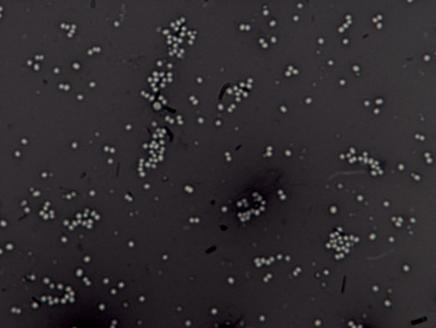
Ex 6 - Negative Staining
What is the Negative Stain Used For?
Negative staining allows the morphology, arrangement and size of bacteria, to be viewed microscopically.
How Do Negative Stains Work?
Negative staining allows the morphology, arrangement and size of bacteria, to be viewed microscopically.
The negative stain uses the dye nigrosin, which is an acidic dye. Acids donate hydrogen ions, which are positively charge protons. As acids loose positive charge, the chromophores of the dye becomes negatively charged.
The cell wall of the bacteria is naturally negatively charged. A rule of chemistry, is that opposite charges attract, and "like charges" (charges that are alike) repel one another.
The result is that the bacteria cell remains unstained an appears as a clear object on the slide, while the area surrounding the bacteria cell is darkly stained by the nigrosin stain (also known as "Indian Ink").
The cell wall of the bacteria is naturally negatively charged. A rule of chemistry, is that opposite charges attract, and "like charges" (charges that are alike) repel one another.
The result is that the bacteria cell remains unstained an appears as a clear object on the slide, while the area surrounding the bacteria cell is darkly stained by the nigrosin stain (also known as "Indian Ink").
How do you determine whether a stain is basic or acidic?
- If the chromophore is positive, it is basic
- If the chromophore is negative, it is acidic
What is considered a simple stain?
Staining procedures that use only one stain
List the steps for preparing a smear.
1-Place a loopful on water on the slide, 2-place a small amount of the culture onto the slide and mix, 3-allow smear to air dry, 4-flame the slide
List the steps of preparing a simple stain.
1-Cover smear with methylene blue for 30 seconds, 2-Wash with DI water
Of what value is a simple stain?
Determining cell morphology, size, and arrangement
What is the purpose of fixing the smear preparation?
Denatures bacterial enzymes
In heat fixing, what would happen if too much heat were applied?
It would damage the cell's structure and can even crack the slide.
Can dyes other than methylene blue be used for direct staining?
Yes any positively charged dye can be used such as safranin and basic fuchsin
Bacteria can be seen without staining, so why is fixing and staining important for microbiology?
It allows for later reexamination
What does the negative stain technique stain?
Background (the area around the cell, but NOT the cell itself)
Why doesn't a negative stain stain the bacteria?
Ionic repulsion; like charges repel. The bacteria cell wall and the chromophores of the acidic stain both have negative charges.
In which procedure are no heat fixing or strong chemicals used and why not?
Negative stain; to keep the bacteria from getting as distorted
When is the negative stain technique especially useful?
When other staining techniques don't clearly show cell morphology or size
List the steps of the negative staining technique.
1-Place a drop of nigrosin on slide, 2-Mix a loopful of broth culture with the nigrosin (no extra water is needed when the culture is taken from solid media as nigrosin contains a lot of water already), 3-Use a second slide to sweep the mixture across the first slide, making a color gradient, 4-Let the smear air dry
How does bacteria from a negative stain differ from that of a simple stain?
It's clearer because only the background is stained
Why is the size more accurate in a negative stain than in a simple stain?
The lack of heat fixing or strong chemicals keeps from distorting the cell
Could any dye be used in place of nigrosin in a negative stain?
No
What type of dye is used for negative staining? (Acidic or Basic)
Acidic
What kind of stain is the gram stain? How does is allow you to classify bacteria?
Differential; as either gram positive or gram negative
Describe the discovery of the gram stain technique.
Discovered accidentally by Hans Christian Gram in 1884 when he attempted to stain cells and found that some lost their color when the excess stain was washed off
In a gram stain, what are bacteria called when they are easily decolorized?
Gram negative
In a gram stain, what are bacteria called when they retain the primary stain?
Gram positive
Why do bacteria stain differently in a gram stain?
Chemical and physical differences in their cell walls
In a gram stain, what type of cell does this describe?
Crystal violet is picked up by the cell. Iodine reacts with the dye in the cytoplasm to form CV-I. The decolorizing agent dissolves the outer lipopolysaccharide layer, and the CV-I washes out through the thin layer of peptidoglycan.
