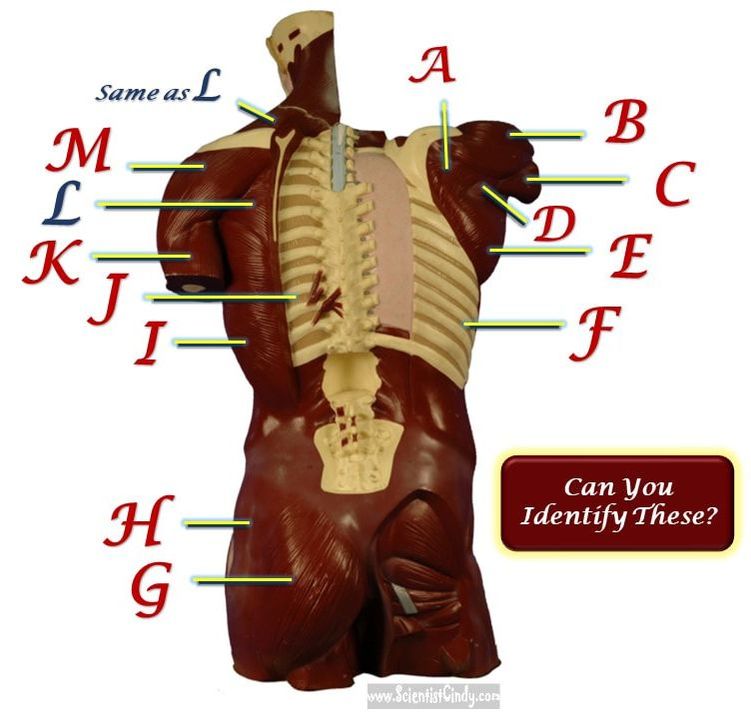
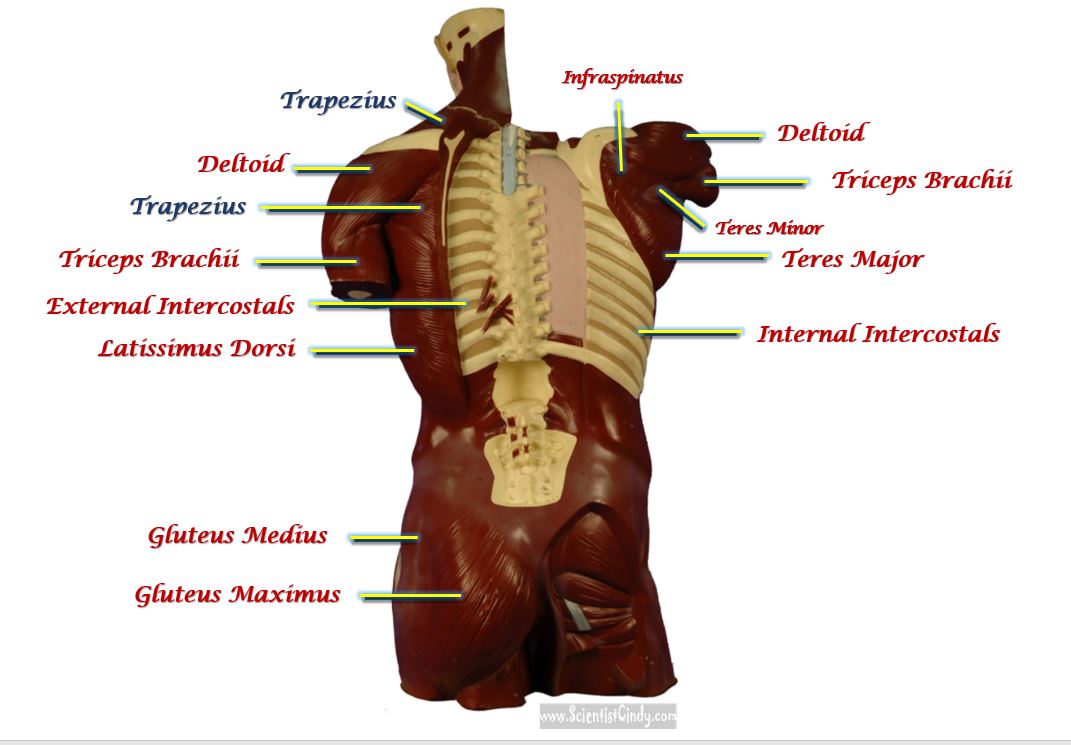
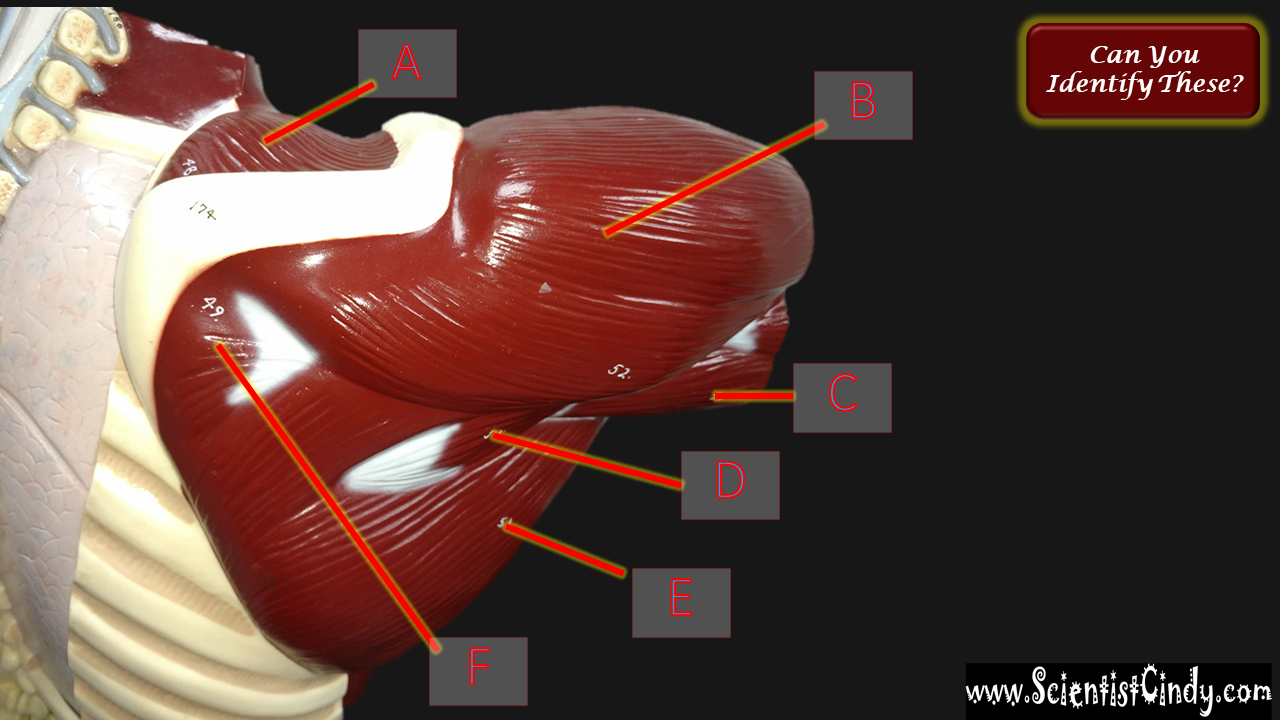
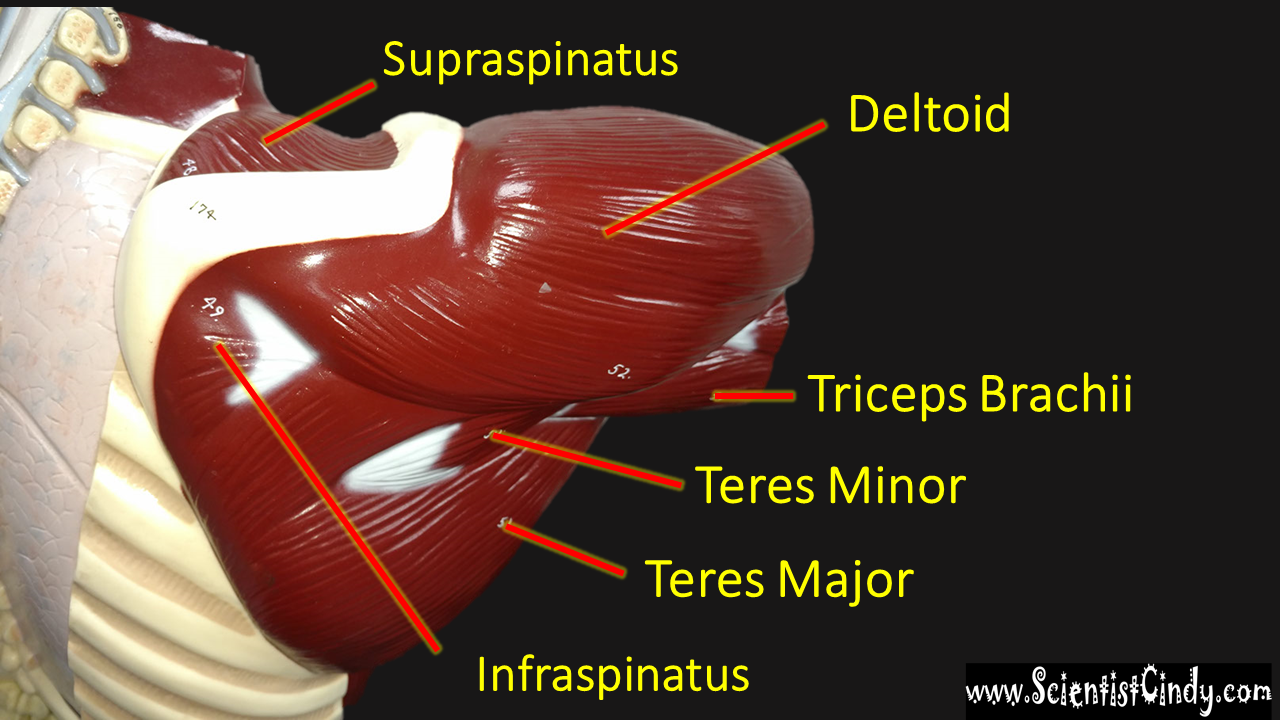
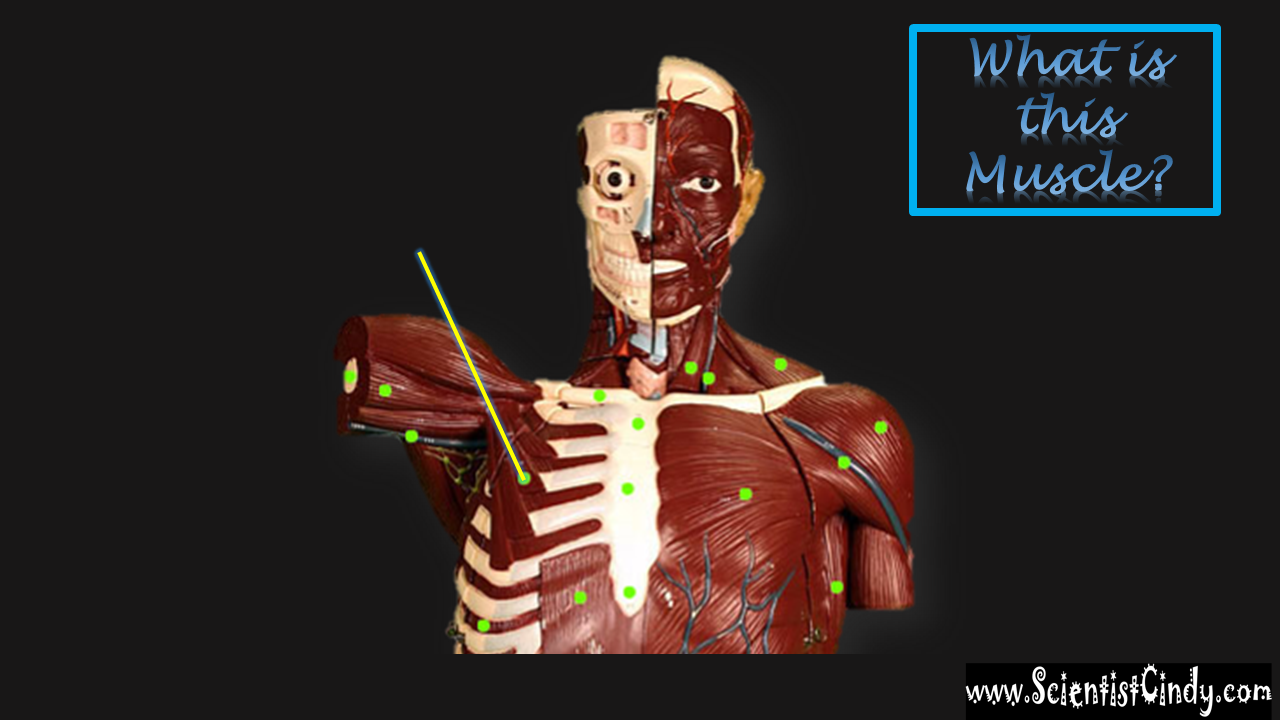
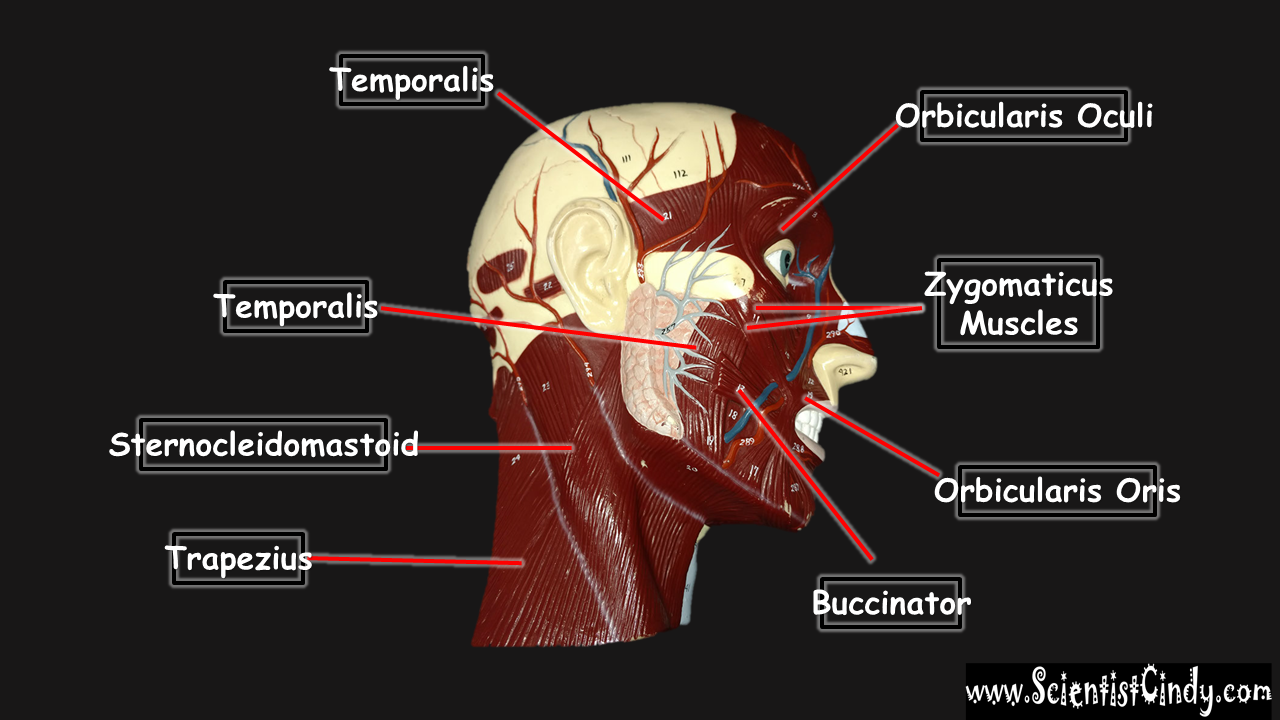
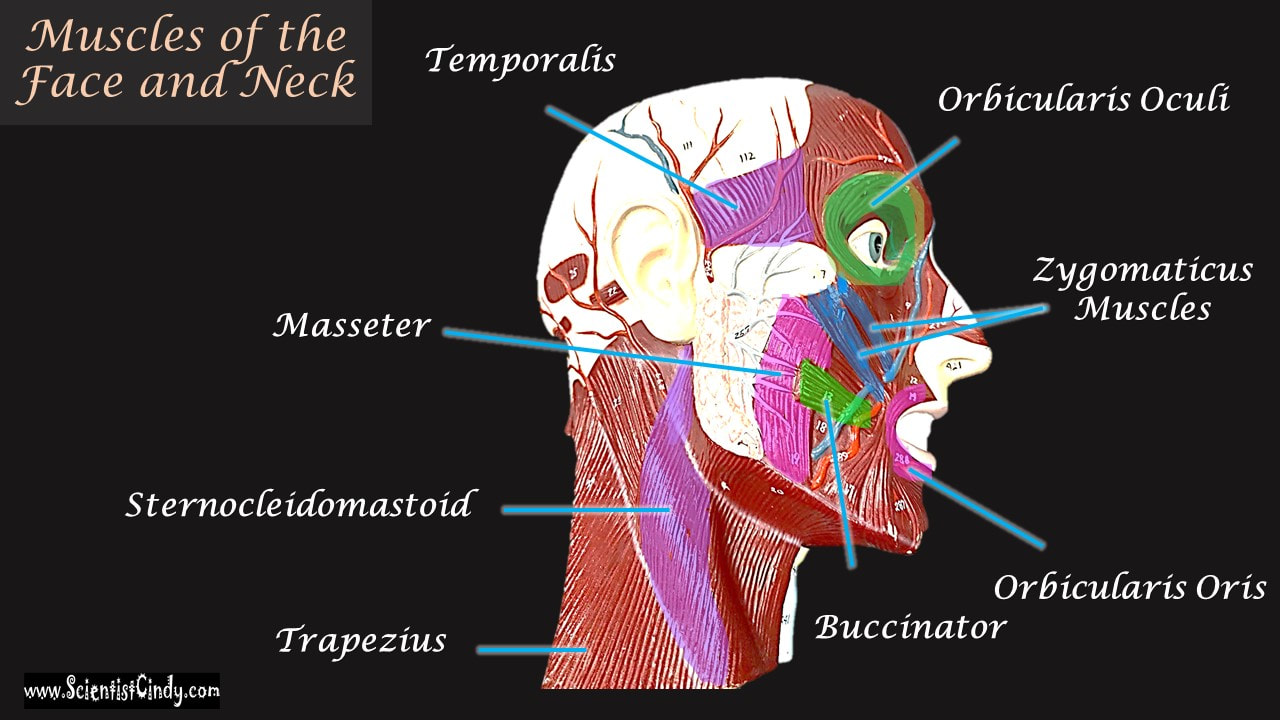
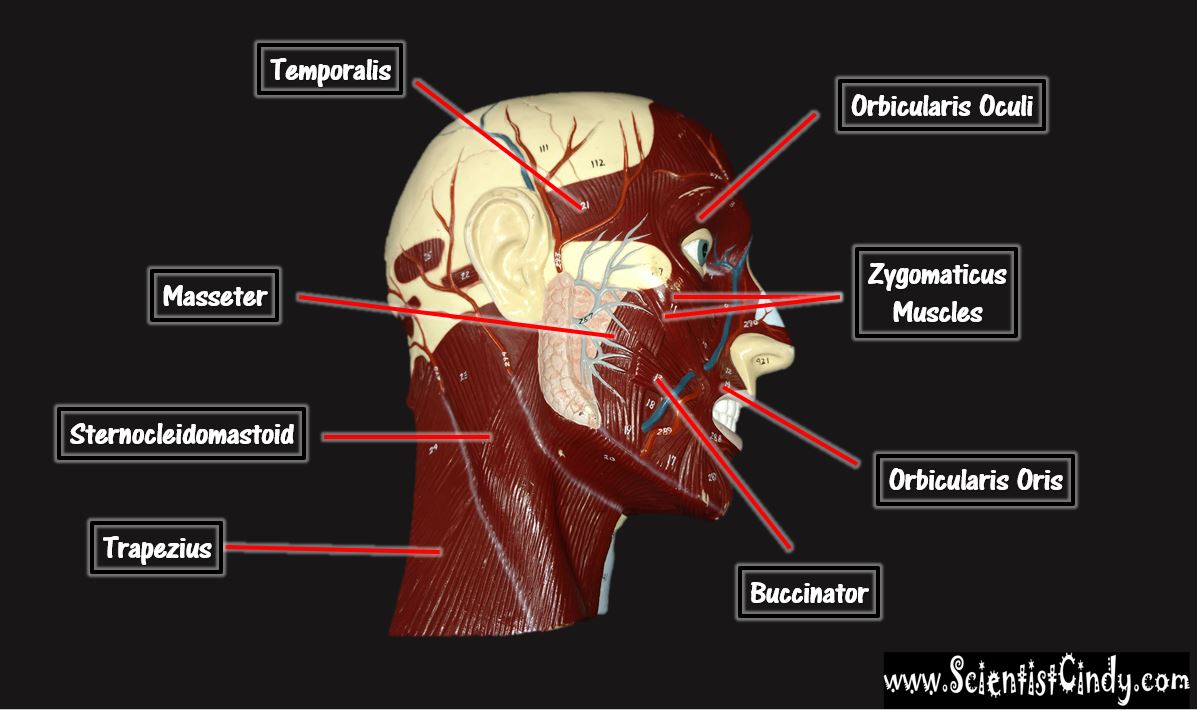
STUDY GUIDE FOR SAN BERNARDINO VALLEY COLLEGE
ANATOMY CLASS
MUSCLE PRACTICAL AND MIDTERM
STUDY GUIDE
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Muscles always PULL they never PUSH - this is why we call it muscle contraction.
- When the muscle contracts it shortens, which applies force on the bones it is attached to by PULLING on them.
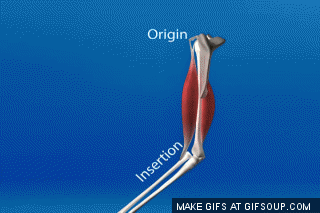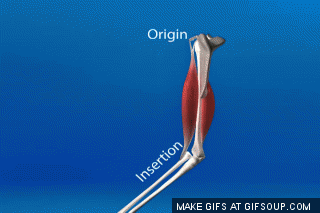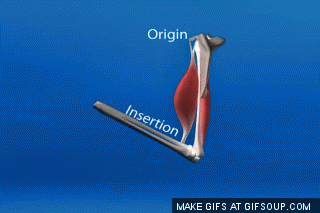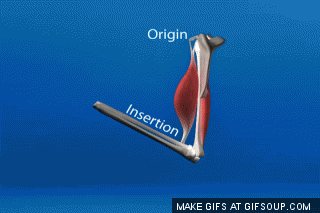
It is Important to be Able to Distinguish Between the Origin and the Insertion Point of a Muscle. This information will tell us the function of the muscle. Remember that structure equals function!
Skeletal muscles attaches to at least 2 bones, and spans one movable joint. The way that these muscles attach to the bones of your body, is through TENDONS. Muscles always PULL they never PUSH. When a muscle contracts, it pulls the bones it connects to closer to one another, by decreasing the angle of the movable joint that is spans.
Typically, when we contract a muscle, one of the bones the muscle attaches to moves a lot, while the other bone(s) the muscle attaches to remains relatively "fixed" in space.
Skeletal muscles attaches to at least 2 bones, and spans one movable joint. The way that these muscles attach to the bones of your body, is through TENDONS. Muscles always PULL they never PUSH. When a muscle contracts, it pulls the bones it connects to closer to one another, by decreasing the angle of the movable joint that is spans.
Typically, when we contract a muscle, one of the bones the muscle attaches to moves a lot, while the other bone(s) the muscle attaches to remains relatively "fixed" in space.
