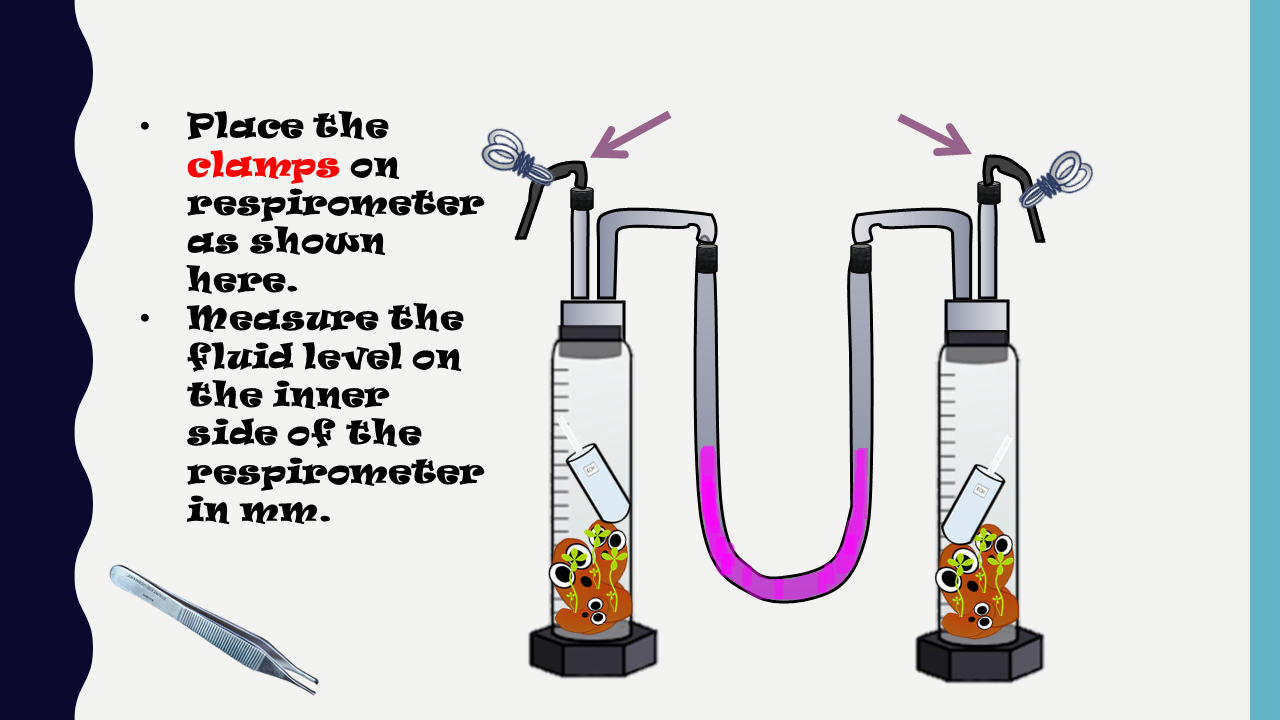
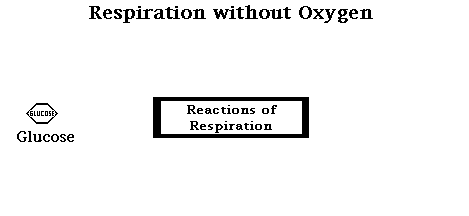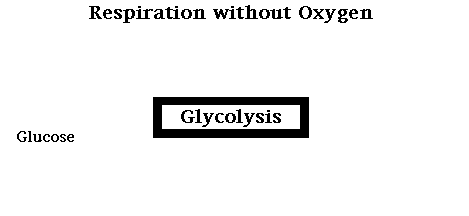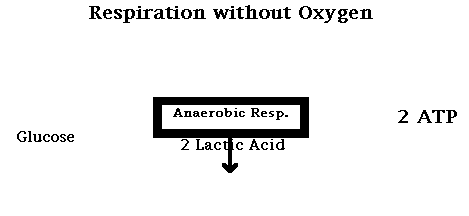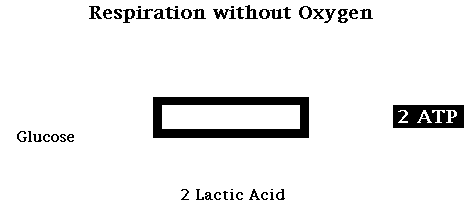|
|
|
ANAEROBIC CELLULAR RESPIRATION
Anaerobic Cellular Respiration is another way organisms can breakdown sugar to generate ATP. Some simple organisms use anaerobic cellular respiration as the only means of generating ATP. The majority of organisms, however, use a combination of aerobic cellular respiration and anaerobic respiration.
|
ANAEROBIC CELLULAR RESPIRATION OCCURS IN THE ABSENCE OF OXYGEN TO YIELD 2 ATP MOLECULES.
|
Anaerobic cellular respiration is also known as fermentation. There are two types of fermentation; alcohol fermentation and lactic acid fermentation.