Gram negative
When is the gram stain most consistent?
When done on cultures less than 24 hours old
List the steps of the gram stain technique.
1-Cover smear with crystal violet for 30 seconds and rinse, 2-Cover smear with Gram's iodine for 10 seconds and rinse, 3-Decolorize with alcohol and rinse, 4-Cover smear with safranin for 30 seconds and rinse
Name some gram positive bacteria.
S. aeru, S. epi, S. pyogenes, B. sub, B, meg
Name some gram negative bacteria.
E. coli, P. vulg, Neisseria
Why will old gram positive cells stain gram negative?
They can't retain the primary stain because with time the lipid layer degrades allowing the stain to reach the peptidoglycan
Can iodine be added before the primary stain in a Gram stain?
No
What color does Crystal Violet turn each of the cells in a gram stain?
Purple
What color does Gram's iodine turn each of the cells in a gram stain?
Purple
What color does ethyl alcohol turn each of the cells in a gram stain?
Gram positive-purple; Gram negative-clear
What color does safranin turn each of the cells in a gram stain?
Gram positive-purple; Gram negative-red
Which step can be omitted without affecting determination of the gram stain reaction?
Safranin
Suppose you gram stained a sample from a pure culture of bacteria and observed a field of red and purple cocci. Adjacent cells were not always the same color. What do you conclude?
The culture is old
Suppose you are viewing a gram stained field of red rods and purple cocci through the microscope. What do you conclude?
The culture has been cross-contaminated
Since you can't identify bacteria from a gram stain, why might a physician perform a gram stain on a sample before perscribing an antibiotic?
Because only certain antibiotics work depending on if the bacteria is gram positive or negative
What type of antibiotics work on gram positive bacteria?
Penicillin
What type of antibiotics work on gram negative bacteria?
Tetracycline
If you gram stained human cells, what would happen?
Primary stain would wash away because humans do not have cell walls
What type of stain is the acid-fast stain?
Differential
What is the value of the acid-fast stain?
Allows diagnosing of Mycobacterium and Nocardia, which do not decolorize with acid alcohol
The cell walls of acid-fast organisms have a wax-like lipid called mycolic acid, which does what?
Makes the cell wall impermeable to most stains
What the difference in the Ziehl-Neelsen acid-fast stain and the Kinyoun acid-fast stain?
In the Kinyoun stain (cold stain), the concentrations of phenol and carbolfuchsin are increased so heating isn't necessary
List the steps of the acid-fast stain.
1-Cover smear with carbolfuchsin for 5 minutes and rinse, 2-Wash smear with acid-alcohol on and off and rinse, Cover smear with Brilliant Green K (Methylene Blue) for 1 minute and rinse
What color will an acid-fast positive bacteria be?
Red
What color will an acid-fast negative bacteria be?
Green
Name an acid-fast negative bacteria
E. coli
Name an acid-fast positive bacteria
M. phlei
What is the decolorizing agent in the Gram stain? In the acid-fast stain?
Ethyl alcohol; Acid-alcohol
What diseases are diagnosed using the acid-fast staining technique?
Tuberculosis and Leprosy
What is phenol and what percent is its usual application?
Disinfectant; 5%
How might the acid-fast characteristic of Mycobacterium enhance the organism's ability to cause disease?
The lipids in their cell wall give extra protection; they are not easily phagocytized
Clinical specimens suspected of containing Mycobacterium are digested with sodium hydroxide for 30 minutes prior to staining. Why is this technique used? Why isn't this technique used for staining other bacteria?
To remove unwanted bacteria from specimen; the sodium hydroxide would kill other bacteria
What are the most familiar genera that form endospores?
Bacillus and Clostridium
Why are endospores called resting bodies?
Because they do not metabolize and are resistant to many harsh conditions
When are endospores formed?
When essential nutrients or water are not available
What happens to the cell when an endospore is formed?
It disintegrates
Many bacteria secrete chemicals that adhere to their surfaces, forming a viscous coat. What is this structure called when it is round or oval shaped? Irregularly shaped and loosely bound?
Capsule; Slime layer
How is a bacteria's ability to form a capsule determined?
Genetically
How is the size of a bacteria's capsule determined?
The medium it's growing on
What are most capsules composed of?
Polysaccharides, which are uncharged
Because of a capsules nonionic nature, _____ stains will not adhere to it.
Simple
How must a capsule be stained in order to view it under a microscope?
The background must be stained, leaving the capsules unstained
Capsules have a very important role in the _____ of some bacteria.
