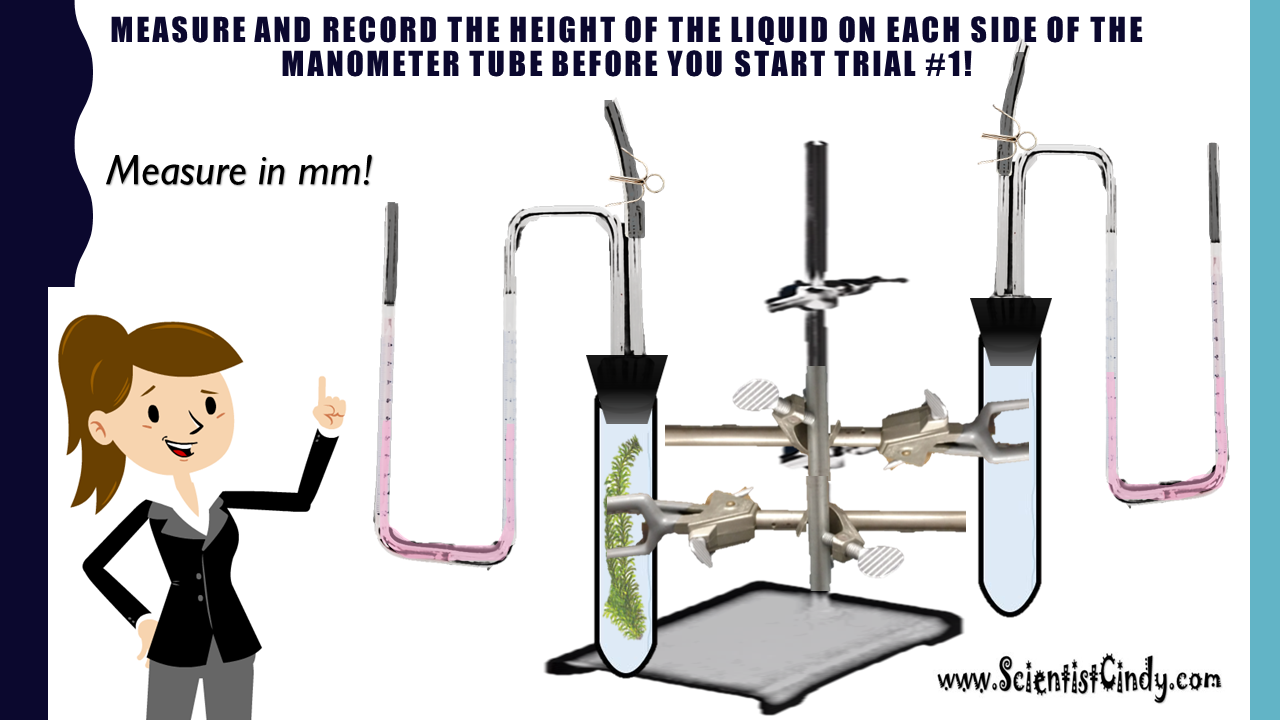
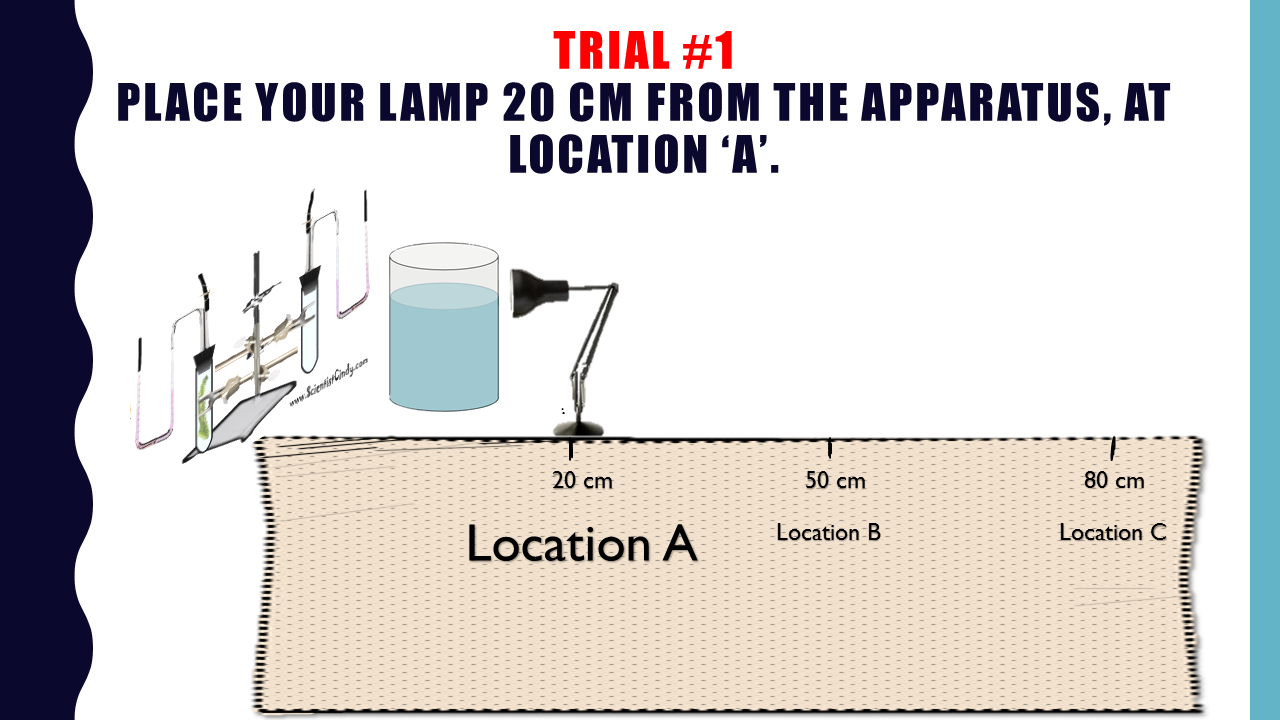