- The origin is the attachment site that remains relatively "fixed in space" during muscle contraction
- The insertion is the attachment site that moves quite a bit during muscle contraction.
|
When a muscle contracts in the body, you will notice one of the bones that muscle attaches to moves quite a bit, but the other moves very little or not at all! Let's look at why.
|
|
|
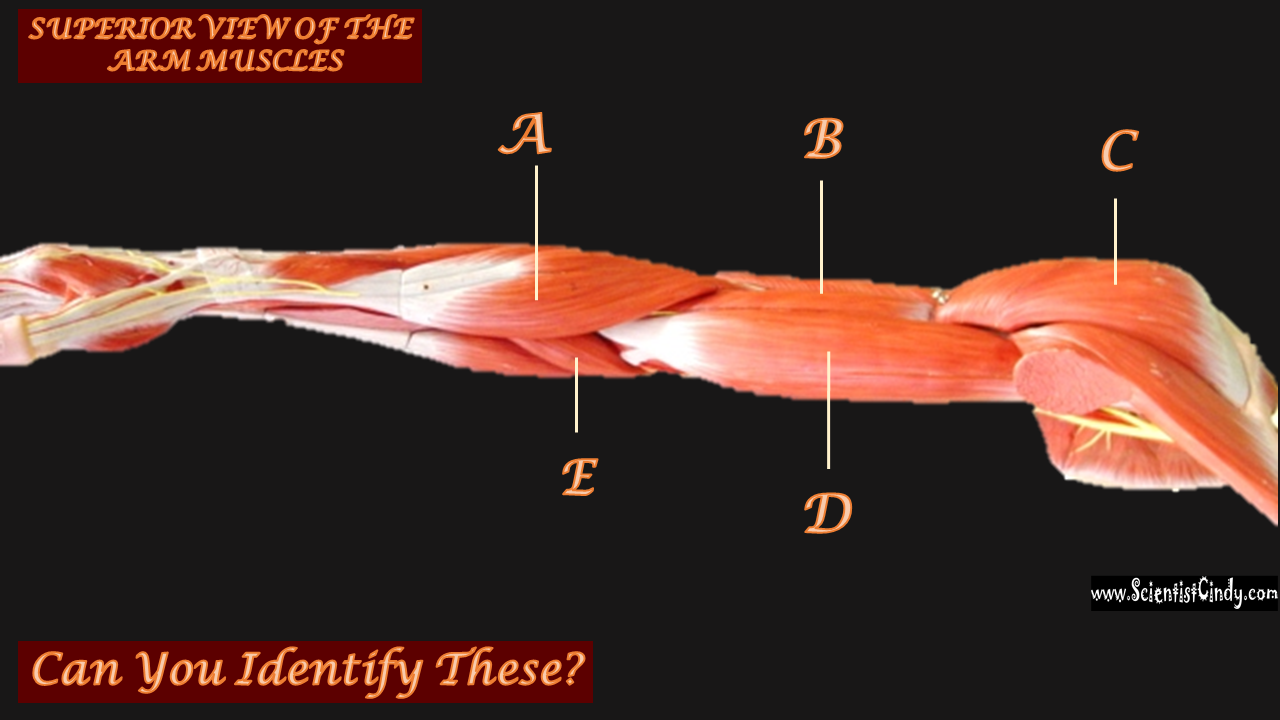
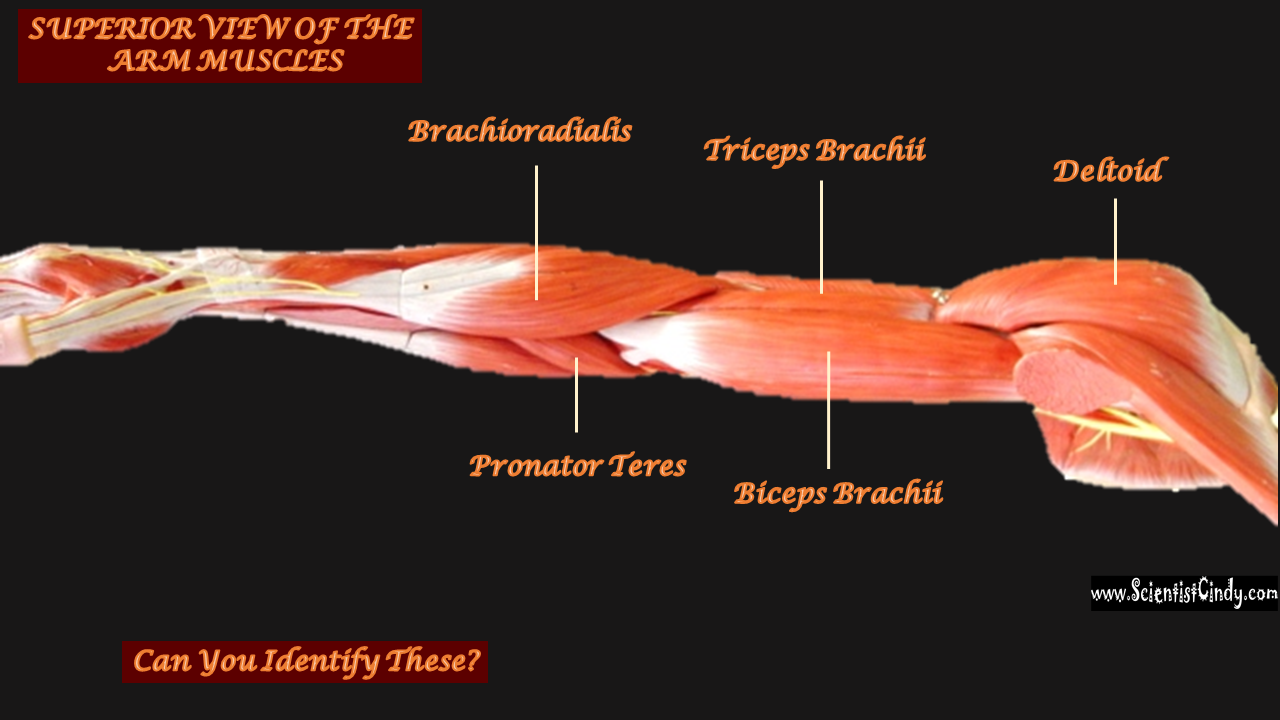
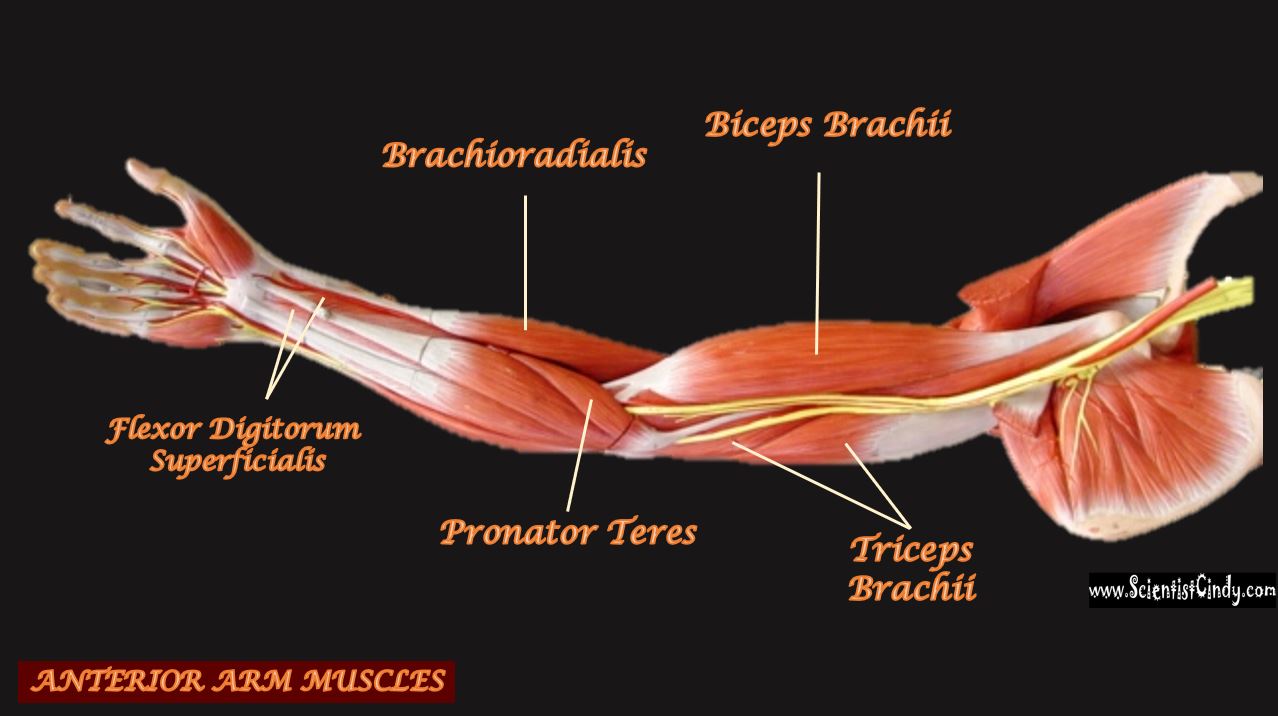
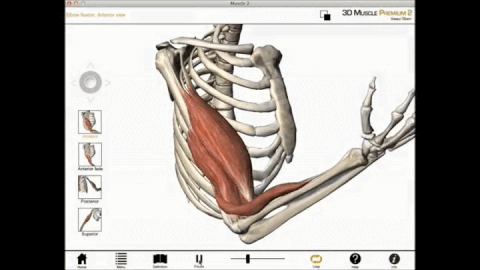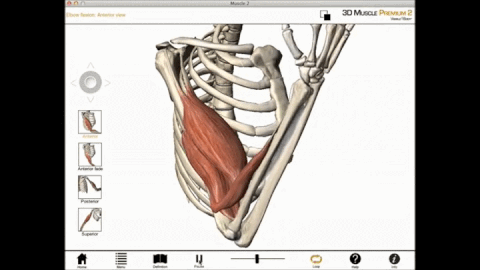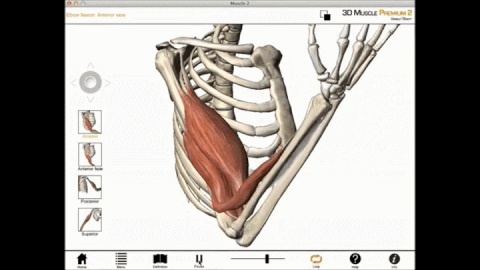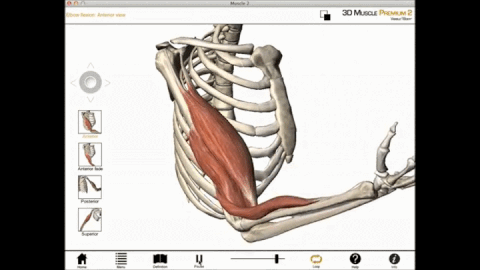
For example, the biceps muscles are muscles that lie in the anterior portion of the upper arm. The biceps attach to the radius of the lower arm and span the elbow which is a movable joint. When the biceps are contracted, the biceps shorten. This shortening of the biceps applies a force on the upper and lower arm bones to which it is attached. The direction of this force is to bring the upper arm bone and lower arm bones closer together. Another way of saying the same thing is to say the force is directed to decrease the angle of the elbow joint.
|
Even though force is applied on both the upper and the lower arm bones, only the lower arm moves, while the upper arm moves relatively little.
|
Since during contraction of the biceps muscles we observe the lower portion of the arm move while the upper arm bone remains relatively stationary, we know that the point of origin for the biceps muscle must be located in the bone of the upper arm (the humerus).
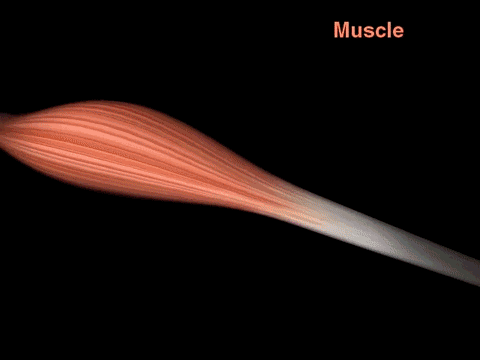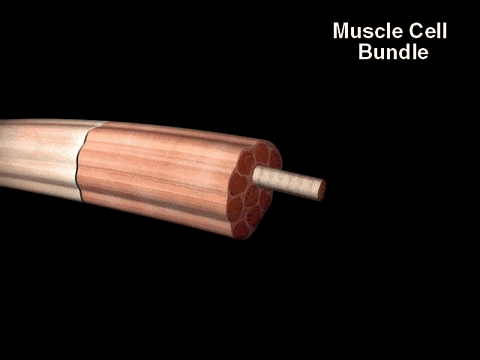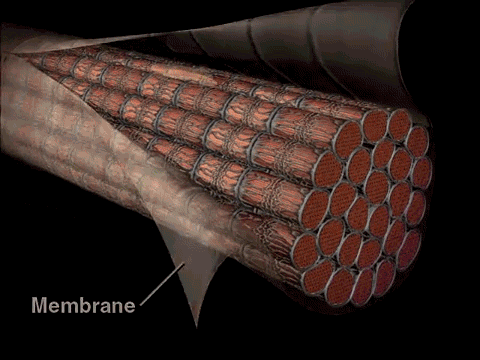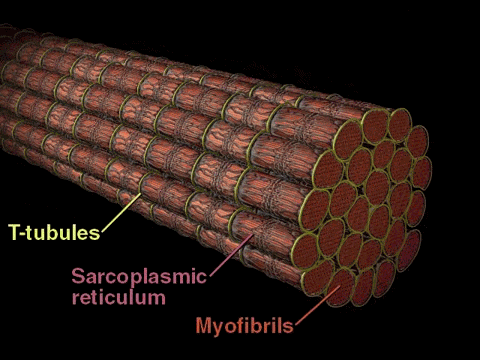
The Muscle Cell is also known as a muscle fiber, because it is long and cylindrical.
