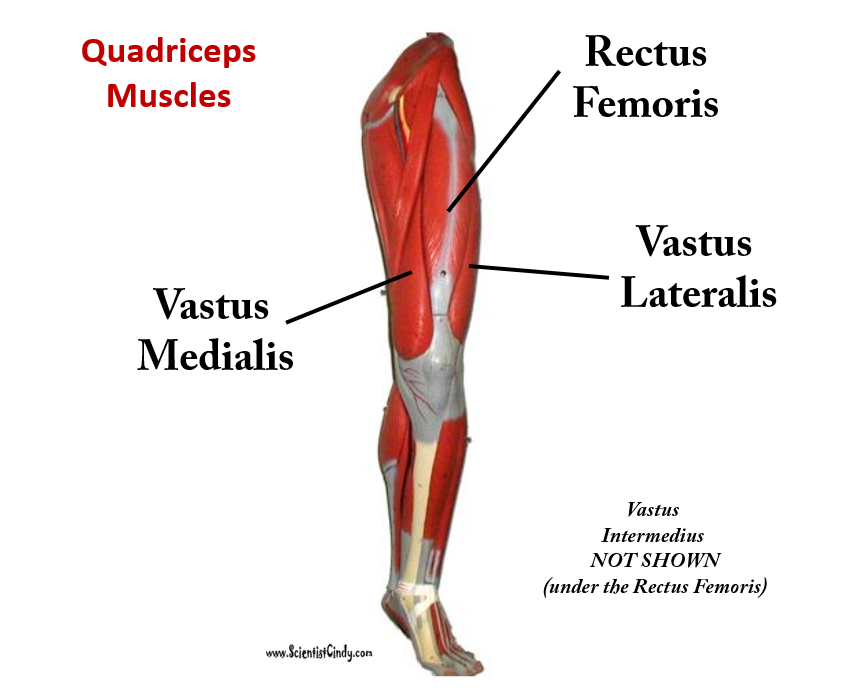
Muscles of the Quadraceps
The quadriceps femoris gets its name from the Latin words that mean "four-headed muscle of the femur". The quadraceps femoris refers to a muscle group that consists of 4 muscles of the anterior (front) thigh area (or the femoral area. The muscles are extensors of the knee.
|
Quick Overview of the Quadriceps
|
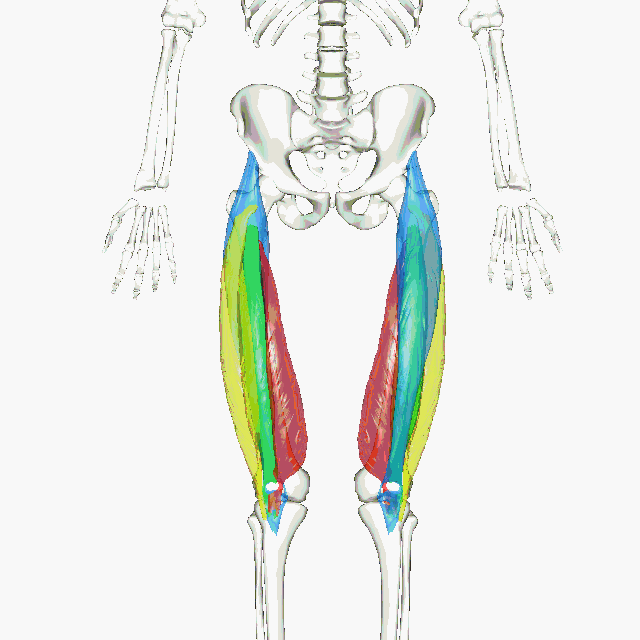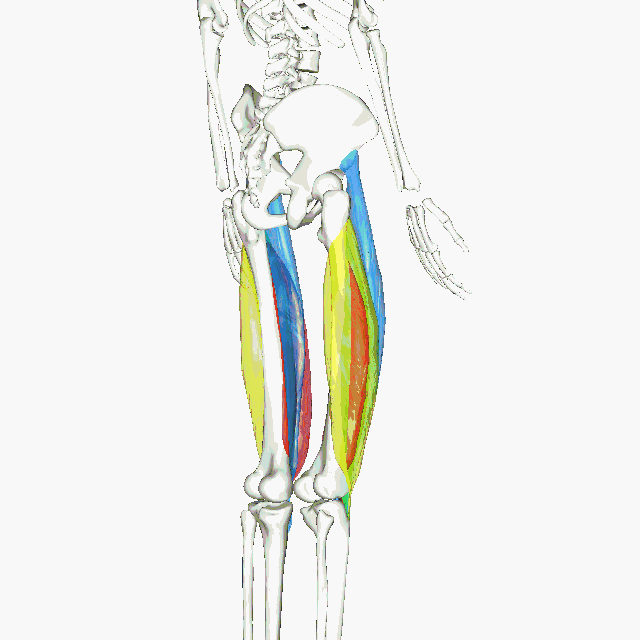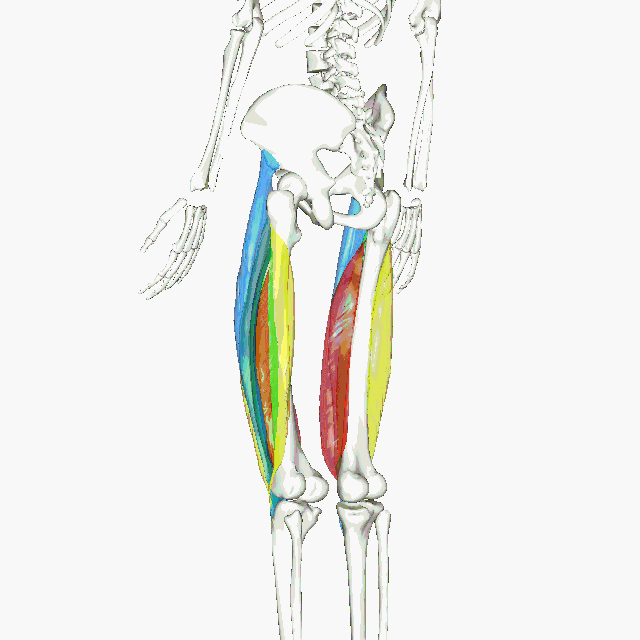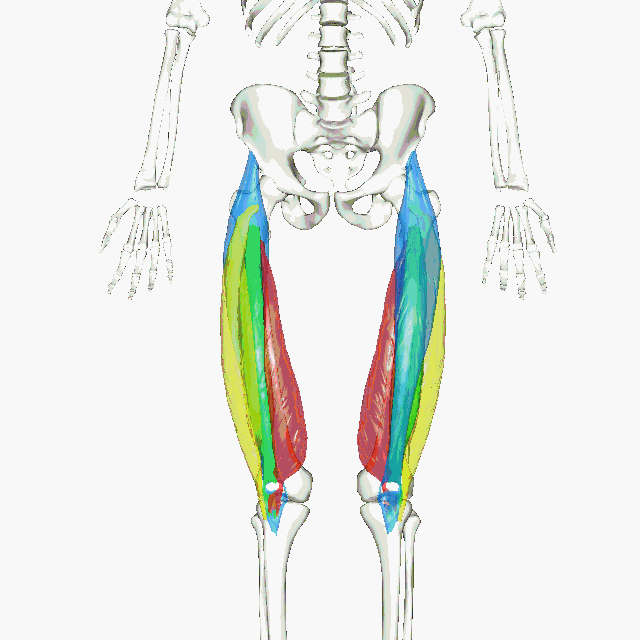
