BIO 111L General Biology Laboratory
Lab 3 - How Do Cell Respond to Changing Environments
Membrane Transport Processes
|
|
WATCH THE VIDEO!
CELL TRANSPORT
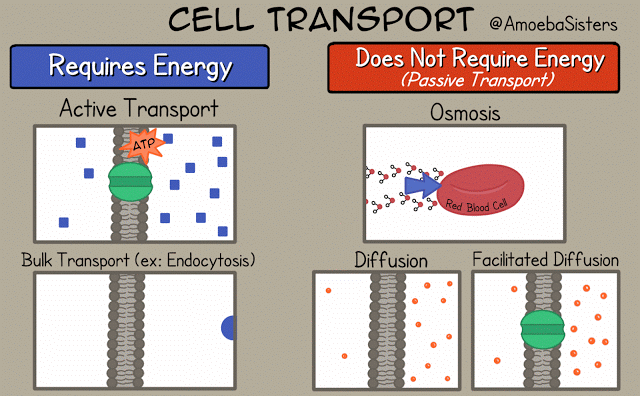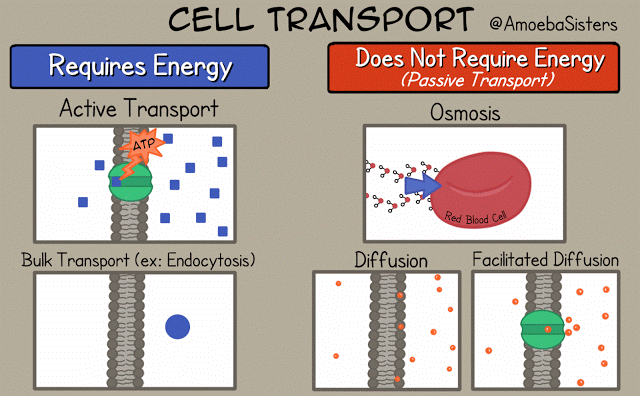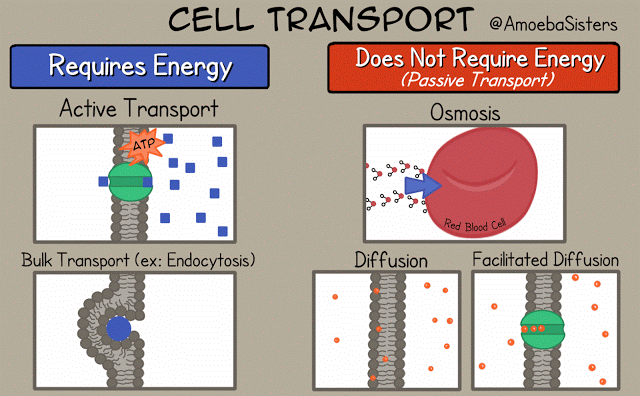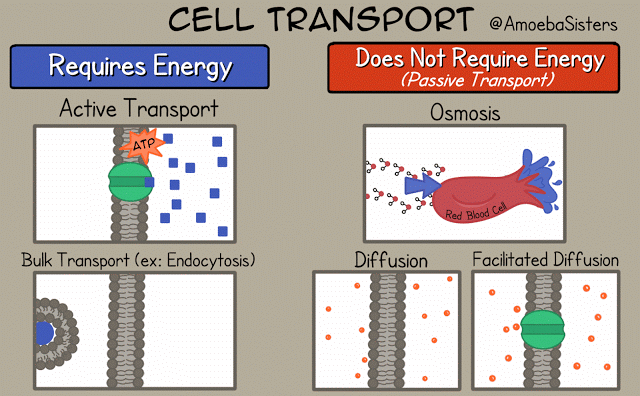
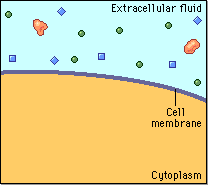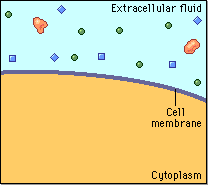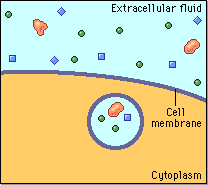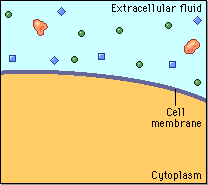
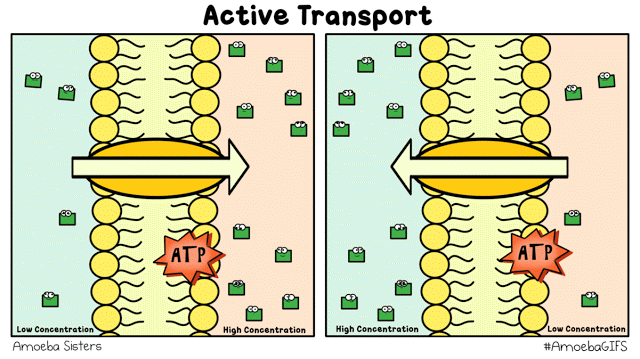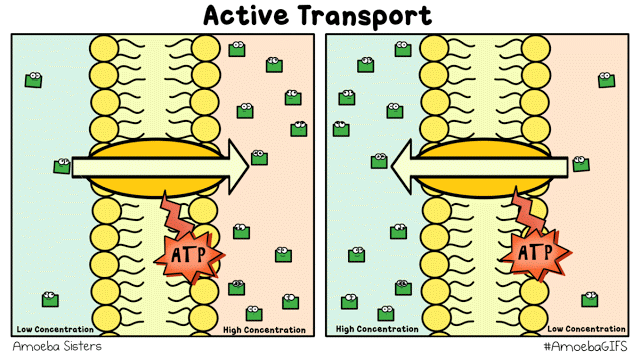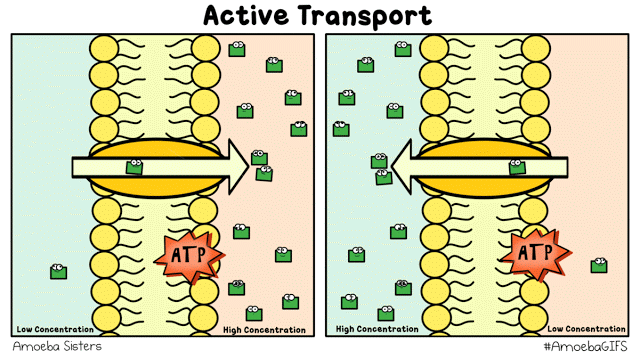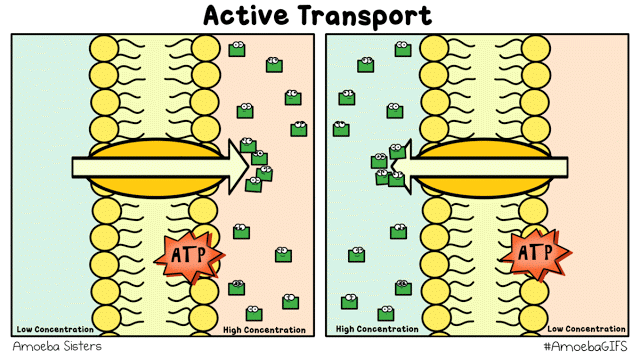
There are different ways that the cell membrane has to get substances from one side to the other. Some of these ways require energy. These ways are termed "active transport". Active