Virulence
How do capsules contribute to the virulence of some bacteria?
Capsules are not easily phagocytized
These thin proteinaceous structures that originate in the cytoplasm and project out from the cell wall are the most common means of motility in bacteria
Flagella
List the steps of an endospore stain.
1-Place a piece of paper towel over the slide, 2-Cover the paper with malachite green, 3-Steam the slide for 5 minutes then rinse, 4-Cover smear with safranin for 30 seconds and rinse
List the steps of a capsule stain.
1-Place a loopful of congo red on slide, 2-Put a thick smear of bacteria in the congo red and mix, 3-Let smear air dry, 4-Drip acid-alcohol on slide for 15 seconds and rinse, 5-Cover smear with acid fuchsin for 1 minute and rinse
What are the gram reactions of Clostridium and Bacillus?
Both are gram positive
How might flagella contribute to pathogenicity?
They help evade the immune response
In an endospore stain, how would slides of 24-hour old Bacillus and 72-hour old Bacillus differ?
At 72 hours, endospores would have formed
Of what morphology are most bacteria possessing flagella?
Bacillus
Which morphology does not usually have flagella?
Coccus
What prevents the cell from appearing green in the finished endospore stain?
Vegetative cells are easily decolorized so the green dye washes off
You can see endospores by simple staining. Why not use this technique?
It would be more difficult to pick them out because they would be transparent
How would an endospore stain of Mycobacterium appear?
Mycobacterium's waxy cell wall would retain the green dye, suggesting that they have endospores when they actually do not
What type of culture medium would increase the size of a bacterial capsule?
A medium rich in polysaccharides
Describe the microscopic appearance of encapsulated Streptococcus if stained with safranin and nigrosin.
The bacteria would be red, the capsule clear, and the background purplish-black
In the Dorner endospore stain, a smear covered with carbolfuchsin is steamed, then decolorized with acid-alcohol and counterstained with nigrosin. Describe the microscopic appearance after this procedure.
The endospores should be very bright pink, the bacteria light pink, and the background purplish-black
What makes an agar deep useful?
Some oxygen prefer to grow in less oxygen
What are two ways to determine motility of a bacteria?
Using an agar deep or the hanging drop technique
What evolutionary advantage would there be to the formation of a pellicle in a liquid medium by a bacterium?
They could form colonies and have a greater chance of survival
How can you tell that a medium is sterile?
Compare it with a control
Why is it desirable that microscope lenses be parfocal?
So you don't have to refocus everytime you change objectives
What controls the amount of light reaching the ocular lens?
Diaphragm
Is you lens corrected for chromatic aberrations?
Yes
Name two ways in which you can enhance the resolving power of a microscope.
Decrease the wavelength of light and increase the numerical aperture
What would occur if water were accidentally used in place of immersion oil?
It would not be as clear because water does not have the same refractive index as glass
What advantages does the low power objective have over the oil immersion objective for viewing fungi?
Fungi cells are large so you can see more of the cell
Staining procedures that use only one stain
List the steps for preparing a smear.
1-Place a loopful on water on the slide, 2-place a small amount of the culture onto the slide and mix, 3-allow smear to air dry, 4-flame the slide
List the steps of preparing a simple stain.
1-Cover smear with methylene blue for 30 seconds, 2-Wash with DI water
Of what value is a simple stain?
Determining cell morphology, size, and arrangement
What is the purpose of fixing the smear preparation?
Denatures bacterial enzymes
In heat fixing, what would happen if too much heat were applied?
It would damage the cell's structure and can even crack the slide.
Can dyes other than methylene blue be used for direct staining?
Yes any positively charged dye can be used such as safranin and basic fuchsin
Bacteria can be seen without staining, so why is fixing and staining important for microbiology?
It allows for later reexamination
What does the negative stain technique stain?
Background (the area around the cell, but NOT the cell itself)
Why doesn't a negative stain stain the bacteria?
Ionic repulsion; like charges repel. The bacteria cell wall and the chromophores of the acidic stain both have negative charges.
In which procedure are no heat fixing or strong chemicals used and why not?
Negative stain; to keep the bacteria from getting as distorted
When is the negative stain technique especially useful?
When other staining techniques don't clearly show cell morphology or size
List the steps of the negative staining technique.
1-Place a drop of nigrosin on slide, 2-Mix a loopful of broth culture with the nigrosin (no extra water is needed when the culture is taken from solid media as nigrosin contains a lot of water already), 3-Use a second slide to sweep the mixture across the first slide, making a color gradient, 4-Let the smear air dry
How does bacteria from a negative stain differ from that of a simple stain?