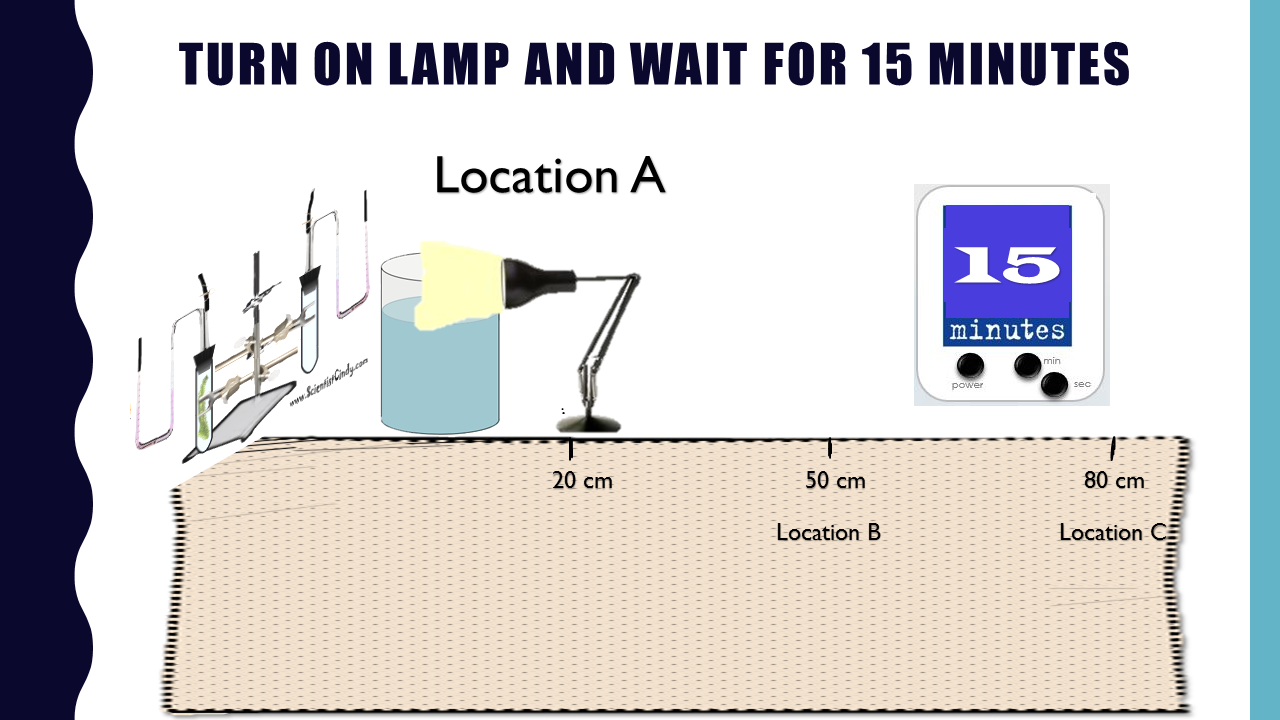
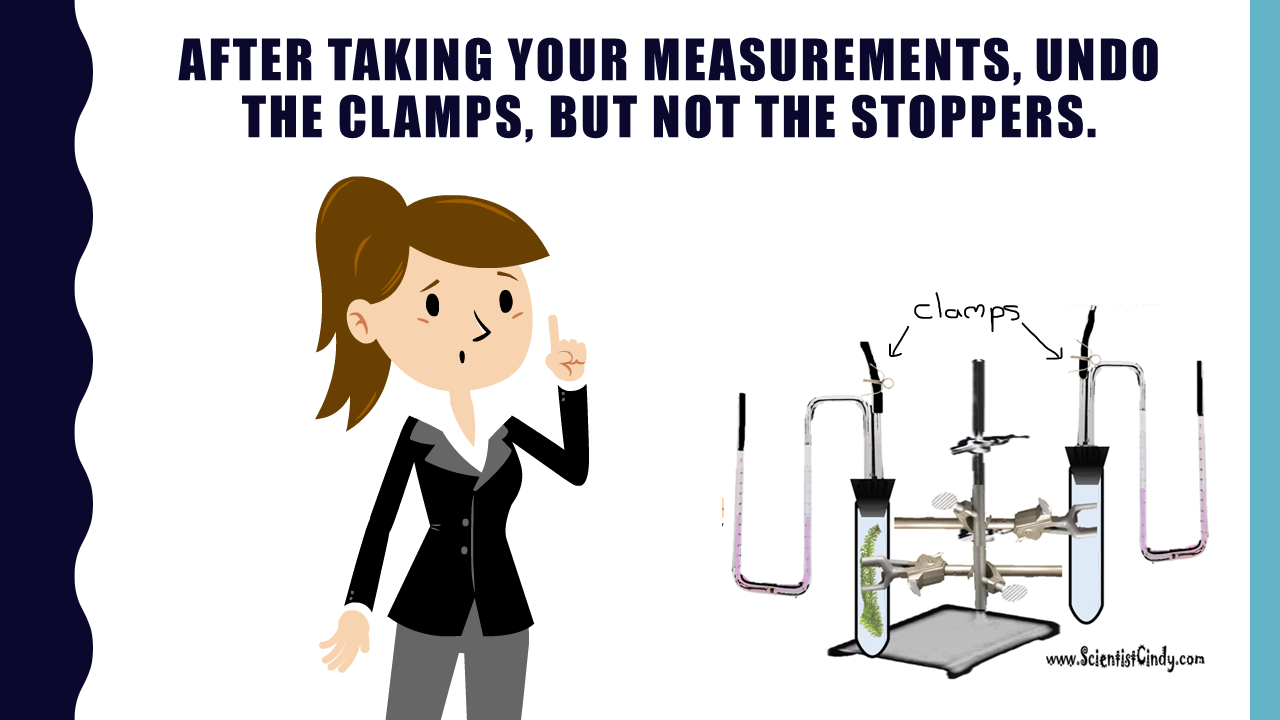
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
To edit, simply click directly on the text and add your own words.