transport includes bulk transport that uses vesicles to move relatively large amounts of substances across the membrane and active transport through specialized channels that use the power of ATP.
Other means of transportation across the membrane do not required energy and are termed "passive transport". Means of passive transport include osmosis, diffusion and facilitated diffusion.
Other means of transportation across the membrane do not required energy and are termed "passive transport". Means of passive transport include osmosis, diffusion and facilitated diffusion.
DIFFUSION
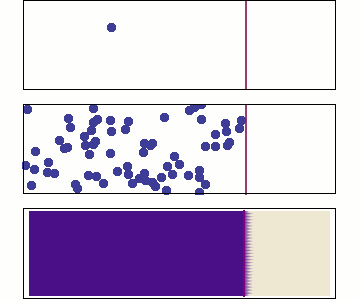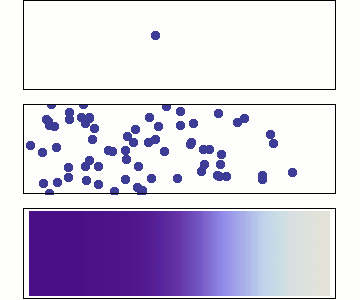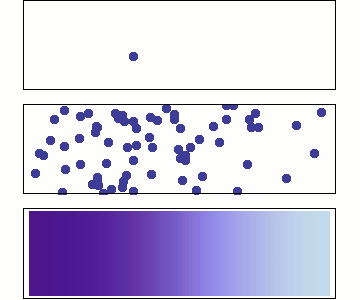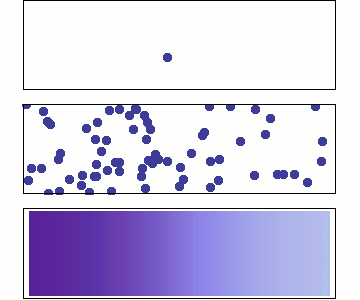 Diffusion occurs because molecules and atoms are always in motion.