The animated GIF shows the 4 muscles of the quadriceps as the following colors:
rectus femoris - blue vastus lateralis - yellow vastus intermedius - green vastus medialis - red |
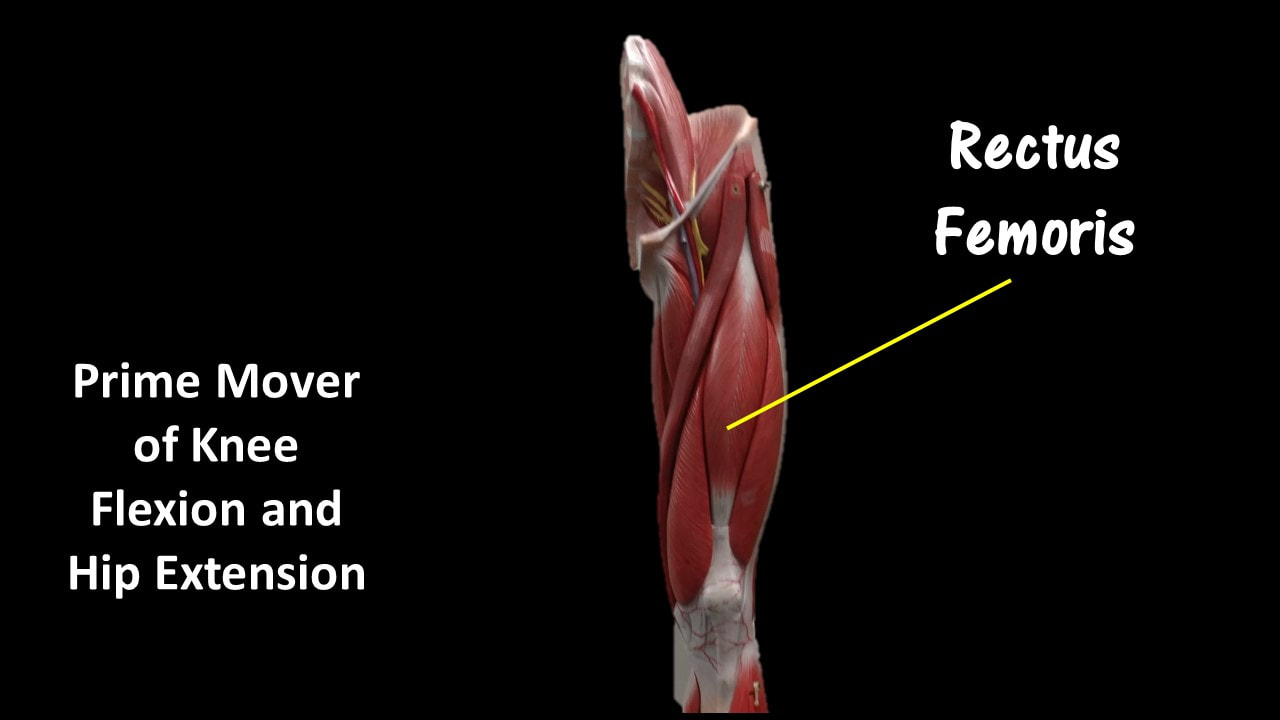
Rectus Femoris
|
Function = Extends leg and flexes thigh (brings thigh up)
The rectus femoris is the quadriceps muscle that lies at the middle of the front part of the thigh. It lies (wholly or partially) on top of the other three quadriceps muscles. It originates on the ilium. It is named from its straight-appearing orientation at the front of the thigh.