Fermentation
|
|

Alcohol Fermentation has been used by humans for thousands of years to make beverages like beer and wine and foods like sour kraut, pickles and yogurt! Fermentation is a process used by yeast and bacteria to break down sugar into alcohols or acids and gases.
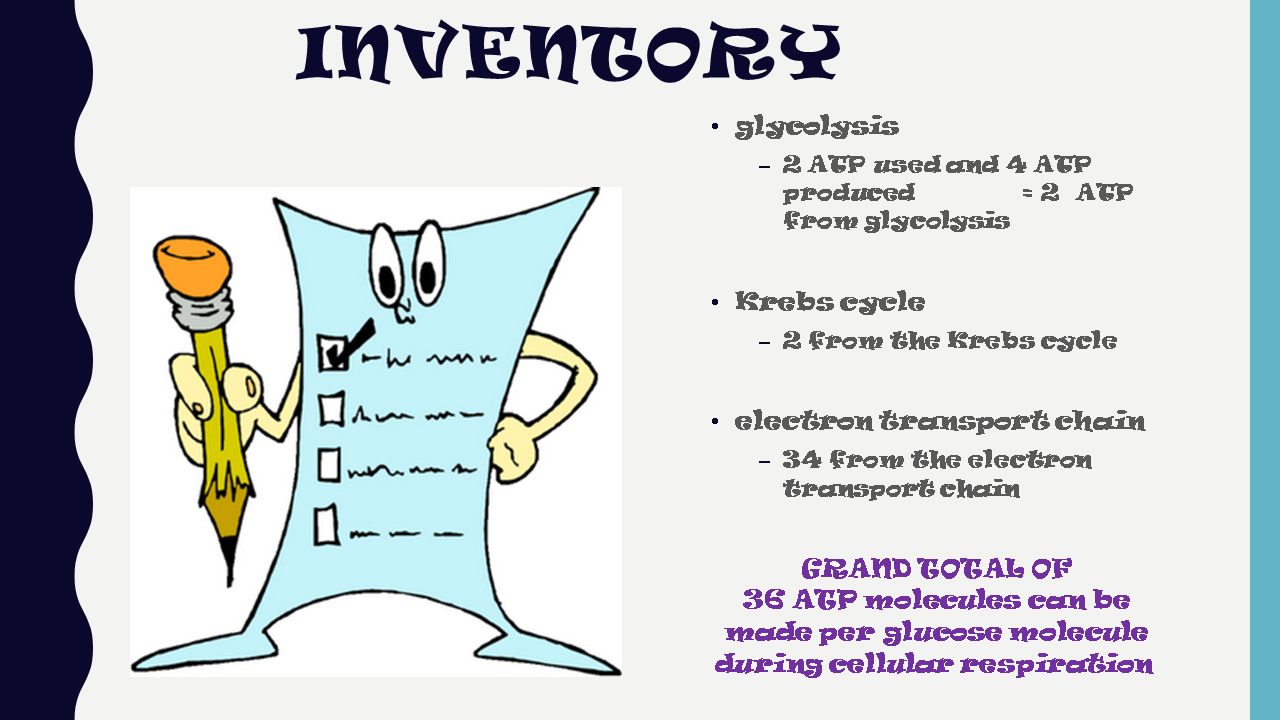
Anaerobic cellular respiration yields only 4 ATP, whereas aerobic cellular respiration yields 36 ATP! Cells only undergo anaerobic cellular respiration as a last resort, when oxygen is unavailable and energy is needed.
Anaerobic cellular respiration yields only 4 ATP, whereas aerobic cellular respiration yields 36 ATP! Cells only undergo anaerobic cellular respiration as a last resort, when oxygen is unavailable and energy is needed.