Diffusion occurs because molecules and atoms are always in motion.
Before we talk about osmosis, we must first understand diffusion. The word diffusion comes from the Latin word for "spreads out". In nature, molecule will behave in such a way to "spread out" from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, until a time in which those concentration become equal. At this state, the substance is said to be at equilibrium. it is this phenomenon that is responsible for the air currents and ocean currents, as well as the diffusion of a substance in liquid. Since our cells are in an aqueous environment, we will be looking at this type of diffusion.
Gasses and liquids behave this way because their atoms are always in motion. This motion is called "Brownian motion". Brownian motion causes molecules to collide with each other which makes them spread out to maximize their area to move in. They want some"elbow room"!
Gasses and liquids behave this way because their atoms are always in motion. This motion is called "Brownian motion". Brownian motion causes molecules to collide with each other which makes them spread out to maximize their area to move in. They want some"elbow room"!
2
After some time, that pee will then spread out evenly over the volume of that pool reaching the unsuspecting pool-dwellers at the far end of the pool.
This is because in diffusion, liquids (or gasses) flow from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, until an equilibrium (no difference in concentration) is achieved. In other words, the pee is equally distributed everywhere.
This is because in diffusion, liquids (or gasses) flow from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, until an equilibrium (no difference in concentration) is achieved. In other words, the pee is equally distributed everywhere.
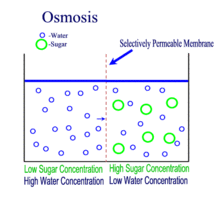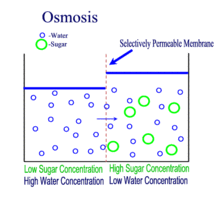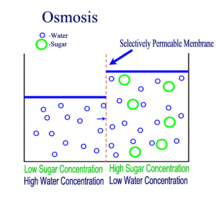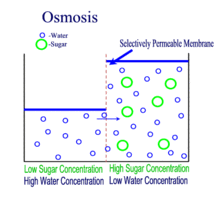
OSMOSIS