It's clearer because only the background is stained
Why is the size more accurate in a negative stain than in a simple stain?
The lack of heat fixing or strong chemicals keeps from distorting the cell
Could any dye be used in place of nigrosin in a negative stain?
No
What type of dye is used for negative staining? (Acidic or Basic)
Acidic
What kind of stain is the gram stain? How does is allow you to classify bacteria?
Differential; as either gram positive or gram negative
Describe the discovery of the gram stain technique.
Discovered accidentally by Hans Christian Gram in 1884 when he attempted to stain cells and found that some lost their color when the excess stain was washed off
In a gram stain, what are bacteria called when they are easily decolorized?
Gram negative
In a gram stain, what are bacteria called when they retain the primary stain?
Gram positive
Why do bacteria stain differently in a gram stain?
Chemical and physical differences in their cell walls
In a gram stain, what type of cell does this describe?
Crystal violet is picked up by the cell. Iodine reacts with the dye in the cytoplasm to form CV-I. The decolorizing agent dissolves the outer lipopolysaccharide layer, and the CV-I washes out through the thin layer of peptidoglycan.
Gram negative
When is the gram stain most consistent?
When done on cultures less than 24 hours old
List the steps of the gram stain technique.
1-Cover smear with crystal violet for 30 seconds and rinse, 2-Cover smear with Gram's iodine for 10 seconds and rinse, 3-Decolorize with alcohol and rinse, 4-Cover smear with safranin for 30 seconds and rinse
Name some gram positive bacteria.
S. aeru, S. epi, S. pyogenes, B. sub, B, meg
Name some gram negative bacteria.
E. coli, P. vulg, Neisseria
Why will old gram positive cells stain gram negative?
They can't retain the primary stain because with time the lipid layer degrades allowing the stain to reach the peptidoglycan
Can iodine be added before the primary stain in a Gram stain?
No
What color does Crystal Violet turn each of the cells in a gram stain?
Purple
What color does Gram's iodine turn each of the cells in a gram stain?
Purple
What color does ethyl alcohol turn each of the cells in a gram stain?
Gram positive-purple; Gram negative-clear
What color does safranin turn each of the cells in a gram stain?
Gram positive-purple; Gram negative-red
Which step can be omitted without affecting determination of the gram stain reaction?
Safranin
Suppose you gram stained a sample from a pure culture of bacteria and observed a field of red and purple cocci. Adjacent cells were not always the same color. What do you conclude?
The culture is old
Suppose you are viewing a gram stained field of red rods and purple cocci through the microscope. What do you conclude?
The culture has been cross-contaminated
Since you can't identify bacteria from a gram stain, why might a physician perform a gram stain on a sample before perscribing an antibiotic?
Because only certain antibiotics work depending on if the bacteria is gram positive or negative
What type of antibiotics work on gram positive bacteria?
Penicillin
What type of antibiotics work on gram negative bacteria?
Tetracycline
If you gram stained human cells, what would happen?
Primary stain would wash away because humans do not have cell walls
What type of stain is the acid-fast stain?
Differential
What is the value of the acid-fast stain?
Allows diagnosing of Mycobacterium and Nocardia, which do not decolorize with acid alcohol
The cell walls of acid-fast organisms have a wax-like lipid called mycolic acid, which does what?
Makes the cell wall impermeable to most stains
What the difference in the Ziehl-Neelsen acid-fast stain and the Kinyoun acid-fast stain?
In the Kinyoun stain (cold stain), the concentrations of phenol and carbolfuchsin are increased so heating isn't necessary
List the steps of the acid-fast stain.
1-Cover smear with carbolfuchsin for 5 minutes and rinse, 2-Wash smear with acid-alcohol on and off and rinse, Cover smear with Brilliant Green K (Methylene Blue) for 1 minute and rinse
What color will an acid-fast positive bacteria be?
Red
What color will an acid-fast negative bacteria be?
Green
Name an acid-fast negative bacteria
E. coli
Name an acid-fast positive bacteria
M. phlei
What is the decolorizing agent in the Gram stain? In the acid-fast stain?
Ethyl alcohol; Acid-alcohol
What diseases are diagnosed using the acid-fast staining technique?
Tuberculosis and Leprosy
What is phenol and what percent is its usual application?
Disinfectant; 5%
How might the acid-fast characteristic of Mycobacterium enhance the organism's ability to cause disease?