The chemical equation for alcohol fermentation is
C6Hl2O6 --> 2 CH3CH2OH + 2 CO2 + 2 ATP
Glucose --> 2 Ethanol + 2 Carbon Dioxide + 2 Adenosine Triphosphate
When yeast ferments in a closed test tube, CO2 production will lead to an increase in pressure inside the tube. This is because in fermentation, CO2 is being produced, but O2 is not being used up. We can measure this change in pressure to indirectly measure the rate of yeast fermentation in the tube.
|
|
Another type of fermentation is lactic acid fermentation. Lactic acid fermentation occurs in animals. Instead of producing alcohol, like yeast cells, animals produce lactic acid as a byproduct. Lactic acid fermentation yields only 2 ATP, while aerobic cellular respiration yields 36 ATP.
Lactic Acid Fermentation
C6Hl2O6 --> 2 C3H6O3 + 2 ATP
Glucose --> 2 Lactic Acid + 2 Adenosine Triphosphate
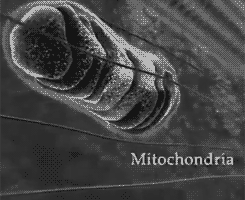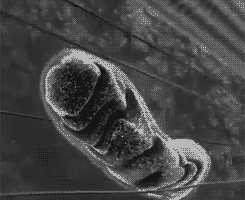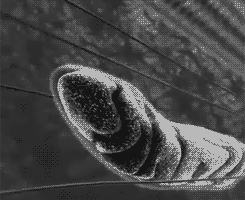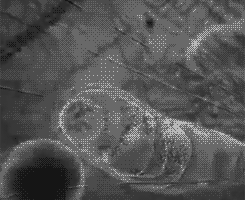
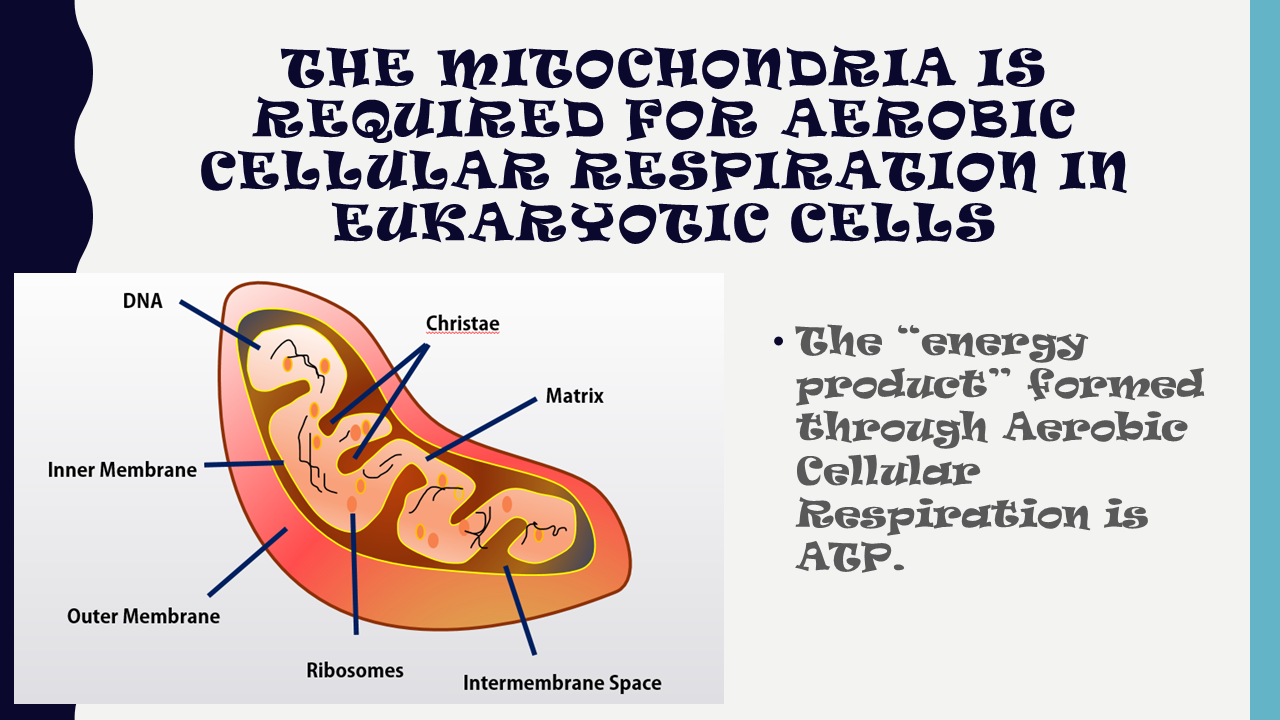
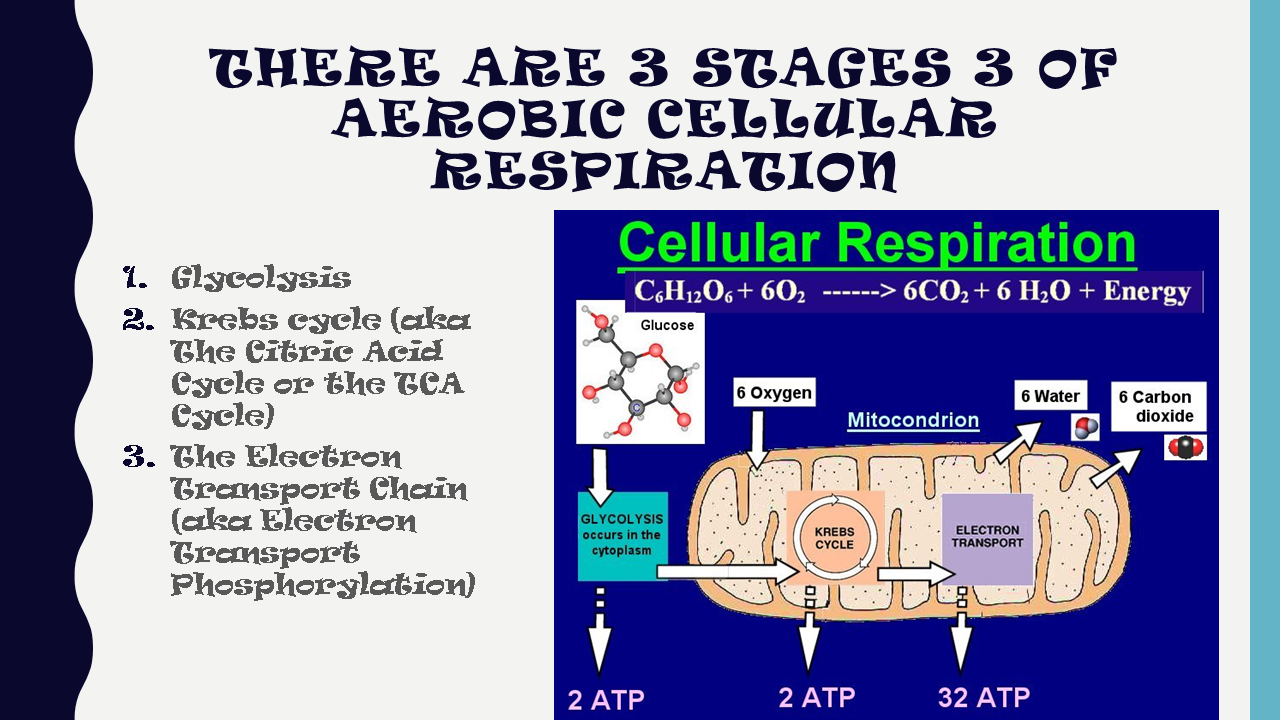
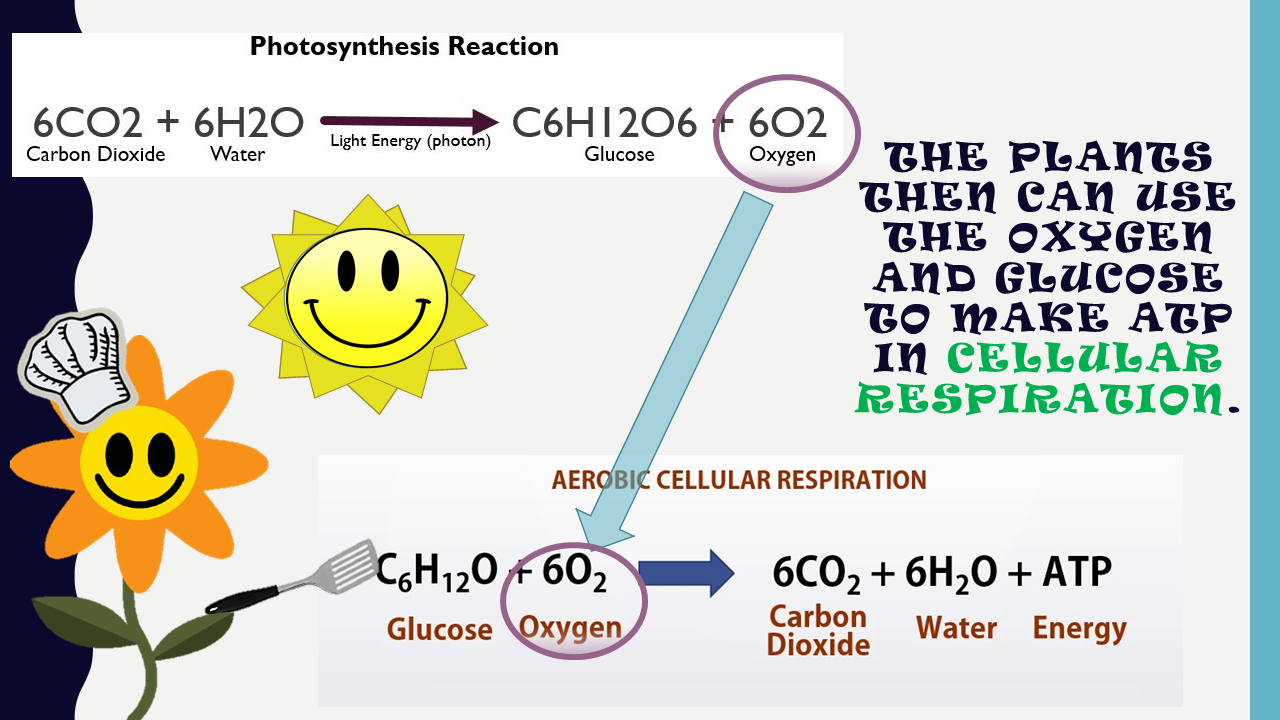
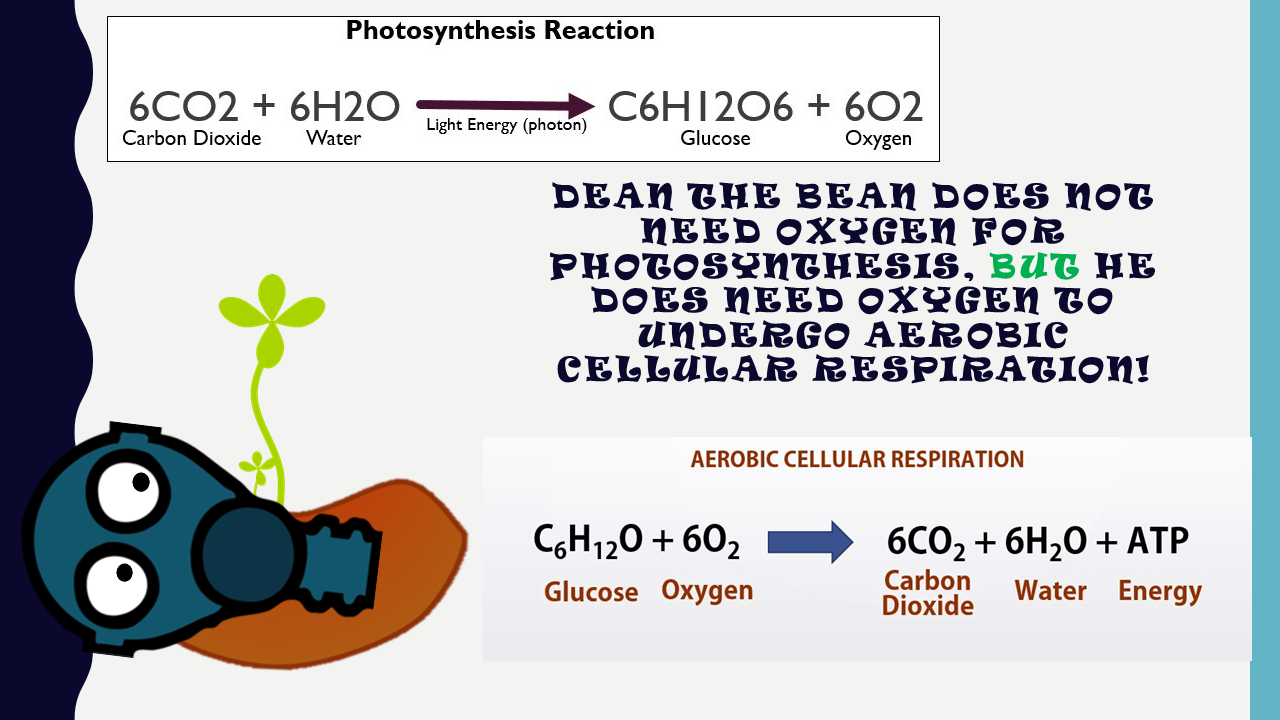
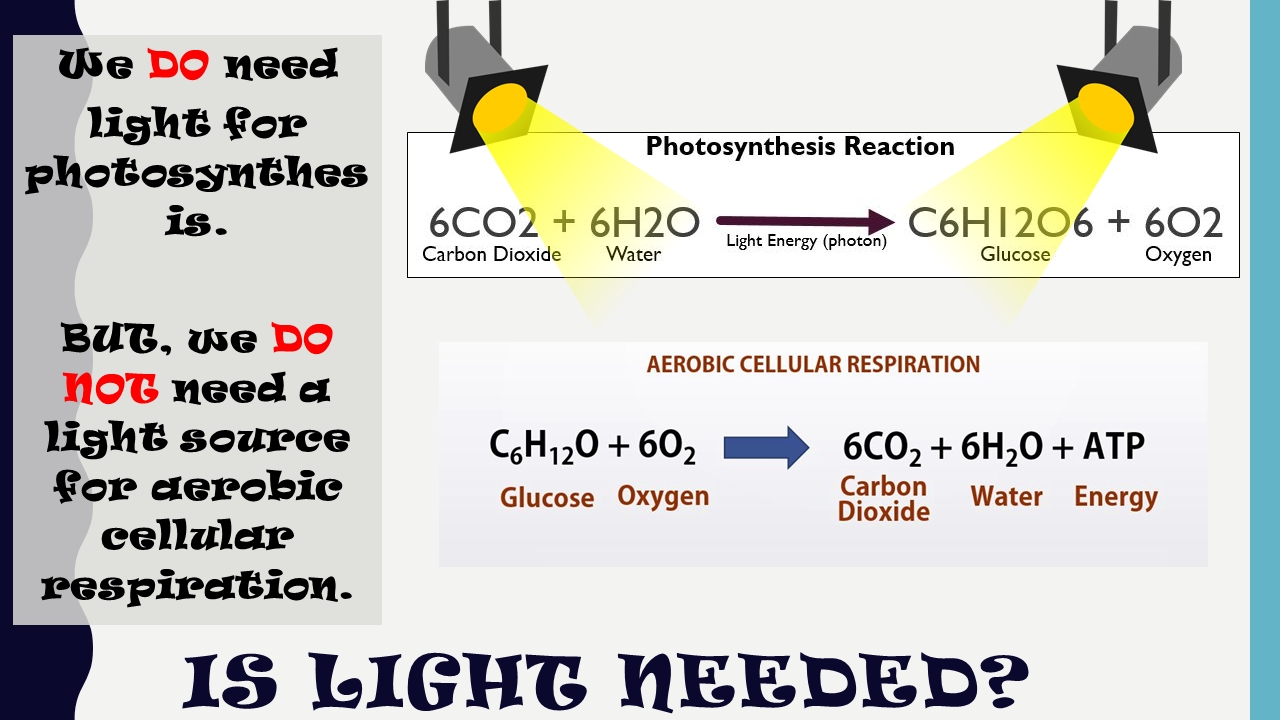
Aerobic respiration occurs in three stages: glycolysis , The Kreb’s cycle , and the electron transport chain . In contrast, alcoholic and lactic acid fermentation involve glycolysis only. The Kreb’s cycle and the electron transport chain require oxygen to function and they both take place in the mitochondria.
|
Aerobic respiration is much more efficient, but the Kreb's cycle and electron transport chain steps cannot be completed without oxygen. Most plants and animals will use anaerobic cellular respiration only as a back-up process to generate ATP in the absence of available oxygen.