Skeletal muscle fibers are extremely long, cylindrical cells. A single muscle fiber can be up to a foot long in some muscles. This unique property is made possible, because the muscle fiber itself is actually formed from the fusion of literally hundreds of embryonic cells that get fused together during development. Since skeletal muscle cells (muscle fibers) are made from the fusion of hundreds of embryonic cells, they contain many nuclei. In other words, they are multinucleated.
Skeletal muscle fibers are extremely long, cylindrical cells. A single muscle fiber can be up to a foot long in some muscles. This unique property is made possible, because the muscle fiber itself is actually formed from the fusion of literally hundreds of embryonic cells that get fused together during development. Since skeletal muscle cells (muscle fibers) are made from the fusion of hundreds of embryonic cells, they contain many nuclei. In other words, they are multinucleated.
FLEXION AND EXTENSION
Remember that muscles only have 2 actions; they can either contract (shorten) or relax. This means that muscles will essentially 'pull' on the bone it attaches to. Rules for determining muscle function:
- When the muscle passes in front of (anterior to) the joint, it functions in FLEXION. Flexion decreases the angle of the joint.
- When the muscle passes in behind (posterior to) the joint, it functions in EXTENSION. Extension increases the angle of the joint.
|
Flexion is movement that decreases the inner angle of the joint. A flexor is a muscle that causes flexion.
Extension is movement that increases the inner angle of the joint. An extensor is a muscle that causes extension. Extension and Flexion are Movements of Hinge Joints, such as the knee and elbow. |
|
How can I tell the function of muscle? The function of a muscle can be inferred by the position of the muscle relative to the joint it crosses.Remember, a muscle attaches to at least 2 bones and spans at least 1 joint. In order to determine the function of the muscle, you need to see if that muscle passes in front or behind the joint it spans.
|
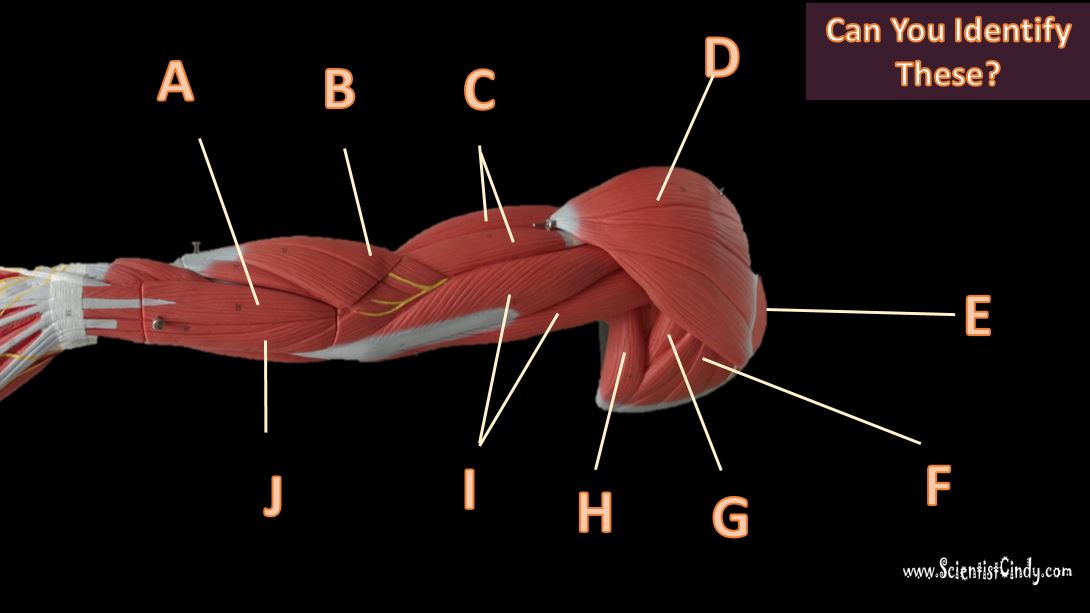
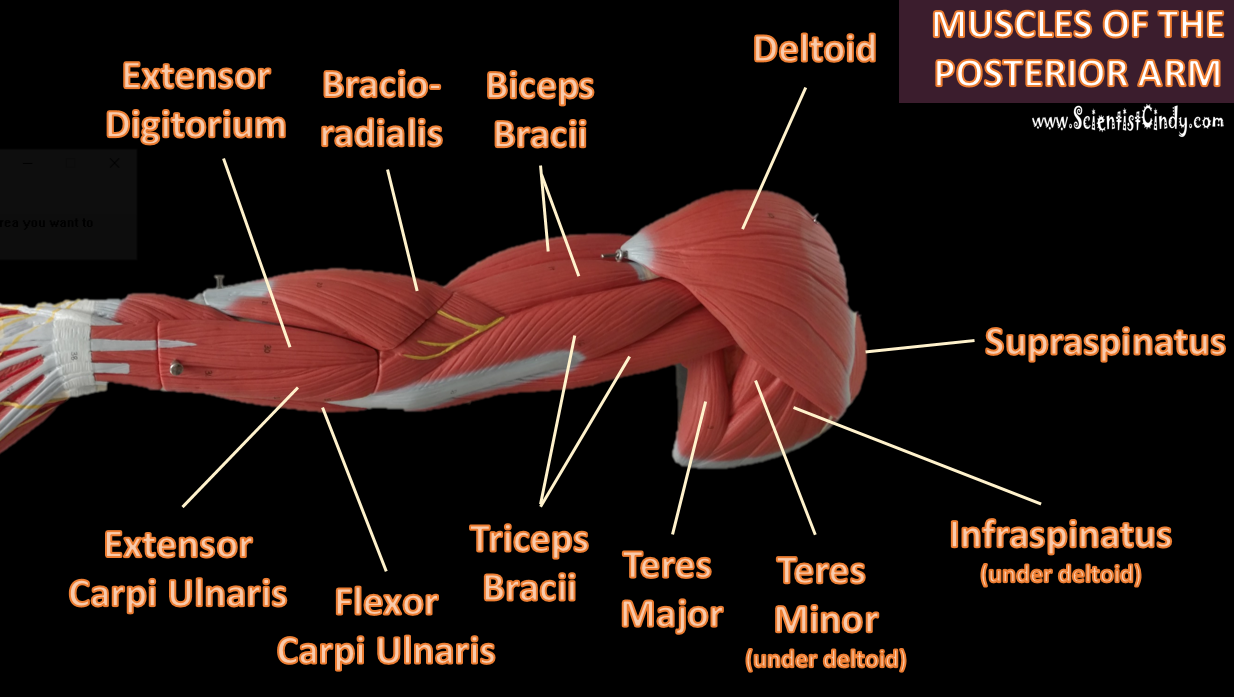
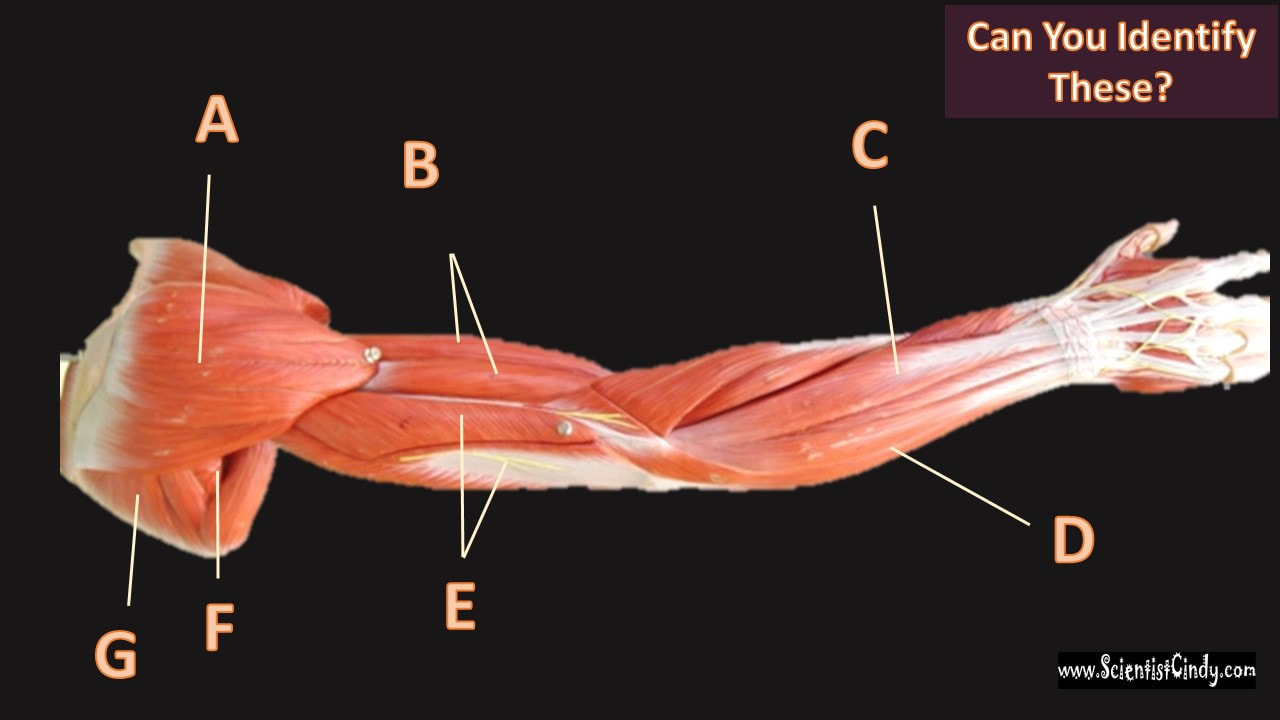
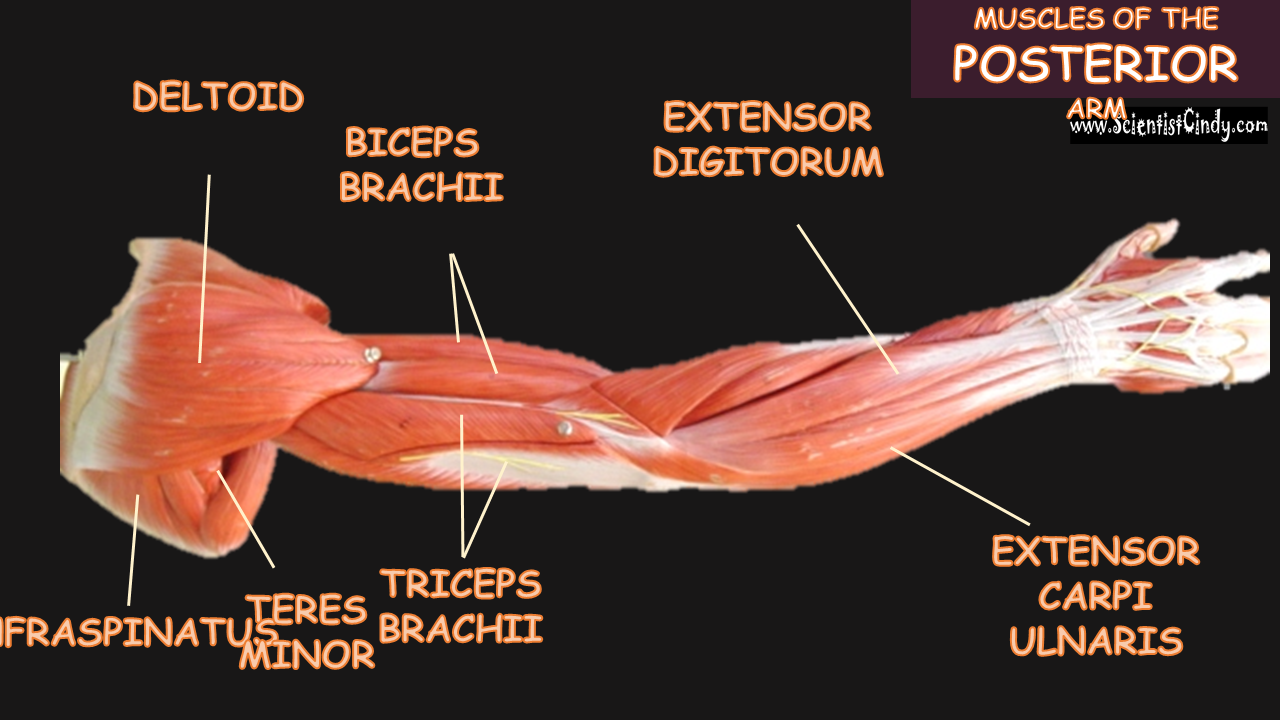
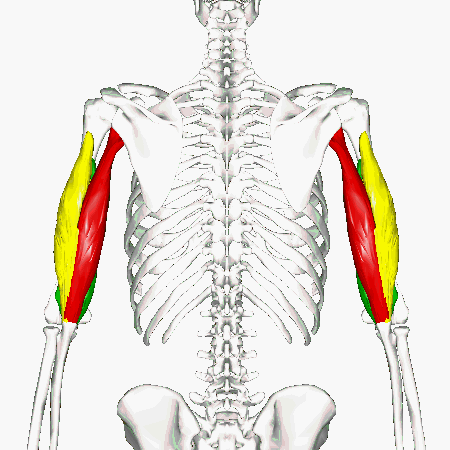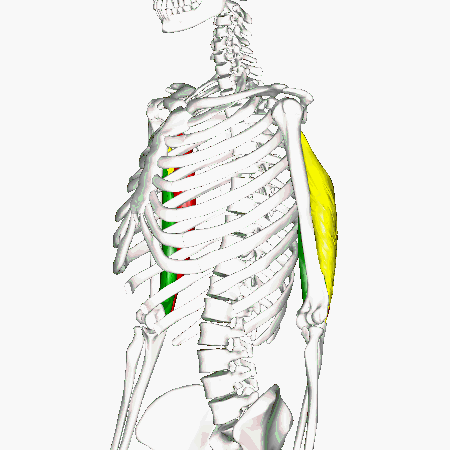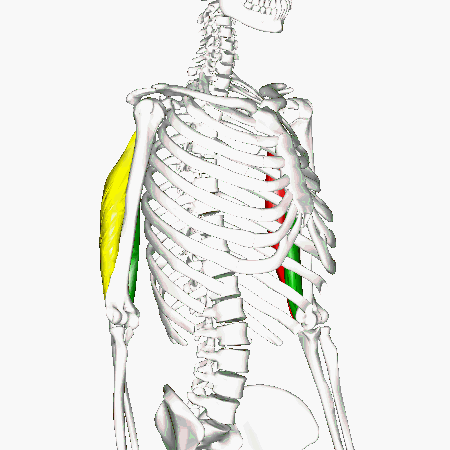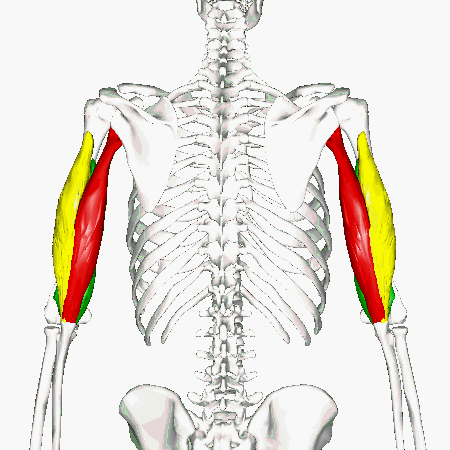
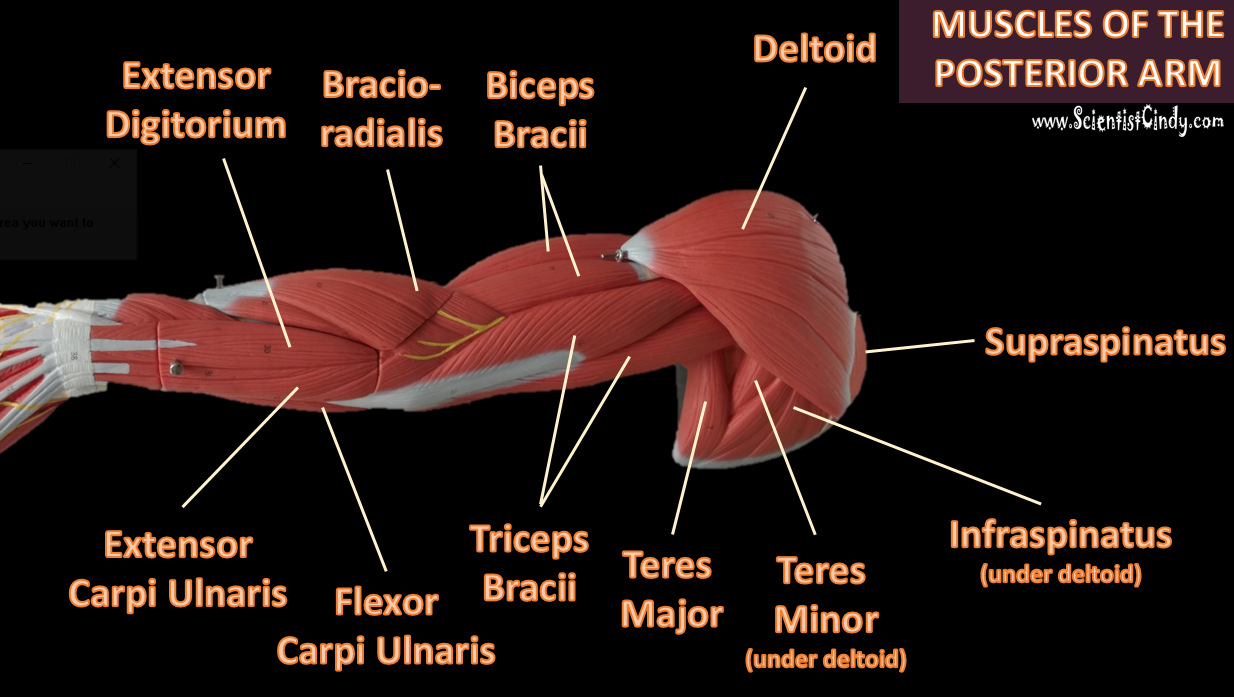
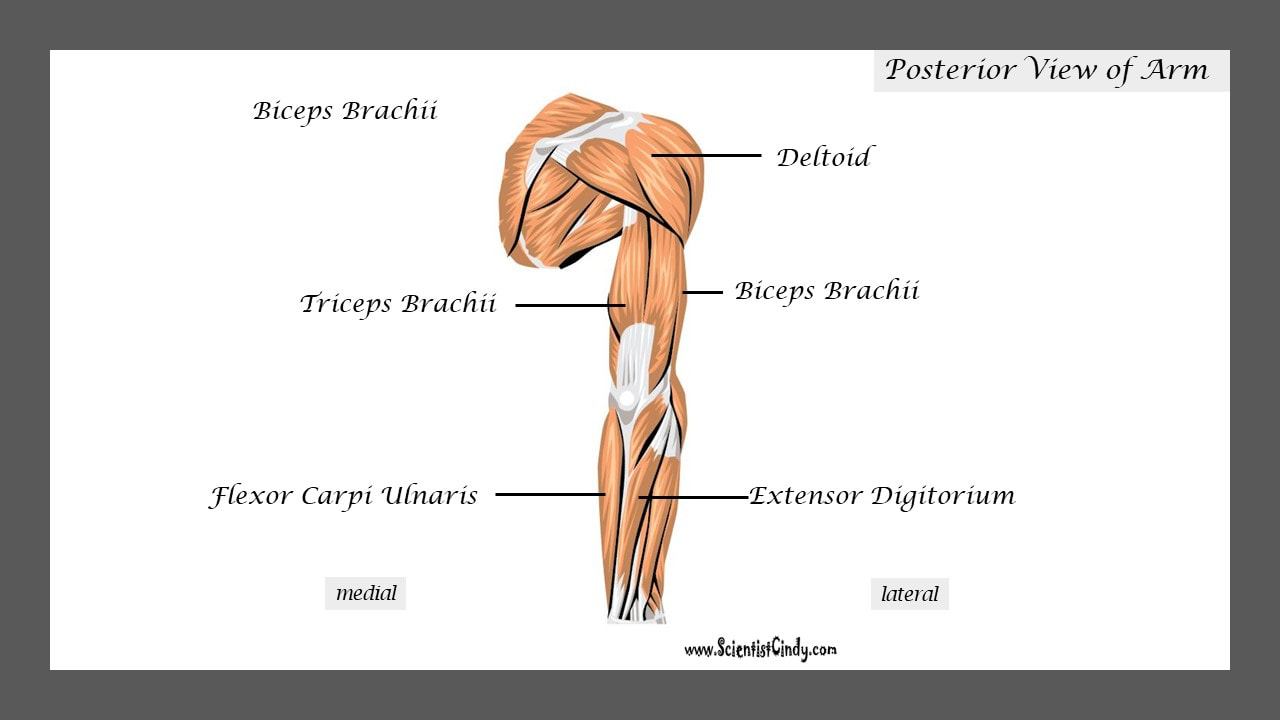
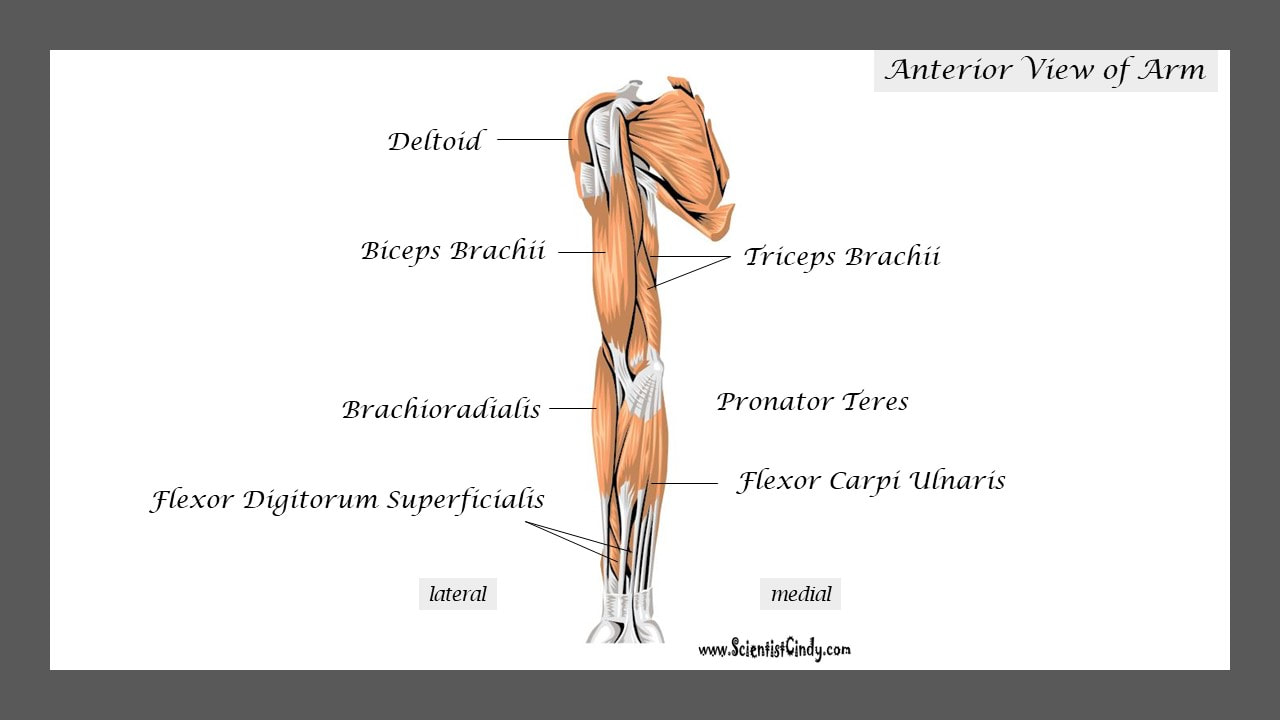
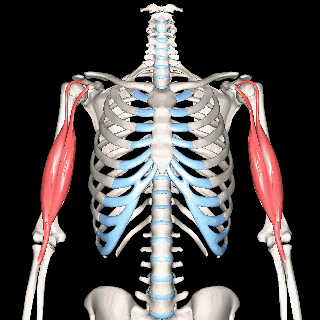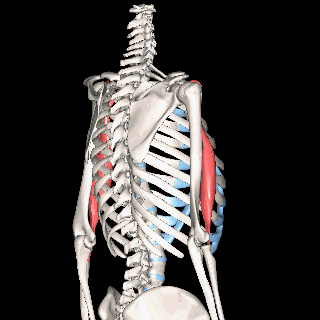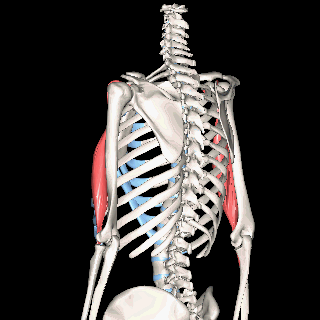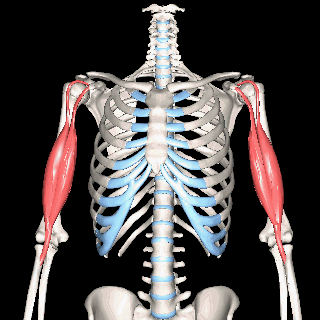 Biceps Brachii
Biceps Brachii
For example,
Muscles that lie on the anterior portion of the arm will be FLEXORS. Muscles that lie on the posterior part of the arm will be EXTENDORS.