Use this text to go into more detail about who you are.
Use this text to go into more detail about who you are.
General Biology Laboratory
PHOTOSYNETHESIS
Terminology
Photosynthetic Pigment - A photosynthetic pigment is a pigment that captures light energy needed for photosynthesis. Sometimes referred to as an accessory pigment.
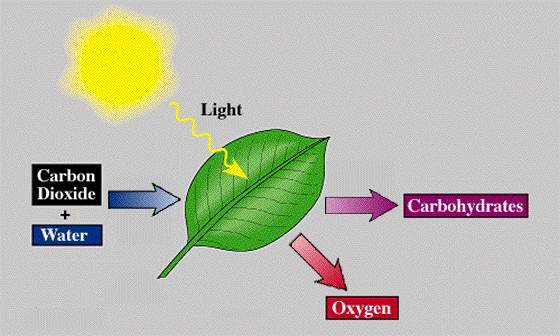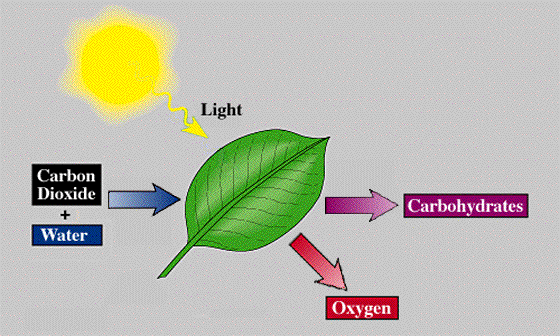
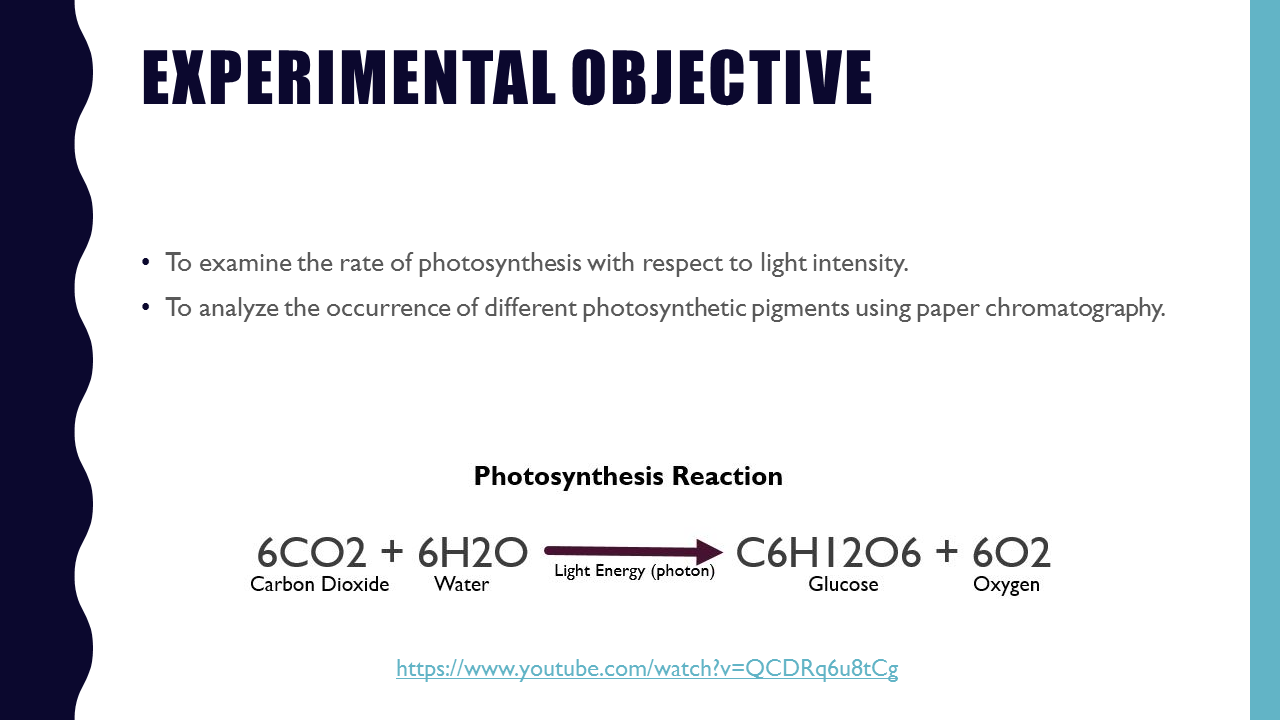
Photosynthesis - The process by which plants (and some bacteria) are able to make glucose from carbon dioxide and water using the energy of sunlight.