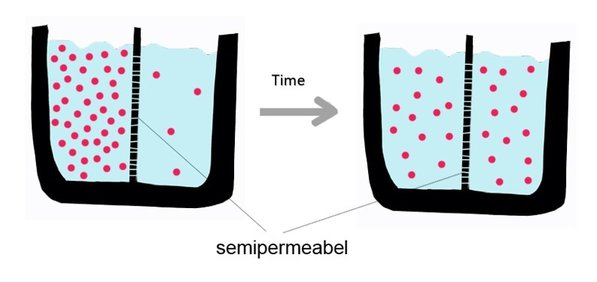
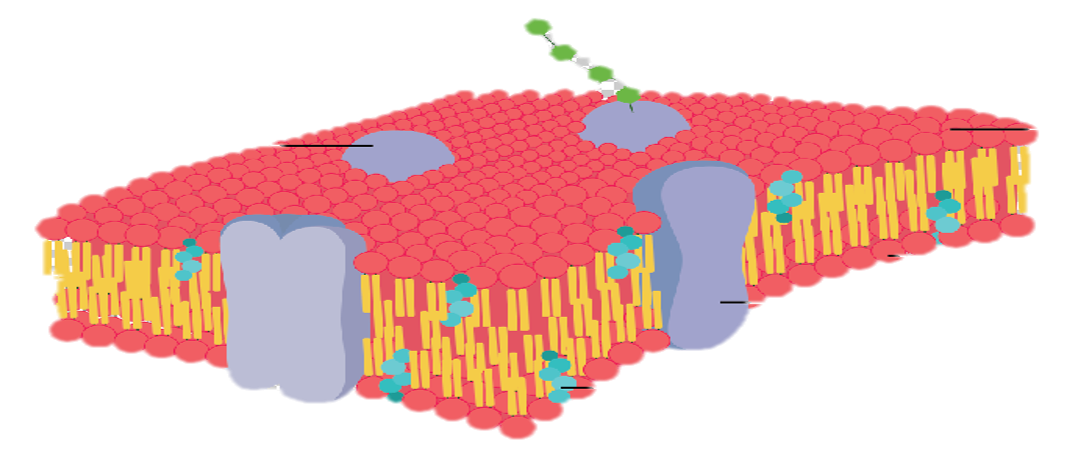
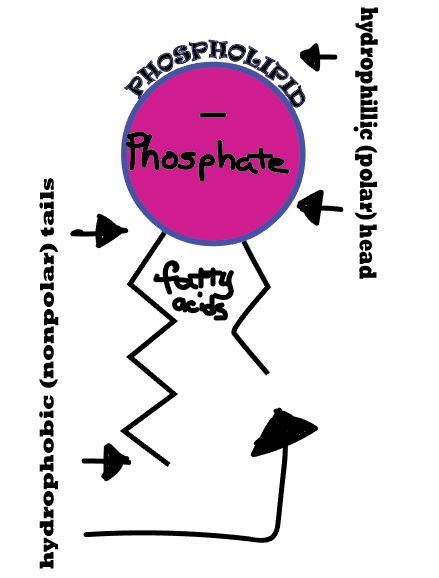
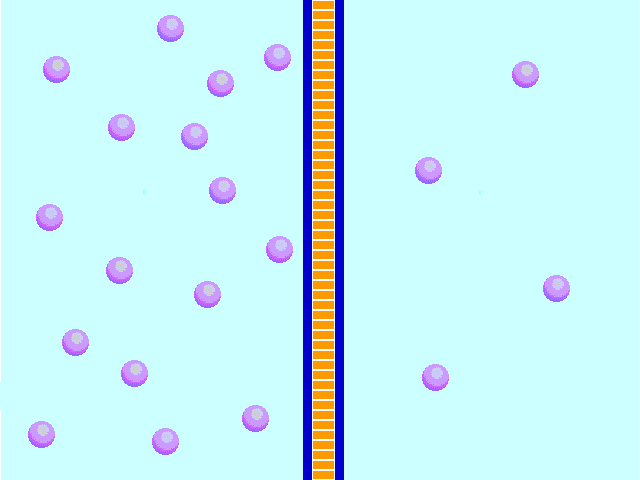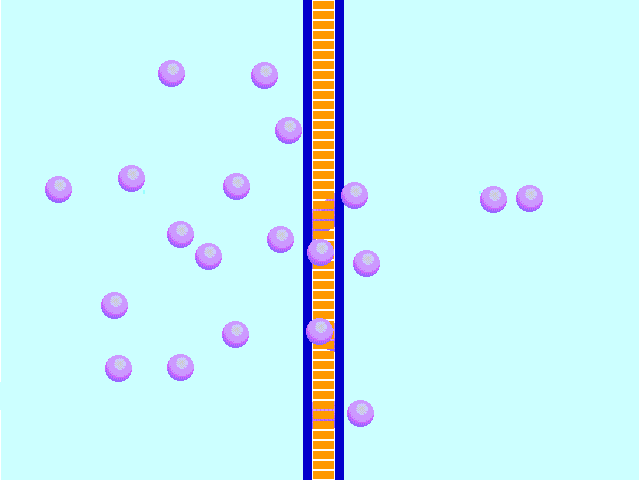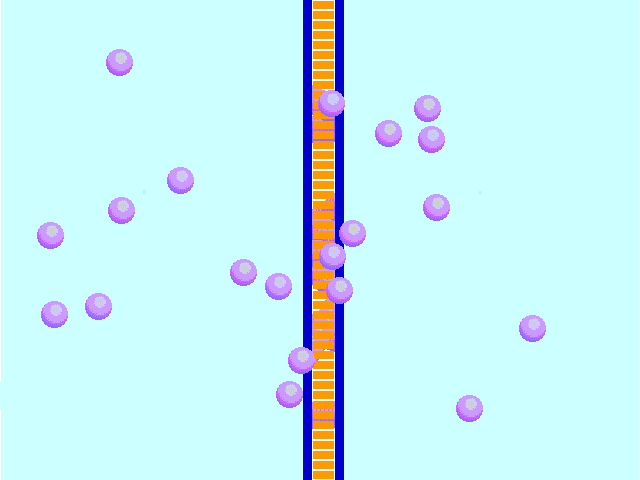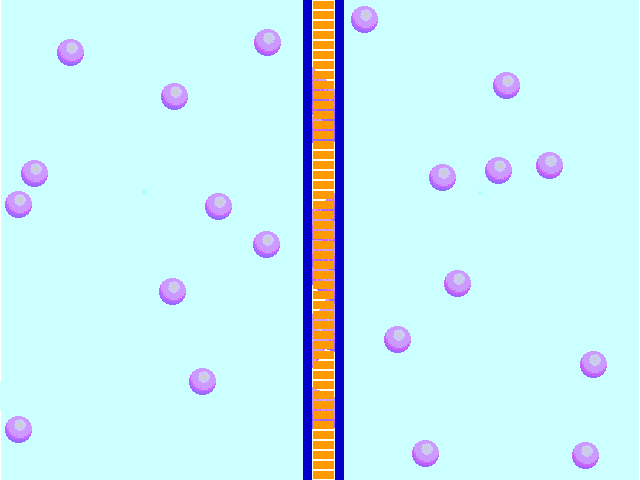
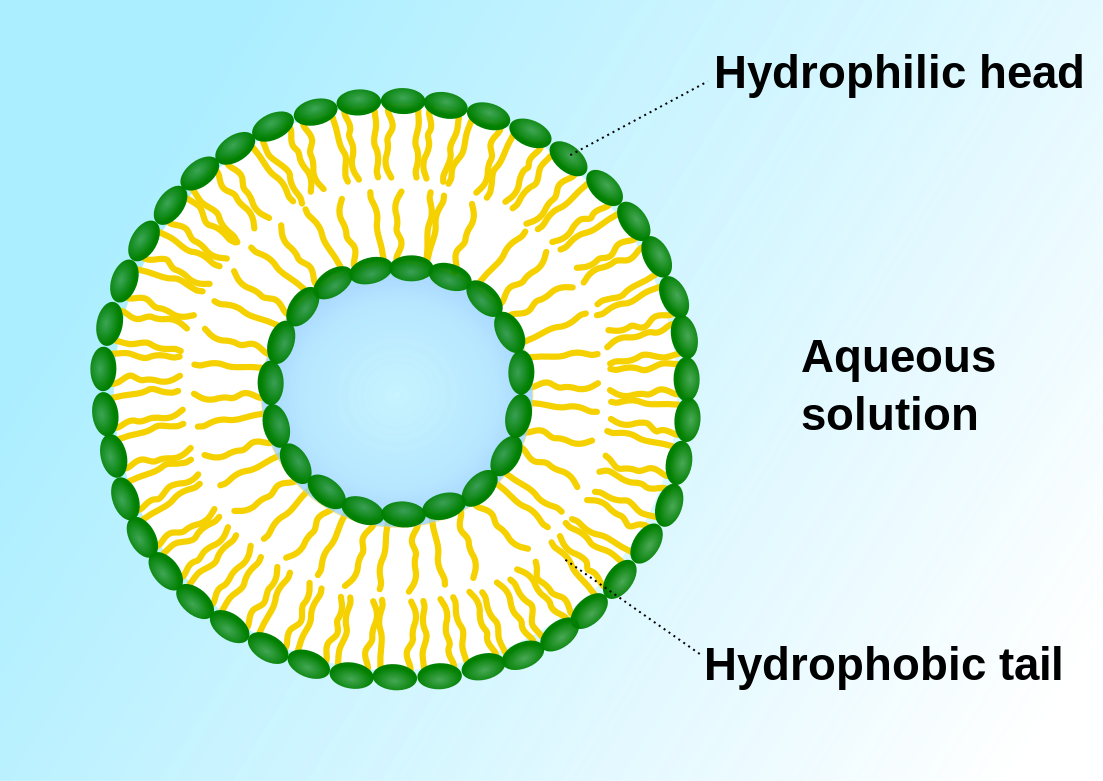
Diffusion behaves in the way just described, because it is able to move freely and unhindered. In biological systems, molecules are not permitted to move freely. The movement of ions and molecules is tightly regulated by the cell membrane. The cell membrane is selectively-permeable . Substances are permitted to pass through under certain conditions through pores or channels or transporters. The movement of water across the membrane is of particular importance to biological systems. Failure of the cell to maintain osmotic balance with its environment can have a catastrophic negative effects. The movement of water molecules across the semi-permeable cell membrane is called osmosis.