We can get more specific than this as well. The muscles that lie on the anterior portion of the upper arm are the biceps brachii muscles. Since these muscles are anterior, we know they will be flexors. The specific joint the biceps brachii will flex, will be the elbow. This is because the elbow is the joint that lies just below the muscle (further from the body).
Muscles that lie on the anterior portion of the arm will be FLEXORS. Muscles that lie on the posterior part of the arm will be EXTENDORS.
We can get more specific than this as well. The muscles that lie on the anterior portion of the upper arm are the biceps brachii muscles. Since these muscles are anterior, we know they will be flexors. The specific joint the biceps brachii will flex, will be the elbow. This is because the elbow is the joint that lies just below the muscle (further from the body).
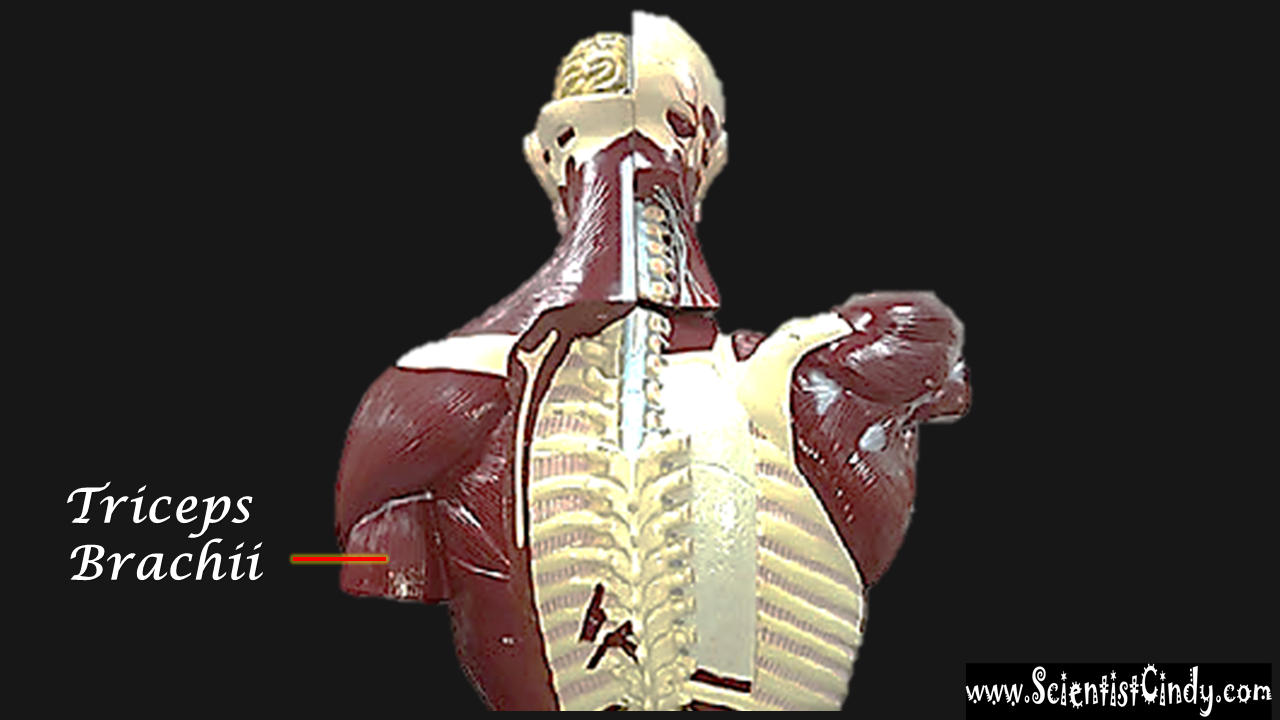
Triceps Brachii
|