Producer / Autotroph - A producer is any organism that can makes its own food using inorganic materials like sunlight or inorganic chemicals like sulfur and oxygen.
Carotinoids - Carotinoids are orange pigments, categorized as an accessory pigments, that exists in plants. They function to transmit (reflect or send out) the light energy that they absorb from chlorophyll.
Chlorophyll - Chlorophyll is a green photosynthetic pigment that exists in chloroplasts in plants and reflects green light. Chlorophyll absorbs light energy especially well in the red and blue wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum. All photosynthetic pigments have the ability to capture energy from sunlight that is needed for photosynthesis.
Xanthophyll - Chlorophyll is a yellow pigment categorized as an accessory pigment that exists in plants that absorbs wavelengths of light that chlorophyll cannot absorb.
Solvent - A solvent is defined as the liquid in which a solute is dissolved.
Solubility - Solubility is the property of a substance that defines how well it can dissolve in a particular solvent. For example, salt is more soluble in water than sugar is in water.
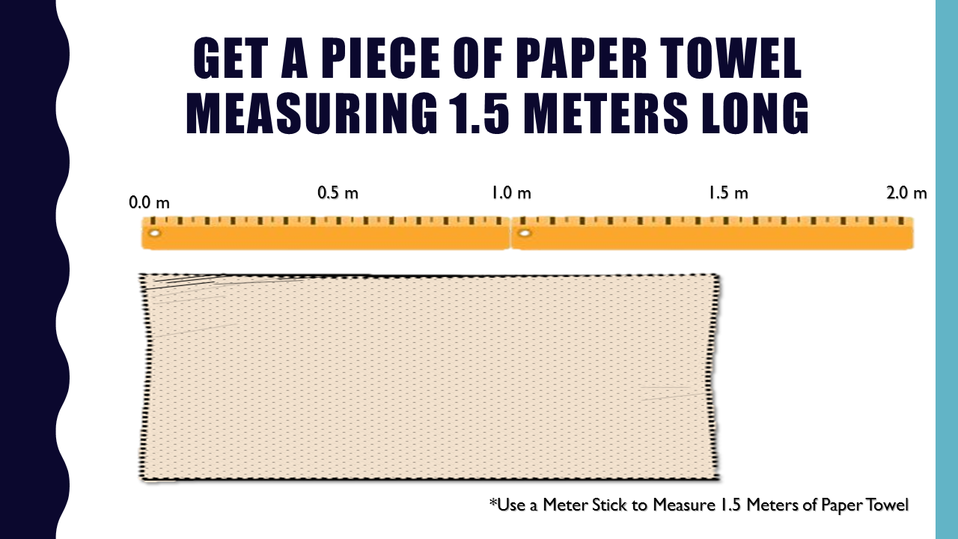
Paper Chromatography - Paper chromatography is a method of chemical analysis that separates different liquids based upon their ability to dissolve in a substance.