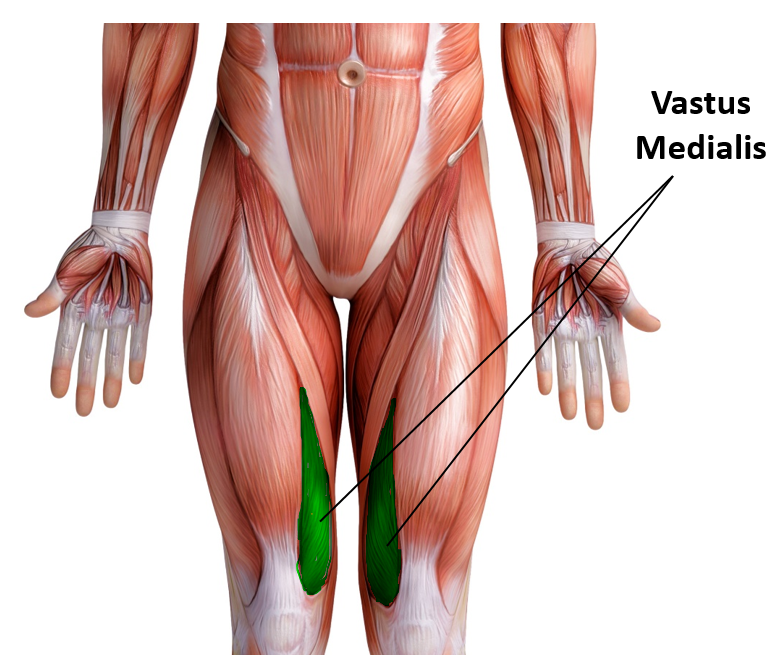
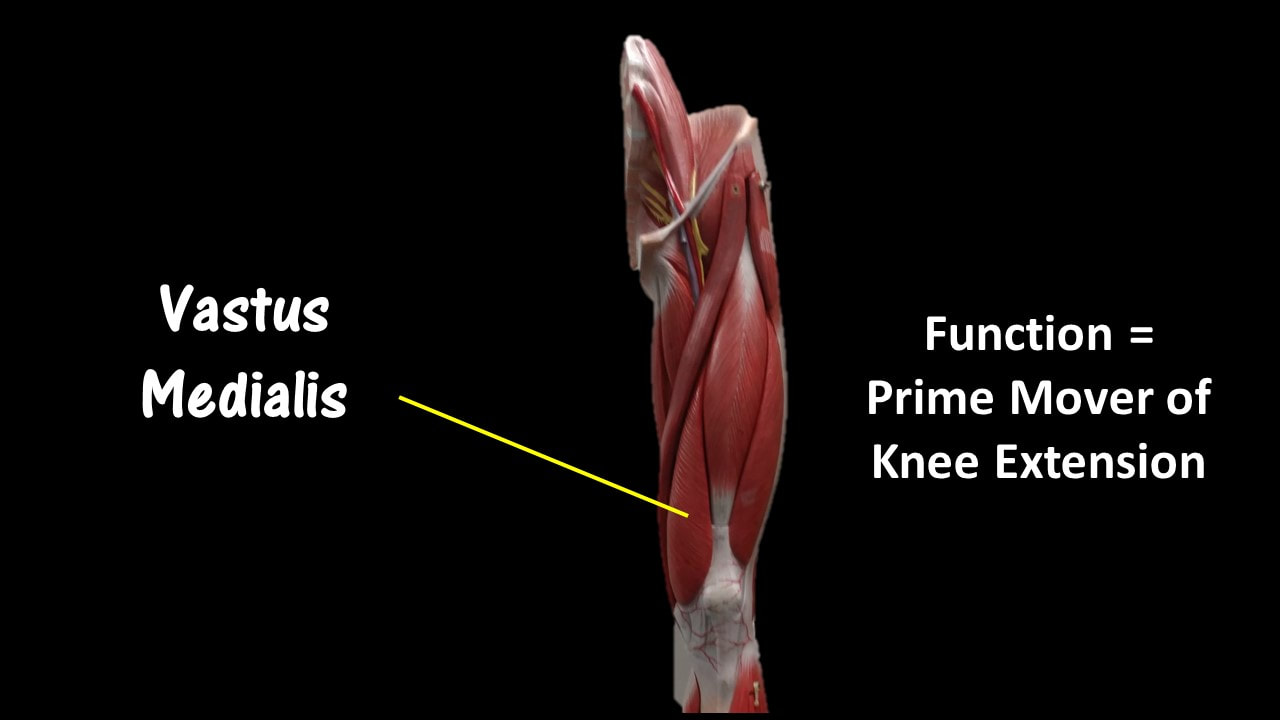
Vastus Medialis
Function = Extends leg; stabilize knee (patella)
|
|
The vastus medialis is located on the front medial portion of the thigh. It is one of the quadraceps muscles. The vastus medialis originates medially along the entire length of the femur. It is connected to the other quadriceps muscle.