The muscles that lie on the posterior portion of the upper arm are the triceps brachii muscles. Since these muscles are posterior, we know they will be extensors. The specific joint the biceps brachii will extend will be the elbow. This is because the elbow is the joint that lie just below the muscle (further from the body).
|
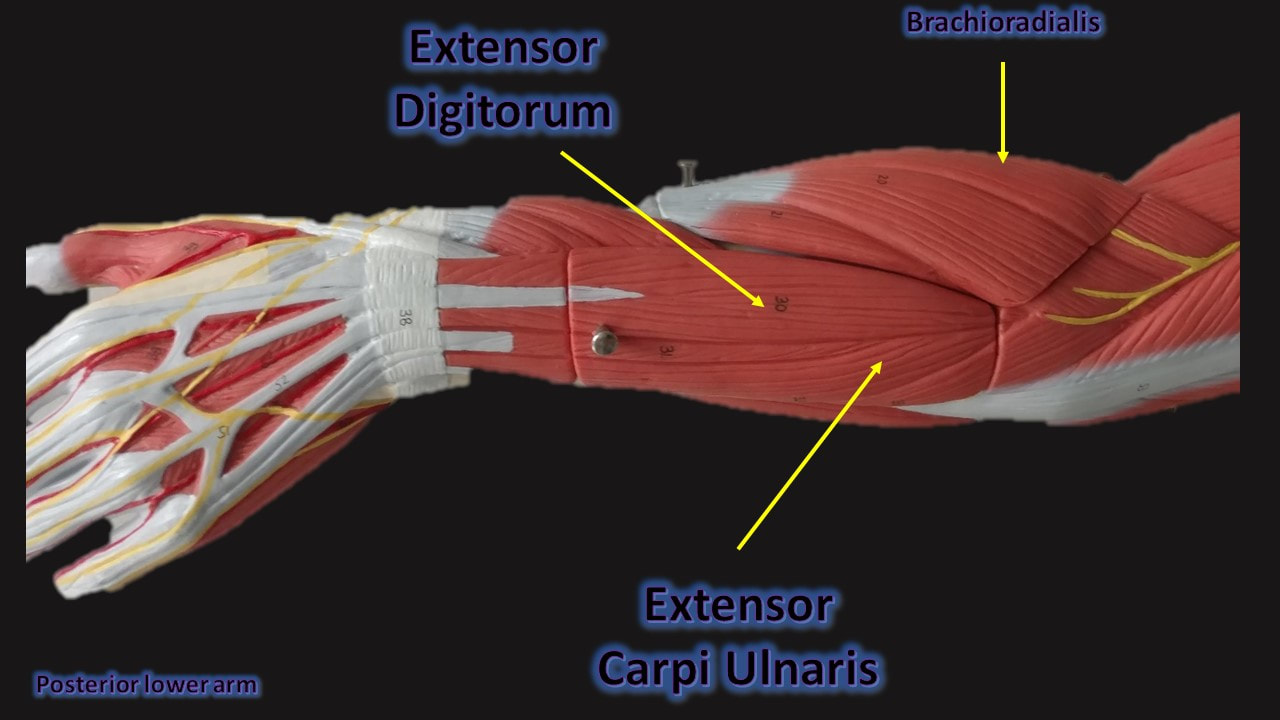
The muscles that lie on the anterior portion of the forearm (the antebrachial region) will be flexors of the carpals or digits.
The muscles that lie on the posterior portion of the forearm (the antebrachial region) will be extensors of the carpals or digits.
|
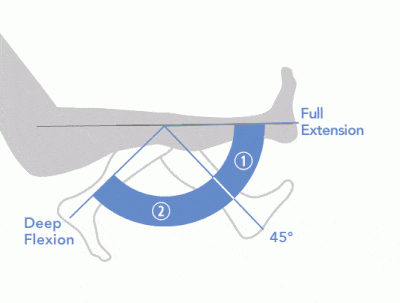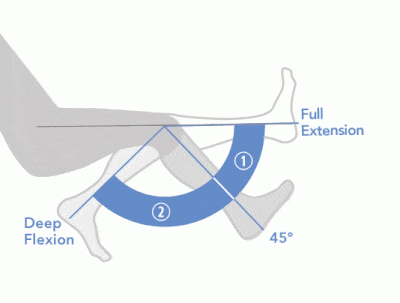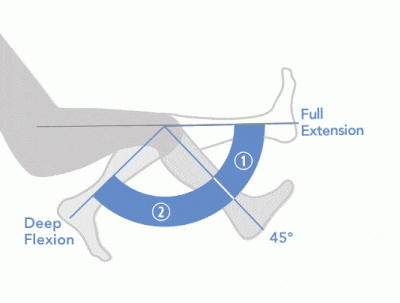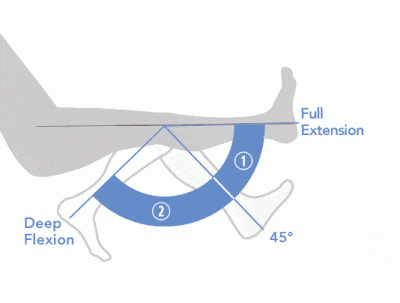
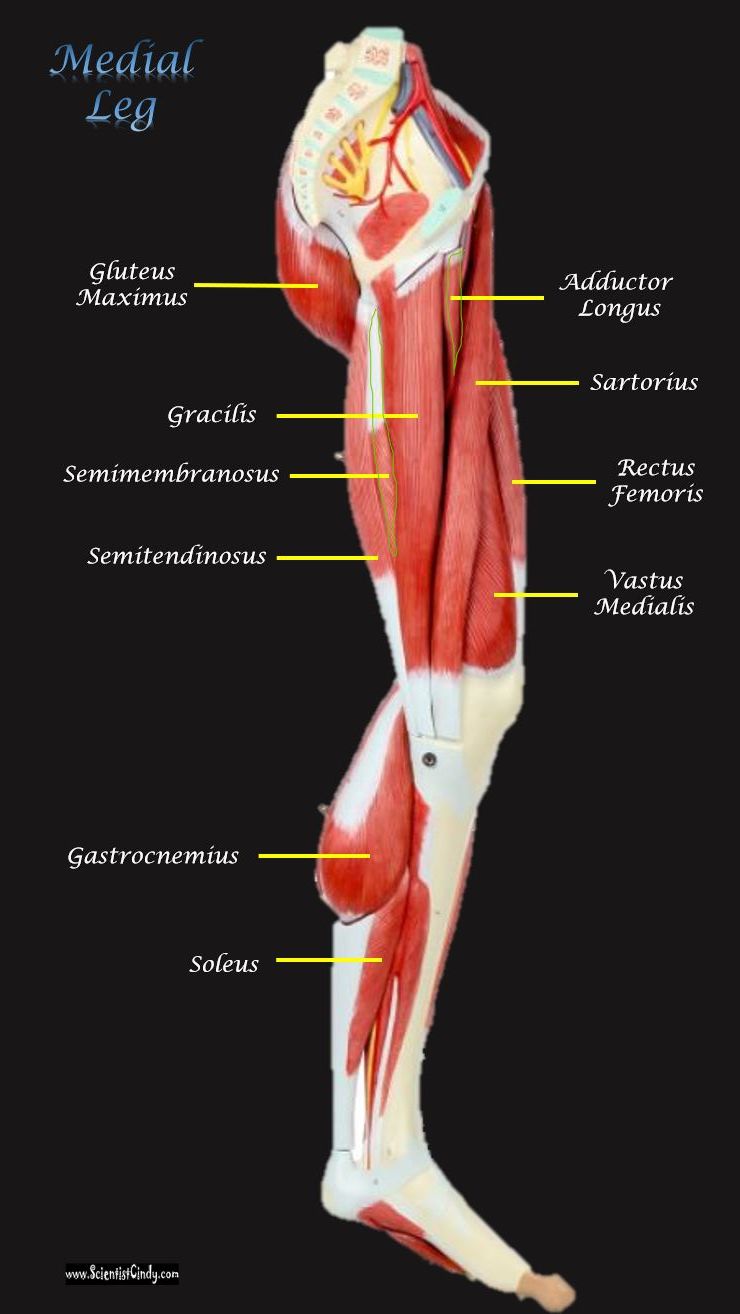
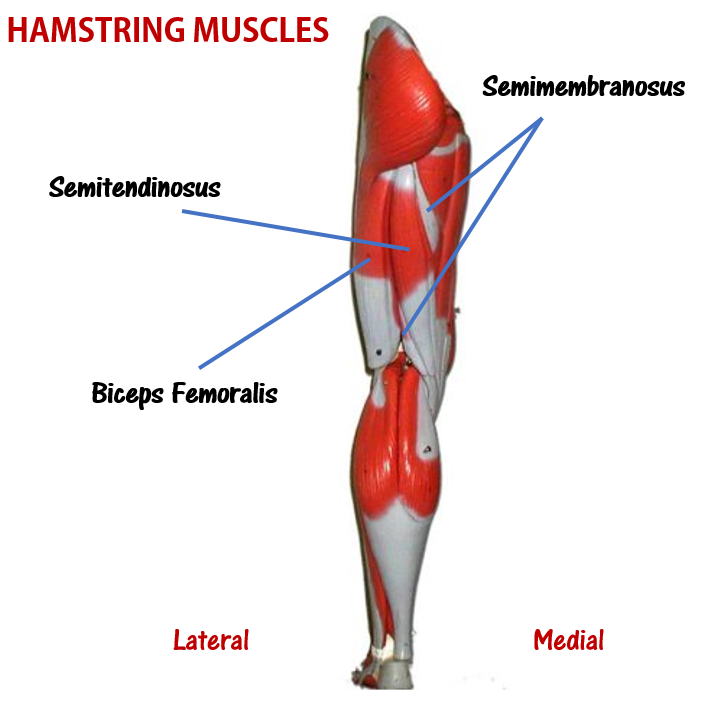
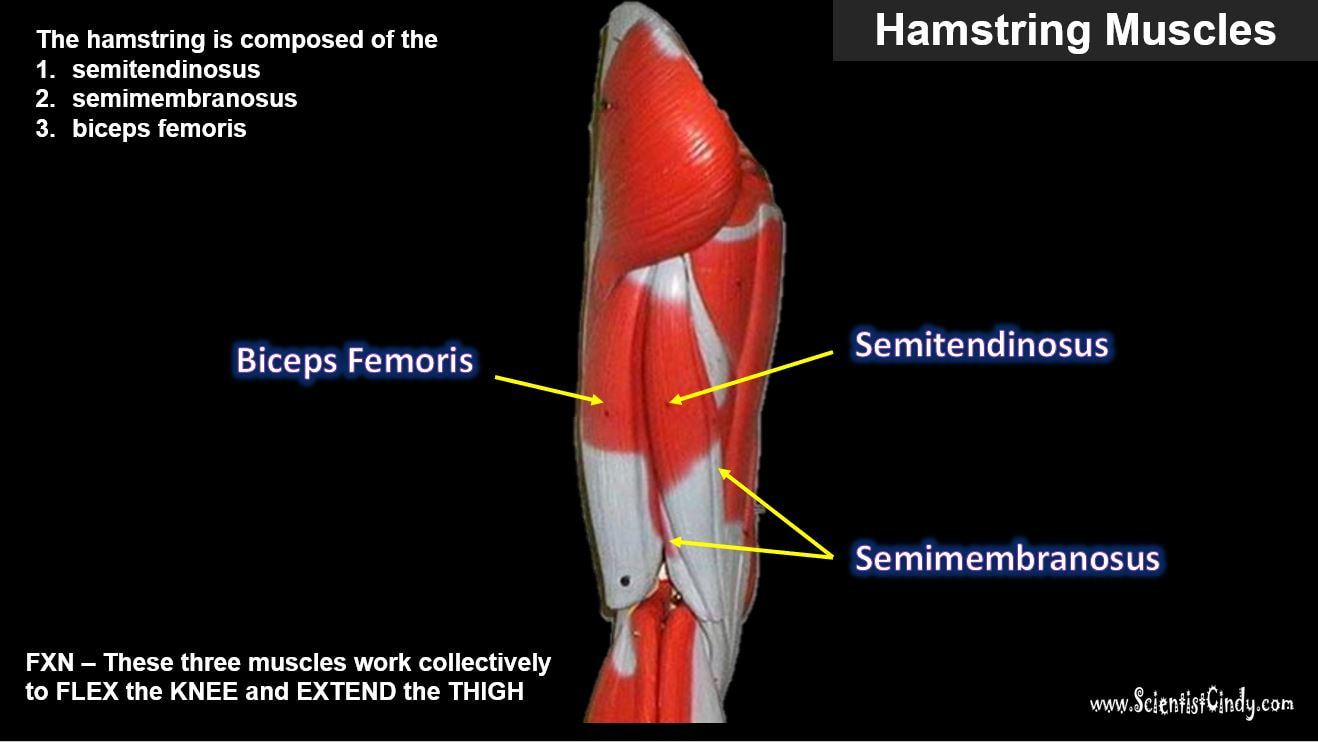
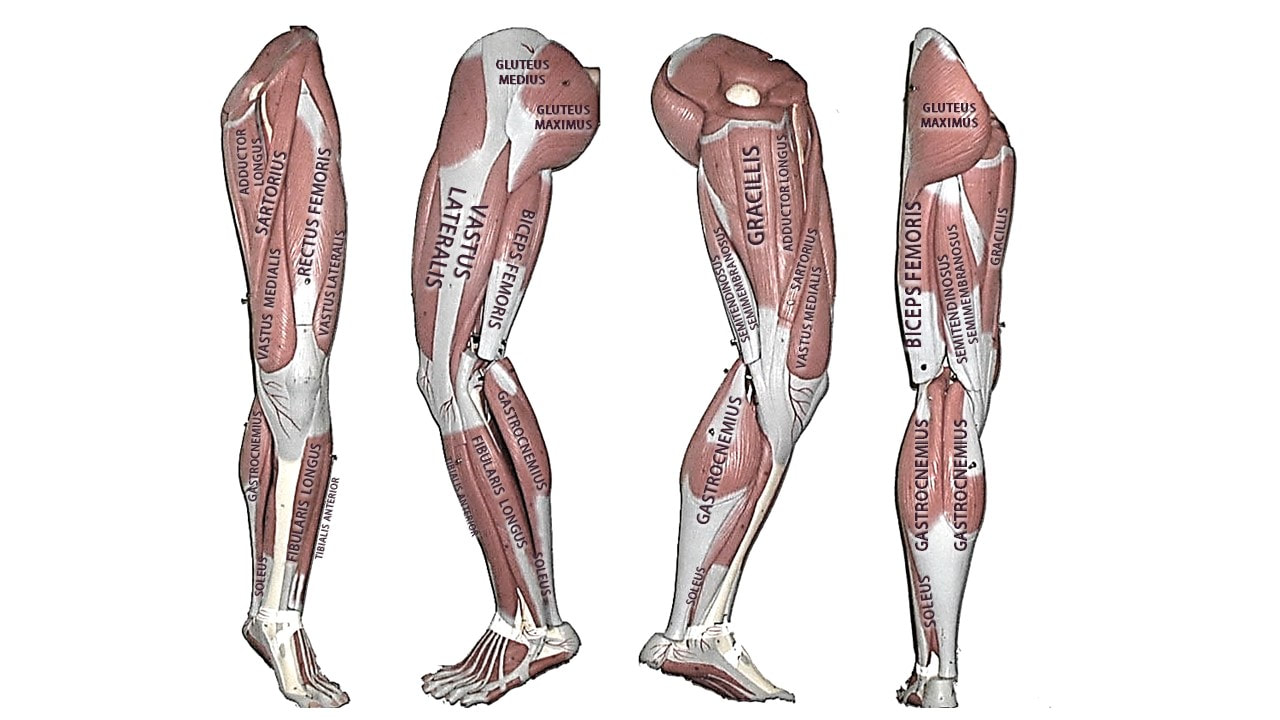
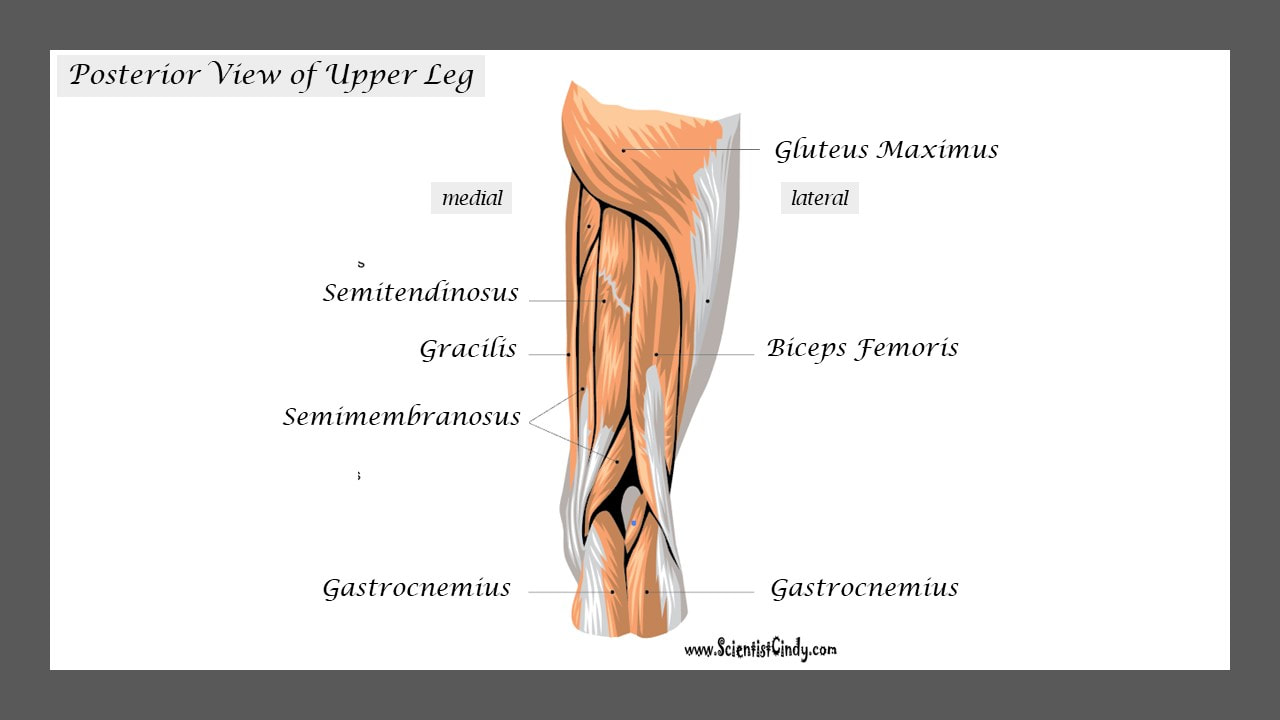
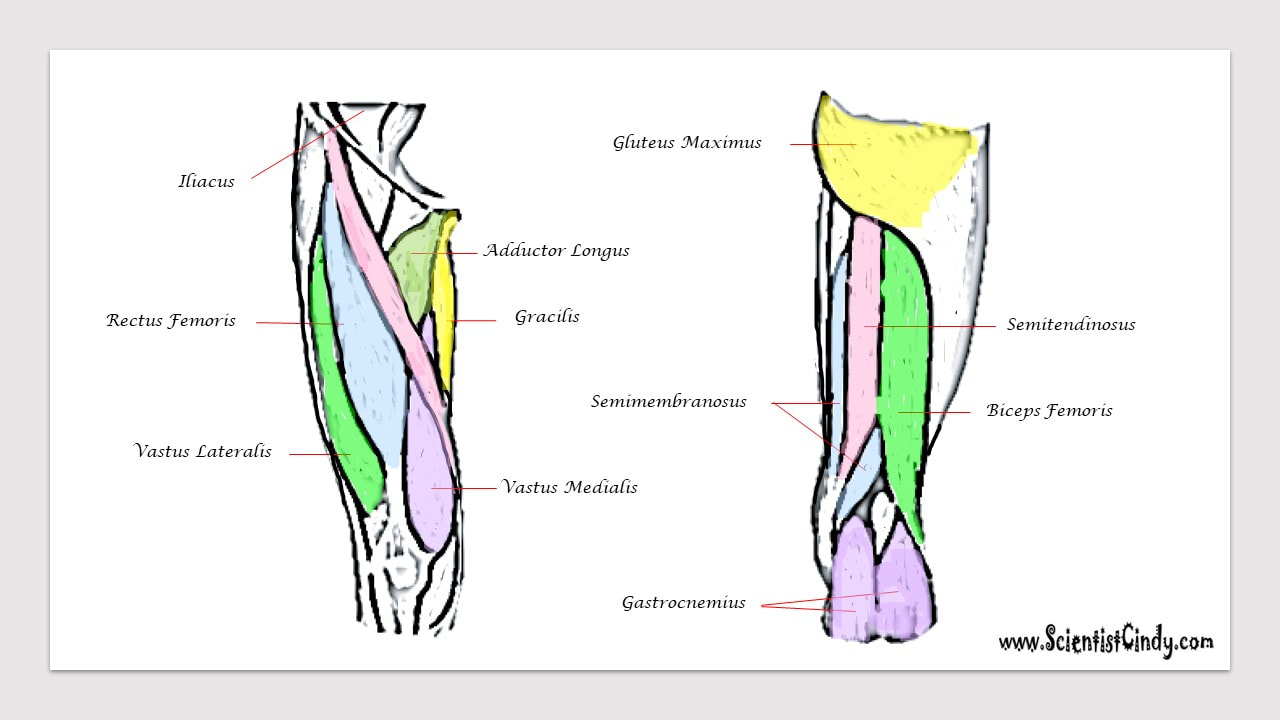
Since our knee joints bend in the opposite direction to our elbows, the position of the flexors and the extensors in the upper leg region (the femoral region) are opposite from what they are in the upper arm.