The lipids in their cell wall give extra protection; they are not easily phagocytized
Clinical specimens suspected of containing Mycobacterium are digested with sodium hydroxide for 30 minutes prior to staining. Why is this technique used? Why isn't this technique used for staining other bacteria?
To remove unwanted bacteria from specimen; the sodium hydroxide would kill other bacteria
What are the most familiar genera that form endospores?
Bacillus and Clostridium
Why are endospores called resting bodies?
Because they do not metabolize and are resistant to many harsh conditions
When are endospores formed?
When essential nutrients or water are not available
What happens to the cell when an endospore is formed?
It disintegrates
Many bacteria secrete chemicals that adhere to their surfaces, forming a viscous coat. What is this structure called when it is round or oval shaped? Irregularly shaped and loosely bound?
Capsule; Slime layer
How is a bacteria's ability to form a capsule determined?
Genetically
How is the size of a bacteria's capsule determined?
The medium it's growing on
What are most capsules composed of?
Polysaccharides, which are uncharged
Because of a capsules nonionic nature, _____ stains will not adhere to it.
Simple
How must a capsule be stained in order to view it under a microscope?
The background must be stained, leaving the capsules unstained
Capsules have a very important role in the _____ of some bacteria.
Virulence
How do capsules contribute to the virulence of some bacteria?
Capsules are not easily phagocytized
These thin proteinaceous structures that originate in the cytoplasm and project out from the cell wall are the most common means of motility in bacteria
Flagella
List the steps of an endospore stain.
1-Place a piece of paper towel over the slide, 2-Cover the paper with malachite green, 3-Steam the slide for 5 minutes then rinse, 4-Cover smear with safranin for 30 seconds and rinse
List the steps of a capsule stain.
1-Place a loopful of congo red on slide, 2-Put a thick smear of bacteria in the congo red and mix, 3-Let smear air dry, 4-Drip acid-alcohol on slide for 15 seconds and rinse, 5-Cover smear with acid fuchsin for 1 minute and rinse
What are the gram reactions of Clostridium and Bacillus?
Both are gram positive
How might flagella contribute to pathogenicity?
They help evade the immune response
In an endospore stain, how would slides of 24-hour old Bacillus and 72-hour old Bacillus differ?
At 72 hours, endospores would have formed
Of what morphology are most bacteria possessing flagella?
Bacillus
Which morphology does not usually have flagella?
Coccus
What prevents the cell from appearing green in the finished endospore stain?
Vegetative cells are easily decolorized so the green dye washes off
You can see endospores by simple staining. Why not use this technique?
It would be more difficult to pick them out because they would be transparent
How would an endospore stain of Mycobacterium appear?
Mycobacterium's waxy cell wall would retain the green dye, suggesting that they have endospores when they actually do not
What type of culture medium would increase the size of a bacterial capsule?
A medium rich in polysaccharides
Describe the microscopic appearance of encapsulated Streptococcus if stained with safranin and nigrosin.
The bacteria would be red, the capsule clear, and the background purplish-black
In the Dorner endospore stain, a smear covered with carbolfuchsin is steamed, then decolorized with acid-alcohol and counterstained with nigrosin. Describe the microscopic appearance after this procedure.
The endospores should be very bright pink, the bacteria light pink, and the background purplish-black
What makes an agar deep useful?
Some oxygen prefer to grow in less oxygen
What are two ways to determine motility of a bacteria?
Using an agar deep or the hanging drop technique
What evolutionary advantage would there be to the formation of a pellicle in a liquid medium by a bacterium?
They could form colonies and have a greater chance of survival
How can you tell that a medium is sterile?
Compare it with a control
Why is it desirable that microscope lenses be parfocal?
So you don't have to refocus everytime you change objectives
What controls the amount of light reaching the ocular lens?
Diaphragm
Is you lens corrected for chromatic aberrations?
Yes
Name two ways in which you can enhance the resolving power of a microscope.
Decrease the wavelength of light and increase the numerical aperture
What would occur if water were accidentally used in place of immersion oil?
It would not be as clear because water does not have the same refractive index as glass
What advantages does the low power objective have over the oil immersion objective for viewing fungi?
Fungi cells are large so you can see more of the cell
Organisms Used:
Escherichia coli (E. coli) - Gram (-) rod
Staphylococcus aureus (Staph. aureus)
- Staphylococcus aureus is a gram-positive bacteria that is round Gram (+) cocci
Here is an example of what Staphylococcus aureus looks like with the negative stain. homepages.wmich.edu/~rossbach/bios312/LabProcedures/Negative%20Stain%20Procedure.html