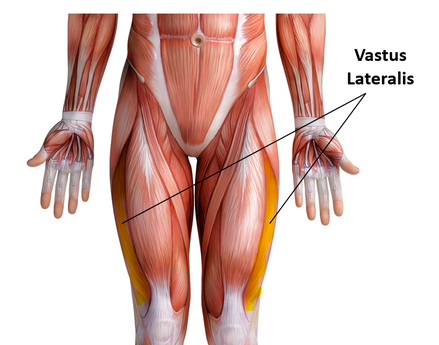
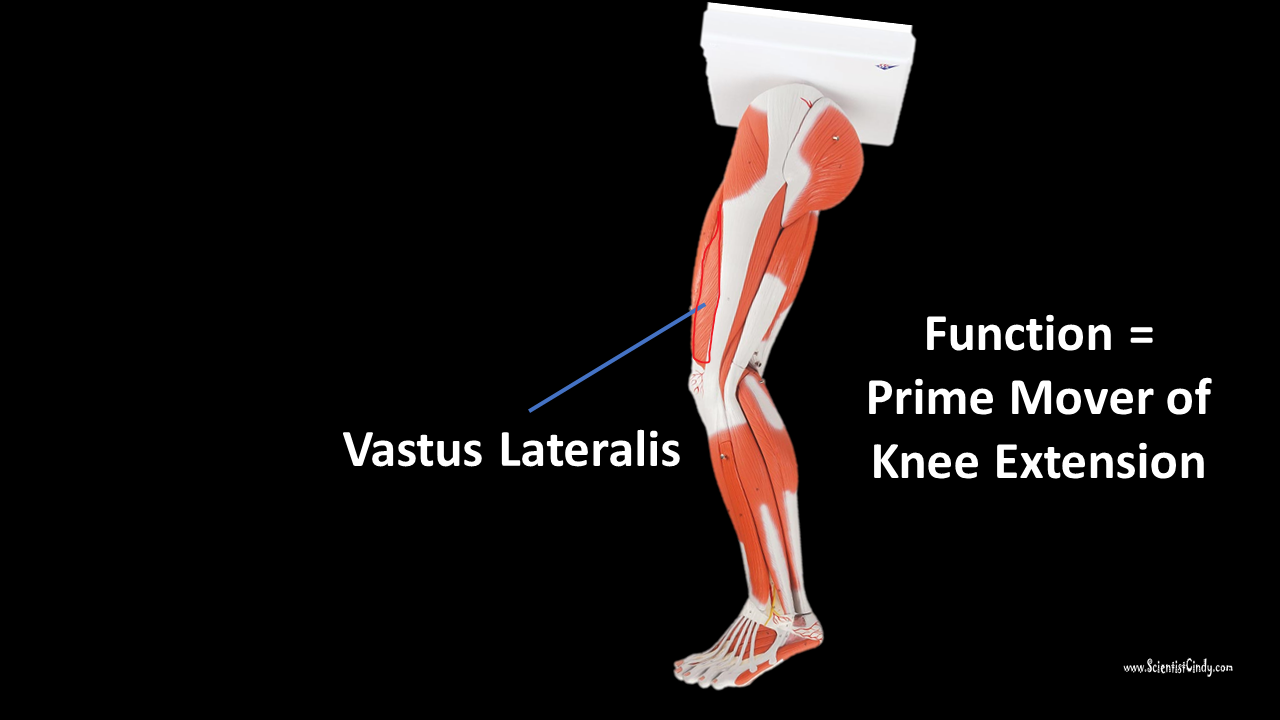
Vastus Lateralis
Function = Extends leg (brings leg straight) and stabilizes knee
The vastus lateralis muscle is the largest head of the
quadriceps group. It forms the lateral aspect of the thigh.
quadriceps group. It forms the lateral aspect of the thigh.
Vastus Intermedius
Function = Extends leg
Vastus Intermedius Cannot be Viewed in the Muscular Leg Model Without Removing the Rectus Femoris.
Vastus intermedius lies between vastus lateralis and vastus medialis on the front of the femur (i.e. on the top or front of the thigh), but underneath (deep) to the rectus femoris. Typically, it cannot be seen without dissection of the rectus femoris. In the 3D model, you will have to remove the rectus femoris in order to view the vastus intermedius.