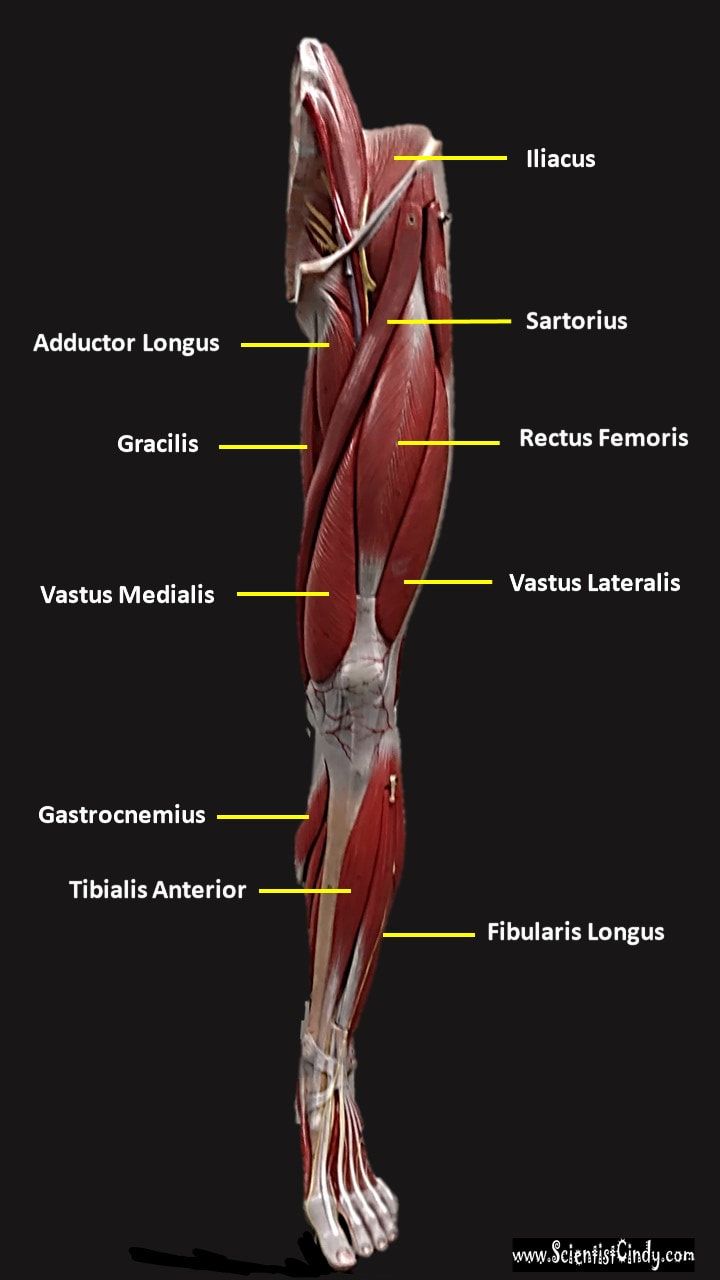
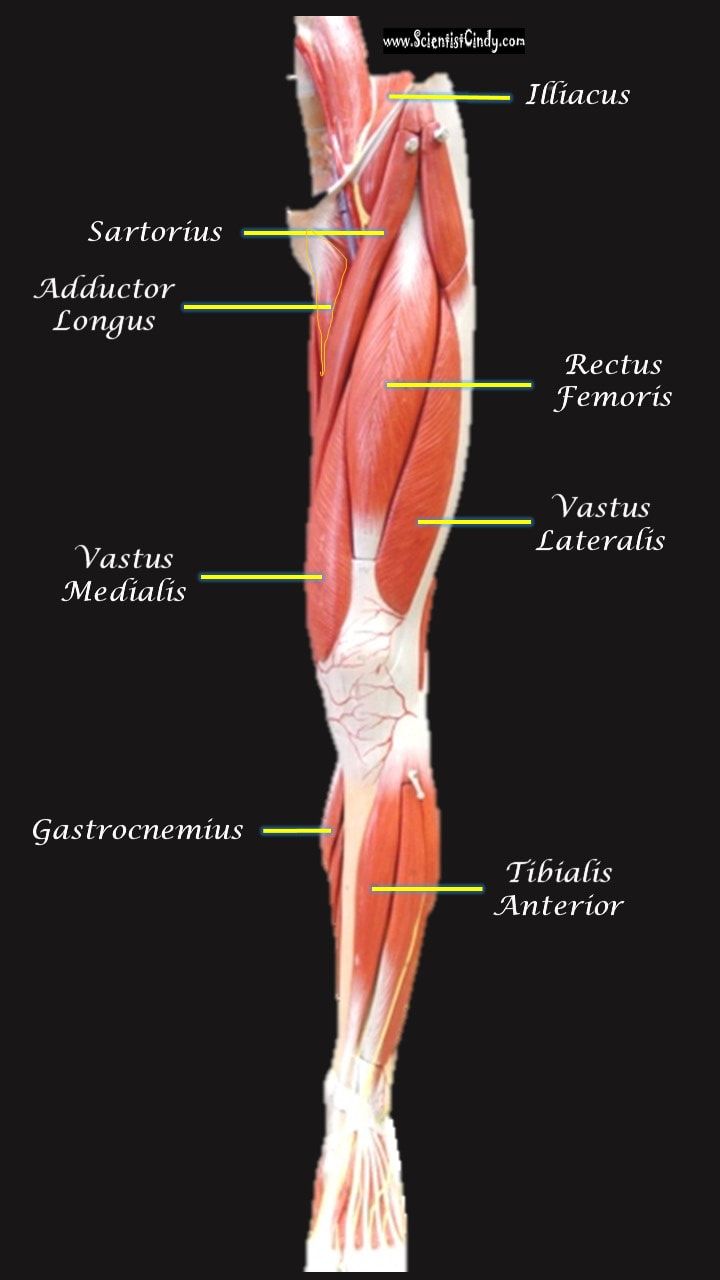
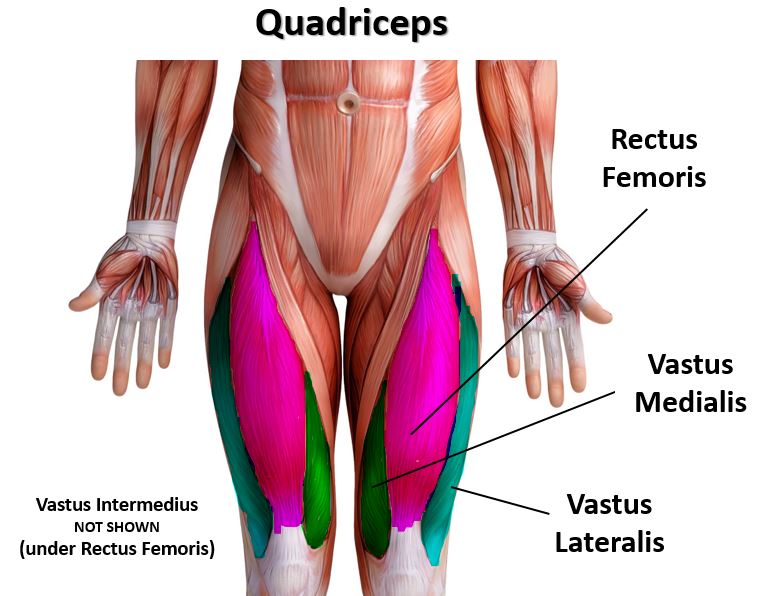
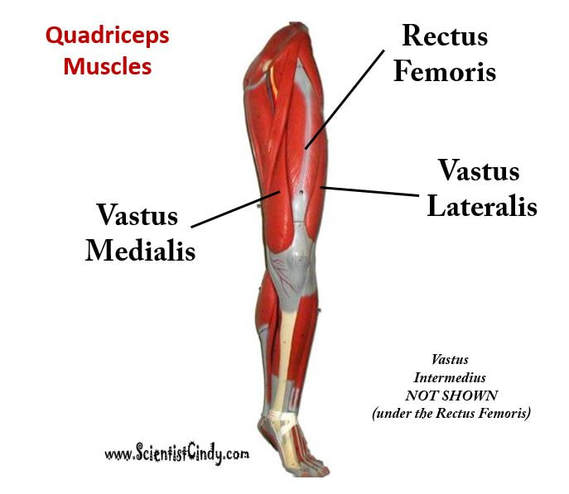
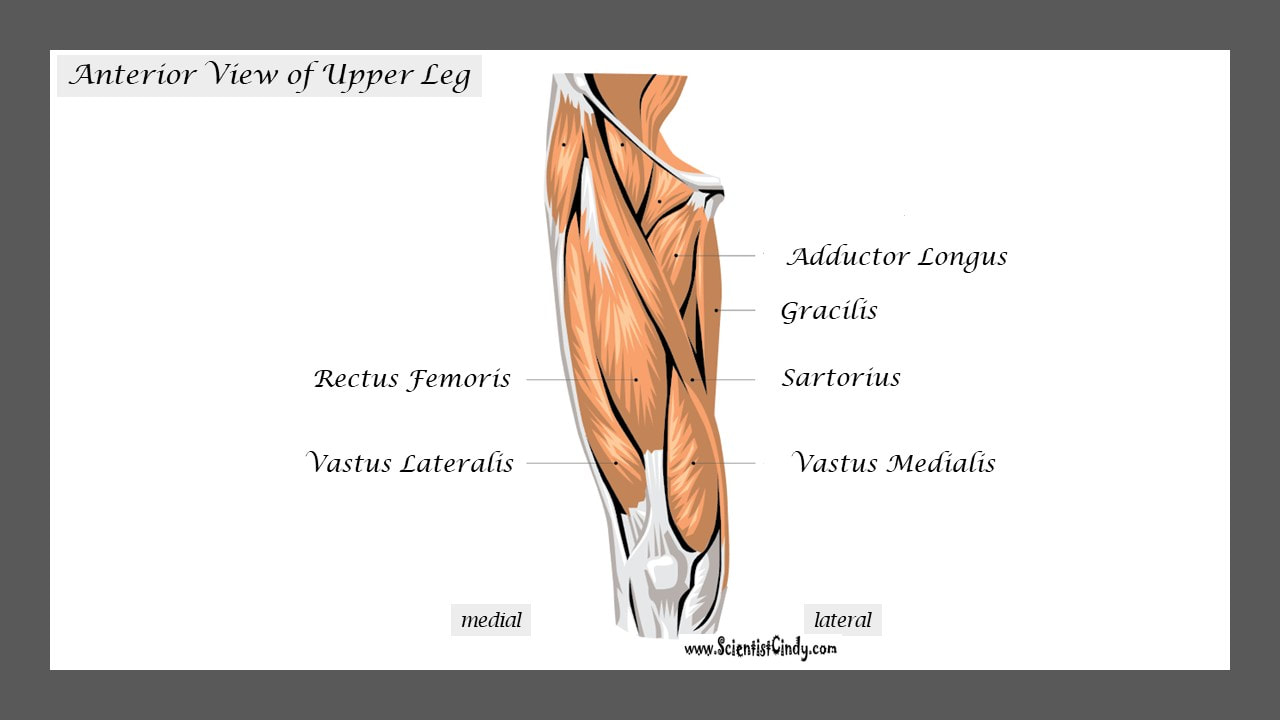
The muscles that lie on the anterior portion of the upper leg will be extensors of the knee. The muscles that have this function are called the quadriceps muscles. The quadriceps muscles include the following 4 muscles:
|
|