Aerobic Cellular Respiration
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 --> 6 H2O + 6 CO2 + 36 ATP
Glucose + 6 Oxygen --> 6 Water + 6 Carbon Dioxide + 36 Adenosine Triphosphate
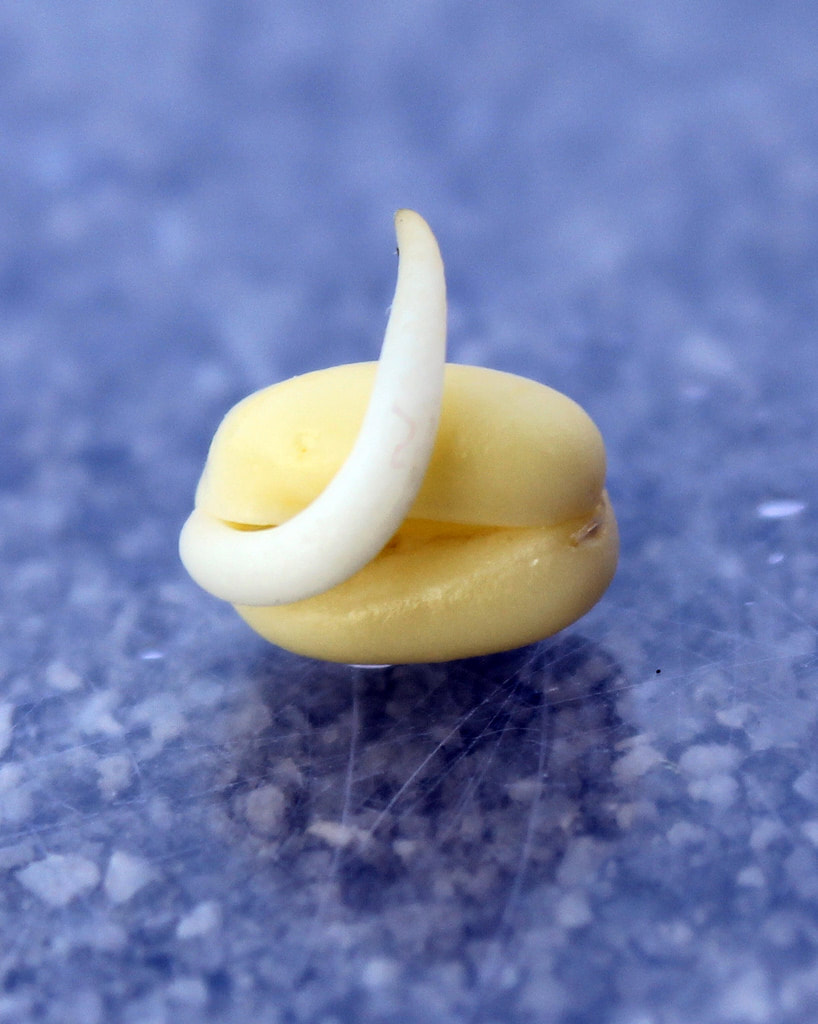
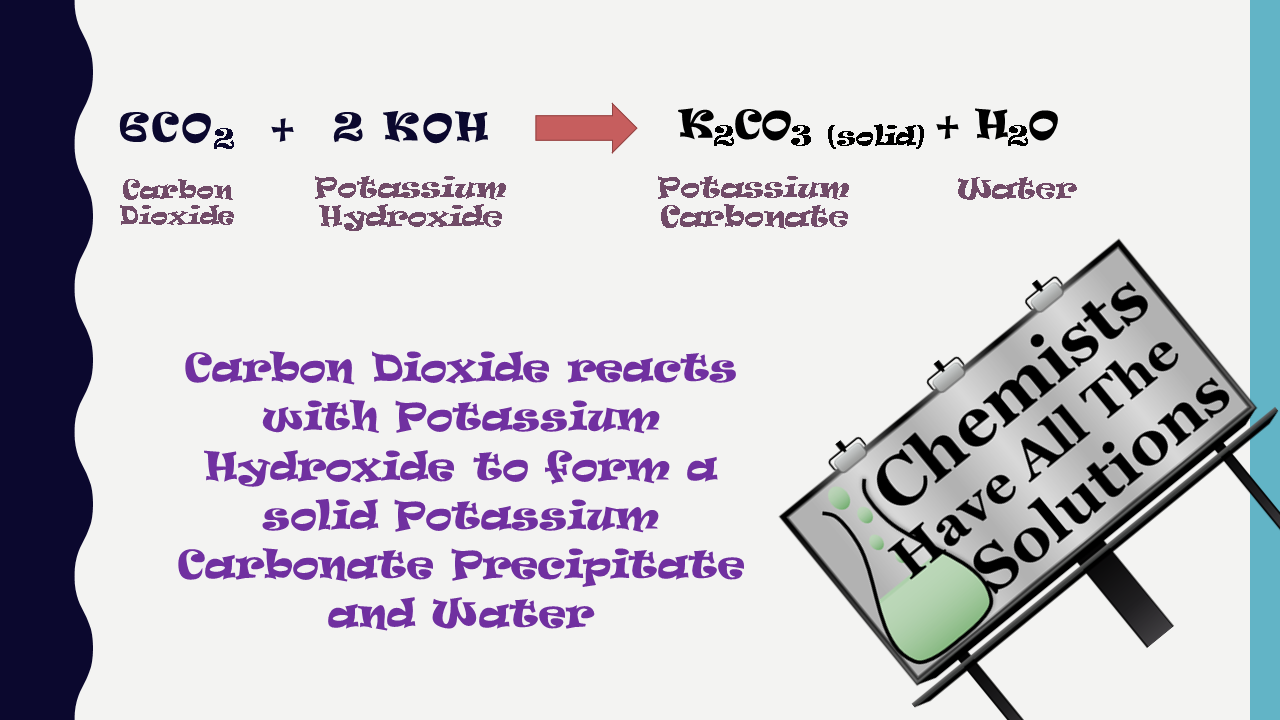
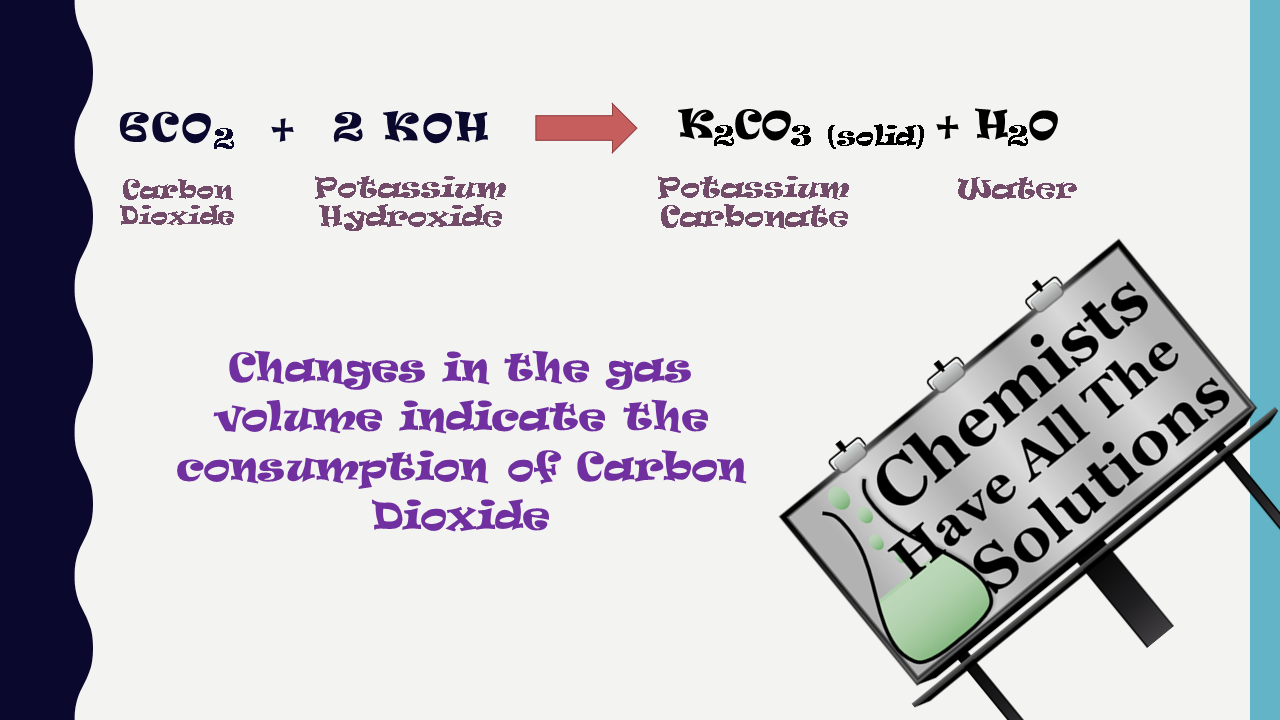
In this lab, we will Explore the Aerobic Cellular Respiration in a Germinating Bean Seedling. As you can see from the chemical equation for aerobic respiration, carbon dioxide is produced as a byproduct of the process. We can use a trick of chemistry to pull out this carbon dioxide so we can easily measure it.
|
A Germinating Bean Seedling
|