Vastus intermedius lies between vastus lateralis and vastus medialis on the front of the femur (i.e. on the top or front of the thigh), but underneath (deep) to the rectus femoris. Typically, it cannot be seen without dissection of the rectus femoris. In the 3D model, you will have to remove the rectus femoris in order to view the vastus intermedius.
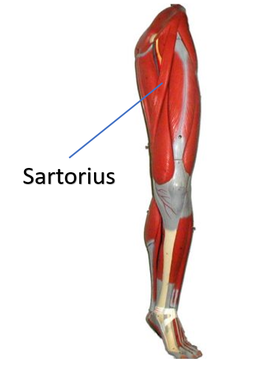
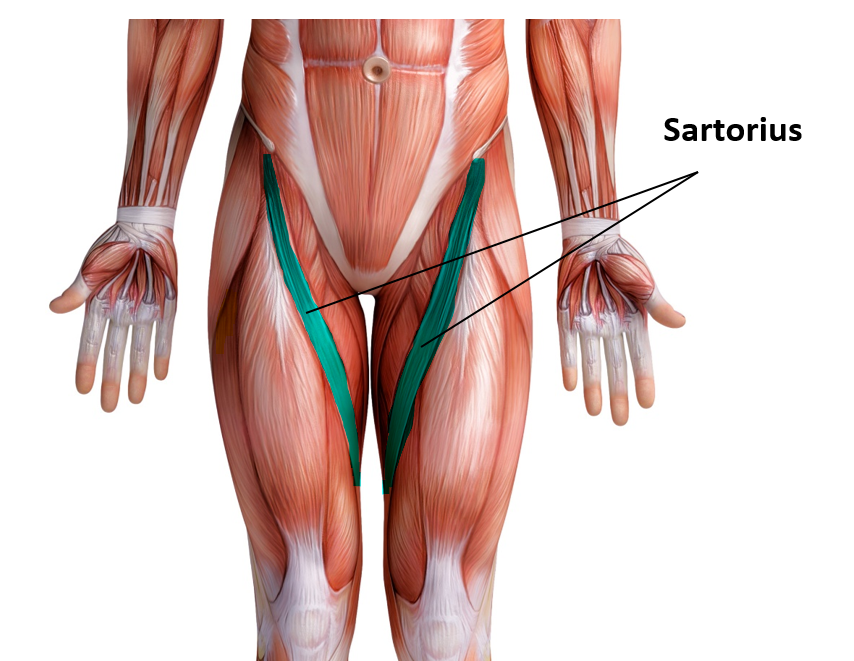
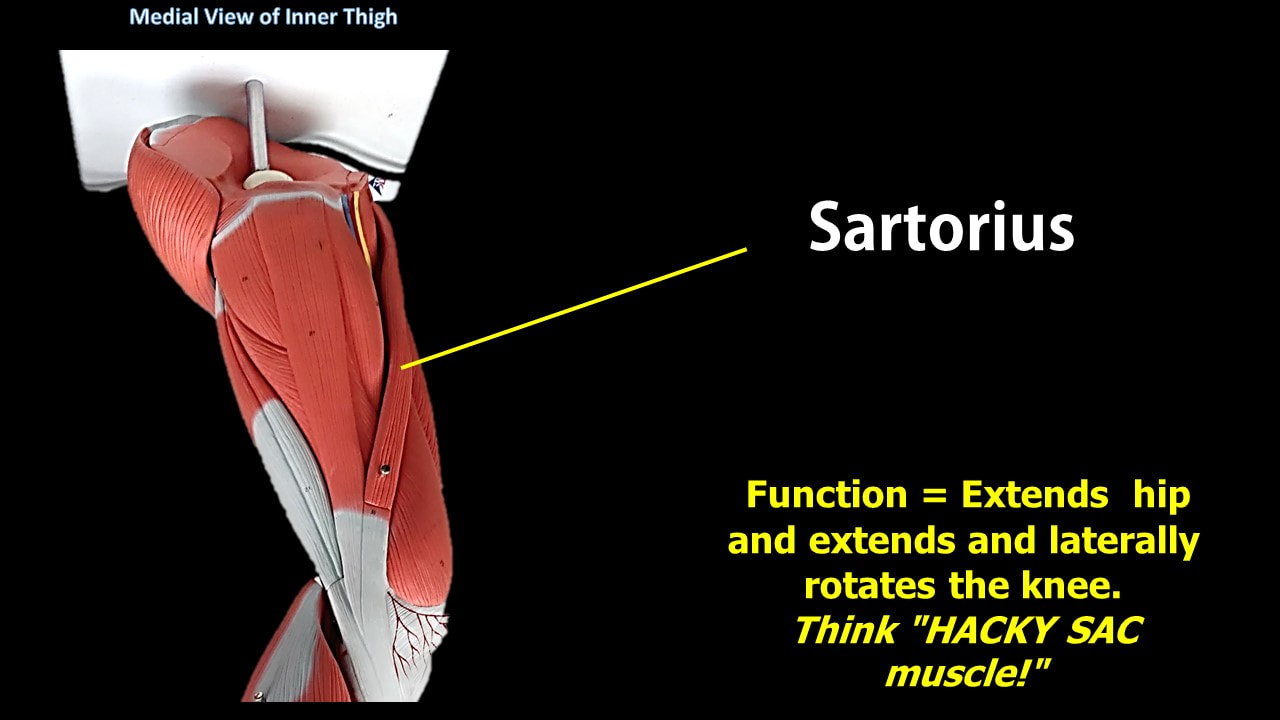
Sartorius Muscles
|
|
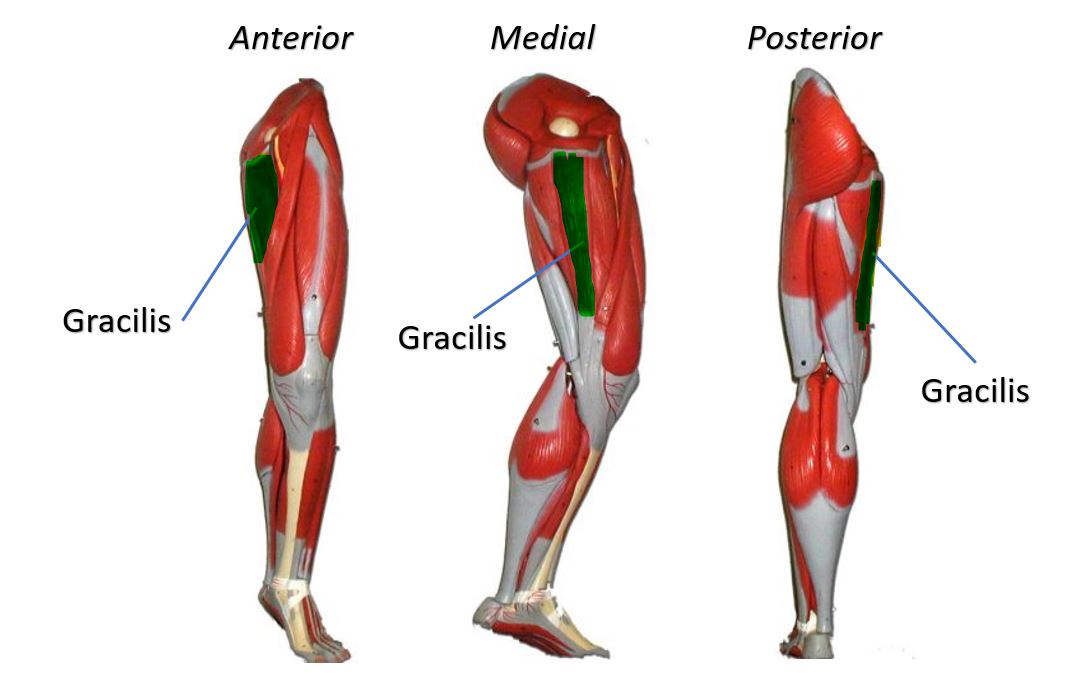
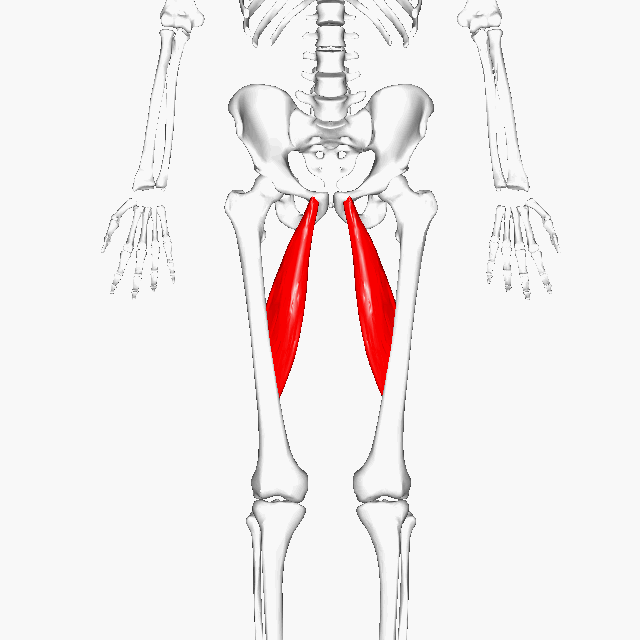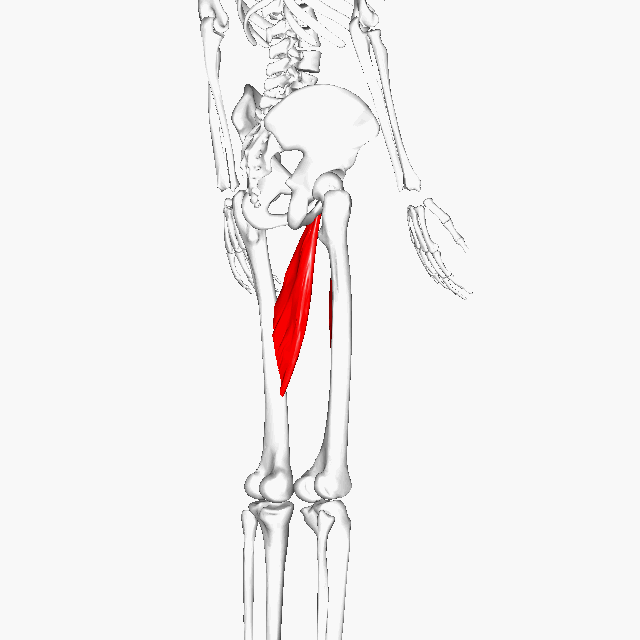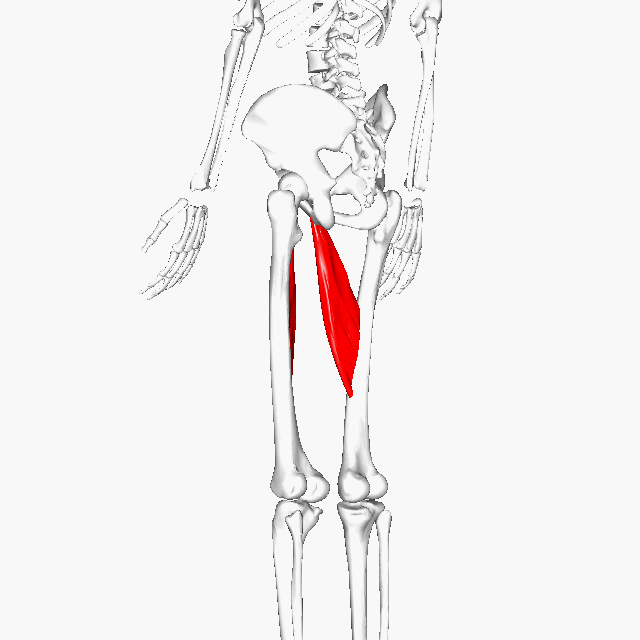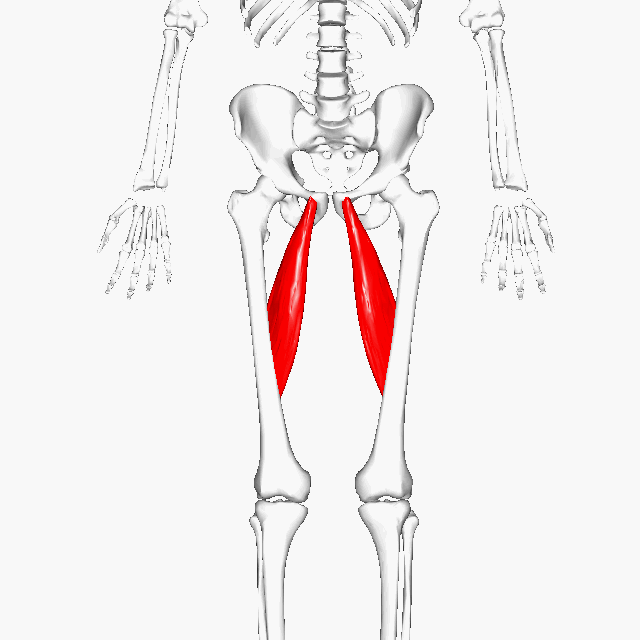
Gracilis MuscleFunction = Aducts thigh, flexes and medially rotates leg
The gracilis muscle is the most superficial muscle on the inner thigh. The muscle fibers originate at the pubis and run vertically downward, spans the knee joint, then inserts into the tibia. The gracilis muscle functions to adduct the lower limb.
The muscle adducts, medially rotates, and flexes the hip as above, and also aids in flexion of the knee. |
There are five groin (adductor) muscles; three of them are called the 'short adductors' (pectineus, adductor brevis andadductor longus) and the other two are called the 'longadductors' and consist of gracilis and adductor magnus.