To understand this concept, it is important to think about a solution in terms of its components.
- The liquid substance that acts to dissolve particles, is called the solvent.
- The particles that get dissolved are called the solute.
In osmosis, we only concern ourselves with the movement of water molecules (H2O) across the cell membrane. As we saw in diffusion, molecules will travel from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
Then we can define solutions in terms of the concentration of solute and define how cells will be effected by exposure to those solutions! We can define solutions in this way as being..
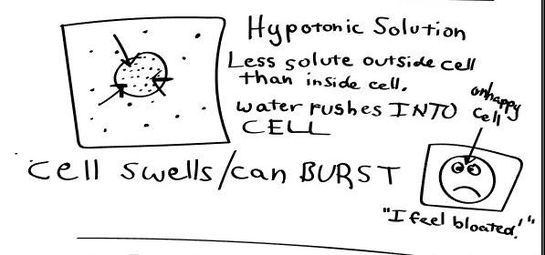
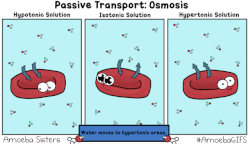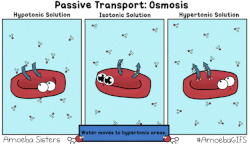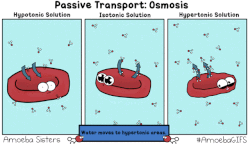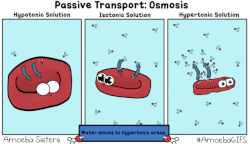
- Hypotonic - a hypotonic solution has a LOWER concentration of solutes than are found in the intracellular fluid
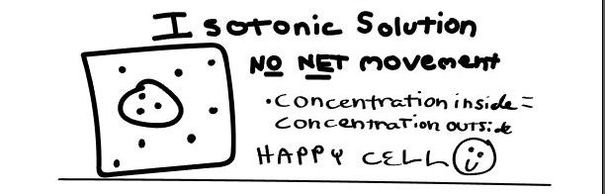
- Isotobic - an isotonic solution is one that has the SAME concentration of solutes that are found in the intracellular fluid
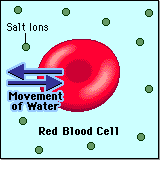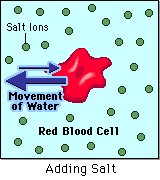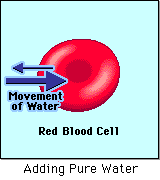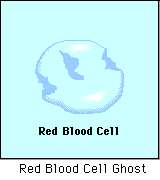
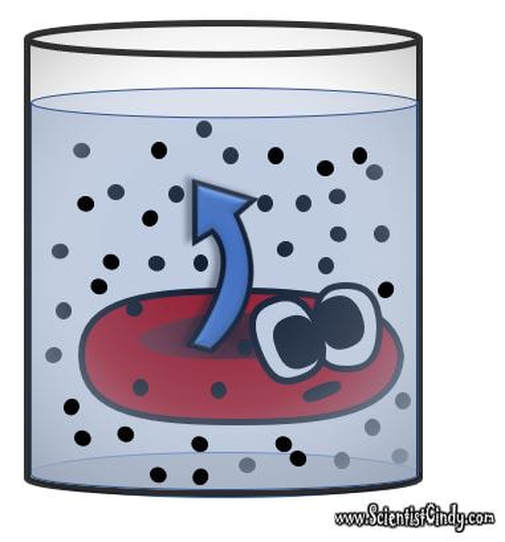
- Hypertonic - a hypertonic solution has a HIGHER concentration of solutes than are found in the intracellular fluid
|
In biological systems, the solute in unable to freely diffuse across the cell membrane, so it builds up a concentration gradient. This means that there is a higher concentration of solute on one side of the membrane than there is on the other.
The water molecules, on the other hand, CAN move freely across the cell membrane and will travel from an area of high concentration to low concentration. This traveling from high concentration to low concentration can be termed as travelling down its concentration gradient. |
|
|
|
HYPOTONIC SOLUTION
ISOTONIC SOLUTION
HYPERTONIC SOLUTION
|
|
|