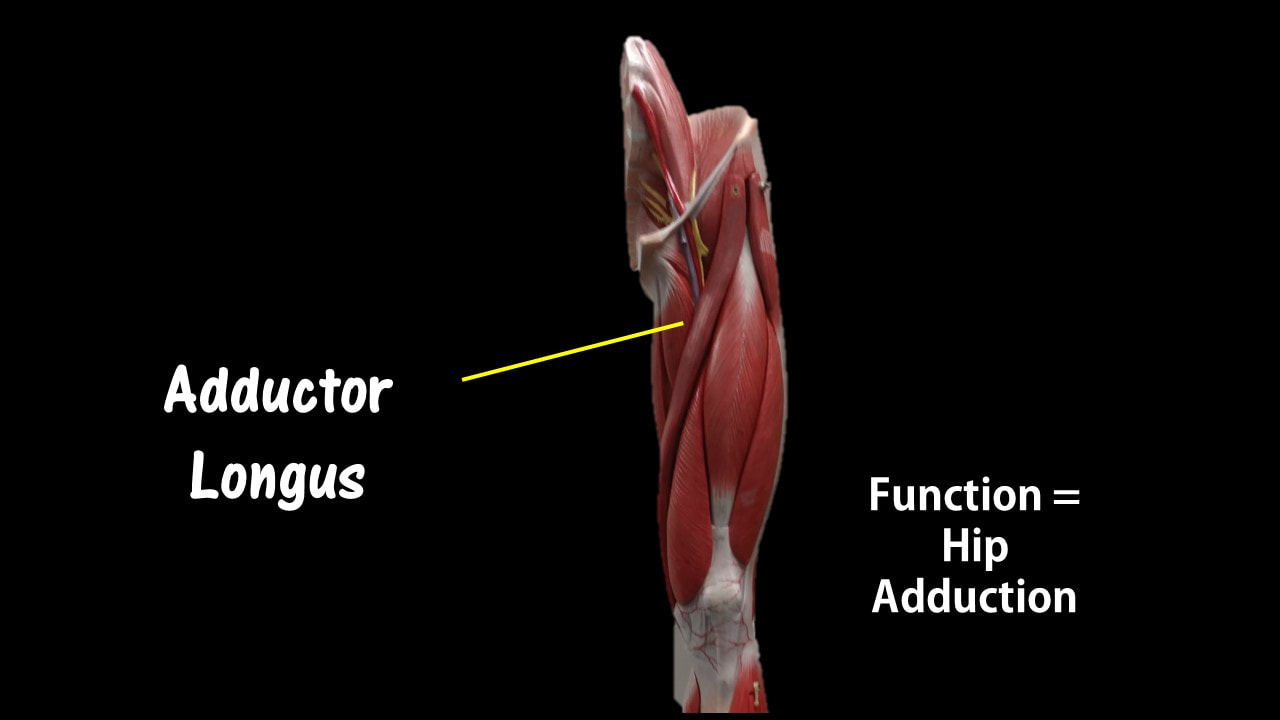
Adductor Longus
Function = adducts the thigh
The adductor longus is a muscle located in the inner thigh area. One of the adductor muscles of the hip, its main function is to adduct the thigh.
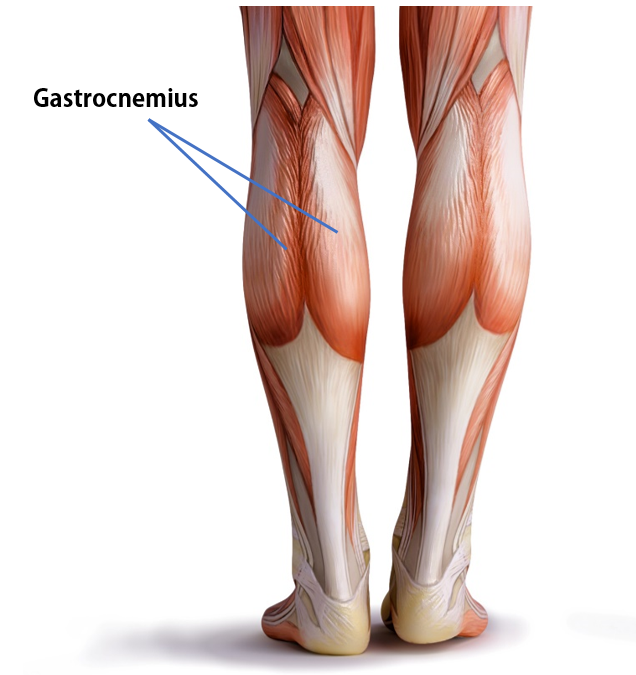
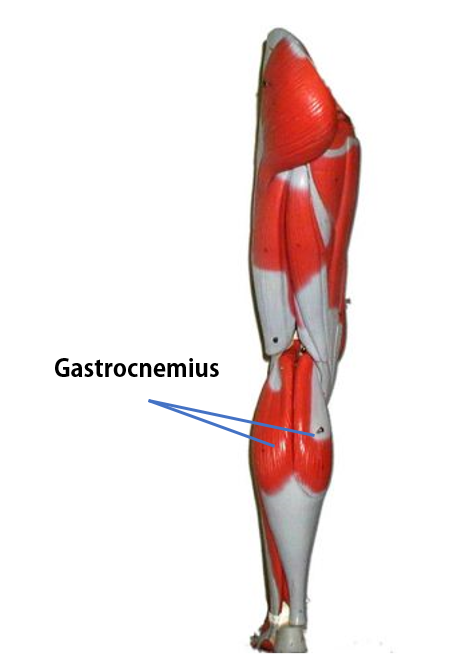
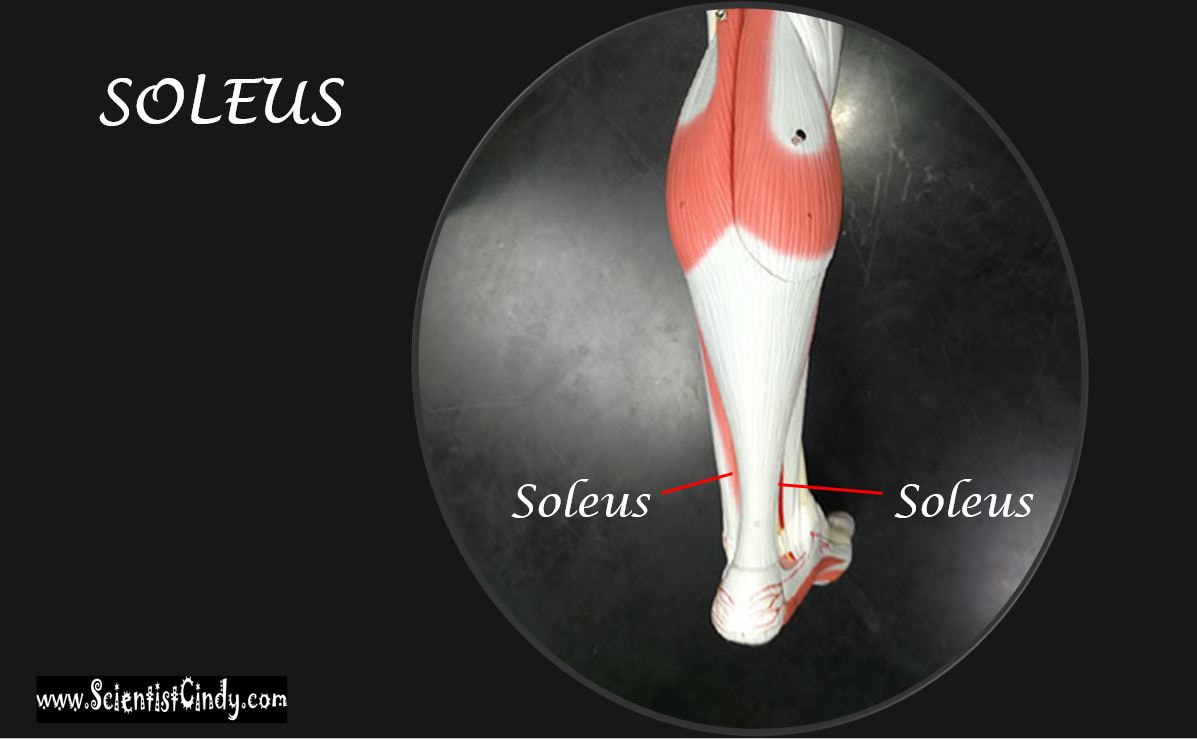
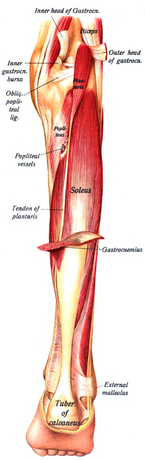
Gastrocnemius Muscle
The anatomical name for your calf muscle is the gastrocnemius. The gastrocnemius muscle is named from the Latin words for "stomach" and "leg", because is kind of looks like a stomach (bulging region) of your leg. It is a powerful muscle of the lower posterior leg that has two heads. The gastrocnemius muscles originate just above the knee and insert at the heel.
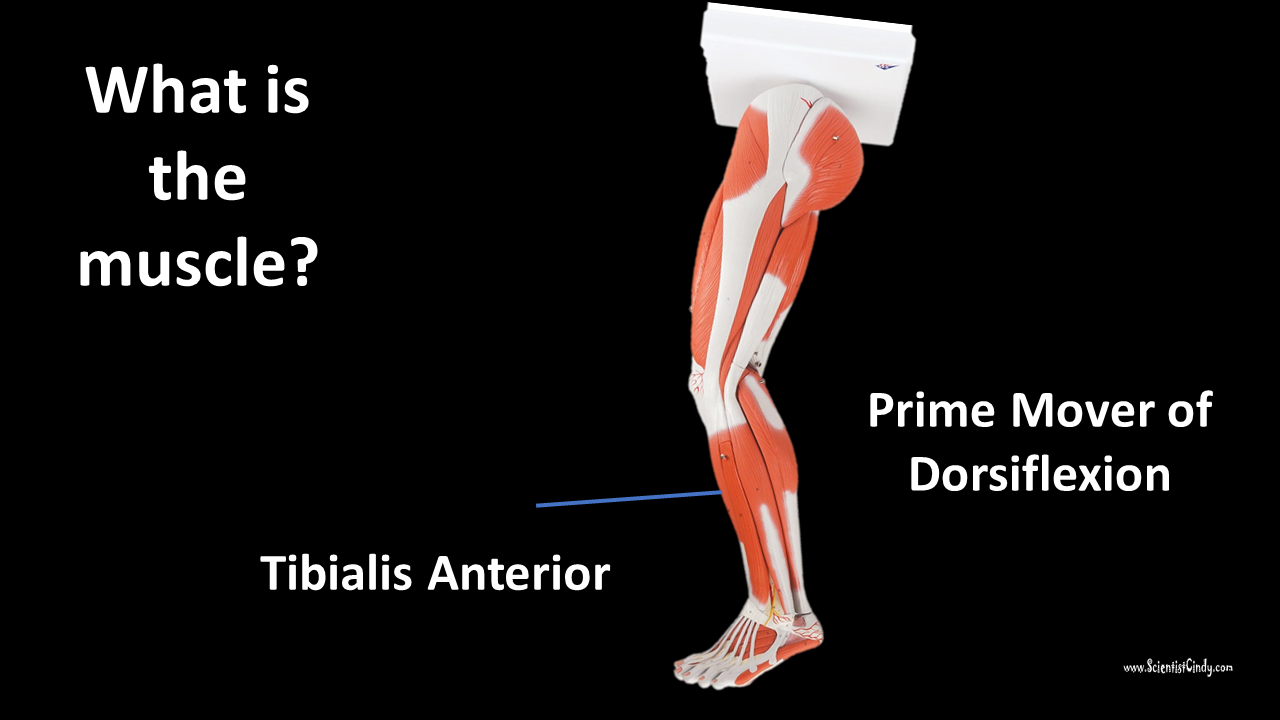
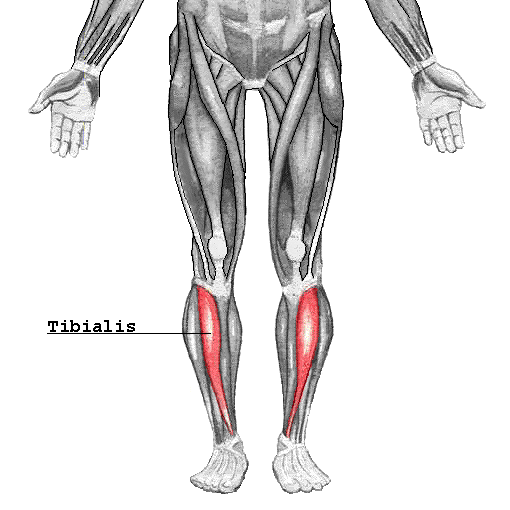
Tibialis Anterior
By Chrizz from sv, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=3086148